A Rapid Method for Optimizing Running Temperature of Electrophoresis through Repetitive On-Chip CE Operations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Design and Fabrication of Temperature Controlled On-Chip CE Device
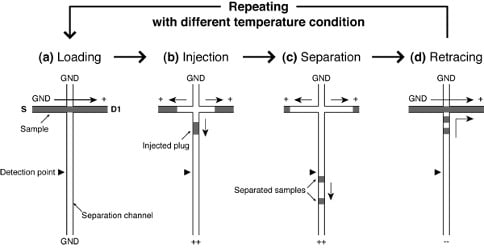
2.2. Process of Repetitive On-Chip CE Operations with Different Temperature Conditions
2.3. Repetitive On-Chip CE Operations for SBS Detection
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
References
- West, J; Becker, M; Tombrink, S; Manz, A. Micro total analysis systems: Latest achievements. Anal. Chem 2008, 80, 4403–4419. [Google Scholar]
- Craighead, H. Future lab-on-a-chip technologies for interrogating individual molecules. Nature 2006, 442, 387–393. [Google Scholar]
- Manz, A; Harrison, DJ; Verpoorte, EMJ; Fettinger, JC; Paulus, A; Lüdi, H; Widmer, HM. Planar chips technology for miniaturization and integration of separation techniques into monitoring systems: Capillary electrophoresis on a chip. J. Chromatogr. A 1992, 593, 253–258. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, DJ; Manz, A; Fan, Z; Luedi, H; Widmer, HM. Capillary electrophoresis and sample injection systems integrated on a planar glass chip. Anal. Chem 1992, 64, 1926–1932. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, DJ; Fluri, K; Seiler, K; Fan, Z; Effenhauser, CS; Manz, A. Micromachining a miniaturized capillary electrophoresis-based chemical analysis system on a chip. Science 1993, 261, 895–897. [Google Scholar]
- Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer. Available online: http://www.chem.agilent.com/en-US/products/instruments/lab-on-a-chip/pages/default.aspx accessed on 30 June 2011.
- MCE®-202 MultiNA|Microchip Electrophoresis System for DNA/RNA Analysis. Available online: http://www.shimadzu-biotech.net/pages/products/2/multina.php accessed on 30 June 2011.
- Woolley, AT; Mathies, RA. Ultra-high-speed DNA fragment separations using microfabricated capillary array electrophoresis chips. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 11348–11352. [Google Scholar]
- Woolley, AT; Mathies, RA. Ultra-high-speed DNA sequencing using capillary electrophoresis chips. Anal. Chem 1995, 67, 3676–3680. [Google Scholar]
- Effenhauser, CS; Manz, A; Widmer, HM. Glass chips for high-speed capillary electrophoresis separations with submicrometer plate heights. Anal. Chem 1993, 65, 2637–2642. [Google Scholar]
- Duffy, DC; McDonald, JC; Schueller, OJA; Whitesides, GM. Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Anal. Chem 1998, 70, 4974–4984. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamadi, MR; Mahmoudian, LM; Kaji, N; Tokeshi, M; Baba, Y. Dynamic coating using methylcellulose and polysorbate 20 for nondenaturing electrophoresis of proteins on plastic microchips. Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 830–836. [Google Scholar]
- McCormick, RM; Nelson, RJ; Alonso-Amigo, MG; Benvegnu, DJ; Hooper, HH. Microchannel electrophoretic separations of DNA in Injection-molded plastic substrates. Anal. Chem 1997, 69, 2626–2630. [Google Scholar]
- Effenhauser, CS; Bruin, GJM; Paulus, A; Ehrat, A. Integrated capillary electrophoresis on flexible silicone microdevices: Analysis of DNA restriction fragments and detection of single DNA molecules on microchips. Anal. Chem 1997, 69, 3451–3457. [Google Scholar]
- Woolley, AT; Sensabaugh, GF; Mathies, RA. High-speed DNA genotyping using microfabricated capillary array electrophoresis chips. Anal. Chem 1997, 69, 2181–2186. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S; Shi, Y; Ja, WW; Mathies, RA. Optimization of high-speed DNA sequencing on microfabricated capillary electrophoresis channels. Anal. Chem 1999, 71, 566–573. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, SC; Ramsey, JM. Integrated microdevice for DNA restriction fragment analysis. Anal. Chem 1996, 68, 720–723. [Google Scholar]
- Woolley, AT; Hadley, D; Landre, P; deMello, AJ; Mathies, RA; Northrup, MA. Functional integration of PCR amplification and capillary electrophoresis in a microfabricated DNA analysis device. Anal. Chem 1996, 68, 4081–4086. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, JW; Fujii, T; Seki, M; Yamamoto, T; Endo, I. Integration of gene amplification and capillary gel electrophoresis on a polydimethylsiloxane-glass hybrid microchip. Electrophoresis 2001, 22, 328–333. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, JR; Burns, MA; Burke, DT; Mastrangelo, CH. Monolithic capillary electrophoresis device with integrated fluorescence detector. Anal. Chem 2001, 73, 1622–1626. [Google Scholar]
- Chabinyc, ML; Chiu, DT; McDonald, JC; Stroock, AD; Christian, JF; Karger, AM; Whitesides, GM. An integrated fluorescence detection system in poly(dimethylsiloxane) for microfluidic applications. Anal. Chem 2001, 73, 4491–4498. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda, S; Ono, K; Fukuba, T; Nojima, T; Yamamoto, T; Fujii, T. Pneumatic handling of droplets on-demand on a microfluidic device for seamless processing of reaction and electrophoretic separation. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 3719–3726. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelgawad, M; Watson, MWL; Wheeler, AR. Hybrid microfluidics: A digital-to-channel interface for in-line sample processing and chemical separations. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, PE; Egholm, M; Berg, RH; Buchardt, O. Sequence-selective recognition of DNA by strand displacement with a thymine-substituted polyamide. Science 1991, 254, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Egholm, M; Buchardt, O; Christensen, L; Behrens, C; Freier, SM; Driver, DA; Berg, RH; Kim, SK; Norden, B; Nielsen, PE. PNA hybridizes to complementary oligonucleotides obeying the Watson-Crick hydrogen-bonding rules. Nature 1993, 365, 566–568. [Google Scholar]
- Basile, A; Giuliani, A; Pirri, G; Chiari, M. Use of peptide nucleic acid probes for detecting DNA single-base mutations by capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2002, 23, 926–929. [Google Scholar]
- Perry-O’Keefe, H; Yao, X-W; Coull, JM; Fuchs, M; Egholm, M. Peptide nucleic acid pre-gel hybridization: An alternative to Southern hybridization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14670–14675. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, T; Fujii, T; Nojima, T. PDMS-glass hybrid microreactor array with embedded temperature control device. Application to cell-free protein synthesis. Lab Chip 2002, 2, 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuba, T; Yamamoto, T; Naganuma, T; Fujii, T. Microfabricated flow-through device for DNA amplification-towards in situ gene analysis. Chem. Eng. J 2004, 101, 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- Hosokawa, K; Fujii, T; Endo, I. Handling of picoliter liquid samples in a poly(dimethylsiloxane)-based microfluidic device. Anal. Chem 1999, 71, 4781–4785. [Google Scholar]
- Cutting, GR; Kasch, LM; Rosenstein, BJ; Zielenski, J; Tsui, L-C; Antonarakis, SE; Kazazian, HH, Jr. A cluster of cystic fibrosis mutations in the first nucleotide-binding fold of the cystic fibrosis conductance regulator protein. Nature 1990, 346, 366–369. [Google Scholar]
- Hosokawa, K; Sato, K; Ichikawa, N; Maeda, M. Power-free poly(dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic devices for gold nanoparticle-based DNA analysis. Lab Chip 2004, 4, 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, T; Inoue, A; Sato, K; Hosokawa, K; Maeda, M. Autonomous polymer loading and sample injection for microchip electrophoresis. Anal. Chem 2005, 77, 4759–4764. [Google Scholar]
- Giesen, U; Kleider, W; Berding, C; Geiger, A; Ørum, H; Nielsen, PE. A formula for thermal stability (Tm) prediction of PNA/DNA duplexes. Nucleic Acids Res 1998, 26, 5004–5006. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, FP; Robinson, S; Butler, JM. Thermodynamic comparison of PNA/DNA and DNA/DNA hybridization reactions at ambient temperature. Nucleic Acids Res 1999, 27, 4792–4800. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, MC; Schwarz, FP. Thermal stability of PNA/DNA and DNA/DNA duplexes by differential scanning calorimetry. Nucleic Acids Res 1999, 27, 4801–4806. [Google Scholar]
- Khrapko, K; Hanekamp, JS; Thilly, WG; Belenkii, A; Foret, F; Karger, BL. Constant denaturant capillary electrophoresis (CDCE): A high resolution approach to mutational anaylsis. Nucleic Acids Res 1994, 22, 364–369. [Google Scholar]
- Bjørheim, J; Abrahamsen, TW; Kristensen, AT; Gaudernack, G; Ekstrøm, PO. Approach to analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms by automated constant denaturant capillary electrophoresis. Mutat. Res 2003, 526, 75–83. [Google Scholar]





| S (V) | D1 (V) | D2 (V) | B (V) | Time (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loading | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 60 |
| Injection/Separation | 100 | 100 | 500 | 0 | 60 |
| Retracing | 0 | 100 | −250 | 0 | 120 |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaneda, S.; Ono, K.; Fukuba, T.; Nojima, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Fujii, T. A Rapid Method for Optimizing Running Temperature of Electrophoresis through Repetitive On-Chip CE Operations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 4271-4281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12074271
Kaneda S, Ono K, Fukuba T, Nojima T, Yamamoto T, Fujii T. A Rapid Method for Optimizing Running Temperature of Electrophoresis through Repetitive On-Chip CE Operations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2011; 12(7):4271-4281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12074271
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaneda, Shohei, Koichi Ono, Tatsuhiro Fukuba, Takahiko Nojima, Takatoki Yamamoto, and Teruo Fujii. 2011. "A Rapid Method for Optimizing Running Temperature of Electrophoresis through Repetitive On-Chip CE Operations" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 12, no. 7: 4271-4281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12074271
APA StyleKaneda, S., Ono, K., Fukuba, T., Nojima, T., Yamamoto, T., & Fujii, T. (2011). A Rapid Method for Optimizing Running Temperature of Electrophoresis through Repetitive On-Chip CE Operations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 12(7), 4271-4281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12074271