Ultrasound-Assisted Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Using Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) for Neutral Red Dye Spectrophotometric Determination
Abstract
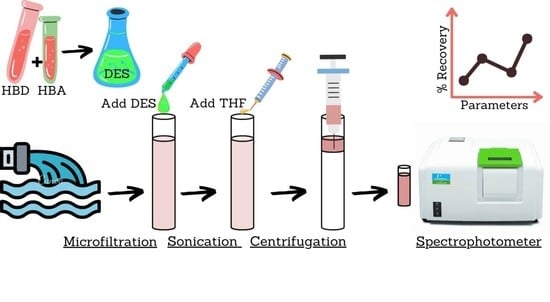
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Optimization of pH during Extraction
2.2. Solvent Selection and Optimization of Extraction Conditions
2.3. Analytical Performance of the Developed Method
2.4. Method Application
2.5. Comparative Study
2.6. Computational Study of DES and NR Interaction
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. DES Preparation
3.4. Sample Preparation and Extraction Experiments
3.5. Determination of Absorption Peak (λmax)
3.6. Calculation of Percentage of Recovery and Validation Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Gupta, V.K.; Jain, R.; Nayak, A.; Agarwal, S.; Shrivastava, M. Removal of the hazardous dye—Tartrazine by photodegradation on titanium dioxide surface. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobya, M.; Gengec, E.; Demirbas, E. Operating parameters and costs assessments of a real dyehouse wastewater effluent treated by a continuous electrocoagulation process. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2016, 101, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, X.; Jin, Y. Characterisation of acute toxicity, genotoxicity and oxidative stress posed by textile effluent on zebrafish. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 2019–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, K.A.; Bello, O.S. Dye sequestration using agricultural wastes as adsorbents. Water Resour. Ind. 2015, 12, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Chen, J.S.; Lou, X.W. Highly efficient removal of organic dyes from waste water using hierarchical NiO spheres with high surface area. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 6873–6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cako, E.; Gunasekaran, K.D.; Soltani, R.D.C.; Boczkaj, G. Ultrafast degradation of brilliant cresyl blue under hydrodynamic cavitation based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs). Water Resour. Ind. 2020, 24, 100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stec, A.A.; Hull, T.R. Fire Toxicity; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Lu, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X. Adsorption of methylene blue on adsorbent materials produced from cotton stalk. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oseroff, A.; Ohuoha, D.; Ara, G.; McAuliffe, D.; Foley, J.; Cincotta, L. Intramitochondrial dyes allow selective in vitro photolysis of carcinoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 9729–9733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayramoglu, G.; Altintas, B.; Arica, M.Y. Adsorption kinetics and thermodynamic parameters of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions by using a new strong cation-exchange resin. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 152, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comm, C.; Energy, J.M.P.E.; Dev, O.P.R. Publication list. Org. Process. Res. Dev 2008, 12, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Bulgarelli, D.L.; Ting, A.Y.; Gordon, B.J.; de Sá Rosa, A.C.J.; Zelinski, M.B. Development of macaque secondary follicles exposed to neutral red prior to 3-dimensional culture. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2018, 35, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, U.; Uddin, M.K.; Gondal, M. Removal of hazardous azo dye from water using synthetic nano adsorbent: Facile synthesis, characterization, adsorption, regeneration and design of experiments. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 584, 124031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, E.; Celeiro, M.; Lamas, J.P.; Llompart, M.; Garcia-Jares, C. Determination of dyes in cosmetic products by micro-matrix solid phase dispersion and liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1415, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balçık, U.; Chormey, D.S.; Ayyıldız, M.F.; Bakırdere, S. Liquid phase microextraction based sensitive analytical strategy for the determination of 22 hazardous aromatic amine products of azo dyes in wastewater and tap water samples by GC-MS system. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Wang, J. Molecularly imprinted polymer for selective extraction of malachite green from seawater and seafood coupled with high-performance liquid chromatographic determination. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2656–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M. Catalytic activity for the oxidation of methanol and the acid-base properties of metal oxides. J. Catal. 1978, 54, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, N.J. Animal communication: When i’m calling you, will you answer too? Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R713–R715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabood, F.; Hussain, Z.; Haq, H.; Arian, M.; Boqué, R.; Khan, K.; Hussain, K.; Jabeen, F.; Hussain, J.; Ahmed, M. Development of new UV–vis spectroscopic microwave-assisted method for determination of glucose in pharmaceutical samples. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 153, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.H.; Kaykhaii, M.; Keikha, A.J.; Sajjadi, Z. Application of Box-Behnken design in response surface methodology for the molecularly imprinted polymer pipette-tip solid phase extraction of methyl red from seawater samples and its determination by spectrophotometery. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, P.A. Handbook of Separation Techniques for Chemical Engineers; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Coutinho, J.A.; Fernandes, A.M.; Freire, M.G. Complete removal of textile dyes from aqueous media using ionic-liquid-based aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 128, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydberg, J.; Musikas, C.; Choppin, G.R. Principles and Practices of Solvent Extraction; M. Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.E.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abbott, A. Deep Eutectic Solvents; Leuven Summer School on Ionic Liquids: Leicester, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Zhang, H.; Row, K.H. Application of deep eutectic solvents in the extraction and separation of target compounds from various samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florindo, C.; Oliveira, F.S.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Fernandes, A.M.; Marrucho, I.M. Insights into the synthesis and properties of deep eutectic solvents based on cholinium chloride and carboxylic acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2416–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, H.U.; Balal, M.; Castro-Muñoz, R.; Hussain, Z.; Safi, F.; Ullah, S.; Boczkaj, G. Deep eutectic solvents based assay for extraction and determination of zinc in fish and eel samples using FAAS. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 333, 115930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchel, M.; Cieśliński, H.; Boczkaj, G. Deep eutectic solvents microbial toxicity: Current state of art and critical evaluation of testing methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, H.U.; Bibi, R.; Arain, M.B.; Safi, F.; Ullah, S.; Castro-Muñoz, R.; Boczkaj, G. Deep eutectic solvent (DES) with silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) based assay for analysis of lead (II) in edible oils. Food Chem. 2022, 379, 132085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraz, N.; Haq, H.U.; Arain, M.B.; Castro-Muñoz, R.; Boczkaj, G.; Khan, A. Deep eutectic solvent based method for analysis of Niclosamide in pharmaceutical and wastewater samples–A green analytical chemistry approach. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 335, 116142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, M.; Mahmoodi-Maymand, M.; Dastmalchi, F. Green, fast and simple dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method by using hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for analysis of folic acid in fortified flour samples before liquid chromatography determination. Food Chem. 2020, 320, 126486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.; Gorbunov, A.; Moskvin, L.; Bulatov, A. Decomposition of deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride and phenol in aqueous phase. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 301, 112380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Gupta, V.B. Methods for the determination of limit of detection and limit of quantitation of the analytical methods. Chron. Young Sci. 2011, 2, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegrini, F.; Olivieri, A.C. IUPAC-consistent approach to the limit of detection in partial least-squares calibration. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7858–7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Environmental Protection Agency. Definition and Procedure for the Determination of the Method Detection Limit, Revision 2; Environmental Protection Agency EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Chen, H.L.; Wei, G.T. The use ionic liquid as the eluent additive for HPLC separation of ionic dyes. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2010, 57, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawed, E.A.; Alqarni, Y. Determination of azine and triphenyl methane dye in wastewater using polyurethane foam functionalized with tannic acid. Sample Prep. 2013, 1, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivas, K.; Wu, H.F. Functionalized-multiwalled carbon nanotubes as a preconcentrating probe for rapid monitoring of cationic dyestuffs in environmental water using AP-MALDI/MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 3603–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-R.; Wang, S. Ionic liquid-based hollow fiber-supported liquid-phase microextraction enhanced electrically for the determination of neutral red. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubalo, M.C.; Radošević, K.; Redovniković, I.R.; Slivac, I.; Srček, V.G. Toxicity mechanisms of ionic liquids. Arh. Za Hig. Rada I Toksikol. 2017, 68, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miehlich, B.; Savin, A.; Stoll, H.; Preuss, H. Results obtained with the correlation energy density functionals of becke and Lee, Yang and Parr. Chem. Phys. Lett 1989, 157, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Check, C.E.; Faust, T.O.; Bailey, J.M.; Wright, B.J.; Gilbert, T.M.; Sunderlin, L.S. Addition of polarization and diffuse functions to the LANL2DZ basis set for p-block elements. J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 8111–8116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, S.; Moellmann, J.; Reckien, W.; Bredow, T.; Grimme, S. System-Dependent dispersion coefficients for the DFT-D3 treatment of adsorption processes on ionic surfaces. ChemPhysChem 2011, 12, 3414–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pick, U.; Avron, M. Neutral red response as a measure of the pH gradient across chloroplast membranes in the light. FEBS Lett. 1976, 65, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banjare, M.K.; Behera, K.; Satnami, M.L.; Pandey, S.; Ghosh, K.K. Self-assembly of a short-chain ionic liquid within deep eutectic solvents. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7969–7979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.C.; Lee, Y.; Lam, H.; Zhang, X.-M. Analytical Method Validation and Instrument Performance Verification; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kazi, T.G.; Shah, F.; Afridi, H.I.; Khan, S.; Arian, S.S.; Brahman, K.D. A green preconcentration method for determination of cobalt and lead in fresh surface and waste water samples prior to flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2012, 2012, 713862. [Google Scholar]
- Asgharinezhad, A.A.; Rezvani, M.; Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Shekari, N.; Ahmadinasab, N.; Loni, M. Solid phase extraction of Pb (II) and Cd (II) ions based on murexide functionalized magnetic nanoparticles with the aid of experimental design methodology. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 10350–10358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asl, Y.A.; Yamini, Y.; Rezazadeh, M.; Seidi, S. Electromembrane extraction using a cylindrical electrode: A new view for the augmentation of extraction efficiency. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | Analyte Added (µg/L) | Analyte Found (µg/L) | % Recovery | % RSD (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wastewater (Industrial effluents) | 0.00 | <LOD | ||
| 5 | 5.11 | 102.2 | ±1.0 | |
| 10 | 10.29 | 102.9 | ±1.5 | |
| 20 | 20.39 | 101.95 | ±1.8 |
| Analytical Method | LOD (µg/L) | RSD (%) | Linearity Range (µg/L) | % Recovery | EF | Estimated Time (min) | Samples Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a HFLPME/b HPLC | 0.3 | 4.3 | 1.0–10.0 | 95.0–112.0 | 00 | ≥28 | Standard only | [38] |
| c FMWCNT/d UV-SP | 1.0 | 12.3 | 12–40 | 88.6–98.4 | --- | ≥40 | Wastewater | [39] |
| e FMCN/f AP-MALDI/MS | 4.47 | 0.14 | 20–32 | ≥50 | River water | [40] | ||
| g IL-HFLPME/d UV-SP | 100 | 1.5 | 96.4 | 15 | ≥33 | Soft drinks | [41] | |
| h DES-LPME/d UV-SP | 2.2 | 1.5 | 2–400 | 102 | 40 | ≤5.5 | Wastewater | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullah, S.; Haq, H.U.; Salman, M.; Jan, F.; Safi, F.; Arain, M.B.; Khan, M.S.; Castro-Muñoz, R.; Boczkaj, G. Ultrasound-Assisted Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Using Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) for Neutral Red Dye Spectrophotometric Determination. Molecules 2022, 27, 6112. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27186112
Ullah S, Haq HU, Salman M, Jan F, Safi F, Arain MB, Khan MS, Castro-Muñoz R, Boczkaj G. Ultrasound-Assisted Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Using Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) for Neutral Red Dye Spectrophotometric Determination. Molecules. 2022; 27(18):6112. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27186112
Chicago/Turabian StyleUllah, Sana, Hameed Ul Haq, Muhammad Salman, Faheem Jan, Faisal Safi, Muhammad Balal Arain, Muhammad Shahzeb Khan, Roberto Castro-Muñoz, and Grzegorz Boczkaj. 2022. "Ultrasound-Assisted Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Using Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) for Neutral Red Dye Spectrophotometric Determination" Molecules 27, no. 18: 6112. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27186112
APA StyleUllah, S., Haq, H. U., Salman, M., Jan, F., Safi, F., Arain, M. B., Khan, M. S., Castro-Muñoz, R., & Boczkaj, G. (2022). Ultrasound-Assisted Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Using Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) for Neutral Red Dye Spectrophotometric Determination. Molecules, 27(18), 6112. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27186112