[18F]fluoride Activation and 18F-Labelling in Hydrous Conditions—Towards a Microfluidic Synthesis of PET Radiopharmaceuticals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. [18F]fluoride Recovery Studies
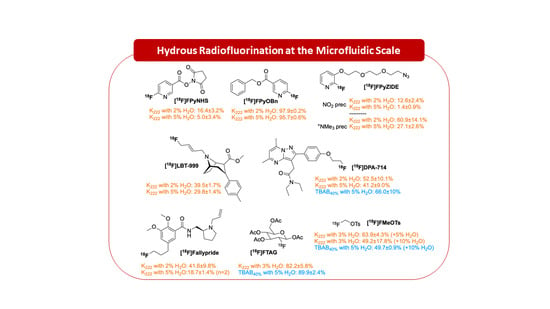
2.2. [18F]fluoride Labelling Studies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Eluent Preparation
4.2.1. Preparation of K222/K2CO3/CH3CN/H2O Solutions
4.2.2. Preparation of 5% H2O TBAB40% Solution
4.3. [18F]fluoride Production
4.4. General Manual [18F]fluoride Elution Method
4.5. General [18F]fluoride Elution Method Using iMiDEVTM
4.6. General Hydrous [18F]fluoride Labelling Method
4.7. Quality Control Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H. Research Progress of 18F Labeled Small Molecule Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Imaging Agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 205, 112629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coenen, H.H.; Ermert, J. 18F-Labelling Innovations and Their Potential for Clinical Application. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2018, 6, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haveman, L.Y.F.; Vugts, D.J.; Windhorst, A.D. State of the Art Procedures towards Reactive [18F]Fluoride in PET Tracer Synthesis. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2023, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Feng, W.; Mou, Z.; Chen, J.; Tang, X.; Li, Z. 18F-Labeling Chemistry in Aqueous Media. Chem. A Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202300248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basuli, F.; Zhang, X.; Blackman, B.; White, M.E.; Jagoda, E.M.; Choyke, P.L.; Swenson, R.E. Fluorine-18 Labeled Fluorofuranylnorprogesterone ([18F]FFNP) and Dihydrotestosterone ([18F]FDHT) Prepared by “Fluorination on Sep-Pak” Method. Molecules 2019, 24, 2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basuli, F.; Zhang, X.; Phelps, T.E.; Jagoda, E.M.; Choyke, P.L.; Swenson, R.E. Automated Synthesis of Fluorine-18 Labeled CXCR4 Ligand via the Conjugation with Nicotinic Acid N-Hydroxysuccinimide Ester (6-[18F]SFPy). Molecules 2020, 25, 3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathiessen, B.; Zhuravlev, F. Automated Solid-Phase Radiofluorination Using Polymer-Supported Phosphazenes. Molecules 2013, 18, 10531–10547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, J.; Voccia, S.; Lemaire, C.; Giacomelli, F.; Goblet, D.; Thonon, D.; Plenevaux, A.; Warnock, G.; Luxen, A. Fast Production of Highly Concentrated Reactive [18F] Fluoride for Aliphatic and Aromatic Nucleophilic Radiolabelling. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balentova, E.; Collet, C.; Lamandé-Langle, S.; Chrétien, F.; Thonon, D.; Aerts, J.; Lemaire, C.; Luxen, A.; Chapleur, Y. Synthesis and Hydrolytic Stability of Novel 3-[18F]Fluoroethoxybis(1-Methylethyl)Silyl]Propanamine-Based Prosthetic Groups. J. Fluor. Chem. 2011, 132, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, C.F.; Aerts, J.J.; Voccia, S.; Libert, L.C.; Mercier, F.; Goblet, D.; Plenevaux, A.R.; Luxen, A.J. Fast Production of Highly Reactive No-Carrier-Added [18F]Fluoride for the Labeling of Radiopharmaceuticals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 3161–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiessen, B.; Jensen, A.T.I.; Zhuravlev, F. Homogeneous Nucleophilic Radiofluorination and Fluorination with Phosphazene Hydrofluorides. Chem. A Eur. J. 2011, 17, 7796–7805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Choe, Y.S.; Chi, D.Y. A New Nucleophilic Fluorine-18 Labeling Method for Aliphatic Mesylates: Reaction in Ionic Liquids Shows Tolerance for Water. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2003, 30, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.W.; Jeong, J.M.; Lee, Y.-S.; Chi, D.Y.; Chung, K.-H.; Lee, D.S.; Chung, J.-K.; Lee, M.C. Rapid Synthesis of [18F]FDG without an Evaporation Step Using an Ionic Liquid. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2004, 61, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergeev, M.E.; Morgia, F.; Lazari, M.; Wang, C., Jr.; van Dam, R.M. Titania-Catalyzed Radiofluorination of Tosylated Precursors in Highly Aqueous Medium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5686–5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossine, A.V.; Brooks, A.F.; Ichiishi, N.; Makaravage, K.J.; Sanford, M.S.; Scott, P.J.H. Development of Customized [18F]Fluoride Elution Techniques for the Enhancement of Copper-Mediated Late-Stage Radiofluorination. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zischler, J.; Kolks, N.; Modemann, D.; Neumaier, B.; Zlatopolskiy, B.D. Alcohol-Enhanced Cu-Mediated Radiofluorination. Chem.—Eur. J. 2017, 23, 3251–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scroggie, K.R.; Perkins, M.V.; Chalker, J.M. Reaction of [18F]Fluoride at Heteroatoms and Metals for Imaging of Peptides and Proteins by Positron Emission Tomography. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 687678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, T. Recent Advances in Synthetic Methodologies to Form C-18F Bonds. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 883866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klenner, M.A.; Pascali, G.; Zhang, B.; Sia, T.R.; Spare, L.K.; Krause-Heuer, A.M.; Aldrich-Wright, J.R.; Greguric, I.; Guastella, A.J.; Massi, M.; et al. A Fluorine-18 Radiolabeling Method Enabled by Rhenium(I) Complexation Circumvents the Requirement of Anhydrous Conditions. Chem. A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 6499–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.N.; Hockley, B.G.; Scott, P.J.H. Green Approaches to Late-Stage Fluorination: Radiosyntheses of 18F-Labelled Radiopharmaceuticals in Ethanol and Water. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 14805–14808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, S.; Rensch, C.; Neubaur, S.; Neumeier, M.; Salvamoser, R.; Samper, V.; Bartenstein, P. Azeotropic Drying Free [18F]FDG Synthesis and Its Application to a Lab-on-Chip Platform. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kniess, T.; Laube, M.; Steinbach, J. “Hydrous 18F-Fluoroethylation”—Leaving off the Azeotropic Drying. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2017, 127, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessmann, S.H.; Henriksen, G.; Wester, H.J. Cryptate mediated nucleophilic 18F-fluorination without azeotropic drying. Nuklearmedizin 2017, 51, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-D.; Son, J.; Yun, M.; Chun, J.-H. Azeotropic Drying-Free Aliphatic Radiofluorination to Produce PET Radiotracers in a Mixed Organic Solvent System. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 2848–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inkster, J.A.H.; Akurathi, V.; Sromek, A.W.; Chen, Y.; Neumeyer, J.L.; Packard, A.B. A Non-Anhydrous, Minimally Basic Protocol for the Simplification of Nucleophilic 18F-Fluorination Chemistry. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok Moon, B.; Hyung Park, J.; Jin Lee, H.; Sun Kim, J.; Sup Kil, H.; Se Lee, B.; Yoon Chi, D.; Chul Lee, B.; Kyeong Kim, Y.; Eun Kim, S. Highly Efficient Production of [18F]Fallypride Using Small Amounts of Base Concentration. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2010, 68, 2279–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brichard, L.; Aigbirhio, F.I. An Efficient Method for Enhancing the Reactivity and Flexibility of [18F]Fluoride Towards Nucleophilic Substitution Using Tetraethylammonium Bicarbonate. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 2014, 6145–6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-D.; Son, J.; Chun, J.-H. Aliphatic radiofluorination using TBAHCO3 eluate in hydrous organic medium. J. Radiopharm. Mol. Probes 2018, 4, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, B.; Liu, J.; Dukic-Stefanovic, S.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Teodoro, R.; Ludwig, F.-A.; Chezal, J.-M.; Moreau, E.; Brust, P.; Maisonial-Besset, A. Targeting Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) in Brain: Toward the Development of a PET Radioligand Labeled with Fluorine-18. Bioorganic Chem. 2019, 86, 346–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Chu, W.; Xu, J.; Schwarz, S.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A. [18F]Tosyl Fluoride as a Versatile [18F]Fluoride Source for the Preparation of 18F-Labeled Radiopharmaceuticals. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pees, A.; Sewing, C.; Vosjan, M.J.W.D.; Tadino, V.; Herscheid, J.D.M.; Windhorst, A.D.; Vugts, D.J. Fast and Reliable Generation of [18F]Triflyl Fluoride, a Gaseous [18F]Fluoride Source. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 10179–10182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Fraser, B.H.; Klenner, M.A.; Chen, Z.; Liang, S.H.; Massi, M.; Robinson, A.J.; Pascali, G. [18F]Ethenesulfonyl Fluoride as a Practical Radiofluoride Relay Reagent. Chem. A Eur. J. 2019, 25, 7613–7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascali, G.; De Simone, M.; Matesic, L.; Greguric, I.; Salvadori, P.A. Tolerance of Water in Microfluidic Radiofluorinations: A Potential Methodological Shift? J. Flow Chem. 2014, 4, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, P.H.; Lazari, M.; Hanet, S.; Narayanam, M.K.; Murphy, J.M.; Van Dam, R.M. Automated Concentration of [18F]Fluoride into Microliter Volumes. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2018, 141, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arima, V.; Pascali, G.; Lade, O.; Kretschmer, H.R.; Bernsdorf, I.; Hammond, V.; Watts, P.; De Leonardis, F.; Tarn, M.D.; Pamme, N.; et al. Radiochemistry on Chip: Towards Dose-on-Demand Synthesis of PET Radiopharmaceuticals. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodnick, M.E.; Brooks, A.F.; Hockley, B.G.; Henderson, B.D.; Scott, P.J.H. A Fully-Automated One-Pot Synthesis of [18F]Fluoromethylcholine with Reduced Dimethylaminoethanol Contamination via [18F]Fluoromethyl Tosylate. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2013, 78, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascali, G.; Nannavecchia, G.; Pitzianti, S.; Salvadori, P.A. Dose-on-Demand of Diverse 18F-Fluorocholine Derivatives through a Two-Step Microfluidic Approach. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2011, 38, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, T.R.; Apana, S.; Berridge, M.S. Improved Synthesis of [18F]Fluoromethyl Tosylate, a Convenient Reagent for Radiofluoromethylations. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2005, 48, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, M.; Specklin, S.; Roche, M.; Hinnen, F.; Kuhnast, B. Original Synthesis of Radiolabeling Precursors for Batch and on Resin One-Step/Late-Stage Radiofluorination of Peptides. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 2507–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, M.; Specklin, S.; Richard, M.; Hinnen, F.; Génermont, K.; Kuhnast, B. [18F]FPyZIDE: A Versatile Prosthetic Reagent for the Fluorine-18 Radiolabeling of Biologics via Copper-Catalyzed or Strain-Promoted Alkyne-Azide Cycloadditions. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2019, 62, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallapura, H.; Tanguy, L.; Långström, B.; Meunier, L.L.; Halldin, C.; Nag, S. Production of [11C]Carbon Labelled Flumazenil and L-Deprenyl Using the iMiDEVTM Automated Microfluidic Radiosynthesizer. Molecules 2022, 27, 8843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, A.; Miraghaie, R.; Kotta, K.; Ball, C.E.; Zhang, J.; Buchsbaum, M.S.; Kolb, H.C.; Elizarov, A. Batch-Reactor Microfluidic Device: First Human Use of a Microfluidically Produced PET Radiotracer. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damont, A.; Hinnen, F.; Kuhnast, B.; Schöllhorn-Peyronneau, M.-A.; James, M.; Luus, C.; Tavitian, B.; Kassiou, M.; Dollé, F. Radiosynthesis of [18F]DPA-714, a Selective Radioligand for Imaging the Translocator Protein (18 kDa) with PET. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2008, 51, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Wang, M.; Mock, B.H.; Glick-Wilson, B.E.; Yoder, K.K.; Hutchins, G.D.; Zheng, Q.-H. An Improved Synthesis of Dopamine D2/D3 Receptor Radioligands [11C]Fallypride and [18F]Fallypride. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2010, 68, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vala, C.; Mothes, C.; Chicheri, G.; Magadur, P.; Viot, G.; Deloye, J.-B.; Maia, S.; Bouvet, Y.; Dupont, A.-C.; Arlicot, N.; et al. Fully Automated Radiosynthesis of [18F]LBT999 on TRACERlab FXFN and AllinOne Modules, a PET Radiopharmaceutical for Imaging the Dopamine Transporter in Human Brain. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2020, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhnast, B.; de Bruin, B.; Hinnen, F.; Tavitian, B.; Dollé, F. Design and Synthesis of a New [18F]Fluoropyridine-Based Haloacetamide Reagent for the Labeling of Oligonucleotides: 2-Bromo-N-[3-(2-[18F]Fluoropyridin-3-Yloxy)Propyl]Acetamide. Bioconjugate Chem. 2004, 15, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovdiichuk, O. Implementation of iMiDEVTM, a New Fully Automated Microfluidic Platform for Radiopharmaceutical Production. Lab Chip 2021, 11, 2272–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovdiichuk, O.; Béen, Q.; Tanguy, L.; Collet, C. Synthesis of [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 Using the iMiDEVTM Microfluidic Platform. React. Chem. Eng. 2023, 8, 1476–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Entry | Method | Tracer(s) | Conditions | Advantages/Drawbacks | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | “18F-radiofluorination on SPE cartridge” | 6-[18F]FPy-TFP; 6-[18F]SFPy; [18F]FFNP; [18F]FDHT | 18F-Elution of triflate precursor in organic solvent through PS-HCO3 | Simplicity of processing Suitable for base and temperature-sensitive starting materials High yields Limited applicability to multiple radiopharmaceuticals | Basuli et al., 2019, 2020 [5,6] |
| 2 | 18F-radiofluorination on modified polymers | [18F]FLT, [18F]FDG and Silicon-based prosthetic groups | 18F-Elution of precursor in organic solvent through modified solid support | Simplicity of processing Column reusability Variability in RCY Column accessibility and packing effects A large amount of precursors required | Mathiessen et al., 2013 [7]; Aerts et al., 2010 [8]; Balentova et al., 2011 [9] |
| 3 | 18F-radiofluorination using strong bases | [18F]FDG and several other aliphatic and aromatic substrates | 18F-Elution and activation with phosphazene bases | High yields Limited application because of strong basicity No standard test for residual phosphazenes quantification | Lemaire et al., 2010 [10]; Mathiessen et al., 2011 [11] |
| 4 | Ionic liquids | Halo- and mesyloxyalkanes, [18F]FDG | Labelling in the presence of various ionic liquids ([bmim][OTf], BMI) | Shorter synthesis time and simplified reaction procedure Limited substrate scope No standard test for residual ionic liquid quantification | Kim et al., 2003, 2004 [12,13] |
| 5 | Transition metal mediated/catalyzed radiofluorination | Wide range of substrates | 18F-Elution with phase transfer catalyst (PTC) or organic base and mixing with precursor in the presence of transition metal containing catalyst | High radiofluorination efficiency Accessibility and versatility of suitable precursors Metal dosage required for QC Complicated automation and scale-up | Sergeev et al., 2015 [14]; Mossine et al., 2017 [15]; Zischler et al., 2017 [16]; Scroggie et al., 2021 [17]; Liu et al., 2022 [18]; Klenner et al., 2017 [19] |
| 6 | Cryptate-mediated 18F-fluorination | Wide range of substrates | 18F-Elution with inorganic base and kryptofix 2.2.2 followed by drying the cartridge with acetonitrile and labelling | Applicability to versatile commercial precursors Standard QC procedure | Stewart et al., 2015 [20]; Lindner et al., 2016 [21]; Kniess et al., 2017 [22]; Wessmann et al., 2017 [23]; Kwon et al., 2018 [24] |
| 7 | Tetraalkylammonium salts (“non-anhydrous, minimally basic (NAMB) approach”) | Wide range of substrates | 18F-Elution with tetraalkylammonium salt followed by drying the cartridge with acetonitrile and labelling | Applicability to versatile commercial precursors Standard QC procedure | Inkster et al., 2020 [25] Seok Moon et al., 2010 [26] Brichard et al., 2014 [27]; Kwon et al., 2018 [28]; Wenzel et al., 2019 [29] |
| 8 | Sulfonyl-18F | A wide range of substrates and sulfonyl fluoride-containing molecules | Production of sulfonyl-[18F]fluoride followed by distillation or SPE purification prior to radiolabelling | Applicability to versatile commercial precursors Complicated automation | Zhou et al., 2023 [30]; Pees et al., 2018 [31]; Zhang et al., 2019 [32] |
| Eluent | Amount of K222 | Addition of Aq. K2CO3 Solution (Corresponding to 150 µmol) | Volume of CH3CN |
|---|---|---|---|
| K222 with 5% H2O | 113 mg (300 µmol) | 250 µL of 0.6 M | 5 mL |
| K222 with 3% H2O | 150 µL of 1 M | ||
| K222 with 2% H2O | 100 µL of 1.5 M | ||
| K222 with 1% H2O | 50 µL of 3 M |
| Radiotracer | Eluant Mixture (v:v) | Rf |
|---|---|---|
| [18F]f− | MeCN:H2O (95:5) | 0 |
| [18F]f− | EtOAc (100) | 0 |
| [18F]f− | Hexanes:EtOAc (80:20) | 0 |
| [18F]FTAG | MeCN:H2O (95:5) | 0.47 |
| [18F]F-Me-OTs | Hexanes:EtOAc (80:20) | 0.45 |
| [18F]Tosyl fluoride | Hexanes:EtOAc (80:20) | 0.57 |
| [18F]DPA-714 | MeCN:H2O (95:5) | 0.9 |
| [18F]DPA-714 | EtOAc (100) | 0.4 |
| [18F]fallypride | EtOAc (100) | 0.4 |
| [18F]LBT-999 | EtOAc (100) | 0.4 |
| [18F]FPy-NHS | EtOAc (100) | 1 |
| [18F]FPyZIDE | EtOAc (100) | 0.9 |
| [18F]FPyOBn | EtOAc (100) | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ovdiichuk, O.; Lahdenpohja, S.; Béen, Q.; Tanguy, L.; Kuhnast, B.; Collet-Defossez, C. [18F]fluoride Activation and 18F-Labelling in Hydrous Conditions—Towards a Microfluidic Synthesis of PET Radiopharmaceuticals. Molecules 2024, 29, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010147
Ovdiichuk O, Lahdenpohja S, Béen Q, Tanguy L, Kuhnast B, Collet-Defossez C. [18F]fluoride Activation and 18F-Labelling in Hydrous Conditions—Towards a Microfluidic Synthesis of PET Radiopharmaceuticals. Molecules. 2024; 29(1):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010147
Chicago/Turabian StyleOvdiichuk, Olga, Salla Lahdenpohja, Quentin Béen, Laurent Tanguy, Bertrand Kuhnast, and Charlotte Collet-Defossez. 2024. "[18F]fluoride Activation and 18F-Labelling in Hydrous Conditions—Towards a Microfluidic Synthesis of PET Radiopharmaceuticals" Molecules 29, no. 1: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010147
APA StyleOvdiichuk, O., Lahdenpohja, S., Béen, Q., Tanguy, L., Kuhnast, B., & Collet-Defossez, C. (2024). [18F]fluoride Activation and 18F-Labelling in Hydrous Conditions—Towards a Microfluidic Synthesis of PET Radiopharmaceuticals. Molecules, 29(1), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010147