Cell Signaling Experiments Driven by Optical Manipulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Apply and Sense Local Forces in Single-Cell Experiments
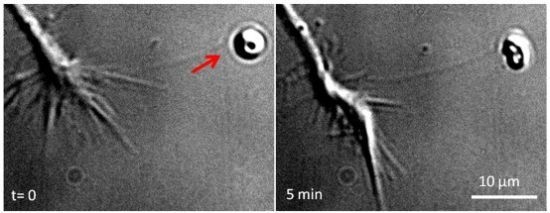
3. Local Delivery
4. Laser Dissection
5. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Berridge, M.J. Cell Signalling Biology; Portland Press Ltd: London, UK, 2012. Available online: http://www.biochemj.org/csb/ (accessed on 10 January 2013). [CrossRef]
- Hell, S.W. Microscopy and its focal switch. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ashkin, A.; Dziedzic, J.M.; Bjorkholm, J.E.; Chu, S. Observation of a single-beam gradient force optical trap for dielectric particles. Opt. Lett 1986, 11, 288–290. [Google Scholar]
- Ashkin, A.; Dziedzic, J.M. Optical trapping and manipulation of viruses and bacteria. Science 1987, 235, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar]
- Ashkin, A.; Dziedzic, J.M.; Yamane, T. Optical trapping and manipulation of single cells using infrared laser beams. Nature 1987, 330, 769–771. [Google Scholar]
- Ashkin, A.; Dziedzic, J.M. Internal cell manipulation using infrared laser traps. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 7914–7918. [Google Scholar]
- Ashkin, A.; Schutze, K.; Dziedzic, J.M.; Euteneuer, U.; Schliwa, M. Force generation of organelle transport measured in vivo by an infrared laser trap. Nature 1990, 348, 346–348. [Google Scholar]
- Grier, D.G. A revolution in optical manipulation. Nature 2003, 424, 810–816. [Google Scholar]
- Neuman, K.C.; Block, S.M. Optical trapping. Rev. Sci. Instrum 2004, 75, 2787–2809. [Google Scholar]
- Moffitt, J.R.; Chemla, Y.R.; Smith, S.B.; Bustamante, C. Recent advances in optical tweezers. Annu. Rev. Biochem 2008, 77, 205–228. [Google Scholar]
- Dholakia, K.; Čižmár, T. Shaping the future of manipulation. Nat. Photonics 2011, 5, 335–342. [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante, C.; Cheng, W.; Mejia, Y.X. Revisiting the central dogma one molecule at a time. Cell 2011, 144, 480–497. [Google Scholar]
- Ashok, P.C.; Dholakia, K. Optical trapping for analytical biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol 2012, 23, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Berns, M.W.; Aist, J.; Edwards, J.; Strahs, K.; Girton, J.; McNeill, P.; Rattner, J.B.; Kitzes, M.; Hammer-Wilson, M.; Liaw, L.H.; et al. Laser microsurgery in cell and developmental biology. Science 1981, 213, 505–513. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Gunn-Moore, F.; Dholakia, K. Optical transfection using an endoscope-like system. J. Biomed. Opt 2011, 16, 028002. [Google Scholar]
- Pinato, G.; Lien, L.T.; D’Este, E.; Torre, V.; Cojoc, D. Neuronal chemotaxis by optically manipulated liposomes. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. Rapid Publ 2011, 6, 11042. [Google Scholar]
- Pinato, G.; Raffaelli, T.; D’Este, E.; Tavano, F.; Cojoc, D. Optical delivery of liposome encapsulated chemical stimuli to neuronal cells. J. Biomed. Opt 2011, 16, 095001. [Google Scholar]
- Greenleaf, W.J.; Woodside, M.T.; Block, S.M. High-resolution, single-molecule measurements of biomolecular motion. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct 2007, 36, 171–190. [Google Scholar]
- Ashkin, A. Forces of a single-beam gradient laser trap on a dielectric sphere in the ray optics regime. Biophys. J 1992, 61, 569–582. [Google Scholar]
- Ghislain, L.P.; Webb, W.W. Scanning-force microscope based on an optical trap. Opt. Lett 1993, 18, 1678–1680. [Google Scholar]
- Florin, E.-L.; Pralle, A.; Heinrich Hörber, J.K.; Stelzer, E.H.K. Photonic force microscope based on optical tweezers and two-photon excitation for biological applications. J. Struct. Biol 1997, 119, 202–211. [Google Scholar]
- Pralle, A.; Florin, E.L.; Stelzer, E.H.K.; Hörber, J.K.H. Photonic force microscopy: A new tool providing new methods to study membranes at the molecular level. Single Mol 2000, 1, 129–133. [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz, M.P.; Dai, J. Modulation of membrane dynamics and cell motility by membrane tension. Trends Cell Biol 1996, 6, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Footer, M.J.; Kerssemakers, J.W.J.; Theriot, J.A.; Dogterom, M. Direct measurement of force generation by actin filament polymerization using an optical trap. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2181–2186. [Google Scholar]
- Cojoc, D.; Difato, F.; Ferrari, E.; Shahapure, R.B.; Laishram, J.; Righi, M.; Di Fabrizio, E.M.; Torre, V. Properties of the force exerted by filopodia and lamellipodia and the involvement of cytoskeletal components. PLoS One 2007, 2, e1072. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, L.; Ercolini, E.; Shahapure, R.; Bisson, G.; Torre, V. The elementary events underlying force generation in neuronal lamellipodia. Sci. Rep 2011, 1, 153. [Google Scholar]
- Guiggiani, A.; Torre, B.; Contestabile, A.; Benfenati, F.; Basso, M.; Vassalli, M.; Difato, F. Long-range and long-term interferometric tracking by static and dynamic force-clamp optical tweezers. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 22364–22376. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, S.; Quatela, A.; Bornschlog, T.; Guadagnini, S.; Bassereau, P.; Tran Van Nhieu, G. Filopodium retraction is controlled by adhesion to its tip. J. Cell Sci 2012, 125, 4999–5004. [Google Scholar]
- Difato, F.; Tsushima, H.; Pesce, M.; Benfenati, F.; Blau, A.; Chieregatti, E. The formation of actin waves during regeneration after axonal lesion is enhanced by BDNF. Sci. Reports 2011, 1, 183. [Google Scholar]
- Mejean, C.O.; Schaefer, A.W.; Millman, E.A.; Forscher, P.; Dufresne, E.R. Multiplexed force measurements on live cells with holographic optical tweezers. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 6209–6217. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Nieminen, T.A.; Mohanty, S.; Miotke, J.; Meyer, R.L.; Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H.; Berns, M.W. A photon-driven micromotor can direct nerve fibre growth. Nat. Photon 2012, 6, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, K.H. Optical tweezers for single cells. J. R. Soc. Interface 2008, 5, 671–690. [Google Scholar]
- Neuman, K.C.; Nagy, A. Single-molecule force spectroscopy: Optical tweezers, magnetic tweezers and atomic force microscopy. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 491–505. [Google Scholar]
- Oddershede, L.B. Force probing of individual molecules inside the living cell is now a reality. Nat. Chem. Biol 2012, 8, 879–886. [Google Scholar]
- Jauffred, L.; Richardson, A.C.; Oddershede, L.B. Three-dimensional optical control of individual quantum dots. Nano Lett 2008, 8, 3376–3380. [Google Scholar]
- Selhuber-Unkel, C.; Zins, I.; Schubert, O.; Sönnichsen, C.; Oddershede, L.B. Quantitative optical trapping of single gold nanorods. Nano Lett 2008, 8, 2998–3003. [Google Scholar]
- Choquet, D.; Felsenfeld, D.P.; Sheetz, M.P. Extracellular matrix rigidity causes strengthening of integrin- cytoskeleton linkages. Cell 1997, 88, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, V. Mechanotransduction involving multimodular proteins: Converting force into biochemical signals. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct 2006, 35, 459–488. [Google Scholar]
- Giannone, G. Talin1 is critical for force-dependent reinforcement of initial integrin-cytoskeleton bonds but not tyrosine kinase activation. J. Cell Biol 2003, 163, 409–419. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, V.; Sheetz, M.P. Cell fate regulation by coupling mechanical cycles to biochemical signaling pathways. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol 2009, 21, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Makale, M. Cellular mechanobiology and cancer metastasis. Birth Defects Res. C 2007, 81, 329–343. [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch, A.; Höckel, M.; Kiessling, T.; Nnetu, K.D.; Wetzel, F.; Zink, M.; Käs, J.A. Are biomechanical changes necessary for tumour progression? Nat. Phys 2010, 6, 730–732. [Google Scholar]
- Suresh, S. Nanomedicine: Elastic clues in cancer detection. Nat. Nanotechnol 2007, 2, 748–749. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Sylvan, J.; Jonas, M.; Barresi, R.; So, P.T.C.; Campbell, K.P.; Lee, R.T. Cell stiffness and receptors: Evidence for cytoskeletal subnetworks. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol 2005, 288, C72–C80. [Google Scholar]
- Geiger, T.R.; Peeper, D.S. Metastasis mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1796, 293–308. [Google Scholar]
- Remmerbach, T.W.; Wottawah, F.; Lincoln, B.; Wittekind, C.; Guck, J. Oral cancer diagnosis by mechanical phenotyping. Cancer Res 2009, 69, 1728–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Kamm, R.D.; Lee, R.T. Cell mechanics and mechanotransduction: Pathways, probes, and physiology. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol 2004, 287, C1–C11. [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz, M.P. Cell control by membrane-cytoskeleton adhesion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2001, 2, 392–396. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, S.; Wirtz, D.; Kuo, S.C. Mechanics of living cells measured by laser tracking microrheology. Biophys. J 2000, 78, 1736–1747. [Google Scholar]
- Heidemann, S.R.; Wirtz, D. Towards a regional approach to cell mechanics. Trends Cell Biol 2004, 14, 160–166. [Google Scholar]
- Raucher, D.; Sheetz, M.P. Characteristics of a membrane reservoir buffering membrane tension. Biophys. J 1999, 77, 1992–2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hochmuth, R.M.; Shao, J.-Y.; Dai, J.; Sheetz, M.P. Deformation and flow of membrane into tethers extracted from neuronal growth cones. Biophys. J 1996, 70, 358–369. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Anvari, B.; Takashima, M.; Brecht, P.; Torres, J.H.; Brownell, W.E. Membrane tether formation from outer hair cells with optical tweezers. Biophys. J 2002, 82, 1386–1395. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.-L.; Liu, C.-X.; Duan, J.-F.; Jiang, Y.-Q.; Han, X.-H.; Li, Z.-L.; Cheng, B.-Y.; Zhang, D.-Z. Mechanical properties of breast cancer cell membrane studied with optical tweezers. Chin. Phys. Lett 2004, 21, 2543–2546. [Google Scholar]
- Pontes, B.; Viana, N.B.; Salgado, L.T.; Farina, M.; Neto, V.M.; Nussenzveig, H.M. Cell cytoskeleton and tether extraction. Biophys. J 2011, 101, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Titushkin, I.; Cho, M. Distinct membrane mechanical properties of human mesenchymal stem cells determined using laser optical tweezers. Biophys. J 2006, 90, 2582–2591. [Google Scholar]
- Farrell, B.; Qian, F.; Kolomeisky, A.; Anvari, B.; Brownell, W.E. Measuring forces at the leading edge: A force assay for cell motility. Integr. Biol 2013, 5, 204–214. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.D.; Pawson, T. Cell signaling in space and time: Where proteins come together and when they’re apart. Science 2009, 326, 1220–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Komarova, N.L.; Zou, X.; Nie, Q.; Bardwell, L. A theoretical framework for specificity in cell signaling. Mol. Syst. Biol 2005, 1, E1–E5. [Google Scholar]
- Greulich, K.O.; Pilarczyk, G.; Hoffmann, A.; Meyer Zu Hörste, G.; Schäfer, B.; Uhl, V.; Monajembashi, S. Micromanipulation by laser microbeam and optical tweezers: From plant cells to single molecules. J. Microsc 2000, 198, 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- Pidoplichko, V.I.; Dani, J.A. Applying small quantities of multiple compounds to defined locations of in vitro brain slices. J. Neurosci. Methods 2005, 142, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, S.R.; Tsien, R.Y. Controlling cell chemistry with caged compounds. Annu. Rev. Physiol 1993, 55, 755–784. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki, M.; Ellis-Davies, G.C.; Nemoto, T.; Miyashita, Y.; Iino, M.; Kasai, H. Dendritic spine geometry is critical for AMPA receptor expression in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Nat. Neurosci 2001, 4, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar]
- Canepari, M.; Nelson, L.; Papageorgiou, G.; Corrie, J.E.; Ogden, D. Photochemical and pharmacological evaluation of 7-nitroindolinyl-and 4-methoxy-7-nitroindolinyl-amino acids as novel, fast caged neurotransmitters. J. Neurosci. Methods 2001, 112, 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, D.T. Manipulating the biochemical nanoenvironment around single molecules contained within vesicles. Chem. Phys 1999, 247, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Chiu, D.T. Synthesis, loading, and application of individual nanocapsules for probing single-cell signaling. Langmuir 2004, 20, 4614–4620. [Google Scholar]
- Kress, H.; Park, J.-G.; Mejean, C.O.; Forster, J.D.; Park, J.; Walse, S.S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; Weiner, O.D.; Fahmy, T.M.; et al. Cell stimulation with optically manipulated microsources. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 905–909. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, R.H.; Mäder, K.; Gohla, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—A review of the state of the art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm 2000, 50, 161–177. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Chiu, D.T. Spatially and temporally resolved delivery of stimuli to single cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2003, 125, 3702–3703. [Google Scholar]
- Pinato, G.; Cojoc, D.; Lien, L.T.; Ansuini, A.; Ban, J.; D’Este, E.; Torre, V. Less than 5 Netrin-1 molecules initiate attraction but 200 Sema3A molecules are necessary for repulsion. Sci. Rep 2012, 2, 675. [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades, E.; Gussakovsky, E.; Haran, G. Watching proteins fold one molecule at a time. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3197–3202. [Google Scholar]
- Boukobza, E.; Sonnenfeld, A.; Haran, G. Immobilization in surface-tethered lipid vesicles as a new tool for single biomolecule spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 12165–12170. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Chiu, D.T. Determination of the encapsulation efficiency of individual vesicles using single-vesicle photolysis and confocal single-molecule detection. Anal. Chem 2005, 77, 2770–2776. [Google Scholar]
- Okumus, B.; Wilson, T.J.; Lilley, D.M.J.; Ha, T. Vesicle encapsulation studies reveal that Single molecule ribozyme heterogeneities are intrinsic. Biophys. J 2004, 87, 2798–2806. [Google Scholar]
- Gallo, G.; Lefcort, F.B.; Letourneau, P.C. The trkA receptor mediates growth cone turning toward a localized source of nerve growth factor. J. Neurosci 1997, 17, 5445–5454. [Google Scholar]
- D’Este, E.; Baj, G.; Beuzer, P.; Ferrari, E.; Pinato, G.; Tongiorgi, E.; Cojoc, D. Use of optical tweezers technology for long-term, focal stimulation of specific subcellular neuronal compartments. Integr. Biol. (Camb) 2011, 3, 568–577. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino, N.; Vatterott, P.; Egwiekhor, A.; Rochlin, M.W. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor attracts geniculate ganglion neurites during embryonic targeting. Dev. Neurosci 2010, 32, 184–196. [Google Scholar]
- Thoumine, O.; Bard, L.; Saint-Michel, E.; Dequidt, C.; Choquet, D. Optical tweezers and fluorescence recovery after photo-bleaching to measure molecular interactions at the cell surface. Cell. Mol. Bioeng 2008, 1, 301–311. [Google Scholar]
- Meloty-Kapella, L.; Shergill, B.; Kuon, J.; Botvinick, E.; Weinmaster, G. Notch ligand endocytosis generates mechanical pulling force dependent on dynamin, epsins, and actin. Dev. Cell 2012, 22, 1299–1312. [Google Scholar]
- Sieben, C.; Kappel, C.; Zhu, R.; Wozniak, A.; Rankl, C.; Hinterdorfer, P.; Grubmuller, H.; Herrmann, A. Influenza virus binds its host cell using multiple dynamic interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13626–13631. [Google Scholar]
- El-Ali, J.; Sorger, P.K.; Jensen, K.F. Cells on chips. Nature 2006, 442, 403–411. [Google Scholar]
- Weibel, D.B.; DiLuzio, W.R.; Whitesides, G.M. Microfabrication meets microbiology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 2007, 5, 209–218. [Google Scholar]
- Whitesides, G.M. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 2006, 442, 368–373. [Google Scholar]
- Umehara, S.; Wakamoto, Y.; Inoue, I.; Yasuda, K. On-chip single-cell microcultivation assay for monitoring environmental effects on isolated cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2003, 305, 534–540. [Google Scholar]
- Enger, J.; Goksör, M.; Ramser, K.; Hagberg, P.; Hanstorp, D. Optical tweezers applied to a microfluidic system. Lab Chip 2004, 4, 196–200. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson, E.; Sott, K.; Lundqvist, F.; Sveningsson, M.; Scrimgeour, J.; Hanstorp, D.; Goksör, M.; Granéli, A. A microfluidic device for reversible environmental changes around single cells using optical tweezers for cell selection and positioning. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 617–625. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, M.; Merenda, F.; Piguet, J.; Salathé, R.-P.; Vogel, H. Microfluidic array cytometer based on refractive optical tweezers for parallel trapping, imaging and sorting of individual cells. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 2432. [Google Scholar]
- Liberale, C.; Cojoc, G.; Bragheri, F.; Minzioni, P.; Perozziello, G.; La Rocca, R.; Ferrara, L.; Rajamanickam, V.; Di Fabrizio, E.; Cristiani, I. Integrated microfluidic device for single-cell trapping and spectroscopy. Sci. Reports 2013, 3, 1258. [Google Scholar]
- Alrifaiy, A.; Ramser, K. How to integrate a micropipette into a closed microfluidic system: Absorption spectra of an optically trapped erythrocyte. Biomed. Opt. Exp 2011, 2, 2299–2306. [Google Scholar]
- Honarmandi, P.; Lee, H.; Lang, M.J.; Kamm, R.D. A microfluidic system with optical laser tweezers to study mechanotransduction and focal adhesion recruitment. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 684–694. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-H.; Provenzano, P.P.; Smith, C.L.; Levchenko, A. Matrix nanotopography as a regulator of cell function. J. Cell Biol 2012, 197, 351–360. [Google Scholar]
- Goldmann, W.H. Mechanotransduction and focal adhesions. Cell Biol. Int 2012, 36, 649–652. [Google Scholar]
- Noguera, R.; Nieto, O.A.; Tadeo, I.; Fariñas, F.; Alvaro, T. Extracellular matrix, biotensegrity and tumor microenvironment. An update and overview. Histol. Histopathol 2012, 27, 693–705. [Google Scholar]
- Dityatev, A.; Schachner, M. Extracellular matrix molecules and synaptic plasticity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci 2003, 4, 456–468. [Google Scholar]
- Magidson, V.; Lončarek, J.; Hergert, P.; Rieder, C.L.; Khodjakov, A. Laser Microsurgery in the GFP era: A cell biologist’s perspective. Methods Cell Biol. 2007, 82, 237–266. [Google Scholar]
- McDougall, C.; Stevenson, D.J.; Brown, C.T.A.; Gunn-Moore, F.; Dholakia, K. Targeted optical injection of gold nanoparticles into single mammalian cells. J. Biophotonics 2009, 2, 736–743. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, D.; Gunn-Moore, F.; Campbell, P.; Dholakia, K. Transfection by Optical Injection. In Handbook of Photonics for Biomedical Science; Tuchin, V., Ed.; CRC Press, Taylor and Francis group: London, UK, 2010; pp. 87–118. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, L.E.; Sul, J.-Y.; Takano, H.; Van Bockstaele, E.J.; Haydon, P.G.; Eberwine, J.H. Region-directed phototransfection reveals the functional significance of a dendritically synthesized transcription factor. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 455–460. [Google Scholar]
- Hosokawa, Y.; Ochi, H.; Iino, T.; Hiraoka, A.; Tanaka, M. Photoporation of biomolecules into single cells in living vertebrate embryos induced by a femtosecond laser amplifier. PLoS One 2011, 6, e27677. [Google Scholar]
- Berns, M.W.; Cheng, W.K. Are chromosome secondary constrictions nucleolar organizers? A re-examination using a laser microbeam. Exp. Cell Res 1971, 69, 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Khodjakov, A.; Cole, R.W.; Oakley, B.R.; Rieder, C.L. Centrosome-independent mitotic spindle formation in vertebrates. Curr. Biol 2000, 10, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Stiess, M.; Maghelli, N.; Kapitein, L.C.; Gomis-Ruth, S.; Wilsch-Brauninger, M.; Hoogenraad, C.C.; Tolic-Norrelykke, I.M.; Bradke, F. Axon extension occurs independently of centrosomal microtubule nucleation. Science 2010, 327, 704–707. [Google Scholar]
- Steubing, R.W.; Cheng, S.; Wright, W.H.; Numajiri, Y.; Berns, M.W. Laser induced cell fusion in combination with optical tweezers: The laser cell fusion trap. Cytometry 1991, 12, 505–510. [Google Scholar]
- Westphal, G.; Burgemeister, R.; Friedemann, G.; Wellmann, A.; Wernert, N.; Wollscheid, V.; Becker, B.; Vogt, T.; Knüchel, R.; Stolz, W.; et al. Noncontact laser catapulting: A basic procedure for functional genomics and proteomics. Meth. Enzymol 2002, 356, 80–99. [Google Scholar]
- Erez, H.; Spira, M.E. Local self-assembly mechanisms underlie the differential transformation of the proximal and distal cut axonal ends into functional and aberrant growth cones. J. Comp. Neurol 2008, 507, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Moutinho-Pereira, S.; Matos, I.; Maiato, H. Drosophila S2 Cells as a model system to investigate mitotic spindle dynamics, architecture, and function. Methods Cell Biol 2010, 97, 243–257. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.; Mohanty, S.K.; Stephens, J.; Heale, J.T.; Gomez-Godinez, V.; Shi, L.Z.; Kim, J.-S.; Yokomori, K.; Berns, M.W. Comparative analysis of different laser systems to study cellular responses to DNA damage in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2009, 37, e68–e68. [Google Scholar]
- Mone, M.J. Local UV-induced DNA damage in cell nuclei results in local transcription inhibition. EMBO Reports 2001, 2, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, S.P.; Bartek, J. The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature 2009, 461, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Ertürk, A.; Hellal, F.; Enes, J.; Bradke, F. Disorganized microtubules underlie the formation of retraction bulbs and the failure of axonal regeneration. J. Neurosci 2007, 27, 9169–9180. [Google Scholar]
- Usher, L.C.; Johnstone, A.; Ertürk, A.; Hu, Y.; Strikis, D.; Wanner, I.B.; Moorman, S.; Lee, J.-W.; Min, J.; Ha, H.-H.; et al. A chemical screen identifies novel compounds that overcome glial-mediated inhibition of neuronal regeneration. J. Neurosci 2010, 30, 4693–4706. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Karthikeyan, K.; Chirvi, S.; Davé, D.P. Neuro-optical microfluidic platform to study injury and regeneration of single axons. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 2576–2581. [Google Scholar]
- Difato, F.; Dal Maschio, M.; Marconi, E.; Ronzitti, G.; Maccione, A.; Fellin, T.; Berdondini, L.; Chieregatti, E.; Benfenati, F.; Blau, A. Combined optical tweezers and laser dissector for controlled ablation of functional connections in neural networks. J. Biomed. Opt 2011, 16, 051306. [Google Scholar]
- Bonifazi, P.; Difato, F.; Massobrio, P.; Breschi, G.L.; Pasquale, V.; Levi, T.; Goldin, M.; Bornat, Y.; Tedesco, M.; Bisio, M.; et al. In vitro large-scale experimental and theoretical studies for the realization of bi-directional brain-prostheses. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 7, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Yanik, M.F.; Cinar, H.; Cinar, H.N.; Chisholm, A.D.; Jin, Y.; Ben-Yakar, A. Neurosurgery: Functional regeneration after laser axotomy. Nature 2004, 432, 822. [Google Scholar]
- Sacconi, L.; O’Connor, R.P.; Jasaitis, A.; Masi, A.; Buffelli, M.; Pavone, F.S. In vivo multiphoton nanosurgery on cortical neurons. J. Biomed. Opt 2007, 12, 050502. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, N.; Schaffer, C.B.; Friedman, B.; Tsai, P.S.; Lyden, P.D.; Kleinfeld, D. Targeted insult to subsurface cortical blood vessels using ultrashort laser pulses: Three models of stroke. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Bradke, F.; Fawcett, J.W.; Spira, M.E. Assembly of a new growth cone after axotomy: The precursor to axon regeneration. Nat. Rev. Neurosci 2012, 13, 183–193. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, K.C.; Pak, C.W.; Shaw, A.E.; Bradke, F.; Bamburg, J.R. Growth cone-like waves transport actin and promote axonogenesis and neurite branching. Dev. Neurobiol 2009, 69, 761–779. [Google Scholar]
- Vignaud, T.; Galland, R.; Tseng, Q.; Blanchoin, L.; Colombelli, J.; Thery, M. Reprogramming cell shape with laser nano-patterning. J. Cell Sci 2012, 125, 2134–2140. [Google Scholar]
- Heinz, W.F.; Hoh, M.; Hoh, J.H. Laser inactivation protein patterning of cell culture microenvironments. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 3336–3346. [Google Scholar]
- Sarig-Nadir, O.; Livnat, N.; Zajdman, R.; Shoham, S.; Seliktar, D. Laser photoablation of guidance microchannels into hydrogels directs cell growth in three dimensions. Biophys. J 2009, 96, 4743–4752. [Google Scholar]
- Difato, F.; Tsushima, H.; Pesce, M.; Guiggiani, A.; Benfenati, F.; Blau, A.; Basso, M.; Vassalli, M.; Chieregatti, E. Axonal Regeneration of Cultured Mouse Hippocampal Neurons Studied by An Optical Nano-Surgery System. Proceedings of SPIE 8207, Photonic Therapeutics and Diagnostics VIII, 820760, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3 February 2012.
- Torres-Mapa, M.L.; Antkowiak, M.; Cizmarova, H.; Ferrier, D.E.K.; Dholakia, K.; Gunn-Moore, F.J. Integrated holographic system for all-optical manipulation of developing embryos. Biomed. Opt. Exp 2011, 2, 1564–1575. [Google Scholar]





© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Difato, F.; Pinato, G.; Cojoc, D. Cell Signaling Experiments Driven by Optical Manipulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8963-8984. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14058963
Difato F, Pinato G, Cojoc D. Cell Signaling Experiments Driven by Optical Manipulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(5):8963-8984. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14058963
Chicago/Turabian StyleDifato, Francesco, Giulietta Pinato, and Dan Cojoc. 2013. "Cell Signaling Experiments Driven by Optical Manipulation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 5: 8963-8984. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14058963
APA StyleDifato, F., Pinato, G., & Cojoc, D. (2013). Cell Signaling Experiments Driven by Optical Manipulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(5), 8963-8984. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14058963