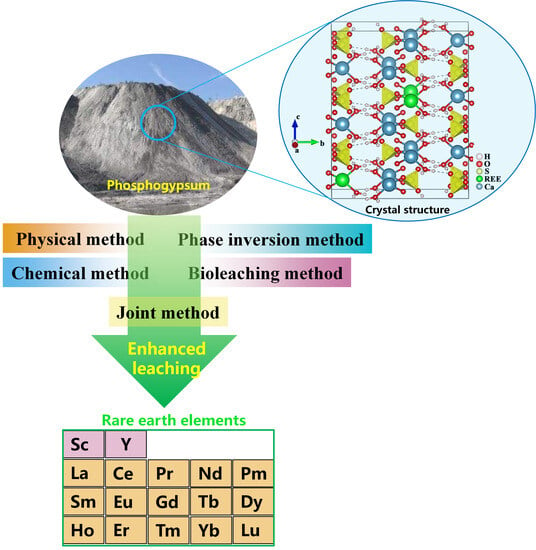
A Critical Review of the Enhanced Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Phosphogypsum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Physically Enhanced Leaching Methods
3. Chemically Enhanced Leaching Methods
3.1. RIL Technology
3.2. Solvometallurgical Method
4. Phase Inversion Enhanced Leaching Methods
4.1. Carbonation
4.2. Recrystallization
5. Bioleaching Methods
6. Joint Methods
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Atwood, D.A. The Rare Earth Elements: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayalakshmi, R.; Mishra, S.; Singh, H.; Gupta, C. Processing of xenotime concentrate by sulphuric acid digestion and selective thorium precipitation for separation of rare earths. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 61, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, A.; Panda, R.; Jha, M.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Kumar, J.R.; Kumar, V. Thermal treatment for the separation of phosphate and recovery of rare earth metals (REMs) from Korean monazite. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 696–703. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Feng, Z.; Huang, X.; Huang, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Long, Z. Recovery of rare earth from the ion-adsorption type rare earths ore: II. Compound leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 163, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, C.; Feng, Z.; Cui, D.; Long, Z. Towards cleaner production of rare earth elements from bastnaesite in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 231–242. [Google Scholar]
- Apergis, E.; Apergis, N. The role of rare earth prices in renewable energy consumption: The actual driver for a renewable energy world. Energy Econ. 2017, 62, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Eggert, R.; Wadia, C.; Anderson, C.; Bauer, D.; Fields, F.; Meinert, L.; Taylor, P. Rare earths: Market disruption, innovation, and global supply chains. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2016, 41, 199–222. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, T.; Gao, T.; Wen, B. China’s rare earth supply and demand pattern and balanced utilization strategy from perspective of elements (in Chinese). Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2022, 37, 1586–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, P.; El-Shall, H.; Moudgil, B.; Huang, X.; Zhang, L. Recovery of rare earth elements from phosphate rock by hydrometallurgical processes—A critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 774–800. [Google Scholar]
- Bandara, H.D.; Field, K.D.; Emmert, M.H. Rare earth recovery from end-of-life motors employing green chemistry design principles. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 753–759. [Google Scholar]
- Machacek, E.; Richter, J.L.; Habib, K.; Klossek, P. Recycling of rare earths from fluorescent lamps: Value analysis of closing-the-loop under demand and supply uncertainties. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 104, 76–93. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Honaker, R. Enhanced leachability of rare earth elements from calcined products of bituminous coals. Miner. Eng. 2019, 142, 105935. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.R. Characterization and recovery of rare earth elements and other critical metals (Co, Cr, Li, Mn, Sr, and V) from the calcination products of a coal refuse sample. Fuel 2020, 267, 117236. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Honaker, R.Q. Rare earth elements recovery using staged precipitation from a leachate generated from coarse coal refuse. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2018, 195, 189–199. [Google Scholar]
- Kovler, K. 8—Radioactive materials. In Toxicity of Building Materials; Pacheco-Torgal, F., Jalali, S., Fucic, A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 196–240. [Google Scholar]
- Jamialahmadi, M.; Müller-Steinhagen, H. Crystallization of calcium sulfate dihydrate from phosphoric acid. Dev. Chem. Eng. Miner. Process. 2000, 8, 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayibi, H.; Choura, M.; López, F.A.; Alguacil, F.J.; López-Delgado, A. Environmental impact and management of phosphogypsum. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2377–2386. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Q.; Sui, Y.; Yu, W.; Bu, Y.; Zeng, C.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Chi, R.-A. Deep removal of phosphorus and synchronous preparation of high-strength gypsum from phosphogypsum by crystal modification in NaCl-HCl solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 298, 121592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Sui, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yu, W.; Bo, Y.; Wang, P.; Peng, W.; Jin, J. Preparation of α-calcium sulfate hemihydrate from industrial by-product gypsum: A review. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2021, 57, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cánovas, C.R.; Macías, F.; Pérez-López, R.; Basallote, M.D.; Millán-Becerro, R. Valorization of wastes from the fertilizer industry: Current status and future trends. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 678–690. [Google Scholar]
- El Afifi, E.; Khalil, M.; El-Aryan, Y. Leachability of radium-226 from industrial phosphogypsum waste using some simulated natural environmental solutions. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 94. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira, S.M.B.; Da Silva, P.S.C.; Mazzilli, B.P.; Favaro, D.I.T.; Saueia, C.H. Rare earth elements as tracers of sediment contamination by phosphogypsum in the Santos estuary, southern Brazil. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 837–850. [Google Scholar]
- Parreira, A.B.; Kobayashi, A.R.K.; Silvestre, O., Jr. Influence of Portland cement type on unconfined compressive strength and linear expansion of cement-stabilized phosphogypsum. J. Environ. Eng. 2003, 129, 956–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, B. Preparation of load-bearing building materials from autoclaved phosphogypsum. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 687–693. [Google Scholar]
- Reijnders, L. Cleaner phosphogypsum, coal combustion ashes and waste incineration ashes for application in building materials: A review. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walawalkar, M.; Nichol, C.K.; Azimi, G. Process investigation of the acid leaching of rare earth elements from phosphogypsum using HCl, HNO3, and H2SO4. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 166, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Değirmenci, N. Utilization of phosphogypsum as raw and calcined material in manufacturing of building products. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, K.; Menezes, M.; Von Sperling, E.; Jacomino, V. Transfer factor of rare earth elements from phosphogypsum amended Brazilian tropical soils to lettuce, corn and soybean. J. Solid Waste Technol. Manag. 2012, 38, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcordo, I.S.; Rechcigl, J.E. Phosphogypsum in agriculture: A review. Adv. Agron. 1993, 49, 55–118. [Google Scholar]
- Smadi, M.M.; Haddad, R.H.; Akour, A.M. Potential use of phosphogypsum in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Sui, Y.; Yu, W.; Bu, Y.; Zeng, C.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Ru-An, C. Moderately efficient leaching of rare earth elements from phosphogypsum via crystal regulation with EDTA-2Na during gypsum phase transformation and recovery by precipitation. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 214, 105963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Pontikes, Y. Towards zero-waste valorisation of rare-earth-containing industrial process residues: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 99, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Meshram, P.; Pandey, B.D. Metallurgical processes for the recovery and recycling of lanthanum from various resources-A review. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 160, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokshin, E.; Tareeva, O.; Elizarova, I. A study of the sulfuric acid leaching of rare-earth elements, phosphorus, and alkali metals from phosphodihydrate. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2010, 83, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychkov, V.N.; Kirillov, E.V.; Kirillov, S.V.; Semenishchev, V.S.; Bunkov, G.M.; Botalov, M.S.; Smyshlyaev, D.V.; Malyshev, A.S. Recovery of rare earth elements from phosphogypsum. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akfas, F.; Elghali, A.; Bodinier, J.-L.; Parat, F.; Muñoz, M. Geochemical and mineralogical characterization of phosphogypsum and leaching tests for the prediction of the mobility of trace elements. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 43778–43794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samonov, A.E. New data on mineral forms of rare metals in phosphogypsum wastes. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2011, 440, 1312–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freyer, D.; Voigt, W. Crystallization and phase stability of CaSO4 and CaSO4–based salts. Monatsh. Chem. 2003, 134, 693–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Malik, M.; Azimi, G. Extraction of Rare Earth Elements from Phosphogypsum Using Mineral Acids: Process Development and Mechanistic Investigation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaramaiah, R.; Lee, W.; Navrotsky, A.; Yu, D.; Kim, P.; Wu, H.; Hu, Z.; Riman, R.; Anderko, A. Location and stability of europium in calcium sulfate and its relevance to rare earth recovery from phosphogypsum waste. Am. Mineral. 2016, 101, 1854–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosiński, A.; Kowalczyk, J.; Mazanek, C. Development of the Polish wasteless technology of apatite phosphogypsum utilization with recovery of rare earths. J. Alloys Compd. 1993, 200, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, J.; Cole, P.; Craig, W.; Feather, A. The recovery of rare earth oxides from a phosphoric acid by-product. Part 1: Leaching of rare earth values and recovery of a mixed rare earth oxide by solvent extraction. Hydrometallurgy 1996, 41, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Reefy, S.; Nayl, A.; Aly, H. Leaching and group separation of lanthanides from phosphogypsum. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference for Nuclear Sciences and Applications, Sharm EI Shiekh, Egypt, 11–14 February 2008; pp. 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Abramov, Y.K.; Veselov, V.M.; Zalevsky, V.M.; Argunov, N.D.; Bogdanova, L.P.; Gukasov, N.A.; Evdokimov, V.D.; Tamurka, V.G.; Motovilova, L.V. Method for Extracting Rare Earth Elements from Phosphogypsum. US Patents US20120114538A1, 25 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Thyabat, S.; Zhang, P. REE extraction from phosphoric acid, phosphoric acid sludge, and phosphogypsum. Miner. Process. Extr. Met. 2015, 124, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, Z.; Elgoud, E.A.; Hai, F.; Ali, I.O.; Gasser, M.; Aly, H. Leaching of some lanthanides from phosphogypsum fertilizers by mineral acids. Arab J. Nucl. Sci. Appl. 2015, 48, 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, P.; Jin, Z.; Depaoli, D. Rare earths recovery and gypsum upgrade from Florida phosphogypsum. Miner. Metall. Process. 2017, 34, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.; Anawati, J.; Walawalkar, M.; Tam, J.; Azimi, G. Innovative application of microwave treatment for recovering of rare earth elements from phosphogypsum. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 16471–16481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cánovas, C.R.; Chapron, S.; Arrachart, G.; Pellet-Rostaing, S. Leaching of rare earth elements (REEs) and impurities from phosphogypsum: A preliminary insight for further recovery of critical raw materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 219, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonick, P.J.; Hu, Z.; Fujita, Y.; Reed, D.W.; Das, G.; Wu, L.; Shivaramaiah, R.; Kim, P.; Eslamimanesh, A.; Lencka, M.M. Bio-and mineral acid leaching of rare earth elements from synthetic phosphogypsum. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 132, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lütke, S.F.; Pinto, D.; Brudi, L.C.; Silva, L.F.; Cadaval, T.R., Jr.; Duarte, F.A.; Ahmad, N.; Nawaz, A.; Dotto, G.L. Ultrasound-assisted leaching of rare earth elements from phosphogypsum. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2023, 191, 109458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lütke, S.F.; Oliveira, M.L.; Waechter, S.R.; Silva, L.F.; Cadaval, T.R., Jr.; Duarte, F.A.; Dotto, G.L. Leaching of rare earth elements from phosphogypsum. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Sui, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, C.; Yu, W.; Gao, Z.; Zang, Z.; Chi, R.-A. Characterization and leaching kinetics of rare earth elements from phosphogypsum in hydrochloric acid. Minerals 2022, 12, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Guan, Q.; Sui, Y.; Yu, W.; Bu, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z. Kinetics of nitric acid leaching of low-grade rare earth elements from phosphogypsum. J. Cent. South Univ. 2022, 29, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, M.; Ismail, Z.; Elgoud, E.A.; Hai, F.A.; Ali, O.; Aly, H. Process for lanthanides-Y leaching from phosphogypsum fertilizers using weak acids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 378, 120762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorovsky, D.; Terziev, A.; Milanova, M. Influence of mechanoactivation on rare earths leaching from phosphogypsum. Hydrometallurgy 1997, 45, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammas-Nasri, I.; Horchani-Naifer, K.; Férid, M.; Barca, D. Rare earths concentration from phosphogypsum waste by two-step leaching method. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2016, 149, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, J. The effect of ultrasound on the process of acidic leaching of apatite phosphogypsum. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 1994, 28, 159–163. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, S.; Walawalkar, M.; Azimi, G. Valorization of rare earth-containing landfilled stocks of industrial process residues: Phosphogypsum and red mud. In Proceedings of the European Real Estate Society (ERES), Santorini, Greece, 28 June–1 July 2017; pp. 164–165. [Google Scholar]
- Padayachee, A.; Johns, M.; Green, B. The use of ion exchange resins to recover rare earths from apatite gypsum residue. Spec. Publ. R. Soc. Chem. 1996, 182, 380–387. [Google Scholar]
- Yahorava, V.; Bazhko, V.; Freeman, M. Viability of phosphogypsum as a secondary resource of rare earth elements. In Proceedings of the International Mineral Processing Congress 2016 (IMPC), Québec City, QC, Canada, 11–15 September 2016; pp. 5239–5254. [Google Scholar]
- Rychkov, V.N.; Kirillov, E.V.; Smirnov, A.L.; Jazev, V.A.; Ivanko, V.A. Method of Extracting Rare-Earth Elements from Phosphogypsum, Russian. RU2509726C2, 20 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kolyasnikov, S.V.; Borisov, M.M.; Kirillov, E.V.; Rybina, M.L. Extraction Method of Rare-Earth Metals from Phosphogypsum. RU Patents RU2487834C1, 20 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Virolainen, S.; Repo, E.; Sainio, T. Recovering rare earth elements from phosphogypsum using a resin-in-leach process: Selection of resin, leaching agent, and eluent. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 189, 105125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkinen, S.; Virolainen, S.; Sainio, T. Recovery of rare earth elements from phosphogypsum waste in resin-in-leach process by eluting with biodegradable complexing agents. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 201, 105569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Didamony, H.; Ali, M.; Awwad, N.; Fawzy, M.; Attallah, M. Treatment of phosphogypsum waste using suitable organic extractants. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2012, 291, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Didamony, H.; Gado, H.; Awwad, N.; Fawzy, M.; Attallah, M. Treatment of phosphogypsum waste produced from phosphate ore processing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masmoudi-Soussi, A.; Hammas-Nasri, I.; Horchani-Naifer, K.; Férid, M. Study of rare earths leaching after hydrothermal conversion of phosphogypsum. Chem. Afr. 2019, 2, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, M.; Ismail, Z.; Abu Elgoud, E.; Hai, F.A.; Ali, I.; Aly, H. Alkali treatment–acid leaching of rare earth elements from phosphogypsum fertilizer: Insight for additional resource of valuable components. BMC Chemistry 2022, 16, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennaciri, Y.; Alaoui-Belghiti, H.E.; Bettach, M. Comparative study of K2SO4 production by wet conversion from phosphogypsum and synthetic gypsum. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 2586–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolokolnikov, V.A.; Kovalev, M.I. Technology for processing technical calcium carbonate obtained from phosphogypsum into pure calcium carbonate and rare-earth element concentrate. Chem. Sustain. Dev. 2009, 17, 387–393. [Google Scholar]
- Masmoudi-Soussi, A.; Hammas-Nasri, I.; Horchani-Naifer, K.; Férid, M. Rare earths recovery by fractional precipitation from a sulfuric leach liquor obtained after phosphogypsum processing. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 191, 105253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammas-Nasri, I.; Horchani-Naifer, K.; Férid, M.; Barca, D. Production of a rare earths concentrate after phosphogypsum treatment with dietary NaCl and Na2CO3 solutions. Miner. Eng. 2019, 132, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourret, O.; Davranche, M.; Gruau, G.; Dia, A. Competition between humic acid and carbonates for rare earth elements complexation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 305, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Guan, B.; Fu, H.; Yang, L. Effect of potassium sodium tartrate and sodium citrate on the preparation of α-calcium sulfate hemihydrate from flue gas desulfurization gypsum in a concentrated electrolyte solution. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 92, 2894–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfred, Z.; Ivan, O.; Felicia, T.; Katarina, B. Autoclave-free formation of α-hemihydrate gypsum. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1991, 74, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Zheng, J.; Ou, X.; Liu, X.; Song, Y.; Tian, C.W.; Shi, Z.; Dang, Z.; Lin, Z. Effective extraction of Cr (VI) from hazardous gypsum sludge via controlling the phase transformation and chromium species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13336–13342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zheng, J.; Liu, Q.; Hu, Q.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Liu, W.; Lin, Z. Efficient removal of iron from red gypsum via synergistic regulation of gypsum phase transformation and iron speciation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, W.; Fan, R.; Sui, Y.; Bu, Y.; Yin, Z.; Chi, R.-A.; Gao, Z. Efficient removal of impurities from phosphogypsum during preparation of α-hemihydrate gypsum. Miner. Eng. 2023, 201, 108203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Hu, Y.; Tang, H.; Sun, W.; Gao, Z. Preparation of α-CaSO4·½H2O with tunable morphology from flue gas desulphurization gypsum using malic acid as modifier: A theoretical and experimental study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 530, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Q.; Sun, W.; Hu, Y.; Yin, Z.C.; Guan, C.; Zhu, X.; Ahmed Khoso, S. Simultaneous control of particle size and morphology of α-CaSO4·1/2H2O with organic additives. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 102, 2440–2450. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Q.; Tang, H.; Sun, W.; Hu, Y.; Yin, Z. Insight into influence of glycerol on preparing α-CaSO4·½H2O from flue gas desulfurization gypsum in glycerol–water solutions with succinic acid and NaCl. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 9831–9838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Sun, N.; Bu, Y.; Fan, R.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, W.; Chi, R.-A.; Gao, Z. Efficient extraction of impurities from phosphogypsum during crystal regulation of α-hemihydrate gypsum. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2023; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Dev, S.; Sachan, A.; Dehghani, F.; Ghosh, T.; Briggs, B.R.; Aggarwal, S. Mechanisms of biological recovery of rare-earth elements from industrial and electronic wastes: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397, 124596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, D.W.; Fujita, Y.; Daubaras, D.L.; Jiao, Y.; Thompson, V.S. Bioleaching of rare earth elements from waste phosphors and cracking catalysts. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 166, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethurajan, M.; Van Hullebusch, E.D.; Fontana, D.; Akcil, A.; Deveci, H.; Batinic, B.; Leal, J.P.; Gasche, T.A.; Ali Kucuker, M.; Kuchta, K. Recent advances on hydrometallurgical recovery of critical and precious elements from end of life electronic wastes-A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 212–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, M.K.; Eksteen, J.J.; Niu, X.-Z.; Croue, J.-P.; Watkin, E.L. Interactions of phosphate solubilising microorganisms with natural rare-earth phosphate minerals: A study utilizing Western Australian monazite. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 40, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopfe, S.; Konsulke, S.; Barthen, R.; Lehmann, F.; Kutschke, S.; Pollmann, K. Screening and selection of technologically applicable microorganisms for recovery of rare earth elements from fluorescent powder. Waste Manag. 2018, 79, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dong, H.; Liu, Y.; Bian, L.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Y. Bioleaching of rare earth elements from bastnaesite-bearing rock by actinobacteria. Chem. Geol. 2018, 483, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, H.; Barmettler, F.; Castelberg, C.; Fabbri, C. Microbial mobilization of rare earth elements (REE) from mineral solids: A mini review. AIMS Microbiol. 2016, 3, 190–204. [Google Scholar]
- Tayar, S.P.; Palmieri, M.C.; Bevilaqua, D. Sulfuric acid bioproduction and its application in rare earth extraction from phosphogypsum. Miner. Eng. 2022, 185, 107662. [Google Scholar]
- Koopman, C.; Witkamp, G. Extraction of lanthanides from the phosphoric acid production process to gain a purified gypsum and a valuable lanthanide by-product. Hydrometallurgy 2000, 58, 51–60. [Google Scholar]














| Origin | Country | REO or REE (wt%) | Leaching Conditions | Leaching Efficiency, % | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaching Regent | Conc. (M a or wt% b) | Temp. (°C) | Time (h) | L/S (mL/g) | |||||
| Kola | Russia | 0.6 | H2SO4 | 10–15 b | 40 | 6 | 2/1 | 52 | Jarosiński et al. [41] |
| Phosphoric Acid Plant at Phalaborwa | South Africa | 6.8 | HNO3 | 2.0 a | 20 | 48 | 3/1 | 57 | Preston et al. [42] |
| Abu-Zaabal Company | Egypt | 0.022 | HNO3; Ca(NO3)2 | 2.0–3.0 a; 0.8 a | 25 | 8 | 1/1 | 76 | El-Reefy et al. [43] |
| HNO3 | 2.0 a | 46 | |||||||
| HCl | 4.0 a | 30 | |||||||
| H2SO4 | 4.0 a | 30 | |||||||
| Private Joint Stock Company ‘Metakhim’ | Russia | 0.414 | H2SO4 | 0.5–4.0 b | 25 | 3025 | 2/1 | 57.1–68.2 | Lokshin et al. [34] |
| Dump PG | Russia | 0.45 | H2SO4; HNO3 | 1.0–3.0 b | — | 8–12 min | 4/1–5/1 | 85–86.1 | Abramov et al. [44] |
| Synthetic PG | USA | 0.034 | H2SO4; H3PO4 | 25 b; 96 b | 72 | 1 | 20/3 | 49 | Al-Thyabat and Zhang [45] |
| Abu-Zaabal Company | Egypt | 0.048 | HNO3 | 3.0 a | 25 | 3 | 2/1 | 43.3 | Ismail et al. [46] |
| HCl | 2.0 a | 11.9 | |||||||
| H2SO4 | 4.0 a | 12.5 | |||||||
| Agrium Fertilizer Plant | Canada | 0.020 | HNO3 | 1.5 a | 80 | 2 | 8/1 | 57 | Walawalkar et al. [26] |
| HCl | 51 | ||||||||
| H2SO4 | 23 | ||||||||
| Mosaic Company | USA | 0.0218 | H2SO4 | 5.0 a | 50 | 3.5 | 4/1 | 43 | Liang et al. [47] |
| Nutrien Ltd.’s Fertilizer Operations | Canada | 0.0317 | HCl | 1.5 a | 85 | 1 | 15/1 | 80–99 | Lambert et al. [48] |
| Huelva PG Stack | Spain | 0.0345 | H2SO4 | 0.5 a | 25 | 2–8 | 20/1 | 41–58 | Cánovas et al. [49] |
| HNO3 | 3.0 a | 75–86 | |||||||
| Synthetic PG | USA | 1.0 | H2SO4 | 0.22 a | 25 | 24 | 50/1 | 76.9–93.7 | Antonick et al. [50] |
| H3PO4 | 5–85 | ||||||||
| Catarinense Carbochemical Industry S/A | Brazil | 0.5 | H2SO4 | 0.6 a | 42 | 1.0 | 20/1.7 | 67.8 | Lütke et al. [51] |
| Catarinense Carbochemical Industry S/A | Brazil | 0.5 | H2SO4 | 2.9 a | 55 | 20 min | 20/1.7 | 90 | Lütke et al. [52] |
| Catarinense Carbochemical Industry S/A | Brazil | 0.5 | Citric acid | 3.0 a | 80 | 1.0 | 20/1 | 62.0 | Lütke et al. [52] |
| Yunnan Phosphate Chemical Group | China | 0.02 | HCl | 1.65 a | 25 | 2.0 | 10/1 | 52 | Guan et al. [53] |
| 60 | 66 | ||||||||
| 80 | 78 | ||||||||
| Yunnan Phosphate Chemical Group | China | 0.02 | HNO3 | 1.65 a | 30 | 2.0 | 10/1 | 58.5 | Zeng et al. [54] |
| 60 | 75.9 | ||||||||
| 80 | 83.4 | ||||||||
| Abu-Zaabal Company | Egypt | 0.048 | Boric acid | 0.5 a | 25 | 20 | 5/1 | 17 | Gasser et al. [55] |
| Malic acid | 1.0 a | 25 | 15 min | 5/1 | 17.7 | ||||
| Citric acid | 1.0 a | 60 | 15 min | 5/1 | 53.3 | ||||
| Methods | Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physically enhanced leaching methods | Mechanical activation | ● Simple and efficient | ● High energy consumption |
| Increasing L/S ratio or number of leaching applications | ● Easy operation | ● High cost of leaching solution treatment | |
| Extending the leaching time | ● Easy operation | ● Low efficiency | |
| Ultrasonic/microwave treatment | ● Greatly promotes REE leaching ● Shortens the leaching time | ● High energy consumption ● Difficult to achieve mass production | |
| Chemically enhanced leaching methods | RIL technology | ● Dilutes H2SO4 as a lixiviant ● A high REE recovery ● A simultaneous leaching and recovery step | ● Significant financial investment ● Vulnerable profitability |
| Solvometallurgical method | ● A high recovery of REEs | ● Difficult to extract REEs locked in the gypsum crystal ● Loss of organic reagents | |
| Phase inversion enhanced leaching methods | Carbonation | ● Enrichment of REEs in an easily leachable solid phase | ● High reagent cost and energy consumption ● Limited market for byproducts |
| Recrystallization | ● Efficient REE extraction and simultaneous preparation of high-value-added gypsum products ● Low-cost, sustainable, and green solution | ● Needs more research and development | |
| Bioleaching methods | ● High metal specificity and leaching efficiency at low concentrations ● Environmentally friendly ● Low operating cost | ● Low yield and rates ● Few studies on the bioleaching of REEs from PG | |
| Joint methods | ● Efficient REE recovery ● Low cost ● Easy to industrialize | ● Needs more research and development | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, G.; Guan, Q.; Zhou, F.; Yu, W.; Yin, Z.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chi, R. A Critical Review of the Enhanced Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Phosphogypsum. Molecules 2023, 28, 6284. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176284
Xie G, Guan Q, Zhou F, Yu W, Yin Z, Tang H, Zhang Z, Chi R. A Critical Review of the Enhanced Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Phosphogypsum. Molecules. 2023; 28(17):6284. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176284
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Gang, Qingjun Guan, Fujia Zhou, Weijian Yu, Zhigang Yin, Honghu Tang, Zhenyue Zhang, and Ru’an Chi. 2023. "A Critical Review of the Enhanced Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Phosphogypsum" Molecules 28, no. 17: 6284. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176284
APA StyleXie, G., Guan, Q., Zhou, F., Yu, W., Yin, Z., Tang, H., Zhang, Z., & Chi, R. (2023). A Critical Review of the Enhanced Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Phosphogypsum. Molecules, 28(17), 6284. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176284