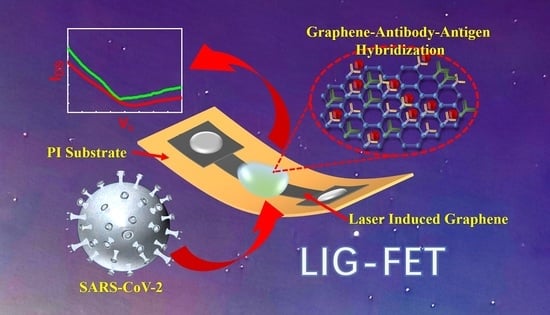
Ultrasensitive Detection of COVID-19 Causative Virus (SARS-CoV-2) Spike Protein Using Laser Induced Graphene Field-Effect Transistor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Device Fabrication and Material Characterization
2.2. Concentration Gradient Detection
2.3. Specificity Detection in PBS and Human Serum
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Echegaray, F. What POST-COVID-19 lifestyles may look like? Identifying scenarios and their implications for sustainability. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Report-51. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200311-sitrep-51-covid-19.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2021).
- Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19—26 October 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-covid-19---26-october-2021 (accessed on 30 October 2021).
- Al-Hatamleh, M.A.I.; Hatmal, M.M.; Alshaer, W.; Rahman, E.N.S.E.A.; Mohd-Zahid, M.H.M.; Alhaj-Qasem, D.M.; Yean, C.Y.; Alias, I.Z.; Jaafar, J.; Ferji, K.; et al. COVID-19 infection and nanomedicine applications for development of vaccines and therapeutics: An overview and future perspectives based on polymersomes. Eur. J. Pharm. 2021, 896, 173930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, C.R.; Townsend, J.P.; Pandey, A.; Moghadas, S.M.; Krieger, G.; Singer, B.; McDonald, R.H.; Fitzpatrick, M.C.; Galvani, A.P. Optimal COVID-19 quarantine and testing strategies. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliga, R.E. Quarantine as a tool of epidemic fight. Sustain. Przegl. Epidemiol. 2020, 74, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, E.; Van Doremalen, N.; Falzarano, D.; Munster, V.J. SARS and MERS: Recent insights into emerging coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Kruger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.-H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.-J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhzadeh, E.; Eissa, S.; Ismail, A.; Zourob, M. Diagnostic techniques for COVID-19 and new developments. Talanta 2020, 220, 121392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, H.N.; Xu, P.; Servellita, V.; Miller, S.; Liu, L.; Gopez, A.; Chiu, C.Y.; Abate, A.R. Digital droplet PCR accurately quantifies SARS-CoV-2 viral load from crude lysate without nucleic acid purification. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yao, H.; Xu, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, M.; Shao, J.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, H. Limits of Detection of 6 Approved RT-PCR Kits for the Novel SARS-Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 977–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pillay, T.S.; Pillay, T.S. Gene of the month: The 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2 novel coronavirus spike protein. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 73, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaile, D.F.; Sepaniak, M.J. Laser-based fluorimetric detection schemes for the analysis of proteins by capillary zone electrophoresis. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 1991, 14, 869–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.-R.; Chiu, C.-M.; Yeh, S.-H.; Huang, W.-H.; Hsueh, P.-R.; Yang, W.-Z.; Yang, J.-Y.; Su, I.-J.; Chang, S.-C.; Chen, P.-J. Evaluation of antibody responses against SARS coronaviral nucleocapsid or spike proteins by immunoblotting or ELISA. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 73, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurkinen, K.M.A.; Koistinaho, J.; Laitinen, J.T. [γ-35S]GTP autoradiography allows region-specific detection muscarinic receptor-dependent G-protein activation in chick optic tectum. Brain Res. 1997, 769, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Zhu, L.; Gan, J.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, L.; Liu, B. Ultrasensitive Detection of Low-Abundance Protein Biomarkers by Mass Spectrometry Signal Amplification Assay. Anal. Chim. 2016, 88, 6767–6772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, A.; Iizuka, A.; Komiyama, M.; Takikawa, M.; Kume, A.; Tai, S.; Ohshita, C.; Kurusu, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Yamamoto, A.; et al. Identification of melanoma antigens using a Serological Proteome Approach (SERPA). Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2010, 7, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wankar, S.; Turner, N.W.; Krupadam, R.J. Polythiophene nanofilms for sensitive fluorescence detection of viruses in drinking water. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 82, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coffman, V.C.; Wu, J.-Q. Counting protein molecules using quantitative fluorescence microscopy. Trends. Biochem. Sci. 2012, 37, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taraska, J.W. Mapping membrane protein structure with fluorescence. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2012, 22, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suhito, I.R.; Koo, K.-M.; Kim, T.-H. Recent advances in electrochemical sensors for the detection of biomolecules and whole cells. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, C.B.; Peairs, M.J.; Venton, B.J. Review: Carbon nanotube based electrochemical sensors for biomolecules. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 662, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Denno, M.E.; Pyakurel, P.; Venton, B.J. Recent trends in carbon nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensors for biomolecules: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 887, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swathi, R.S.; Sebastian, K.L. Long range resonance energy transfer from a dye molecule to graphene has (distance)−4 dependence. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 086101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinsella, J.M.; Ivanisevic, A. Taking charge of biomolecules. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 596–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layouni, R.; Choudhury, M.H.; Laibinis, P.E.; Weiss, S.M. Thermally Carbonized Porous Silicon for Robust Label-Free DNA Optical Sensing. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Wang, S.; Huang, L.; Ning, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, G.-J. Ultrasensitive label-free detection of PNA–DNA hybridization by reduced graphene oxide field-effect transistor biosensor. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2632–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Shi, K.; Dou, B.; Xiang, Y.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, R. In situ DNA-templated synthesis of silver nanoclusters for ultrasensitive and label-free electrochemical detection of microRNA. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 1188–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Mok, S.M.; Yu, J.; Chan, H.L.W.; Yang, M. Label-free DNA sensor based on organic thin film transistors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Peng, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Chen, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, G.; Liu, C.; et al. Suspended CNT-Based FET sensor for ultrasensitive and label-free detection of DNA hybridization. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 137, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Chand, R.; Kim, Y.-S. Microscale loop-mediated isothermal amplification of viral DNA with real-time monitoring on solution-gated graphene FET microchip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, S.; Hu, G.; Li, X.; Zou, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; et al. Graphene foam field-effect transistor for ultra-sensitive label-free detection of ATP. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 284, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielson, E.; Sontakke, V.A.; Porkovich, A.J.; Wang, Z.; Kumar, P.; Ziadi, Z.; Yokobayashi, Y.; Sowwan, M. Graphene based field-effect transistor biosensors functionalized using gas-phase synthesized gold nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 320, 128432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-H.; Yang, H.-H.; Zhu, C.-L.; Chen, X.; Chen, G.-N. A graphene platform for sensing biomolecules. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4785–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eng, A.Y.S.; Ambrosi, A.; Chua, C.K.; Sanek, F.; Sofer, Z.; Pumera, M. Unusual inherent electrochemistry of graphene oxides prepared using permanganate oxidants. Eur. J. Chem. 2013, 19, 12673–12683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, G.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Q.; Fang, H.; Zhou, R. Adsorption of villin headpiece onto graphene, carbon nanotube, and C60: Effect of contacting surface curvatures on binding affinity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 23323–23328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, G.-J. Gold nanoparticles-decorated graphene field-effect transistor biosensor for femtomolar MicroRNA detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, M.; Shen, Z. A review on mechanical exfoliation for the scalable production of graphene. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2015, 3, 11700–11715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdock, A.T.; Koos, A.; Britton, T.B.; Houben, L.; Batten, T.; Zhang, T.; Wilkinson, A.J.; Dunin-Borkowski, R.E.; Lekka, C.E.; Grobert, N. Controlling the orientation, edge geometry, and thickness of chemical vapor deposition graphene. ACS Nano. 2013, 7, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.; Cheng, H.M. The reduction of graphene oxide. Carbon 2012, 50, 3210–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Gou, G.; Wu, F.; Jian, J.; Li, X.; Hirtz, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhi, Y.; Wang, F.; Tian, H.; et al. Graphene-Based Thermoacoustic Sound Source. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 3779–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Peng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ruiz-Zepeda, F.; Ye, R.; Samuel, E.L.G.; Yacaman, M.J.; Yakobson, B.I.; Tour, J.M. Laser-induced porous graphene films from commercial polymers. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Peng, Z.; Li, Y.; Gao, C.; Ji, Y.; Ye, R.; Kim, N.D.; Zhong, Q.; Yang, Y.; et al. High-Performance Pseudocapacitive Microsupercapacitors from Laser-Induced Graphene. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jian, J.; Li, M.; Jiang, G.; Li, X.; Deng, G.; Ji, S.; Wei, Y.; Pang, Y.; et al. Multifunctional and high-performance electronic skin based on silver nanowires bridging graphene. Carbon 2020, 156, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.-Q.; Tian, H.; Liu, Y.; Ju, Z.-Y.; Pang, Y.; Chen, Y.-Q.; Wang, D.-Y.; Tian, X.-G.; Yan, J.-C.; Deng, N.-Q.; et al. An intelligent artificial throat with sound-sensing ability based on laser induced graphene. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tarasov, A.; Tsai, M.-Y.; Flynn, E.M.; Joiner, C.A.; Taylor, R.C.; Vogel, E.M. Gold-coated graphene field-effect transistors for quantitative analysis of protein-antibody interactions. 2D Mater. 2015, 2, 044008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Qiu, J.; Gao, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Han, L. Ultrasensitive, high-throughput, and rapid simultaneous detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigens and IgG/IgM antibodies within 10 min through an immunoassay biochip. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P. Oyster reef restoration in controlling coastal pollution around India: A viewpoint. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenihan, H.S.; Peterson, C.H. How habitat degradation through fishery disturbance enhances impacts of hypoxia on oyster reefs. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, G.H.; Fountain, A.W., III. Development and characterization of electrochemical devices using ultraviolet laser induced carbonization of polyimide films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1997, 144, 3769–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Meyer, J.C.; Scardaco, V.; Casiraghi, C.; Lazzeri, M.; Mauri, F.; Piscanec, S.; Jiang, D.; Roth, S.; Geim, A.K. Raman Spectrum of Graphene and Graphene Layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 187401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haque, A.M.J.; Park, H.; Sung, D.; Jon, S.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, K. An electrochemically reduced graphene oxide-based electrochemical immunosensing platform for ultrasensitive antigen detection. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, T.-R.; Qiao, Y.-C.; Gao, J.-W.; Wang, C.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Han, L.; Yang, Y.; Ren, T.-L. Ultrasensitive Detection of COVID-19 Causative Virus (SARS-CoV-2) Spike Protein Using Laser Induced Graphene Field-Effect Transistor. Molecules 2021, 26, 6947. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26226947
Cui T-R, Qiao Y-C, Gao J-W, Wang C-H, Zhang Y, Han L, Yang Y, Ren T-L. Ultrasensitive Detection of COVID-19 Causative Virus (SARS-CoV-2) Spike Protein Using Laser Induced Graphene Field-Effect Transistor. Molecules. 2021; 26(22):6947. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26226947
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Tian-Rui, Yan-Cong Qiao, Jian-Wei Gao, Chun-Hua Wang, Yu Zhang, Lin Han, Yi Yang, and Tian-Ling Ren. 2021. "Ultrasensitive Detection of COVID-19 Causative Virus (SARS-CoV-2) Spike Protein Using Laser Induced Graphene Field-Effect Transistor" Molecules 26, no. 22: 6947. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26226947
APA StyleCui, T. -R., Qiao, Y. -C., Gao, J. -W., Wang, C. -H., Zhang, Y., Han, L., Yang, Y., & Ren, T. -L. (2021). Ultrasensitive Detection of COVID-19 Causative Virus (SARS-CoV-2) Spike Protein Using Laser Induced Graphene Field-Effect Transistor. Molecules, 26(22), 6947. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26226947