Characterization of a Deswapped Triple Mutant Bovine Odorant Binding Protein
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Stability and Functionality of GCC-bOBP at Neutral pH
2.2. Binding of AMA to Native GCC-bOBP
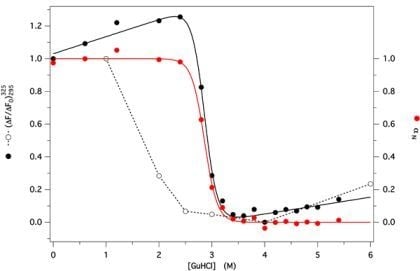
2.3. GdnHCl-Induced Unfolding and Refolding of GCC-bOBP
2.4. Protein Fluorescence Lifetime
2.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulations at Neutral pH
2.6. Fret Efficiency Determination
2.7. GCC-bOBP Stability at Acidic pH
2.8. Molecular Dynamics Simulations at Acidic pH
3. Experimental Section
3.1. GCC-bOBP
3.2. Spectroscopic Measurements
3.3. Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer
3.4. Fluorescence Lifetimes
3.5. Functional Assays
3.6. Unfolding and Refolding Measurements
3.7. Molecular Dynamics
4. Conclusions
Abbreviations:
| AMA: | 1-amino-anthracene; |
| ANS: | 1-anilino-naphtalene sulfonate; |
| bOBP: | bovine OBP; |
| CD: | circular dichroism; |
| FRET: | fluorescence resonance energy transfer; |
| FWHH: | full width at half height; |
| GCC-bOBP: | triple mutant (Gly-Cys-Cys) bOBP; |
| GdnHCl: | guanidinium chloride; |
| MD: | molecular dynamics; |
| NATA: | N-acetyl-tryptophanamide; |
| OBP: | odorant binding protein; |
| pOBP: | porcine OBP; |
| P buffer: | 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer; |
| RMSD: | root mean square deviation; |
| wt: | wild type. |
Acknowledgments
References
- Flower, DR. The Lipocalin Protein Family: Structure and Function. Biochem. J 1996, 318, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Pelosi, P. Odorant-Binding Proteins. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol 1994, 29, 199–228. [Google Scholar]
- Flower, DR. Beyond the superfamily: The lipocalin receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1482, 327–336. [Google Scholar]
- Skerra, A. Lipocalins as a Scaffold. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1482, 337–350. [Google Scholar]
- Grolli, S; Merli, E; Conti, V; Scaltriti, E; Ramoni, R. Odorant Binding Protein Has the Biochemical Properties of a Scavenger for 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal in Mammalian Nasal Mucosa. FEBS J 2006, 273, 5131–5142. [Google Scholar]
- Tegoni, M; Pelosi, P; Vincent, F; Spinelli, S; Campanacci, V; Grolli, S; Ramoni, R; Cambillau, C. Mammalian Odorant Binding Proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1482, 229–240. [Google Scholar]
- Ramoni, R; Vincent, F; Grolli, S; Conti, V; Malosse, C; Boyer, FD; Nagnan-Le Meillour, P; Spinelli, S; Cambillau, C; Tegoni, M. Control of domain swapping in bovine odorant-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem 2001, 276, 7150–7155. [Google Scholar]
- Pevsner, J; Hou, V; Snowman, AM; Snyder, SH. Odorant-Binding Protein. Characterization of Ligand Binding. J. Biol. Chem 1990, 265, 6118–6125. [Google Scholar]
- Fersht, A. Structure and Mechanism in Protein Science; W.H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USQA, 1999; pp. 420–456. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, MJ; Schlunegger, MP; Eisenberg, D. 3D Domain Swapping: A Mechanism for Oligomer Assembly. Protein Sci 1995, 4, 2455–2468. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, F; Ramoni, R; Spinelli, S; Grolli, S; Tegoni, M; Cambillau, C. Crystal Structures of Bovine Odorant-Binding Protein in Complex with Odorant Molecules. Eur. J. Biochem 2004, 271, 3832–3842. [Google Scholar]
- Ramoni, R; Vincent, F; Ashcroft, AE; Accornero, P; Grolli, S; Valencia, C; Tegoni, M; Cambillau, C. Control of Domain swapping in Bovine Odorant-Binding Protein. Biochem. J 2002, 365, 739–748. [Google Scholar]
- Spinelli, S; Ramoni, R; Grolli, S; Bonicel, J; Cambillau, C; Tegoni, M. The Structure of the Monomeric Porcine Odorant Binding Protein Sheds Light on the Domain Swapping Mechanism. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 7913–7918. [Google Scholar]
- Greene, LH; Hamada, D; Eyles, SJ; Brew, K. Conserved Signature Proposed for Folding in the Lipocalin Superfamily. FEBS Lett 2003, 553, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Parisi, M; Mazzini, A; Sorbi, RT; Ramoni, R; Grolli, S; Favilla, R. Role of the Disulphide Bridge in Folding, Stability and Function of Porcine Odorant Binding Protein: Spectroscopic Equilibrium Studies on C63A/C155A Double Mutant. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1750, 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ramoni, R; Staiano, M; Bellucci, S; Grycznyski, I; Grycznyski, Z; Crescenzo, R; Iozzino, L; Bharill, S; Conti, V; Grolli, S; et al. Carbon nanotube-based biosensors. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- D’Auria, S; Staiano, M; Varriale, A; Gonnelli, M; Marabotti, A; Rossi, M; Strambini, GB. The tryptophan phosphorescence of porcine and mutant bovine odorant-binding proteins: A probe for the local protein structure and dynamics. J. Proteome Res 2008, 7, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Marabotti, A; Lefevre, T; Staiano, M; Crescenzo, R; Varriale, A; Rossi, M; Pezolet, M; D'Auria, S. Mutant bovine odorant-binding protein: Temperature affects the protein stability and dynamics as revealed by infrared spectroscopy and molecular dynamics simulations. Proteins 2008, 72, 769–778. [Google Scholar]
- Marabotti, A; Scirè, A; Staiano, M; Crescenzo, R; Aurilia, V; Tanfani, F; D’Auria, S. Wild-type and mutant bovine odorant-binding proteins to probe the role of the quaternary structure organization in the protein thermal stability. J. Proteome Res 2008, 7, 5221–5229. [Google Scholar]
- Ramoni, R; Bellucci, S; Grycznyski, I; Grycznyski, Z; Grolli, S; Staiano, M; de Bellis, G; Micciulla, F; Pastore, R; Tiberia, A; et al. The protein scaffold of the lipocalin odorant-binding protein is suitable for the design of new biosensors for the detection of explosive components. J Phys Condens Matter 2007, 19, 395012:1–395012:7. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, PL; Liu, ZP; Zhang, J. Intrinsic Tryptophans of CRAPBI as probes of structure and folding. Protein Sci 1996, 5, 1108–1117. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzini, A; Maia, A; Parisi, M; Sorbi, RT; Ramoni, R; Grolli, S; Favilla, R. Reversible Unfolding of Bovine Odorant Binding Protein Induced by Guanidinium Hydrochloride at Neutral pH. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1599, 90–101. [Google Scholar]
- Parisi, M; Mazzini, A; Sorbi, RT; Ramoni, R; Grolli, S; Favilla, R. Unfolding and Refolding of Porcine Odorant Binding Protein in Guanidinium Hydrochloride: Equilibrium Studies at Neutral pH. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1652, 115–125. [Google Scholar]
- Paolini, S; Tanfani, F; Fini, C; Bertoli, E; Pelosi, P. Porcine odorant-binding protein: Structural stability and ligand anities measured by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and fluorescence spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1431, 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, CA; Rees, WT. Correction of Fluorescence Spectra and Measurements of Fluorescence Quantum Efficiency. Analyst 1960, 85, 587–600. [Google Scholar]
- Valeur, B; Weber, G. Resolution of the Fluorescence Excitation Spectrum of Indole into the 1La and 1Lb Excitation Bands. Photochem. Photobiol 1977, 25, 441–444. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzini, A; Polverini, E; Parisi, M; Sorbi, RT; Favilla, R. Dissociation and Unfolding of Bovine Odorant Binding Protein at Acidic pH. J. Struct. Biol 2007, 159, 82–91. [Google Scholar]
- Nagnan-Le Meillour, P; Lagant, P; Cornard, JP; Brimau, F; Le Danvic, C; Vergoten, G; Michalski, JC. Phenylalanine 35 and tyrosine 82 are involved in the uptake and release of ligand by porcine odorant-binding protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1794, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Tegoni, M; Ramoni, R; Bignetti, E; Spinelli, S; Cambillau, C. Domain Swapping Creates a Third Putative Combining Site in Bovine Odorant Binding Protein Dimer. Nat. Struct. Biol 1996, 3, 863–867. [Google Scholar]
- Polverini, E. University of Parma, Parma, Italy. Unpublished work,. 2011.
- Hodson, ME; Cistola, DP. Ligand binding alters the backbone mobility of intestinal fatty acid-binding protein as monitored by N-15 NMR relaxation and H-1 exchange. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 2278–2290. [Google Scholar]
- Mittag, T; Franzoni, L; Cavazzini, D; Schaffhausen, B; Rossi, GL; Günther, UL. Retinol Modulates Site-Specific Mobility of Apo-Cellular Retinol-Binding Protein to Promote Ligand Binding. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2006, 128, 9844–9848. [Google Scholar]
- Lakowitz, J. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Kluwer Academics Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 368–394. [Google Scholar]
- Semisotnov, GV; Rodionova, NA; Razgulyaev, OI; Uversky, VN; Gripas, AF; Gilmanshin, RI. Study of the “molten globule” intermediate state in protein folding by a hydrophobic fluorescent probe. Biopolymers 1991, 31, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Povarova, OI; Kuznetsova, IM; Turoverov, KK. Differences in the pathways of protein unfolding induced by urea and guanidine hydrochloride: molten globule state and aggregates. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15035. [Google Scholar]
- Bignetti, E; Cavaggioni, A; Pelosi, P; Persaud, KC; Sorbi, RT; Tirindelli, R. Purification and characterisation of an odorant-binding protein from cow nasal tissue. Eur. J. Biochem 1985, 149, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Favilla, R; Goldoni, M; Mazzini, A; Di Muro, P; Salvato, B; Beltramini, M. Guanidinium Chloride Induced Unfolding of a Hemocyanin Subunit from Carcinus aestuarii. I. Apo Form. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1597, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, HM; Westbrook, J; Feng, Z; Gilliland, G; Bhat, TN; Weissig, H; Shindyalov, IN; Bourne, PE. The protein data bank. Nucleic Acid Res 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- van der Spoel, D; Lindhal, E; Hess, B; Groenhof, G; Mark, AE; Berendsen, HJC. GROMACS: Fast, flexible and free. J. Comp. Chem 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar]
- Oostenbrink, C; Villa, A; Mark, AE; van Gunsteren, WF. A biomolecular force field based on the free enthalpy of hydration and solvation: The GROMOS force-field parameter sets 53A5 and 53A6. J. Comput. Chem 2004, 25, 1656–1676. [Google Scholar]
- Schuettelkopf, AW; van Aalten, DMF. Prodrg: A tool for high-throughput crystallography of protein-ligand complexes. Acta Cryst 2004, D60, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, W; Dalke, A; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Guex, N; Peitsch, MC. SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: An environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 1997, 18, 2714–2723. [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch, W; Sander, C. Dictionary of protein secondary structure: Pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers 1983, 22, 2577–2637. [Google Scholar]
Appendix
Estimation of Kd for AMA-GCC-bOBP Complex
Protein Fluorescence
- P0 = total protein concentration;
- PL = protein-ligand complex concentration;
- F, F0, F∞ = fluorescence intensities in the absence of AMA, in the presence of AMA, at infinite AMA concentration, respectively.
Ligand Fluorescence









| Protein* | W17 | W133 | W64 |
|---|---|---|---|
| pOBP | 1 | - | - |
| GCC-bOBP | 1 | 2.15 | - |
| bOBP | 1 | 2.15 | 1.88 |
| Parameter | GCC-bOBP a | bOBP b | pOBP c |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1/2 (M) | 2.90 ± 0.01 | 2.65 ± 0.03 | 2.37 ± 0.02 |
| m (kJ mol−1 M−1) | 14.3 ± 1.0 | 8.4 ±0.8 | 8.4 ± 0.4 |
| ΔG°un (kJ M−1) | 41.5 ± 3.0 | 22.2 ± 2.4 | 19.8 ± 1.1 |
| Conditions | τ1 (ns) | τ2 (ns) |
|---|---|---|
| N | 2.9 ± 0.2 0.45 ± 0.05 | 8.0 ± 0.3 0.55 ± 0.05 |
| N + AMA | 2.8 ± 0.1 | - |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Polverini, E.; Lardi, P.; Mazzini, A.; Sorbi, R.T.; Virna, C.; Ramoni, R.; Favilla, R. Characterization of a Deswapped Triple Mutant Bovine Odorant Binding Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 2294-2314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12042294
Polverini E, Lardi P, Mazzini A, Sorbi RT, Virna C, Ramoni R, Favilla R. Characterization of a Deswapped Triple Mutant Bovine Odorant Binding Protein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2011; 12(4):2294-2314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12042294
Chicago/Turabian StylePolverini, Eugenia, Paolo Lardi, Alberto Mazzini, Robert T. Sorbi, Conti Virna, Roberto Ramoni, and Roberto Favilla. 2011. "Characterization of a Deswapped Triple Mutant Bovine Odorant Binding Protein" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 12, no. 4: 2294-2314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12042294
APA StylePolverini, E., Lardi, P., Mazzini, A., Sorbi, R. T., Virna, C., Ramoni, R., & Favilla, R. (2011). Characterization of a Deswapped Triple Mutant Bovine Odorant Binding Protein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 12(4), 2294-2314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12042294