Cellular Delivery of Doxorubicin via pH-Controlled Hydrazone Linkage Using Multifunctional Nano Vehicle Based on Poly(β-L-Malic Acid)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
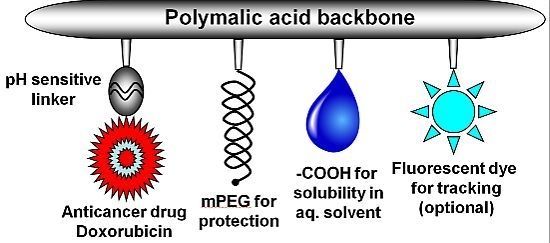
2.1. Synthesis of Nanoconjugates
2.2. Characterization of Nanoconjugates
2.3. Drug Release from the P/PEG(5%)/GH-DOX (5%) Nanoconjugate
2.4. Effect of Nanoconjugates on Cell Viability
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Analytical Methods Used in Chemical Synthesis
3.3. Size and Zeta Potential Measurements
3.4. Synthesis of Nanoconjugate P/PEG(5%)/GH(5%)
3.5. Synthesis of Nanoconjugate P/PEG(5%)/GH-DOX (5%)
3.6. Release of DOX from the Nanoconjugate
3.7. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Wiernik, P.H.; Dutcher, J.P. Clinical importance of anthracyclines in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 1992, 6, 67–69. [Google Scholar]
- Lown, J.W. Anthracycline and anthraquinone anticancer agents: Current status and recent developments. Pharmacol. Ther 1993, 60, 185–214. [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman, M.M.; Pastan, I. Biochemistry of multidrug resistance mediated by the multidrug transporter. Annu. Rev. Biochem 1993, 62, 385–427. [Google Scholar]
- Germann, U.A. P-Glycoprotein—A mediator of multidrug resistance in tumour cells. Eur. J. Cancer 1996, 32A, 927–944. [Google Scholar]
- Borst, P.; Evers, R.; Kool, M.; Wijnholds, J. A family of drug transporters: The multidrug resistance-associated proteins. J. Natl. Cancer Inst 2000, 92, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Marie, J.P.; Zhou, D.C.; Gurbuxani, S.; Legrand, O.; Zittoun, R. MDR1/P-Glycoprotein in haematological neoplasms. Eur. J. Cancer 1996, 32A, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Kopecek, J.; Kopeckova, P.; Minko, T.; Lu, Z. HPMA copolymer-anticancer drug conjugates: Design, Activity, and mechanism of action. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm 2000, 50, 61–81. [Google Scholar]
- Seymour, L.W.; Ulbrich, K.; Steyger, P.S.; Brereton, M.; Subr, V.; Strohalm, J.; Duncan, R. Tumour tropism and anti-cancer efficacy of polymer-based doxorubicin prodrugs in the treatment of subcutaneous murine B16F10 melanoma. Br. J. Cancer 1994, 70, 636–641. [Google Scholar]
- Rihova, B.; Bilej, M.; Vetvicka, V.; Ulbrich, K.; Strohalm, J.; Kopecek, J.; Duncan, R. Biocompatibility of N-(2-Hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide copolymers containing adriamycin: Immunogenicity, and effect on haematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow in vivo and mouse splenocytes and human peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro. Biomaterials 1989, 10, 335–342. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, P.C.; Beyer, U.; Schumacher, P.; Roth, T.; Fiebig, H.H.; Unger, C.; Messori, L.; Orioli, P.; Paper, D.H.; Mulhaupt, R.; et al. Acid-Sensitive polyethylene glycol conjugates of doxorubicin: Preparation, in vitro efficacy and intracellular distribution. Bioorg. Med. Chem 1999, 7, 2517–2524. [Google Scholar]
- Ulbrich, K.; Etrych, T.; Chytil, P.; Jelinkova, M.; Rihova, B. HPMA copolymers with pH-controlled release of doxorubicin: In vitro cytotoxicity and in vivo antitumor activity. J. Control. Release 2003, 87, 33–47. [Google Scholar]
- Nori, A.; Kopecek, J. Intracellular targeting of polymer-bound drugs for cancer chemotherapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev 2005, 57, 609–636. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, R.; Vicent, M.J.; Greco, F.; Nicholson, R.I. Polymer-Drug conjugates: Towards a novel approach for the treatment of endrocine-related cancer. Endocr. Related Cancer 2005, 12, S189–S199. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, H.; Fang, J.; Inutsuka, T.; Kitamoto, Y. Vascular permeability enhancement in solid tumor: Various factors, mechanisms involved and its implications. Int. Immunopharmacol 2003, 3, 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, M.; Lee, B.S.; Khazenzon, N.M.; Penichet, M.L.; Wawrowsky, K.A.; Patil, R.; Ding, H.; Holler, E.; Black, K.L.; Ljubimova, J.Y. Brain tumor tandem targeting using a combination of monoclonal antibodies attached to Biopoly(β-l-Malic Acid). J. Control. Release 2007, 122, 356–363. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.S.; Fujita, M.; Khazenzon, N.M.; Wawrowsky, K.A.; Wachsmann-Hogiu, S.; Farkas, D.L.; Black, K.L.; Ljubimova, J.Y.; Holler, E. Polycefin, a new prototype of a multifunctional nanoconjugate based on Poly(β-l-Malic Acid) for drug delivery. Bioconjug. Chem 2006, 17, 317–326. [Google Scholar]
- Segal, E.; Satchi-Fainaro, R. Design and development of polymer conjugates as anti-angiogenic agents. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev 2009, 61, 1159–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Peer, D.; Karp, J.M.; Hong, S.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Margalit, R.; Langer, R. Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol 2007, 2, 751–760. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, M. Cancer nanotechnology: Opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 161–171. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, R. The dawning era of polymer therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 2003, 2, 347–360. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov, S.V.; Batrakova, E.V.; Li, S.; Kabanov, A.V. Mixed polymer micelles of amphiphilic and cationic copolymers for delivery of antisense oligonucleotides. J. Drug Target 2004, 12, 517–526. [Google Scholar]
- Kabanov, A.V.; Batrakova, E.V.; Sriadibhatla, S.; Yang, Z.; Kelly, D.L.; Alakov, V.Y. Polymer genomics: Shifting the gene and drug delivery paradigms. J. Control. Release 2005, 101, 259–271. [Google Scholar]
- Barenholz, Y. Doxil®—The first fda-approved nano-drug: Lessons learned. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 117–134. [Google Scholar]
- Ulbrich, K.; Etrych, T.; Chytil, P.; Jelinkova, M.; Rihova, B. Antibody-targeted polymer-doxorubicin conjugates with pH-controlled activation. J. Drug Target 2004, 12, 477–489. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.C.; Gillies, E.R.; Fox, M.E.; Guillaudeu, S.J.; Frechet, J.M.; Dy, E.E.; Szoka, F.C. A single dose of doxorubicin-functionalized bow-tie dendrimer cures mice bearing C-26 colon carcinomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16649–16654. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, R.; Portilla-Arias, J.; Ding, H.; Inoue, S.; Konda, B.; Hu, J.; Wawrowsky, K.A.; Shin, P.K.; Black, K.L.; Holler, E.; et al. Temozolomide delivery to tumor cells by a multifunctional nano vehicle based on Poly(β-l-Malic Acid). Pharm. Res 2010, 27, 2317–2329. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Inoue, S.; Ljubimov, A.V.; Patil, R.; Portilla-Arias, J.; Hu, J.; Konda, B.; Wawrowsky, K.A.; Fujita, M.; Karabalin, N.; et al. Inhibition of brain tumor growth by intravenous Poly(β-l-Malic Acid) nanobioconjugate with pH-Dependent drug release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18143–18148. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, S.; Ding, H.; Portilla-Arias, J.; Hu, J.; Konda, B.; Fujita, M.; Espinoza, A.; Suhane, S.; Riley, M.; Gates, M.; et al. Polymalic acid-based nanobiopolymer provides efficient systemic breast cancer treatment by inhibiting both Her2/Neu receptor synthesis and activity. Cancer Res 71, 1454–1464.
- Inoue, S.; Patil, R.; Portilla-Arias, J.; Ding, H.; Konda, B.; Espinoza, A.; Mongayt, D.; Markman, J.L.; Elramsisy, A.; Phillips, H.W.; et al. Nanobiopolymer for direct targeting and inhibition of EGFR expression in triple negative breast cancer. PLoS One 2012, 7, e31070. [Google Scholar]
- Coessens, V.; Schacht, E.; Domurado, D. Synthesis of polyglutamine and dextran conjugates of streptomycin with an acid-sensitive drug-carrier linkage. J. Control. Release 1996, 38, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Li, R.T.; Qian, H.Q.; Yang, M.; Zhu, Z.S.; Wu, W.; Qian, X.P.; Yu, L.X.; Jiang, X.Q.; Liu, B.R. Gelatinase-Stimuli Strategy enhances the tumor delivery and therapeutic efficacy of docetaxel-loaded Poly(Ethylene Glycol)-Poly(Varepsilon-Caprolactone) nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed 2012, 7, 281–295. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Y.L.; Nan, K.; Nie, G.; Chen, H. Enhanced anti-tumor efficacy by co-delivery of doxorubicin and paclitaxel with amphiphilic methoxy PEG-PLGA copolymer nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8281–8290. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yang, C.; Lu, W.; Yang, Y.H. Camptothecin derivative-loaded Poly(Caprolactone-Co-Lactide)-b-PEG-b-Poly(Caprolactone-Co-Lactide) nanoparticles and their biodistribution in mice. J. Control. Release 2004, 96, 135–148. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, E.T.; Yamaguchi, N.H. Treatment advances for glioblastoma. Expert Rev. Neurother 2011, 11, 1343–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Madhankumar, A.B.; Slagle-Webb, B.; Mintz, A.; Sheehan, J.M.; Connor, J.R. Interleukin-13 receptor-targeted nanovesicles are a potential therapy for glioblastoma multiforme. Mol. Cancer Ther 2006, 5, 3162–3169. [Google Scholar]
- Bolhuis, H.; van Veen, H.W.; Poolman, B.; Driessen, A.J.; Konings, W.N. Mechanisms of multidrug transporters. FEMS Microbiol. Rev 1997, 21, 55–84. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, V.; Xu, J.; Pabbisetty, S.K.; Alonso, M.M.; Liu, D.; Lee, O.H.; Gumin, J.; Bhat, K.P.; Colman, H.; Lang, F.F.; et al. Tie2-Mediated multidrug resistance in malignant gliomas is associated with upregulation of ABC transporters. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2358–2363. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, T.A.; Workman, P. Exploiting the cancer genome: Strategies for the discovery and clinical development of targeted molecular therapeutics. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol 2012, 52, 549–573. [Google Scholar]
- Holler, E. Poly(malic Acid) from Natural Sources. In Handbook of Engineering Polymeric Materials; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 997, pp. 93–103. [Google Scholar]
- Hiemenz, P.C. Light Scattering by Polymer Solutions. In Polymer Chemistry: The Basic Concepts; Marcel Decker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 659–719. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO), Methods for Determination of Particle Size Distribution Part 8: Photon Correlation Spectroscopy; International Standard ISO 13321, ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- Mosmann, T.J. Rapid colorimetric assays for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar]






| Nanoconjugates | Size in nm | Zeta Potential in mV | Polydispersity Index (PDI) | Molecular Weight in kDa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMLA | 5.6 (±0.1) | −22.9 | 0.1 (±0.01) | 70 |
| P/PEG(5%)/GH(5%) | 6.2 (±0.5) | −11.45 | 0.64 (±0.03) | 223 |
| P/PEG(5%)/GH-DOX(5%) | nd | −5.34 | nd | 239 |
| Cell Lines | DOX IC50 (μM) | P/PEG(5%)/GH-DOX(5%) IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| MDA-MB-231 | 0.11 (±0.04) | 0.52 (±0.2) |
| MDA-MB-468 | 0.14 (±0.05) | 0.51(±0.1) |
| U87MG | 2.16 (±0.5) | 5.73 (±2.1) |
| U251 | 5.7 (±0.8) | 0.8 (±0.3) |
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Patil, R.; Portilla-Arias, J.; Ding, H.; Konda, B.; Rekechenetskiy, A.; Inoue, S.; Black, K.L.; Holler, E.; Ljubimova, J.Y. Cellular Delivery of Doxorubicin via pH-Controlled Hydrazone Linkage Using Multifunctional Nano Vehicle Based on Poly(β-L-Malic Acid). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 11681-11693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130911681
Patil R, Portilla-Arias J, Ding H, Konda B, Rekechenetskiy A, Inoue S, Black KL, Holler E, Ljubimova JY. Cellular Delivery of Doxorubicin via pH-Controlled Hydrazone Linkage Using Multifunctional Nano Vehicle Based on Poly(β-L-Malic Acid). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(9):11681-11693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130911681
Chicago/Turabian StylePatil, Rameshwar, Jose Portilla-Arias, Hui Ding, Bindu Konda, Arthur Rekechenetskiy, Satoshi Inoue, Keith L. Black, Eggehard Holler, and Julia Y. Ljubimova. 2012. "Cellular Delivery of Doxorubicin via pH-Controlled Hydrazone Linkage Using Multifunctional Nano Vehicle Based on Poly(β-L-Malic Acid)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 9: 11681-11693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130911681
APA StylePatil, R., Portilla-Arias, J., Ding, H., Konda, B., Rekechenetskiy, A., Inoue, S., Black, K. L., Holler, E., & Ljubimova, J. Y. (2012). Cellular Delivery of Doxorubicin via pH-Controlled Hydrazone Linkage Using Multifunctional Nano Vehicle Based on Poly(β-L-Malic Acid). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(9), 11681-11693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130911681