Multielement Determination in Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) Using Different Digestion Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Methodology
2.1.1. Sample Preparation
2.1.2. Quantification of the Elements by Atomic Spectrometry
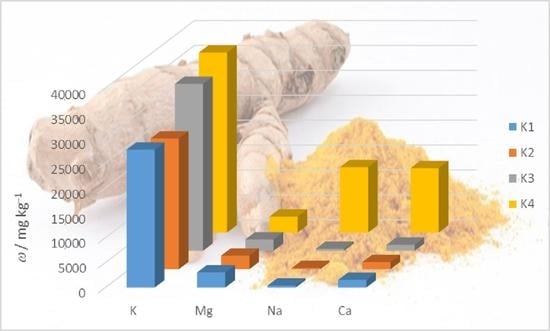
2.2. Elemental Composition of Turmeric Samples
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Samples
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. Measurements
3.4. Data Evaluation and Statistics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nwankwo, C. Nutritional Composition of Turmeric (Curcuma longa) and its Antimicrobial Properties. Int. J. Eng. Res. 2014, 5, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Turmeric, the Golden Spice: From Traditional Medicine to Modern Medicine. In Herbal Medicine: Biomolecular and Clinical Aspects, 2nd ed.; Benzie, I.F.F., Wachtel-Galor, S., Eds.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; Chapter 13. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92752/# (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Li, S.Y.; Yuang, W.; Deng, G.; Wang, P.; Yang, P.; Aggarwal, B.B. Chemical composition and product quality control of turmeric (Curcuma longa L.). Pharm. Crops 2011, 2, 28–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosoky, N.S.; Setzer, W.N. Chemical Composition and Biological Activities of Essential Oils of Curcuma Species. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, S.C.; Sung, B.; Kim, J.H.; Prasad, S.; Li, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Multitargeting by turmeric, the golden spice: From kitchen to clinic. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1510–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewlings, S.J.; Kalman, D.S. Curcumin: A Review of Its Effects on Human Health. Foods 2017, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verpoort, R.; Contin, A.; Memelink, J. Biotechnology for the production of plant secondary metabolites. Phytochem. Rev. 2002, 1, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasim, S.A.; Dhir, B. Heavy metals alter the potency of medicinal plants. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 203, 139–149. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Quality Control Methods for Medicinal Plant Materials; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/41986 (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Khalid, S.; Schreck, E.; Xiong, T.; Niazi, N.K. Foliar heavy metal uptake, toxicity and detoxification in plants: A comparison of foliar and root metal uptake. J. Hazard Mater. 2017, 5, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goyer, R.A. Toxic and essential metal interactions. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1997, 17, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghrabi, I. Determination of some mineral and heavy metals in Saudi Arabia popular herbal drugs using modern techniques. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 8, 893–898. [Google Scholar]
- Muralidharan, L.; Muralidharan, C.; Gaur, S. Analysis of Heavy and Trace Metals in Golden Ingredient Turmeric (Curcuma longa) of Mumbai, Maharashtra. 2019. Available online: 10.13140/RG.2.2.25945.88168 (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Silva, P.; Francisconi, L.; Gonçalves, R. Evaluation of Major and Trace Elements in Medicinal Plants. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2016, 27, 2273–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiner, M.; Cindrić, I.J. Review–trace determination of potentially toxic elements in (medicinal) plant materials. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1550–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyn, J.; Ramsey, M.; Fussell, R.; Wood, R. Measurement uncertainty from physical sample preparation: Estimation including systematic error. Analyst 2003, 128, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, M.; Rostron, P.; Ellison, S. Eurachem/EUROLAB/CITAC/Nordtest/AMC Guide: Measurement Uncertainty Arising from Sampling: A Guide to Methods and Approach, 2nd ed.; Eurachem: Brighton, UK, 2019; Available online: https://www.eurachem.org/images/stories/Guides/pdf/UfS_2019_EN_P2.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Bendicho, C.; Lavilla, I.; Pena-Pereira, F.F.; Romero, V. Green chemistry in analytical atomic spectrometry: A review. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2012, 27, 1831–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.; Fernandes, A.D.; Babos, D.; Castro, J.; Costa, V.; Sperança, M.A.; Garcia, J.; Gamela, R.; Filho, E. Solid sampling: Advantages and challenges in atomic spectrometry—A critical review. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2019, 35, 54–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, M.; Uyanik, A.; Cay, S.; Icbudak, H. Effect of the Adsorptive Character of Filter Papers on the Concentrations Determined in Studies Involving Heavy Metal Ions. Adsorp. Sci. Technol. 2010, 28, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, T.W.; Wiedmeyer, R.H. A Table of Polyatomic Interferences in ICP-MS. At. Spectrosc. 1998, 19, 150–155. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiner, M.; Kuhar, A.; Cindrić, I.J. Geographic Differences in Element Accumulation in Needles of Aleppo Pines (Pinus halepensis Mill.) Grown in Mediterranean Region. Molecules 2019, 24, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeiner, M.; Cindrić, I.J.; Nemet, I.; Franjković, K.; Salopek Sondi, B. Influence of Soil Salinity on Selected Element Contents in Different Brassica Species. Molecules 2022, 27, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, A.; Lichtscheidl, I. Strontium in the environment: Review about reactions of plants towards stable and radioactive strontium isotopes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 1458–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, A.L.; Ara, A.; Usmani, J.A. Lead toxicity: A review. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2015, 8, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koons, A.L.; Rajasurya, V. Cadmium Toxicity. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536966/ (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Andersson, C.M. Determination of Bio-Accessible Amounts of Metal Trace Elements in Baby Food Using In Vitro Artificial Digestion. Bachelor’s Thesis, Örebro University, Örebro, Sweden, 2022. [Google Scholar]





| Parameter | ICP-OES * | ICP-MS ** |
|---|---|---|
| Instrument | Prodigy High Dispersive ICP-AES (Teledyne Leeman, Hudson, NH, USA) | Agilent 7500cx ICP-MS (Agilent, Tokyo, Japan) |
| Output power | 1100 W | 1500 W |
| Argon flows | Plasma:18 L/min | Plasma:15 L/min |
| Auxiliary: 0.8 L/min | Auxiliary: 0.9 L/min | |
| Nebulizer: 1 L/min | Nebulizer: 0.2 L/min | |
| Collison cell | ------- | On/off depending on element |
| Nebulizer | Pneumatic (glass concentric) | MicroMist |
| Spray chamber | Glass cyclonic | Scott double pass |
| Sample flow | 1.0 mL/min | 0.3 mL/min |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeiner, M.; Šoltić, M.; Nemet, I.; Juranović Cindrić, I. Multielement Determination in Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) Using Different Digestion Methods. Molecules 2022, 27, 8392. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238392
Zeiner M, Šoltić M, Nemet I, Juranović Cindrić I. Multielement Determination in Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) Using Different Digestion Methods. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8392. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238392
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeiner, Michaela, Monika Šoltić, Ivan Nemet, and Iva Juranović Cindrić. 2022. "Multielement Determination in Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) Using Different Digestion Methods" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8392. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238392
APA StyleZeiner, M., Šoltić, M., Nemet, I., & Juranović Cindrić, I. (2022). Multielement Determination in Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) Using Different Digestion Methods. Molecules, 27(23), 8392. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238392