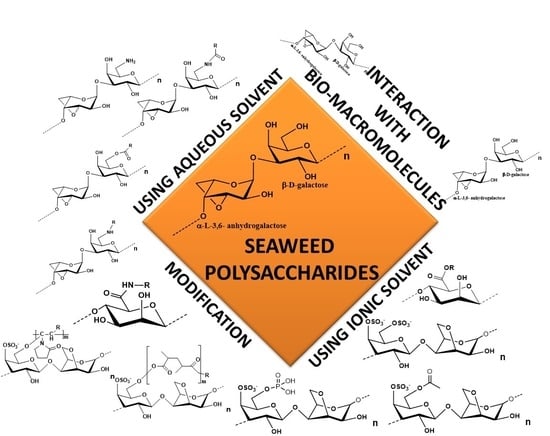
Seaweed Polysaccharide Based Products and Materials: An Assessment on Their Production from a Sustainability Point of View
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Agar and Agarose
1.2. Alginic Acid
1.3. Carrageenan
2. Chemical and Physical Modification of Seaweed Polysaccharides
3. Ionic Solvents
3.1. Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents
3.2. Sustainable Extraction of Seaweed Polysaccharides Using Ionic Solvents
3.3. Modification of Seaweed Polysaccharides in Ionic Solvent
4. Functionalization of Seaweed Polysaccharides by Interaction with Other Bio Macromolecules
5. Future Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schuerch, C. Encyclopaedia of Polymer Science and Engineering, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1986; Volume 13, pp. 87–162. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.M.; Nie, S.P. The functional and nutritional aspects of hydrocolloids in foods. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 53, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentati, F.; Tounsi, L.; Djomdi, D.; Pierre, G.; Delattre, C.; Ursu, A.V.; Fendri, I.; Abdelkafi, S.; Michaud, P. Bioactive Polysaccharides from Seaweeds. Molecules 2020, 25, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H. Marine seaweed polysaccharides-based engineered cues for the modern biomedical sector. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Atanase, L.I. Micellar Drug Delivery Systems Based on Natural Biopolymers. Polymers 2021, 13, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanase, L.I.; Desbrieres, J.; Riess, G. Micellization of synthetic and polysaccharides-based graft copolymers in aqueous media. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 73, 32–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Gao, X.; Cheng, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Han, X. The Structural Characteristics of Seaweed Polysaccharides and Their Application in Gel Drug Delivery Systems. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.E.; Kim, H.; Seo, C.; Park, T.; Lee, K.B.; Yoo, S.Y.; Hong, S.C.; Kim, J.T.; Lee, J. Marine polysaccharides: Therapeutic efficacy and biomedical applications. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2017, 40, 1006–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, M.J.; Costa, R.R.; Mano, J.F. Marine origin polysaccharides in Drug Delivery Systems. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albertus, J.S. Medicinal and pharmaceutical uses of seaweed natural products: A review. J. Appl. Phycol. 2004, 16, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, J.; Lowe, B.; Sukumaran, A.; Manivasagan, P.; Al Kheraif, A.A.; Kang, K.-H.; Kim, S.-K. Seaweed polysaccharides and their potential biomedical applications. Starch/Stärke 2015, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tønnesen, H.H.; Karlsen, J. Alginate in drug delivery systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2002, 28, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatfieid, S. A comparison of the efficacy of the alginate preparation, Gaviscon Advance, with placebo in the treatment of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 1999, 15, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draget, K.I.; Taylor, C. Chemical, physical and biological properties of alginates and their biomedical implications. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalau, J.; Bresson, R.; Charpentier, P.; Coliche, V.; Erlher, S.; Ha Van, G.; Magalon, G.; Martini, J.; Moreau, Y.; Pradines, S.; et al. Efficacy and tolerance of calcium alginate versus Vaseline gauze dressings in the treatment of diabetic foot lesions. Diabetes Metab. 2008, 28, 223–229. [Google Scholar]
- Yuvarani, I.; Kumar, S.S.; Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.-K.; Sudha, P. Preparation and characterization of curcumin coated chitosan-alginate blend for wound dressing application. J. Biomater. Tissue Eng. 2012, 2, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Hydrogels for tissue engineering. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Aoki, H.; Nakamura, S.; Nakamura, S.-i.; Takikawa, M.; Hanzawa, M.; Kishimoto, S.; Hattori, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Kiyosawa, T.; et al. Hydrogel blends of chitin/chitosan, fucoidan and alginate as healing-impaired wound dressings. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, H.M.; Aly, A.A.; Sayed, S.M.; Abou-Okeil, A. κ-carrageenan/Na-alginate woulnd dressing with sustainable drug delivery properties. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.V.; Boppana, R.; Krishna Mohan, G.; Mutalik, S.; Kalyane, N.V. pH-responsive interpenetrating network hydrogel beads of poly (acrylamide)-g-carrageenan and sodium alginate for intestinal targeted drug delivery: Synthesis, in vitroand in vivo evaluation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 367, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavas, E.; Koutris, E.; Papadopoulos, A.G.; Sigalas, M.P.; Nanaki, S.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Achilias, D.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N. Application of density functional theory in combination with FTIR and DSC to characterise polymer drug interactions for the preparation of sustained release formulations between fluvastatin and carrageenans. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 466, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenha, A.; Gomes, M.E.; Rodrigues, M.; Santo, V.E.; Mano, J.F.; Never, N.M.; Reis, R.L. Development of new chitosan/carrageenan nanoparticles for drug delivery applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 92, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shikov, A.N.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Pozharitskaya, O.N. Pharmacokinetics of marine-derived drugs. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerns, E.H.; Li, D. Drug-Like Properties: Concept, Structure Design and Methods; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; p. 552. [Google Scholar]
- Hessami, M.J.; Salleh, A.; Phang, S.M. Bioethanol a by-product of agar and carrageenan production industry from the tropical red seaweeds, Gracilaria manilaensis and Kappaphycus alvarezii. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2020, 19, 942–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Market Data Forecast. Available online: https://www.marketdataforecast.com/market-reports/carrageenan-market (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Globefish Research Programme. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/ca1121en/CA1121EN.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Grand View Research. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/global-agar-agar-gum-market (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Hay, I.D.; Rehman, Z.U.; Moradali, M.F.; Wang, Y.; Rehm, B.H. Microbial alginate production, modification and its applications. Microb. Biotechnol. 2013, 6, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grand View Research. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/alginate-market (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Pereiira, L.; Cotas, J. Alginates—A General Overview, Alginates Recent Uses of This Natural Polymer; Introductory Chaper: Alginates—A over view; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gustavsson, E.; Larsson, O. Monolithic Polysaccharide Materials. In Monolithic Materials: Preparation, Properties and Applications (Journal of Chromatography Library); Svec, F., Tennikova, T.B., Deyl, Z., Eds.; Elsevier: Lund, Sweden, 2003; Volume 67, pp. 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yermak, I.M.; Kim, Y.H.; Titlynov, E.A.; Isakov, V.V.; Solov’eva, T.F. Chemical structure and gel properties of carrageenans from algae belonging to the Gigartinaceae and Tichocarpaceae, collected from the Russian Pacific coast. In Sixteenth International Seaweed Symposium; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidgell, J.T.; Magnusson, M.; Nys, R.; Glasson, C. Ulvan: A systematic review of extraction, composition and function. Algal. Res. 2019, 39, 101422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, F.; Wei, X.; Zhao, R. Fucoidan: Structure and bioactivity. Molecules 2008, 13, 1671–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morelli, A.; Puppi, D.; Chiellini, F. Perspectives on biomedical applications of ulvan. In Seaweed Polysaccharides, 1st ed.; Venkatesan, J., Anil, S., Kim, S.-K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Chapter 16; pp. 305–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadnik, M.J.; Freitas, M.B.D. Algal polysaccharides as source of plant resistance inducers. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2014, 39, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, L.; Gheda, S.F.; Ribeiro-Claro, P.J. Analysis by vibrational spectroscopy of seaweed polysaccharides with potential use in food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries. Int. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2013, 2013, 537202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddhanta, A.K.; Sanandiya, N.D.; Chejara, D.R.; Kondaveeti, S. Functional modification mediated value addition of seaweed polysaccharides—A perspective. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 59226–59239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafavi, F.S.; Zaeim, D. Agar-based edible films for food packaging applications-A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.K.; Lim, Y.Y.; Leow, A.T.C.; Namasivayam, P.; Abdullah, J.O.; Ho, C.L. Biosynthesis of agar in red seaweeds: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y. Relation between structure and rheological/thermal properties of agar. A mini-review on the effect of alkali treatment and the role of agaropectin. Food Struct. 2017, 13, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demchenko, D.V.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shikov, A.N.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Rusak, A.V.; Makarov, V.G. Rheological study of agar hydrogels for soft capsule shells. Pharm. Chem. J. 2014, 47, 556–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikov, A.N.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Makarov, V.G.; Makarova, M.N. New technology for preparation of herbal extracts and soft halal capsules on its base. Am. Eurasian J. Sustain. Agric. 2009, 3, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, D.; Bhattacharya, S. Hydrocolloids as thickening and gelling agents in food: A critical review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 47, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellis, A.; Jacquier, J.C. Manufacture and characterisation of agarose microparticles. J. Food Eng. 2009, 90, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabani, H.; Alexovič, M.; Sabo, J.; Payán, M.R. An overview on the recent applications of agarose as a green biopolymer in micro-extraction-based sample preparation techniques. Talanta 2020, 121892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, R.; Prasad, K.; Siddhanta, A.K. Development of a stable hydrogel network based on agar-kappa-carrageenan blend cross-linked with genipin. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, G.K.; Kondaveeti, S.; Siddhanta, A.K. Facile synthesis of agarose-L- phenylalanine ester hydrogels. Polym. Chem. 2011, 2, 2334–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Mora, V.; Velasco, D.; Hernández, R.; Mijangos, C.; Kumacheva, E. Chitosan/agarose hydrogels: Cooperative properties and microfluidic preparation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kondaveeti, S.; Mehta, G.K.; Siddhanta, A.K. Modification of agarose: 6-Aminoagarose mediated syntheses of fluorogenic pyridine carboxylic acid amides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 106, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondaveeti, S.; Chejara, D.R.; Siddhanta, A.K. A facile one-pot synthesis of a fluorescent agarose-O-naphthylacetyl adduct with slow release properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oza, M.D.; Meena, R.; Siddhanta, A.K. Facile synthesis of fluorescent polysaccharides: Cytosine grafted agarose and κ-carrageenan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oza, M.D.; Prasad, K.; Siddhanta, A.K. One-pot synthesis of fluorescent polysaccharides: Adenine grafted agarose and carrageenan. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 357, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oza, M.D.; Meena, R.; Prasad, K.; Paul, P.; Siddhanta, A.K. Functional modification of agarose: A facile synthesis of a fluorescent agarose-guanine derivative. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondaveeti, S.; Chejara, D.R.; Siddhanta, A.K. Synthesis of self-assembly of agarose-fatty acid ester nanoparticles. Indian J. Chem. —Sect. A Inorg. Phys. Theor. Anal. Chem. 2014, 53, 679–687. [Google Scholar]
- Chhatbar, M.U.; Godiya, C.B.; Siddhanta, A.K. Functional modification of agarose: A facile synthesis of an agarose-saccharate derivative. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, R.; Chaudhary, J.P.; Agarwal, P.K.; Maiti, P.; Chatterjee, S.; Raval, H.D.; Agarwal, P.; Siddhanta, A.K.; Prasad, K.; Ghosh, P.K. Surfactant-induced coagulation of agarose from aqueous extract of Gracilaria dura seaweed as an energy-efficient alternative to the conventional freeze–thaw process. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 28093–28098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.; Kadokawa, J.-I. Alginate-based blends and nano/micro-beads. In Alginates: Biology & Applications; Rehm, B.H.A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 13, pp. 175–210. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Shen, P.; Peng, Q. Structures, properties and application of alginic acid: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, P.; Pal, P.; Panday, J.P.; Mishra, S.; Sen, G. Alginic acid derivatives: Synthesis, characterization and application in wastewater treatment. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 2769–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, M.I.; Xu, X.; Li, L. A review on biodegradable polymeric materials for bone tissue engineering applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 5713–5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabbas, R.; Sanchez-Ballester, N.M.; Bataille, B.; Leclercq, L.; Sharkawi, T.; Soulairol, I. Structure-properties relationship in the evaluation of alginic acid functionality for tableting. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, D.J. A Guide to the Seaweed Industry, Publishing Management Service: Information Division; FAO‘: Rome, Italy, 2003; Chapter 8. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, D.; Nayak, S.K.; Maji, S.; Kim, D.; Banerjee, I.; Pal, K. Carrageenan: A wonder polymer from marine algae for potential drug delivery applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 1172–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Quito, E.M.; Ruiz-Caro, R.; Veiga, M.D. Carrageenan: Drug Delivery Systems and Other Biomedical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhan, X.; Wan, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Review for carrageenan-based pharmaceutical biomaterials: Favourable physical features versus adverse biological effects. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKim, J.M. Food additive carrageenan: Part I: A critical review of carrageenan in vitro studies, potential pitfalls, and implications for human health and safety. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 211–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, M.L. Food additive carrageenan: Part II: A critical review of carrageenan in vivo safety studies. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 244–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedayu, B.B.; Cran, M.J.; Bigger, S.W. A review of property enhancement techniques for carrageenan-based films and coatings. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 216, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ni, R.; Shao, Y.; Mao, S. Carrageenan and its applications in drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S. Carrageenan for encapsulation and immobilization of flavor, fragrance, probiotics, and enzymes: A review. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2017, 36, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, T.; Yang, Y.; Meng, F.; Zhan, F.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, X. Anti-cancer activity of porphyran and carrageenan from red seaweeds. Molecules 2019, 24, 4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Butler, B.; Vergano, P.; Testin, R.; Bunn, J.; Wiles, J. Mechanical and Barrier Properties of Edible Chitosan Films as affected by Composition and Storage. J. Food Sci. 1996, 61, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Misra, B.N. Grafting: A versatile means of Polymer modification Techniques, factors and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2004, 29, 767–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkovic, I.; Hricovini, H.; Mendichi, R.; Zeroen, J.G. Cross-linking of starch with 1, 2, 3, 4-diepoxybutane or 1, 2, 7, 8-diepoxyoctane. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 55, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenneth, B.G. Modified Agarose and Agar and Method of Making Same. U.S. Patent No 3,956,273, 11 May 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, I.J. Manufacture of and Uses for Low Molecular Weight Agars and Agaroids. U.S. Patent No. 6,322,814, 27 November 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Harzandi, A.M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Modified carrageenan 3. Synthesis of a novel polysaccharide-based superabsorbent hydrogel via graft copolymerization of acrylic acid onto kappa-carrageenan in air. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchipunov, Y.A. Sol–gel-derived biomaterials of silica and carrageenans. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 268, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.; Siddhanta, A.K.; Rakshit, A.K.; Bhattacharya, A.; Ghosh, P.K. On the properties of agar gel containing ionic and non-ionic surfactants. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2005, 35, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Lü, X.; Li, N.; Gao, X.; Song, J. Preparation and in vitro antioxidant activity of κ-carrageenan oligosaccharides and their oversulfated, acetylated, and phosphorylated derivatives. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.; Meena, R.; Siddhanta, A.K. Microwave-induced rapid one-pot synthesis of κ-carrageenan-g-PMMA copolymer by potassium persulphate initiating system. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, R.; Prasad, K.; Mehta, G.; Siddhanta, A.K. Synthesis of the copolymer hydrogel κ-carrageenan-graft-PAAm: Evaluation of its absorbent and adhesive properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 5144–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, V.L.; Kawano, D.F.; da Silva, D.B.; Carvalho, I. Carrageenans: Biological properties, chemical modifications and structural analysis—A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.N.; Edgar, K.J. Alginate derivatization: A review of chemistry, properties and applications. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3279–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabbas, R.; Sanchez-Ballester, N.M.; Bataille, B.; Sharkawi, T.; Soulairol, I. Development and pharmaceutical performance of a novel co-processed excipient of alginic acid and microcrystalline cellulose. Powder Technol. 2021, 378, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, S.F.; Rocha, M.J.; Ferro, M.; Amorim, C.O.; Amaral, J.S.; Trindade, T.; Daniel-da-Silva, A.L. Magnetic nanosorbents with siliceous hybrid shells of alginic acid and carrageenan for removal of ciprofloxacin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Li, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, X.; Liu, B. Dual-functional alginic acid hybrid nanospheres for cell imaging and drug delivery. Small 2009, 5, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Ishii, D.; Iwata, T. Synthesis and characterization of alginic acid ester derivatives. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 171, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, K.M.; Tabasum, S.; Nasif, M.; Sultan, N.; Aslam, N.; Noreen, A.; Zuber, M. A review on synthesis, properties and applications of natural polymer based carrageenan blends and composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 96, 282–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, C.; Jeon, W.; Woo, H.C.; Kim, D.H. Catalytic Hydrogenation of Macroalgae-Derived Alginic Acid into Sugar Alcohols. ChemSusChem. 2017, 10, 4891–4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhatbar, M.U.; Meena, R.; Prasad, K.; Chejara, D.R.; Siddhanta, A.K. Microwave-induced facile synthesis of water-soluble fluorogenic alginic acid derivatives. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Chhatbar, M.U.; Mahato, P.; Praveen, L.; Siddhanta, A.K.; Das, A. Rhodamine-alginate conjugate as self indicating gel beads for efficient detection and scavenging of Hg2+ and Cr3+ in aqueous media. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1659–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chejara, D.R.; Kondaveeti, S.; Prasad, K.; Siddhanta, A.K. Studies on the structure-property relationship of sodium alginate based thixotropic hydrogels. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 15744–15751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhatbar, M.U.; Prasad, K.; Chejara, D.R.; Siddhanta, A.K. Synthesis of sodium alginate based sprayable new soft gel system. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 1837–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chejara, D.R.; Kondaveeti, S.; Siddhanta, A.K. Facile synthesis of new sodium alginate—Anthracene based photosensitizers. Polym. Bull. 2014, 72, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhatbar, M.U.; Meena, R.; Prasad, K.; Siddhanta, A.K. Agar/sodium alginate-graft-polyacrylonitrile, a stable hydrogel system. Indian J. Chem. Sect. A 2009, 46A, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Sequeira, R.A.; Bhatt, J.; Prasad, K. Recent Trends in Processing of Proteins and DNA in Alternative Solvents: A Sustainable Approach. Sustain. Chem. 2020, 1, 116–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lu, Q.; Ye, C.; Liu, W.; Cui, Z. Friction and wear behaviors of ionic liquid of alkylimidazolium hexafluorophosphates as lubricants for steel/steel contact. Wear 2004, 256, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Qu, J. Ionic liquids as lubricant additives: A review. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3209–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, D.; Song, W. High performance, flexible and renewable nano-biocomposite artificial muscle based on mesoporous cellulose/ ionic liquid electrolyte membrane. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 283, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.W.; Zhang, L.K.; He, L.; Gross, M.L. Ionic liquids as matrixes for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 3679–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, M.; Loidl, J.; Laus, G.; Schottenberger, H.; Bentivoglio, G.; Wurst, K.; Ongania, K.H. Ionic liquids as advantageous solvents for headspace gas chromatography of compounds with low vapor pressure. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusey, M.L.; Paley, M.S.; Turner, M.B.; Rogers, R.D. Protein crystallization using room temperature ionic liquids. Cryst. Growth Des. 2007, 7, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, R.A.; Dubey, S.; Pereira, M.M.; Maity, T.K.; Singh, S.; Mishra, S.; Prasad, K. Neoteric solvent systems as sustainable media for dissolution and film preparation of Poly-[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate]. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 12005–12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, R.A.; Singh, N.; Pereira, M.M.; Chudasama, N.A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Sharma, M.; Mondal, D.; Prasad, K. High concentration solubility and stability of ɛ-poly-l-lysine in an ammonium-based ionic liquid: A suitable media for polypeptide packaging and biomaterial preparation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jitkumar, B.; Sequeira, R.A.; Vohra, A.; Devkar, R.V.; Maity, T.K.; Prasad, K. Ionic Liquid-Mediated Preparation of Noncytotoxic Hemocompatible Stable DNA− ε-Poly-l-lysine Polyplexes: A New Sustainable Approach for the Bulk Production of Potential Nonviral Vectors for Gene Delivery Applications. ACS Sustain. Che. Eng. 2021, 9, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriguchi, T.; Yanagi, T.; Kunimori, M.; Wada, T.; Sekine, M. Synthesis and properties of aminoacylamido-AMP: Chemical optimization for the construction of an N-acyl phosphoramidate linkage. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 8229–8238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, Y.; Kawai, R.; Hirata, A.; Sugimoto, J.I.; Kataoka, M.; Sakakura, A.; Hirose, M.; Noyori, R. Acid/azole complexes as highly effective promoters in the synthesis of DNA and RNA oligomers via the phosphoramidite method. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 8165–8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, M.; Villela Filho, M.; Liese, A.; Kragl, U. Use of an ionic liquid in a two-phase system to improve an alcohol dehydrogenase catalysed reductionElectronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Experimental section. Chem. Commun. 2004, 1084–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; He, P.; Liu, H.; Li, J. Highly active horseradish peroxidase immobilized in 1-butyl-3- methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate room-temperature ionic liquid based sol-gel host materials. Chem. Commun. 2005, 1778–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Antonietti, M. Synthesis of Very Small TiO 2 Nanocrystals in a Room-Temperature Ionic Liquid and Their Self-Assembly toward Mesoporous Spherical Aggregates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 14960–14961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Antonietti, M. A Series of Highly Ordered, Super-Microporous, Lamellar Silicas Prepared by Nanocasting with Ionic Liquids. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrey, J.D.; Seddon, K.R. Tetrafluoroborates: Ionic liquids and ionic liquid crystals. J. Chem. Soc. Dalt. Trans. 1999, 2133–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haristoy, D.; Tsiourvas, D. Novel ionic liquid-crystalline compounds bearing oxadiazole and pyridinium moieties as prospective materials for optoelectronic applications. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 2079–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernikova, E.A.; Glukhov, L.M.; Krasovskiy, V.G.; Kustov, L.M.; Vorobyeva, M.G.; Koroteev, A.A. Ionic liquids as heat transfer fluids: Comparison with known systems, possible applications, advantages and disadvantages. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2015, 84, 875–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanes, E.G.; Gratz, S.R.; Baldwin, M.J.; Robison, S.E.; Stalcup, A.M. Capillary electrophoretic application of 1-Alkyl-3-methylimidazolium-based ionic liquids. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 3838–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzeo, M.C.; Hardacre, C.; Compton, R.G. Use of room temperature ionic liquids in gas sensor design. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 4583–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Masuda, G.; Takagi, K. Electrochemical properties of novel ionic liquids for electric double layer capacitor applications. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 3603–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, R.A.; Sharma, M.; Pereira, M.M.; Singh, N.; Bhattacharya, S.; Chudasama, N.A.; Prasad, K. One step selective partition of ε-polylysine present in broth cultures in ionic liquid-based aqueous biphasic systems. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jork, C.; Seiler, M.; Beste, Y.A.; Arlt, W. Influence of ionic liquids on the phase behavior of aqueous azeotropic systems. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2004, 49, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, R.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Reis, M.A.M.; Crespo, J.G. Supported liquid membranes using ionic liquids: Study of stability and transport mechanisms. J. Memb. Sci. 2004, 242, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep Eutectic Solvents formed between choline chloride and carboxylic acids: Versatile alternatives to ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdanowicz, M.; Wilpiszewska, K.; Spychaj, T. Deep eutectic solvents for polysaccharides processing. A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 200, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; De Oliveira Vigier, K.; Royer, S.; Jérôme, F. Deep eutectic solvents: Syntheses, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Sequeira, R.A.; Pereira, M.M.; Maity, T.K.; Chudasama, N.A.; Prasad, K. Are ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents the same?: Fundamental investigation from DNA dissolution point of view. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 328C, 115386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-P.; Chang, L.-L.; Chang, S.-N.; Wang, E.-C.; Hwang, L.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Wang, Y.-M. Successful preparation and characterization of biotechnological grade agarose from indigenous Gelidium amansii of Taiwan. Process. Biochem. 2012, 47, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, T.J.; Kumar, A. Efficient Extraction of Agarose from Red Algae Using Ionic Liquids. Green Sustain. Chem. (GSC) 2014, 4, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, M.; Chaudhary, J.P.; Mondal, D.; Meena, R.; Prasad, K. A green and sustainable approach to utilize bio-ionic liquids for the selective precipitation of high purity agarose from an agarophyte extract. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2867–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Sequeira, R.A.; Maity, T.K.; Prasad, K. Bio-ionic liquid promoted selective coagulation of κ-carrageenan from Kappaphycus alvarezii extract. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Sharma, M.; Mondal, D.; Prasad, K. Deep eutectic solvents as efficient solvent system for the extraction of k-carrageenan from Kappaphycus alvarezii. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumpstey, I. Chemical Modification of Polysaccharides. ISRN Org. Chem. 2013, 2013, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebert, T.; Heinze, T. Interaction of ionic liquids wlth polysaccharides 5. Solvents and reaction media for the modification of cellulose. Bioresources 2008, 3, 576–601. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; He, J.; Ren, Q.; Guo, M. Homogeneous acetylation of cellulose in a new ionic liquid. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, S.C.; Li, B.; Xu, D.; Edgar, K.J. Regioselective esterification and etherification of cellulose: A review. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1956–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinze, T.; Schwikal, K.; Barthel, S. Ionic liquids as reaction medium in cellulose functionalization. Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugesan, S.; Linhardt, R. Ionic Liquids in Carbohydrate Chemistry—Current Trends and Future Directions. Curr. Org. Synth. 2005, 2, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamaru, S.I.; Tokunaga, D.; Hori, K.; Matsuda, S.; Shinkai, S. Giant amino acids designed on the polysaccharide scaffold and their protein-like structural interconversion. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Stability and rheological implications of electrostatic milk protein- polysaccharide interactions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1998, 9, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, N.; Singh, H. Milk Protein‒Polysaccharide Interactions in Food Systems. In Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry; Varelis, P., Melton, L., Shahidi, F., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 431–438. ISBN 9780128140260. [Google Scholar]
- Phizicky, E.M.; Fields, S. Protein-Protein Interactions: Methods for Detection and Analysis. Microbiol. Rev. 1995, 59, 94–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstoguzov, V.B. Protein-polysaccharide interactions. Food Proteins Their Appl. 2017, 5, 171–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, F.; Carvajal, M.T.; Harris, M.T. Interactions between bovine serum albumin and alginate: An evaluation of alginate as protein carrier. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 332, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudasama, N.A.; Siddhanta, A.K. Facile synthesis of nano-sized agarose based amino acid—Its pH-dependent protein-like behavior and interactions with bovine serum albumin. Carbohydr. Res. 2015, 417, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudasama, N.A.; Prasad, K.; Siddhanta, A.K. Agarose functionalization: Synthesis of PEG-agarose amino acid nano-conjugate—Its structural ramifications and interactions with BSA in a varying pH regime. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Chudasama, N.A.; Prasad, K.; Siddhanta, A.K. Agarose based large molecular systems: Synthesis of fluorescent aromatic agarose amino acid nano-conjugates—their pH-stimulated structural variations and interactions with BSA. Carbohydr. Res. 2017, 449, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Name | Origin | Main Sugar Moieties | Seaweeds | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate | Cell wall of brown seaweeds and exopolysaccharides of Azoto bacter vinelandii | (1,4)-linked β-D-mannuronic acid and (1,4)-linked α-L-glucuronic acid | Ascophyllum nodosum, Laminariahyperborea, Macrocystispyrifera, and Sargassum | [31] |
| Agar | Cell wall of red seaweeds | (1,3) linked β-D-galactopyranose and (1,4) linked α-3,6-anhydro-L-galactopyranose | Acanthopeltis spp., Campylaephora spp., Ceramium spp., Gelidium spp., Gracilaria spp., Pterocladia | [32] |
| Carrageenan | Cell wall of red seaweeds | (1,3) linked α-D-galactopyranose and (1,4) linked β-(3,6-anhydro)-D-galactopyranose | Sarcothalia crispate, Gigartina skottsbergii, Eucheuma denticulatum, Kappaphycus alvarezii and Chondrus crispus | [33] |
| Ulvan | Sulphated polysaccharides obtained from Ulva and Enteromorpha | (1,4)-, (1,3)-, (1,3,4)-linked rhamnose and (1,4)-, (1,2,4)-linked xylose | Ulva lactuca, Ulva faciata, Ulva reticulata | [34] |
| Fucoidan | Sulphated polysaccharide obtained from brown seaweeds | (1,3)-linked α-L-fucopyranosyl residue | Ascophyllum nodosum, Laminariahyperborea, Macrocystispyrifera | [35] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chudasama, N.A.; Sequeira, R.A.; Moradiya, K.; Prasad, K. Seaweed Polysaccharide Based Products and Materials: An Assessment on Their Production from a Sustainability Point of View. Molecules 2021, 26, 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092608
Chudasama NA, Sequeira RA, Moradiya K, Prasad K. Seaweed Polysaccharide Based Products and Materials: An Assessment on Their Production from a Sustainability Point of View. Molecules. 2021; 26(9):2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092608
Chicago/Turabian StyleChudasama, Nishith A., Rosy Alphons Sequeira, Kinjal Moradiya, and Kamalesh Prasad. 2021. "Seaweed Polysaccharide Based Products and Materials: An Assessment on Their Production from a Sustainability Point of View" Molecules 26, no. 9: 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092608
APA StyleChudasama, N. A., Sequeira, R. A., Moradiya, K., & Prasad, K. (2021). Seaweed Polysaccharide Based Products and Materials: An Assessment on Their Production from a Sustainability Point of View. Molecules, 26(9), 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092608