Determination of Luteolin 7-Glucuronide in Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. Leaf Extracts from Different Regions of China and Republic of Korea and Its Cholesterol-Lowering Effect
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
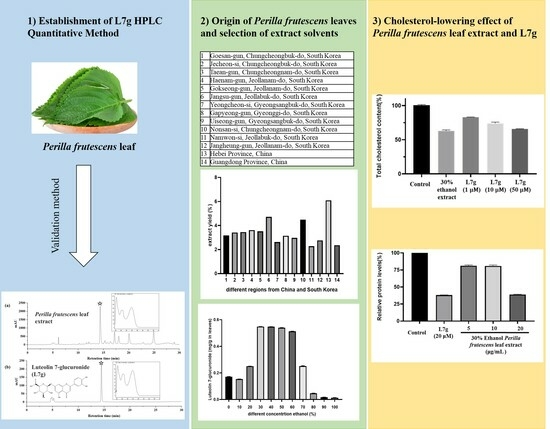
2.1. Method Validation
2.2. Selection of Origin of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. Leaves and Optimization of Extraction Conditions
2.3. Cholesterol-Lowering Effects of Luteolin 7-Glucuronide and P. frutescens (L.) Britt. Leaf Extract
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of Perilla frutescens Leaf Extract
3.3. HPLC Analysis of Luteolin 7-Glucuronide
3.4. Method Validation
3.5. Cell Culture
3.6. Cellular Cholesterol Content Analysis
3.7. Western Blotting
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Jones, L.K.; Sturm, A.C.; Seaton, T.L.; Gregor, C.; Gidding, S.S.; Williams, M.S.; Rahm, A.K. Barriers, facilitators, and solutions to familial hypercholesterolemia treatment. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khera, A.V.; Won, H.H.; Peloso, G.M.; Lawson, K.S.; Bartz, T.M.; Deng, X.; van Leeuwen, E.M.; Natarajan, P.; Emdin, C.A.; Bick, A.G.; et al. Diagnostic Yield and Clinical Utility of Sequencing Familial Hypercholesterolemia Genes in Patients With Severe Hypercholesterolemia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 2578–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordestgaard, B.G.; Chapman, M.J.; Humphries, S.E.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Masana, L.; Descamps, O.S.; Wiklund, O.; Hegele, R.A.; Raal, F.J.; Defesche, J.C.; et al. Familial hypercholesterolaemia is underdiagnosed and undertreated in the general population: Guidance for clinicians to prevent coronary heart disease: Consensus statement of the European Atherosclerosis Society. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 3478–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.S.; Sung, J.H.; Lee, S.K. Inhibition of Cholesterol Synthesis in HepG2 Cells by GINST-Decreasing HMG-CoA Reductase Expression Via AMP-Activated Protein Kinase. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2700–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscica, M.; Ferri, N.; Banach, M.; Sirtori, C.R.; Corsini, A. Side effects of statins: From pathophysiology and epidemiology to diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 118, 3288–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruckert, E.; Hayem, G.; Dejager, S.; Yau, C.; Begaud, B. Mild to moderate muscular symptoms with high-dosage statin therapy in hyperlipidemic patients--the PRIMO study. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2005, 19, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederberg, H.; Stancakova, A.; Yaluri, N.; Modi, S.; Kuusisto, J.; Laakso, M. Increased risk of diabetes with statin treatment is associated with impaired insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion: A 6 year follow-up study of the METSIM cohort. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.M. Ethnomedicinal, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Investigations of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. Molecules 2018, 24, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S. Perilla frutescens detoxifies the toxicity of fish and crab. Zhong Hua Yang Sheng Bao Jian 2012, 9, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, T.; Netala, V.R.; Zhang, H.; Xing, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z. Perilla frutescens: A Rich Source of Pharmacological Active Compounds. Molecules 2022, 27, 3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Qiu, J.F.; Ma, L.J.; Hu, Y.J.; Li, P.; Wan, J.B. Phytochemical and phytopharmacological review of Perilla frutescens L. (Labiatae), a traditional edible-medicinal herb in China. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 108 Pt B, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Jin, X.; Shang, Y.; Wang, L.; Du, K.; Chen, S.; Li, J.; He, J.; Fang, S.; Chang, Y. A comprehensive review of the botany, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicity and quality control of Perillae Fructus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 304, 116022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, T.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Park, H.J.; Chae, B.S.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, H.M. Inhibitory effect of mast cell-mediated immediate-type allergic reactions in rats by Perilla frutescens. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2000, 22, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.H.; Chen, C.S.; Lin, J.Y. Dietary perilla oil lowers serum lipids and ovalbumin-specific IgG1, but increases total IgE levels in ovalbumin-challenged mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Choi, U.K. Optimization of antibacterial activity of Perilla frutescens var. acuta leaf against Staphylococcus aureus using evolutionary operation factorial design technique. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 2395–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Zang, S.Y.; Jiang, Z.H.; Chen, Y.Y.; Ji, X.H.; Lu, B.F.; Wu, J.H.; Qin, G.W.; Guo, L.H. Postischemic administration of liposome-encapsulated luteolin prevents against ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2011, 22, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.J.; Yan, L.L.; Yin, P.P.; Shi, L.L.; Zhang, J.H.; Liu, Y.J.; Ma, C. Structural characterisation and antioxidant activity evaluation of phenolic compounds from cold-pressed Perilla frutescens var. arguta seed flour. Food Chem. 2014, 164, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.-J.; Yu, C.-H.; Ying, K.-J.; Hua, J.; Dai, X.-Y. Hypolipidemic and antioxidant effects of total flavonoids of Perilla Frutescens leaves in hyperlipidemia rats induced by high-fat diet. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhang, M.; Wei, S.; Zhu, Y.; Ouyang, H.; He, J. Quantitative Comparison and Chemical Profile Analysis of Different Medicinal Parts of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. from Different Varieties and Harvest Periods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8838–8853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guo, L.; Yang, G.; Yang, A.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, L. Metabolomic profiling of developing perilla leaves reveals the best harvest time. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 989755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, J.O.; de Souza, M.C.; da Silva, L.C.; Lachos-Perez, D.; Torres-Mayanga, P.C.; Machado, A.; Forster-Carneiro, T.; Vazquez-Espinosa, M.; Gonzalez-de-Peredo, A.V.; Barbero, G.F.; et al. Extraction of Flavonoids From Natural Sources Using Modern Techniques. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 507887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ran, L.; Chen, N.; Fan, X.; Ren, D.; Yi, L. Polarity-dependent extraction of flavonoids from citrus peel waste using a tailor-made deep eutectic solvent. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.H.; Wang, Z.; Hwang, S.H.; Kang, Y.-H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lim, S.S. Comprehensive evaluation of the antioxidant capacity of Perilla frutescens leaves extract and isolation of free radical scavengers using step-wise HSCCC guided by DPPH-HPLC. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20 (Suppl. 1), 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heera, R.; Chandra, K.; Karishma, S.; Anita, S.; Jaykaran, C.; Paras, S.; Rajsekhar, R.; Surajit, G. In-vitro and in-silico determinations of HMG-CoA reductase inhibition potential of caffeic acid for therapeutics of hypercholesterolemia. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 12, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexsandra, M.H.-R.; July, A.L.-G.; Carmen, R.S.-C.; William Antonio, S.-G.; Cesar, D.G.-S. In silico Analysis of the Polyphenolic Metabolites of Zea mays L. “Purple Corn” on HMG-CoA Reductase. Pharmacogn. J. 2022, 14, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Xiao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Mo, Z.; Chen, Y.; Peng, X.; Xiang, C.; Li, Y.; Li, W. Chlorogenic acid-enriched extract from Eucommia ulmoides leaves inhibits hepatic lipid accumulation through regulation of cholesterol metabolism in HepG2 cells. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruit, J.K.; Groen, A.K.; van Berkel, T.J.; Kuipers, F. Emerging roles of the intestine in control of cholesterol metabolism. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 6429–6439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.; Li, Y.M.; He, Z.; Hao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, H.; Kwek, E.; Ma, K.Y.; He, W.S.; et al. Rutin and Quercetin Decrease Cholesterol in HepG2 Cells but Not Plasma Cholesterol in Hamsters by Oral Administration. Molecules 2021, 26, 3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, S.J.; Barnhart, R.L.; Martin, G.A.; Flanagan, M.A.; Jackson, R.L. Differential regulation of hepatic triglyceride lipase and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase gene expression in a human hepatoma cell line, HepG2. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 22474–22479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.; Han, B.; Wang, Y.; Huang, T.; He, K.; Han, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ye, X.; Li, X. Synergetic cholesterol-lowering effects of main alkaloids from Rhizoma Coptidis in HepG2 cells and hypercholesterolemia hamsters. Life Sci. 2016, 151, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tocmo, R.; Nauman, M.C.; Haughan, M.A.; Johnson, J.J. Defining the Cholesterol Lowering Mechanism of Bergamot (Citrus bergamia) Extract in HepG2 and Caco-2 Cells. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavan, M.; Hanachi, P.; Mirjalili, M.H.; Dashtbani-Roozbehani, A. Comparative assessment of the biological activity of the green synthesized silver nanoparticles and aqueous leaf extract of Perilla frutescens (L.). Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchadapirom, P.; Suttajit, M.; Thongpraditchote, S.; Kitphati, W.; Tammasakchai, A. GenotoxicityEvaluationofEthanolicLeafExtractofThaiPerillaPerillafrutescensL.Britt.usingMicronucleusAssayinV79Cell Line. Thai J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 42, 5–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mungmai, L.; Preedalikit, W.; Pintha, K.; Tantipaiboonwong, P.; Aunsri, N. Collagenase and Melanogenesis Inhibitory Effects of Perilla Frutescens Pomace Extract and Its Efficacy in Topical Cosmetic Formulations. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technnical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. ICH Harmonised Guideline. Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/ICH_Q2R2_Document_Step2_Guideline_2022_0324.pdf (accessed on 6 October 2022).



| Analyte | Linearity (μg/mL) | Regression Equation | R2 | LOD (μg/mL) | LOQ (μg/mL) | RSD (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.5 mg/mL | 5.0 mg/mL | 10 mg/mL | |||||||||
| Intra | Inter | Intra | Inter | Intra | Inter | ||||||
| luteolin 7- glucuronide | 0.98–980 | Y = 22,850 X + 185.59 | 0.999 | 6 | 17 | 0.99 | 2.03 | 2.96 | 2.39 | 1.54 | 2.74 |
| Analyte | 30 μg/mL | 40 μg/mL | 50 μg/mL | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | |
| luteolin 7- glucuronide | 89.66 | 4.62 | 94.79 | 3.05 | 99.50 | 0.77 |
| Sample No. | Location | Extract Yield (g/kg) | Luteolin 7-Glucuronide (mg/g in P. frutescens (L.) Britt. Leaves) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Goesan-gun, Chungcheongbuk-do, Republic of Korea | 31.7 | 0.539 ± 0.001 |
| 2 | Jecheon-si, Chungcheongbuk-do, Republic of Korea | 34.2 | 0.549 ± 0.005 |
| 3 | Taean-gun, Chungcheongnam-do, Republic of Korea | 34.5 | 0.325 ± 0.001 |
| 4 | Haenam-gun, Jeollanam-do, Republic of Korea | 36.2 | 0.689 ± 0.008 |
| 5 | Gokseong-gun, Jeollanam-do, Republic of Korea | 35.2 | 0.285 ± 0.003 |
| 6 | Jangsu-gun, Jeollabuk-do, Republic of Korea | 47.2 | 0.391 ± 0.026 |
| 7 | Yeongcheon-si, Gyeongsangbuk-do, Republic of Korea | 26.3 | 0.406 ± 0.013 |
| 8 | Gapyeong-gun, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea | 31.4 | 0.059 ± 0.026 |
| 9 | Uiseong-gun, Gyeongsangbuk-do, Republic of Korea | 29.7 | 0.758 ± 0.076 |
| 10 | Nonsan-si, Chungcheongnam-do, Republic of Korea | 44.9 | 1.335 ± 0.076 |
| 11 | Namwon-si, Jeollabuk-do, Republic of Korea | 22.8 | 0.127 ± 0.007 |
| 12 | Jangheung-gun, Jeollanam-do, Republic of Korea | 27.6 | 0.293 ± 0.012 |
| 13 | Anguo City, Hebei Province, China | 60.9 | 0.445 ± 0.001 |
| 14 | Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province, China | 23.6 | 0.026 ± 0.001 |
| Sample No. | Ethanol Concentration (%) | Extract Yield (g/kg) | Luteolin 7-Glucuronide (mg/g in P. frutescens (L.) Britt. Leaves) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 47.1 | 0.171 ± 0.017 |
| 2 | 10 | 62.1 | 0.154 ± 0.006 |
| 3 | 20 | 59.9 | 0.250 ± 0.005 |
| 4 | 30 | 62.7 | 0.548 ± 0.009 |
| 5 | 40 | 57.1 | 0.548 ± 0.005 |
| 6 | 50 | 59.4 | 0.540 ± 0.016 |
| 7 | 60 | 56.9 | 0.513 ± 0.016 |
| 8 | 70 | 56.3 | 0.251 ± 0.028 |
| 9 | 80 | 52.2 | 0.046 ± 0.020 |
| 10 | 90 | 35.2 | 0.017 ± 0.001 |
| 11 | 100 | 24.0 | 0.013 ± 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; Lee, S.; Kang, B.; Lee, S.; Koo, K.; Lee, J.; Lim, S. Determination of Luteolin 7-Glucuronide in Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. Leaf Extracts from Different Regions of China and Republic of Korea and Its Cholesterol-Lowering Effect. Molecules 2023, 28, 7007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207007
Wu Z, Lee S, Kang B, Lee S, Koo K, Lee J, Lim S. Determination of Luteolin 7-Glucuronide in Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. Leaf Extracts from Different Regions of China and Republic of Korea and Its Cholesterol-Lowering Effect. Molecules. 2023; 28(20):7007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207007
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zhaoyang, Sangyoun Lee, Beomgoo Kang, Sookyeong Lee, Kyochul Koo, Jaeyong Lee, and Soonsung Lim. 2023. "Determination of Luteolin 7-Glucuronide in Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. Leaf Extracts from Different Regions of China and Republic of Korea and Its Cholesterol-Lowering Effect" Molecules 28, no. 20: 7007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207007
APA StyleWu, Z., Lee, S., Kang, B., Lee, S., Koo, K., Lee, J., & Lim, S. (2023). Determination of Luteolin 7-Glucuronide in Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. Leaf Extracts from Different Regions of China and Republic of Korea and Its Cholesterol-Lowering Effect. Molecules, 28(20), 7007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207007