Plant Dependence on Rhizobia for Nitrogen Influences Induced Plant Defenses and Herbivore Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effects of Nitrogen Source on Plant Characteristics
2.2. Soybean-Rhizobia Interactions with a Chewing Herbivore
2.2.1. Growth Rate and Preference Tests
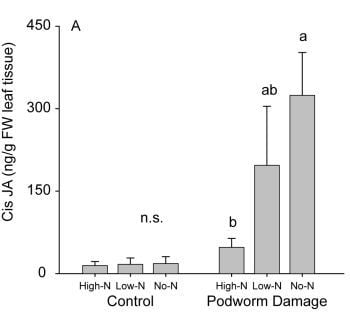
2.2.2. Induced Hormone Accumulation
2.3. Soybean-Rhizobia Interactions with a Phloem-Feeding Herbivore
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Plant Growth
3.2. Insects
3.3. Plant Assessments
3.4. Herbivory by Soybean Podworm
3.5. Herbivory by Soybean Aphid
3.6. Phytohormone Analyses
3.7. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bennett, A.; Bever, J.D. Mycorrhizal species differentially alter plant growth and response to herbivory. Ecology 2007, 88, 210–218. [Google Scholar]
- Brockwell, J.; Bottomley, P.; Thies, J. Manipulation of rhizobia microflora for improving legume productivity and soil fertility-A critical-assessment. Plant Soil 1995, 174, 143–180. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, J.; Mescher, M.C.; de Moraes, C.M. Plant-rhizobia mutualism influences aphid abundance on soybean. Plant Soil 2009, 323, 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffries, P.; Gianinazzi, S.; Perotto, S.; Turnau, K.; Barea, J. The contribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in sustainable maintenance of plant health and soil fertility. Biol. Fert. Soils 2003, 37, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Laguerre, G.; Depret, G.; Bourion, V.; Duc, G. Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae genotypes interact with pea plants in developmental responses of nodules, roots and shoots. N. Phytol 2007, 176, 680–690. [Google Scholar]
- Borowicz, V.A. A fungal root symbiont modifies plant resistance to an insect herbivore. Oecologia 1997, 112, 534–542. [Google Scholar]
- Gange, A.C.; West, H.M. Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and foliar-feeding insects in Plantago lanceolata L. N. Phytol 1994, 128, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Goverde, M.; van der Heijden, M.; Wiemken, A.; Sanders, I.; Erhardt, A. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi influence life history traits of a lepidopteran herbivore. Oecologia 2000, 125, 362–369. [Google Scholar]
- Pozo, M.; Azcón-Aguilar, C. Unraveling mycorrhiza-induced resistance. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol 2007, 10, 393–398. [Google Scholar]
- Kempel, A.; Brandl, R.; Schadler, M. Symbiotic soil microorganisms as players in aboveground plant-herbivore interactions—The role of rhizobia. Oikos 2009, 4, 634–640. [Google Scholar]
- Thamer, S.; Schädler, M.; Bonte, D.; Ballhorn, D.J. Dual benefit from a belowground symbiosis: nitrogen fixing rhizobia promote growth and defense against a specialist herbivore in a cyanogenic plant. Plant Soil 2010, 341, 209–219. [Google Scholar]
- Katayama, N.; Nishida, T.; Zhang, Z.; Ohgushi, T. Belowground microbial symbiont enhances plant susceptibility to a spider mite through change in soybean leaf quality. Popul. Ecol 2010, 52, 499–506. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.; Hirsch, A.M. Choreographing the complex interaction between legumes and a- and b-rhizobia. Plant Signal. Behav 2006, 1, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Zamioudis, C.; Pieterse, C.M.J. Modulation of host immunity by beneficial microbes. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact 2012, 25, 139–150. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Wilkerson, C.; Kuchar, J.; Phinney, B.; Howe, G. Jasmonate-inducible plant enzymes degrade essential amino acids in the herbivore midgut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 19237–19242. [Google Scholar]
- Farmer, E.; Johnson, R.; Ryan, C. Regulation of expression of proteinase-inhibitor genes by methyl jasmonate and jasmonic acid. Plant Physiol 1992, 98, 995–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Schmelz, E.A.; Alborn, H.T.; Banchio, E.; Tumlinson, J.H. Quantitative relationships between induced jasmonic acid levels and volatile emission in Zea mays during Spodoptera exigua herbivory. Planta 2003, 216, 665–673. [Google Scholar]
- Thaler, J.S.; Farag, M.A.; Pare, P.W.; Dicke, M. Jasmonate-deficient plants have reduced direct and indirect defences against herbivores. Ecol. Lett. Ecol. Lett 2002, 5, 764–774. [Google Scholar]
- Métraux, J.P.; Signer, H.; Ryals, J.; Ward, E.; Wyss-Benz, M.; Gaudin, J.; Raschdorf, K.; Schmid, E.; Blum, W.; Inverardi, B. Increase in salicylic acid at the onset of systemic acquired resistance in cucumber. Science 1990, 250, 1004–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wees, S.C.M.; Glazebrook, J. Loss of non-host resistance of Arabidopsis NahG to Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola is due to degradation products of salicylic acid. Plant J 2003, 33, 733–742. [Google Scholar]
- Horváth, E.; Szalai, G.; Janda, T. Induction of abiotic stress tolerance by salicylic acid signaling. J. Plant Growth Regul 2007, 26, 290–300. [Google Scholar]
- Walling, L.L. The myriad plant responses to herbivores. J. Plant Growth Regul 2000, 19, 195–216. [Google Scholar]
- Runyon, J.B.; Mescher, M.C.; de Moraes, C.M. Parasitism by Cuscuta pentagona attenuates host plant defenses against insect herbivores. Plant Physiol 2008, 146, 987–995. [Google Scholar]
- Felton, G.W.; Korth, K.L.; Bi, J.L.; Wesley, S.V.; Huhman, D.V.; Mathews, M.C.; Murphy, J.B.; Lamb, C.; Dixon, R.A. Inverse relationship between systemic resistance of plants to microorganisms and to insect herbivory. Curr. Biol 1999, 9, 317–320. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.; Boyko, E. The molecular bases of plant resistance and defense responses to aphid feeding: Current status. Entomol. Exp. Appl 2007, 122, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Thaler, J.S.; Karban, R.; Ullman, D.E.; Boege, K.; Bostock, R.M. Cross-talk between jasmonate and salicylate plant defense pathways: Effects on several plant parasites. Oecologia 2002, 131, 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan, B.B.; Gruissem, W.; Jones, R.L. Biochemistry & Molecular Biology of Plants; American Society of Plant Physiologists: Rockville, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Allos, H.F.; Bartholomew, W.V. Replacement of symbiotic fixation by available nitrogen. Soil Sci 1959, 87, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, T.; Yatazawa, M.; Yamamoto, Y. Effects of exogenous nitrogen compounds on concentrations of allantoin and various constituents in several organs of soybean plants. Plant Cell Physiol 1977, 18, 613–624. [Google Scholar]
- McClure, P.R.; Israel, D.W. Transport of nitrogen in the xylem of soybean plants. Plant Physiol 1979, 64, 411–416. [Google Scholar]
- Cockfield, S. Relative availability of nitrogen in host plants of invertebrate herbivores-3 possible nutritional and physiological definitions. Oecologia 1988, 77, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Felton, G. Nutritive quality of plant protein: Sources of variation and insect herbivore responses. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol 1996, 32, 107–130. [Google Scholar]
- Mattson, W.J. Herbivory in relation to plant nitrogen content. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst 1980, 11, 119–161. [Google Scholar]
- Schoonhoven, L.M.; van Loon, J.J.A.; Dicke, M. Insect-Plant Biology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, K.G.; Stinner, R.E. A potential influence of rhizobium activity on the availability of nitrogen to legume herbivores. Oecologia 1984, 61, 337–341. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.; Tripathi, S.; Negi, P. Yield and nitrogen content of nonnodulating soybean grown in association with nodulating lines. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. B 1974, 40, 507–511. [Google Scholar]
- Barbulova, A.; Rogato, A.; D’Apuzzo, E.; Omrane, S.; Chiurazzi, M. Differential effects of combined n sources on early steps of the nod factor-dependent transduction pathway in Lotus japonicus. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact 2007, 20, 994–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Bisseling, T.; Vandenbos, R.; Vankammen, A. Effect of ammonium-nitrate on synthesis of nitrogenase and concentration of leghemoglobin in pea root-nodules induced by Rhizobium leguminosarum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1978, 539, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, K. Products of biological nitrogen fixation in higher plants: Synthesis, transport, and metabolism. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol 1986, 37, 539–537. [Google Scholar]
- Howe, G.; Jander, G. Plant immunity to insect herbivores. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol 2008, 59, 41–66. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, J.; Felton, G.; Mueller, A. Induced resistance in soybean to Helicoverpa zea—Role of plant protein-quality. J. Chem. Ecol 1994, 20, 183–198. [Google Scholar]
- Van Loon, L.; Bakker, P.; Pieterse, C. Systemic resistance induced by rhizosphere bacteria. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol 1998, 36, 453–483. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wees, S.C.M.; van der Ent, S.; Pieterse, C.M.J. Plant immune responses triggered by beneficial microbes. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol 2008, 11, 443–448. [Google Scholar]
- Conrath, U.; Beckers, G.J.M.; Flors, V.; Garcia-Agustin, P.; Jakab, G.; Mauch, F.; Newman, M.-A.; Pieterse, C.M.J.; Poinssot, B.; Pozo, M.J.; et al. Priming: Getting ready for battle. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact 2006, 19, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, C.J.; Appel, H.M.; Carlson, J.E.; de Moraes, C.M.; Mescher, M.C.; Schultz, J.C. Within-plant signalling via volatiles overcomes vascular constraints on systemic signalling and primes responses against herbivores. Ecol. Lett 2007, 10, 490–498. [Google Scholar]
- Van Oosten, V.; Bodenhausen, N.; Reymond, P.; van Pelt, J.; van Loon, L.; Dicke, M. Differential effectiveness of microbially induced resistance against herbivorous insects in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact 2008, 21, 919–930. [Google Scholar]
- Pineda, A.; Zheng, S.-J.; van Loon, J.J.A.; Dicke, M. Rhizobacteria modify plant-aphid interactions: a case of induced systemic susceptibility. Plant Biol 2012, 14, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, S.; Simpson, C. The mechanisms of nutritional compensation by phyotphabous insects. In Insect-Plant Interactions; Bernays, E., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990; pp. 111–160. [Google Scholar]
- Todd, C.; Tipton, P.; Blevins, D.; Piedras, P.; Pineda, M.; Polacco, J. Update on ureide degradation in legumes. J. Exp. Bot 2005, 57, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Pate, J.; Peoples, M.; Atkins, C. Spontaneous phloem bleeding from cryopunctured fruits of a ureide-producing legume. Plant Physiol 1984, 74, 499–505. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, C.; Li, Y.; Hartman, G. Resistance to the soybean aphid in soybean germplasm. Crop Sci 2004, 44, 98–106. [Google Scholar]
- Young, E.; Conway, C. On the estimation of Aln by the Rimini-Schryver reaction. J. Biol. Chem 1942, 142, 839–853. [Google Scholar]
- Farrar, R.; Barbour, J.; Kennedy, G. Quantifying food-consumption and growth in insects. Annu. Entomol. Soc. Am 1989, 82, 593–598. [Google Scholar]
- Schmelz, E.A.; Engelberth, J.; Tumlinson, J.H.; Block, A.; Alborn, H.T. The use of vapor phase extraction in metabolic profiling of phytohormones and other metabolites. Plant J 2004, 39, 790–808. [Google Scholar]
- Tooker, J.; de Moraes, C.M. Jasmonate, salicylate, and benzoate in insect eggs. J. Chem. Ecol 2007, 33, 331–343. [Google Scholar]





© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Dean, J.M.; Mescher, M.C.; De Moraes, C.M. Plant Dependence on Rhizobia for Nitrogen Influences Induced Plant Defenses and Herbivore Performance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 1466-1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15011466
Dean JM, Mescher MC, De Moraes CM. Plant Dependence on Rhizobia for Nitrogen Influences Induced Plant Defenses and Herbivore Performance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(1):1466-1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15011466
Chicago/Turabian StyleDean, Jennifer M., Mark C. Mescher, and Consuelo M. De Moraes. 2014. "Plant Dependence on Rhizobia for Nitrogen Influences Induced Plant Defenses and Herbivore Performance" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 1: 1466-1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15011466
APA StyleDean, J. M., Mescher, M. C., & De Moraes, C. M. (2014). Plant Dependence on Rhizobia for Nitrogen Influences Induced Plant Defenses and Herbivore Performance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(1), 1466-1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15011466