Ultrasound Targeted Microbubble Destruction Stimulates Cellular Endocytosis in Facilitation of Adeno-Associated Virus Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. UTMD Enhances the Gene Transduction of AAV in a Dose-Dependent Manner
2.2. UTMD Facilitates Viral Entry into the Cytoplasm and Nucleus
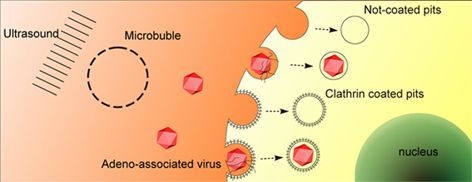
2.3. UTMD Stimulates Cellular Endocytosis
2.4. UTMD-Enhanced Transduction of AAV Partially Depends on Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. UTMD Protocols
4.3. Gene Transduction Efficiency Assays
4.4. Confocal Immunofluorescence Microscopy
4.5. Real-Time PCR
4.6. Cell Fractionation
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.9. Inhibition of Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Hernot, S.; Klibanov, A.L. Microbubbles in ultrasound-triggered drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev 2008, 60, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, R.; Oda, Y.; Utoguchi, N.; Maruyama, K. Progress in the development of ultrasound-mediated gene delivery systems utilizing nano- and microbubbles. J. Control. Release 2011, 149, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, R.; Takizawa, T.; Negishi, Y.; Utoguchi, N.; Maruyama, K. Effective gene delivery with novel liposomal bubbles and ultrasonic destruction technology. Int. J. Pharm 2008, 354, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana, K.; Uchida, T.; Ogawa, K.; Yamashita, N.; Tamura, K. Induction of cell-membrane porosity by ultrasound. Lancet 1999, 353, 1409. [Google Scholar]
- Taniyama, Y. Local delivery of plasmid DNA into rat carotid artery using ultrasound. Circulation 2002, 105, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wamel, A.; Kooiman, K.; Harteveld, M.; Emmer, M.; ten Cate, F.J.; Versluis, M.; de Jong, N. Vibrating microbubbles poking individual cells: Drug transfer into cells via sonoporation. J. Control. Release 2006, 112, 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- Mehier-Humbert, S.; Bettinger, T.; Yan, F.; Guy, R.H. Plasma membrane poration induced by ultrasound exposure: Implication for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2005, 104, 213–222. [Google Scholar]
- Brayman, A.A.; Coppage, M.L.; Vaidya, S.; Miller, M.W. Transient poration and cell surface receptor removal from human lymphocytes in vitro by 1 MHz ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol 1999, 25, 999–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Taniyama, Y.; Tachibana, K.; Hiraoka, K.; Aoki, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Nakamura, T.; Ogihara, T.; Kaneda, Y.; Morishita, R. Development of safe and efficient novel nonviral gene transfer using ultrasound: Enhancement of transfection efficiency of naked plasmid DNA in skeletal muscle. Gene Ther 2002, 9, 372–380. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S. Efficient gene delivery to pancreatic islets with ultrasonic microbubble destruction technology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8469–8474. [Google Scholar]
- Meijering, B.D.M.; Henning, R.H.; van Gilst, W.H.; Gavrilović, I.; van Wamel, A.; Deelman, L.E. Optimization of ultrasound and microbubbles targeted gene delivery to cultured primary endothelial cells. J. Drug Target 2007, 15, 664–671. [Google Scholar]
- Geers, B.; Lentacker, I.; Alonso, A.; Sanders, N.N.; Demeester, J.; Meairs, S.; de Smedt, S.C. Elucidating the mechanisms behind sonoporation with adeno-associated virus-loaded microbubbles. Mol. Pharm 2011, 8, 2244–2251. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.L.; Zheng, X.Z.; Wang, H.P.; Li, F.; Wu, Y.; Du, L.F. Ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction enhances AAV-mediated gene transfection in human RPE cells in vitro and rat retina in vivo. Gene Ther 2009, 16, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Du, L.; Wang, H.; Gu, Q. A novel approach to attenuate proliferative vitreoretinopathy using ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction and recombinant adeno-associated virus-mediated RNA interference targeting transforming growth factor-β2 and platelet-derived growth factor-B. J. Gene Med 2012, 14, 339–347. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, B.R.; Chamberlain, J.S. Recombinant adeno-associated virus transduction and integration. Mol. Ther 2008, 16, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar]
- Sonntag, F.; Bleker, S.; Leuchs, B.; Fischer, R.; Kleinschmidt, J.A. Adeno-Associated virus type 2 capsids with externalized VP1/VP2 trafficking domains are generated prior to passage through the cytoplasm and are maintained until uncoating occurs in the nucleus. J. Virol 2006, 80, 11040–11054. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Yan, Z.; Luo, M.; Zak, R.; Li, Z.; Driskell, R.R.; Huang, Y.; Tran, N.; Engelhardt, J.F. Targeted Correction of single-base-pair mutations with adeno-associated virus vectors under nonselective conditions. J. Virol 2004, 78, 4165–4175. [Google Scholar]
- Duvshani-Eshet, M.; Machluf, M. Therapeutic ultrasound optimization for gene delivery: A key factor achieving nuclear DNA localization. J. Control. Release 2005, 108, 513–528. [Google Scholar]
- Duvshani-Eshet, M.; Baruch, L.; Kesselman, E.; Shimoni, E.; Machluf, M. Therapeutic ultrasound-mediated DNA to cell and nucleus: bioeffects revealed by confocal and atomic force microscopy. Gene Ther 2005, 13, 163–172. [Google Scholar]
- Juffermans, L.J.M.; Kamp, O.; Dijkmans, P.A.; Visser, C.A.; Musters, R.J.P. Low-Intensity ultrasound-exposed microbubbles provoke local hyperpolarization of the cell membrane via activation of BKCa channels. Ultrasound Med. Biol 2008, 34, 502–508. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, P.E. Calcium increases endocytotic vesicle size and accelerates membrane fission in insulin-secreting INS-1 cells. J. Cell Sci 2005, 118, 5911–5920. [Google Scholar]
- Saliez, J.; Bouzin, C.; Rath, G.; Ghisdal, P.; Desjardins, F.; Rezzani, R.; Rodella, L.F.; Vriens, J.; Nilius, B.; Feron, O.; et al. Role of caveolar compartmentation in endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor-mediated relaxation: Ca2+ signals and gap junction function are regulated by caveolin in endothelial cells. Circulation 2008, 117, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Meijering, B.D.M.; Juffermans, L.J.M.; van Wamel, A.; Henning, R.H.; Zuhorn, I.S.; Emmer, M.; Versteilen, A.M.G.; Paulus, W.J.; van Gilst, W.H.; Kooiman, K.; et al. Ultrasound and microbubble-targeted delivery of macromolecules is regulated by induction of endocytosis and pore formation. Circ. Res 2009, 104, 679–687. [Google Scholar]
- Hauser, J.; Ellisman, M.; Steinau, H.-U.; Stefan, E.; Dudda, M.; Hauser, M. Ultrasound enhanced endocytotic activity of human fibroblasts. Ultrasound Med. Biol 2009, 35, 2084–2092. [Google Scholar]
- Lionetti, V.; Fittipaldi, A.; Agostini, S.; Giacca, M.; Recchia, F.A.; Picano, E. Enhanced caveolae-mediated endocytosis by diagnostic ultrasound in vitro. Ultrasound Med. Biol 2009, 35, 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Seisenberger, G. Real-Time single-molecule imaging of the infection pathway of an adeno-associated virus. Science 2001, 294, 1929–1932. [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett, J.S.; Wilcher, R.; Samulski, R.J. Infectious entry pathway of adeno-associated virus and adeno-associated virus vectors. J. Virol 2000, 74, 2777–2785. [Google Scholar]
- Bantel-Schaal, U.; Hub, B.; Kartenbeck, J. Endocytosis of adeno-associated virus type 5 leads to accumulation of virus particles in the golgi compartment. J. Virol 2002, 76, 2340–2349. [Google Scholar]
- Nonnenmacher, M.; Weber, T. Adeno-Associated virus 2 infection requires endocytosis through the CLIC/GEEC pathway. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 10, 563–576. [Google Scholar]
- Uhrig, S.; Coutelle, O.; Wiehe, T.; Perabo, L.; Hallek, M.; Buning, H. Successful target cell transduction of capsid-engineered rAAV vectors requires clathrin-dependent endocytosis. Gene Ther 2012, 19, 210–218. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.; Warrington, K.H.; Hearing, P.; Hughes, J.; Muzyczka, N. Adenovirus-Facilitated nuclear translocation of adeno-associated virus type 2. J. Virol 2002, 76, 11505–11517. [Google Scholar]
- Lux, K.; Goerlitz, N.; Schlemminger, S.; Perabo, L.; Goldnau, D.; Endell, J.; Leike, K.; Kofler, D.M.; Finke, S.; Hallek, M.; et al. Green fluorescent protein-tagged adeno-associated virus particles allow the study of cytosolic and nuclear trafficking. J. Virol 2005, 79, 11776–11787. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.S.; Samulski, R.J. Enhancement of adeno-associated virus infection by mobilizing capsids into and out of the nucleolus. J. Virol 2008, 83, 2632–2644. [Google Scholar]
- Yumoto, R.; Suzuka, S.; Oda, K.; Nagai, J.; Takano, M. Endocytic uptake of FITC-Albumin by human alveolar epithelial cell line A549. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet 2012, 27, 336–343. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.H.; Rothberg, K.G.; Anderson, R.G. Mis-assembly of clathrin lattices on endosomes reveals a regulatory switch for coated pit formation. J. Cell Biol 1993, 123, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar]
- Blitzer, J.T.; Nusse, R. A critical role for endocytosis in Wnt signaling. BMC Cell. Biol 2006, 7, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Bantel-Schaal, U.; Braspenning-Wesch, I.; Kartenbeck, J. Adeno-associated virus type 5 exploits two different entry pathways in human embryo fibroblasts. J. Gen. Virol 2009, 90, 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, P.J.; Samulski, R.J. Cytoplasmic trafficking, endosomal escape, and perinuclear accumulation of adeno-associated virus Type 2 particles are facilitated by microtubule network. J. Virol 2012, 86, 10462–10473. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, J. Infection of purified nuclei by adeno-associated virus 2. Mol. Ther 2001, 4, 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, J.; Qing, K.; Srivastava, A. Adeno-Associated virus type 2-mediated gene transfer: Altered endocytic processing enhances transduction efficiency in murine fibroblasts. J. Virol 2001, 75, 4080–4090. [Google Scholar]





© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, L.-F.; Li, F.; Wang, H.-P.; Wei, F.; Qin, P.; Du, L.-F. Ultrasound Targeted Microbubble Destruction Stimulates Cellular Endocytosis in Facilitation of Adeno-Associated Virus Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9737-9750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059737
Jin L-F, Li F, Wang H-P, Wei F, Qin P, Du L-F. Ultrasound Targeted Microbubble Destruction Stimulates Cellular Endocytosis in Facilitation of Adeno-Associated Virus Delivery. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(5):9737-9750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059737
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Li-Fang, Fan Li, Hui-Ping Wang, Fang Wei, Peng Qin, and Lian-Fang Du. 2013. "Ultrasound Targeted Microbubble Destruction Stimulates Cellular Endocytosis in Facilitation of Adeno-Associated Virus Delivery" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 5: 9737-9750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059737
APA StyleJin, L. -F., Li, F., Wang, H. -P., Wei, F., Qin, P., & Du, L. -F. (2013). Ultrasound Targeted Microbubble Destruction Stimulates Cellular Endocytosis in Facilitation of Adeno-Associated Virus Delivery. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(5), 9737-9750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059737