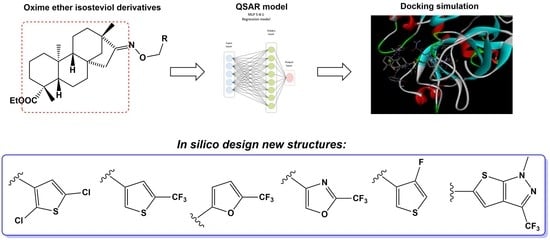
Novel Isosteviol-Based FXa Inhibitors: Molecular Modeling, In Silico Design and Docking Simulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Molecular Modeling
2.2. Molecular Docking
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Molecular Modeling
4.1.1. Energy Optimization of Isosteviol Analogues
 | ||||
| Compound | Sample | R * | Optimized Molecular Structure | Inhibition Constant (Ki), µM ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | train |  |  | 9.253 |
| b | train |  |  | 4.333 |
| d | train |  |  | 9.786 |
| e | train |  |  | 2.693 |
| f | train |  |  | 1.023 |
| g | train |  |  | 0.321 |
| h | test |  |  | 9.877 |
| i | train |  |  | 0.515 |
| j | test |  |  | 1.941 |
| k | train |  |  | 0.015 |
| l | train |  |  | 4.025 |
| m | train |  |  | 2.875 |
| n | train |  |  | 1.809 |
| o | train |  |  | 1.612 |
| p | validation |  |  | 0.028 |
| q | train |  |  | 0.785 |
| r | validation |  |  | 8.607 |
4.1.2. Molecular Descriptors
4.1.3. Regression Analysis
4.2. Molecular Docking Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Kushnir, M.; Choi, Y.; Eisenberg, R.; Rao, D.; Tolu, S.; Gao, J.; Mowrey, W.; Billett, H.H. Efficacy and Safety of Direct Oral Factor Xa Inhibitors Compared with Warfarin in Patients with Morbid Obesity: A Single-Centre, Retrospective Analysis of Chart Data. Lancet Haematol. 2019, 6, e359–e365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariño-Ocampo, N.; Rodríguez, D.F.; Guerra Díaz, D.; Zúñiga-Núñez, D.; Duarte, Y.; Fuentealba, D.; Zacconi, F.C. Direct Oral FXa Inhibitors Binding to Human Serum Albumin: Spectroscopic, Calorimetric, and Computational Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreuder, M.; Reitsma, P.H.; Bos, M.H.A. Reversal Agents for the Direct Factor Xa Inhibitors: Biochemical Mechanisms of Current and Newly Emerging Therapies. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2020, 46, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, H.; Shimada, M.; Narita, M.; Narita, I.; Kimura, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Osanai, T.; Okumura, K.; Tomita, H. Rivaroxaban, a Direct Factor Xa Inhibitor, Ameliorates Hypertensive Renal Damage Through Inhibition of the Inflammatory Response Mediated by Protease-Activated Receptor Pathway. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e012195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Urquhart, L. Top Companies and Drugs by Sales in 2021. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, R.C.; Adcock, D.M.; Douxfils, J. An Update on Laboratory Assessment for Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs). Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2019, 41, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Yuan, J.; Fu, X.; Meng, F.; Zhang, S.; Xu, W.; Xu, Y.; Huang, C. Novel Anthranilamide-Based FXa Inhibitors: Drug Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation. Molecules 2016, 21, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez, D.F.; Durán-Osorio, F.; Duarte, Y.; Olivares, P.; Moglie, Y.; Dua, K.; Zacconi, F.C. Green by Design: Convergent Synthesis, Computational Analyses, and Activity Evaluation of New FXa Inhibitors Bearing Peptide Triazole Linking Units. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gackowski, M.; Golec, K.S.; Katarzyna, M.; Pluskota, R.; Koba, M. Quantitative Structure—Activity Relationship Analysis of Isosteviol—Related Compounds as Activated Coagulation Factor X (FXa) Inhibitors. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, D.; Li, M.; Wu, Q.; Lam, Y.P.Y.; Guo, Y.; Chen, C.; Bai, N.; Malhotra, S.; Li, W.; et al. Discovery of Novel, Potent, Isosteviol-Based Antithrombotic Agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 183, 111722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, M.L.; Ellis, C.D.; Liauw, A.Y.; Alexander, R.S.; Knabb, R.M.; Lam, G.; Wright, M.R.; Wong, P.C.; Wexler, R.R. Design and Synthesis of Isoxazoline Derivatives as Factor Xa Inhibitors. 2. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 2760–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, D.A.; Bunker, A.M.; Chi, L.; Cody, W.L.; Holland, D.R.; Ignasiak, D.P.; Janiczek-Dolphin, N.; McClanahan, T.B.; Mertz, T.E.; Narasimhan, L.S.; et al. Rational Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity of Benzoxazinones as Novel Factor Xa Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 4063–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasov, A.G.; Zotchev, S.B.; Dirsch, V.M.; Orhan, I.E.; Banach, M.; Rollinger, J.M.; Barreca, D.; Weckwerth, W.; Bauer, R.; Bayer, E.A.; et al. Natural Products in Drug Discovery: Advances and Opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, H.; Xu, F.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; Xu, S.; Zhang, D.; Wu, X.; Xu, J.; Hua, H.; et al. Diterpenoid Lead Stevioside and Its Hydrolysis Products Steviol and Isosteviol: Biological Activity and Structural Modification. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 156, 885–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Munir, S.; Mabkhot, Y. Bioactivity Profile of the Diterpene Isosteviol and Its Derivatives. Molecules 2019, 24, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ooms, F. Molecular Modeling and Computer Aided Drug Design. Examples of Their Applications in Medicinal Chemistry. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 7, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydın, S.G. Review on Molecular Modeling and Docking. SAR J. Sci. Res. 2022, 5, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadendla, R.R. Molecular Modeling: A Powerful Tool for Drug Design and Molecular Docking. Resonance 2004, 9, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talete SRL List of Molecular Descriptors Calculated by Dragon. Available online: http://www.talete.mi.it/products/dragon_molecular_descriptor_list.pdf (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- Consonni, V.; Todeschini, R.; Pavan, M.; Gramatica, P. Structure/Response Correlations and Similarity/Diversity Analysis by GETAWAY Descriptors. 2. Application of the Novel 3D Molecular Descriptors to QSAR/QSPR Studies. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2002, 42, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.Y.; Mercader, A.G.; Saavedra, L.M.; Honarparvar, B.; Romanelli, G.P.; Duchowicz, P.R. QSAR Analysis on Tacrine-Related Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors. J. Biomed. Sci. 2014, 21, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fatemi, M.H.; Gharaghani, S.; Mohammadkhani, S.; Rezaie, Z. Prediction of Selectivity Coefficients of Univalent Anions for Anion-Selective Electrode Using Support Vector Machine. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 4276–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, R.M.V.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Queiroz, M.J.R.P. QSAR Model for Predicting Radical Scavenging Activity of Di(Hetero)Arylamines Derivatives of Benzo[b]Thiophenes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 1952–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, P.M.; Rasulev, B.; Roy, K. QSPR Modeling of the Refractive Index for Diverse Polymers Using 2D Descriptors. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 13374–13386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Consonni, V.; Todeschini, R. Multivariate Analysis of Molecular Descriptors. In Statistical Modelling of Molecular Descriptors in QSAR/QSPR; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; Volume 2, pp. 111–147. ISBN 9783527324347. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva Rocha, S.F.L.; Olanda, C.G.; Fokoue, H.H.; Sant’Anna, C.M.R. Virtual Screening Techniques in Drug Discovery: Review and Recent Applications. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1751–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Mehrotra, R. An Overview of Molecular Simulation. JSM Chem. 2016, 4, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Pan, B.W.; Li, W.C.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Pan, M.; Fu, H.Z. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Isosteviol Derivatives as FXa Inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 126585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobchev, D.; Karelson, M. Have Artificial Neural Networks Met Expectations in Drug Discovery as Implemented in QSAR Framework? Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2016, 11, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TIBCO Statistica® User’s Guide Statistica Automated Neural Networks (SANN)—Neural Networks Overview. Available online: https://docs.tibco.com/pub/stat/14.0.0/doc/html/UsersGuide/GUID-F60C241F-CD88-4714-A8C8-1F28473C52EE.html (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Pappachen, L.K.; Zachariah, S.M.; Chandran, D. In Silico Design, Synthesis and Characterization of Some Novel Benzothiazole Derivatives as Anticancer Agents. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2017, 10, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- RCSB Protein Data Bank 2P16: Factor Xa in Complex with the Inhibitor Apixaban (BMS-562247) AKA 1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-7-OXO-6-(4-(2-OXO-1-Piperidinyl)Phenyl)-4,5,6,7-Tetrahydro-1H-Pyrazolo[3, 4-C]Pyridine-3-Carboxamide. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/2P16 (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Morsy, M.A.; Ali, E.M.; Kandeel, M.; Venugopala, K.N.; Nair, A.B.; Greish, K.; El-Daly, M. Screening and Molecular Docking of Novel Benzothiazole Derivatives as Potential Antimicrobial Agents. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; You, T.; Li, Q.; Chen, G.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; Tang, C.; et al. Molecular Docking-Assisted Screening Reveals Tannic Acid as a Natural Protein Disulphide Isomerase Inhibitor with Antiplatelet and Antithrombotic Activities. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 14257–14269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| MLP 5-8-1 Model | |
|---|---|
| Learning algorithm | BFGS 31 |
| Activation function (Hidden layer) | Logistic |
| Activation function (Output layer) | Tanh |
| Name | Definition | Category | Dimensionality | Error MLP 5-8-1 | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GATS8p | Geary autocorrelation of lag 8 weighted by polarizability [19] | 2D autocorrelations | 2D | 16.75531 | 1 |
| HATS2i | leverage-weighted autocorrelation of lag 2/weighted by ionization potential [19] | GETAWAY descriptors | 3D | 14.49011 | 2 |
| R5e | R autocorrelation of lag 5/weighted by Sanderson electronegativity [19] | GETAWAY descriptors | 3D | 13.33332 | 3 |
| HATS2e | leverage-weighted autocorrelation of lag 2/weighted by Sanderson electronegativity [19] | GETAWAY descriptors | 3D | 8.866242 | 4 |
| SpMAD_B(v) | spectral mean absolute deviation from Burden matrix weighted by van der Waals volume [19] | 2D-matrix-based descriptors | 2D | 8.699860 | 5 |
 | ||
| Compound | R * | Predicted Inhibition Activity Against FXa: Inhibition Constant (Ki), [µM] ** |
|---|---|---|
| e1 |  | 9.785990 |
| e2 |  | 1.118201 |
| e3 |  | 0.645249 |
| e4 |  | 9.282278 |
| e5 |  | 3.984843 |
| e6 |  | 6.454281 |
| e7 |  | 2.640193 |
| e8 |  | 1.421969 |
| e9 |  | 4.412301 |
| e10 |  | 1.569841 |
| e11 |  | 1.133094 |
| e12 |  | 0.936761 |
| e13 |  | 0.372101 |
| e14 |  | 0.544725 |
| e15 |  | 0.906731 |
| e16 |  | 0.947983 |
| e17 |  | 0.936441 |
| e18 |  | 0.650819 |
| e19 |  | 0.493827 |
| e20 |  | 0.673789 |
| e21 |  | 0.656182 |
| e22 |  | 0.749590 |
| e23 |  | 0.554588 |
| e24 |  | 0.642575 |
| e25 |  | 0.687738 |
| e26 |  | 0.854700 |
| Compound | Binding-Free Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|
| a | −8.7 |
| b | −8.3 |
| d | −9.3 |
| e | −8.1 |
| f | −8.8 |
| g | −8.3 |
| h | −8.4 |
| i | −7.4 |
| j | −8.0 |
| k | −8.1 |
| l | −8.7 |
| m | −7.8 |
| n | −6.9 |
| o | −7.7 |
| p | −7.0 |
| q | −8.0 |
| r | −6.8 |
| e1 | −6.9 |
| e2 | −7.7 |
| e3 | −8.0 |
| e4 | −7.4 |
| e5 | −7.2 |
| e6 | −7.1 |
| e7 | −7.4 |
| e8 | −7.4 |
| e9 | −7.5 |
| e10 | −7.6 |
| e11 | −7.3 |
| e12 | −7.7 |
| e13 | −7.7 |
| e14 | −7.2 |
| e15 | −8.3 |
| e16 | −6.9 |
| e17 | −7.7 |
| e18 | −7.4 |
| e19 | −6.9 |
| e20 | −8.1 |
| e21 | −8.3 |
| e22 | −7.0 |
| e23 | −8.1 |
| e24 | −8.2 |
| e25 | −8.2 |
| e26 | −7.0 |
| apixaban | −10.3 |
| edoxaban | −8.8 |
| rivaroxaban | −9.4 |
| Action | Reason | Number |
|---|---|---|
| deleted | constant | 1856 |
| near constant | 95 | |
| all missing | 2 | |
| one missing | 2 | |
| highly correlated (|r| > 0.95) | 1658 | |
| standard deviation < 0.0001 | 1856 | |
| retained | suitable for model-building | 1274 |
| Symbol | Variable Rank | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| GATS8p | 100 | 1 |
| R5e | 100 | 1 |
| HATS2i | 100 | 1 |
| HATS2e | 100 | 1 |
| SpMAD_B(v) | 100 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gackowski, M.; Madriwala, B.; Studzińska, R.; Koba, M. Novel Isosteviol-Based FXa Inhibitors: Molecular Modeling, In Silico Design and Docking Simulation. Molecules 2023, 28, 4977. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28134977
Gackowski M, Madriwala B, Studzińska R, Koba M. Novel Isosteviol-Based FXa Inhibitors: Molecular Modeling, In Silico Design and Docking Simulation. Molecules. 2023; 28(13):4977. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28134977
Chicago/Turabian StyleGackowski, Marcin, Burhanuddin Madriwala, Renata Studzińska, and Marcin Koba. 2023. "Novel Isosteviol-Based FXa Inhibitors: Molecular Modeling, In Silico Design and Docking Simulation" Molecules 28, no. 13: 4977. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28134977
APA StyleGackowski, M., Madriwala, B., Studzińska, R., & Koba, M. (2023). Novel Isosteviol-Based FXa Inhibitors: Molecular Modeling, In Silico Design and Docking Simulation. Molecules, 28(13), 4977. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28134977