The Discovery of Aurora Kinase Inhibitor by Multi-Docking-Based Virtual Screening
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The Selection of Compounds

| Fragments | Dock Score | No. of Non-Hydrogen Atoms of the Fragments | Ligand Efficiency (LE) b | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2NP8 a | 2X6D | 3FDN | 3MYG | 3P9J | |||
| 1 | − c | − | 48.05 | − | − | 15 | 3.20 |
| 2 | − | 40.70 | − | − | 33.82 | 24 | 1.55 |
| 3 | 31.00 | 35.70 | 33.85 | 34.41 | 37.35 | 25 | 1.38 |
| 4 | 50.33 | − | 46.34 | 51.84 | 55.99 | 20 | 2.56 |
| 5 | − | − | 31.55 | − | 31.42 | 15 | 2.10 |
| 6 | − | − | − | − | 32.59 | 18 | 1.81 |
| 7 | 53.69 | − | 48.64 | 54.98 | 53.74 | 21 | 2.51 |
| 8 | − | − | 28.83 | − | 27.84 | 15 | 1.89 |
| 9 | − | − | − | − | 28.95 | 16 | 1.81 |
| 10 | − | − | 35.45 | 3.76 | 10.23 | 19 | 0.87 |
| 11 | 51.44 | − | 44.62 | 36.03 | 30.65 | 21 | 1.94 |
| 12 | − | − | − | − | 62.06 | 15 | 4.14 |
| 13 | − | − | 13.95 | − | 24.95 | 17 | 1.14 |
| 14 | 15.59 | 57.47 | 37.42 | 15.34 | 49.61 | 23 | 1.53 |
| 15 | 55.56 | 54.99 | 55.43 | 57.07 | 55.17 | 22 | 2.53 |
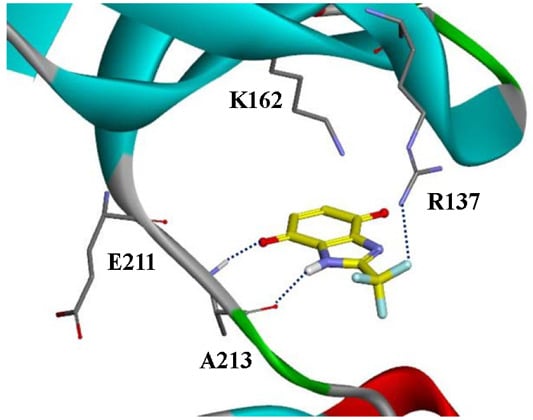
2.2. The Biological Evaluation and Optimization
| Fragments | Structure | % Inhibition a | Fragment | Structure | % Inhibition a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | 75 ± 1 | 9 |  | 8 ± 10 |
| 2 |  | 13 ± 12 | 10 |  | – |
| 3 |  | 56 ± 6 | 11 |  | 25 ± 2 |
| 4 |  | 28 ± 1 | 12 |  | 93 ± 2 |
| 5 |  | 31 ± 6 | 13 |  | 61 ± 2 |
| 6 |  | 19 ± 2 | 14 |  | 39 ± 3 |
| 7 |  | 35 ± 3 | 15 |  | 2 ± 15 |
| 8 |  | 24 ± 4 | |||
| Compounds | Structure | ACD/logp a | Dock Score | IC50 (μM) c | % Inhibition d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3P9J b | Aurora-A (h) | Aurora-B (h) | Aurora-C (h) | ||||
| 16 |  | 3.41 | 72.26 | 9.17 | 52 | 84 ± 1 | 8 ± 8 |
| 17 |  | 3.56 | 75.05 | 7.47 | 65 | 76 ± 1 | 17 ± 4 |
| [17] | Staurosporine | 4.4 | 81.53 | 0.08 (0.1) e | 100 | – | – |

3. Experimental Section
3.1. The Filtering Process
3.2. Docking Study
3.3. Biological Assay
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heron, N.M.; Anderson, M.; Blowers, D.P.; Breed, J.; Eden, J.M.; Green, S.; Hill, G.B.; Jognson, T.; Jung, F.H.; Mcmiken, H.H.J.; et al. SAR and inhibitor complex structure determination of a novel class of potent and specific aurora kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 1320–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.J.; Gadhwal, M.K.; Joshi, U.J. A combined approach based on 3D pharmacophore and docking for identification of new aurora-A kinase inhibitors. Med. Chem. Res. 2014, 23, 1414–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coumar, M.S.; Leou, J.S.; Shukla, P.; Wu, J.S.; Dixit, A.K.; Lin, W.H.; Chang, C.Y.; Lien, T.W.; Tan, U.K.; Chen, C.H.; et al. Structure-based drug design of novel aurora kinase A inhibitors: Structural basis for potency and specificity. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Midgley, C.A.; Scaërou, F.; Grabarek, J.B.; Griffiths, G.; Jackson, W.; Kontopidis, G.; McClue, S.J.; McInnes, C.; Meades, C.; et al. Discovery of N-phenyl-4-(thiazol-5-yl) pyrimidin-2-amine aurora kinase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4367–4378. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Deng, Y.Q.; Wang, J.; Long, Z.J.; Tu, Z.C.; Peng, W.; Zang, J.Q.; Liu, Q.; Lu, Gui. Design, synthesis and bioevaluation of N-trisubstituted pyrimidine derivatives as potent aurora-A kinase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 78, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Chae, C.H.; Kang, S.M.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, G.N.; Hwang, S.H.; Kang, N.S. The predictive QSAR model for hERG inhibitors using Bayesian and random forest classification method. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, 32, 1237–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, D.B.; Decornez, H.; Furr, J.R.; Bajorath, J. Docking and scoring in virtual screening for drug discovery: Methods and applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RCSB Protein Data Bank. Available online: http://www.rcsb.org (accessed on 1 January 2014).
- Yu, T.; Tagat, J.R.; Kerekes, A.D.; Doll, R.J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Esposite, S.; Belanger, D.B.; Curran, P.J.; Mandal, A.K.; et al. Discovery of a potent and injectable inhibitor of aurora kinases A and B based on the imidazo-[1,2-a]-pyrazine core. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavetsias, V.; Large, J.M.; Sun, C.; Bouloc, N.; Kosmopoulou, M.; Matteucci, M.; Wilsher, N.E.; Martins, V.; Reynisson, J.; Atrash, B.; et al. Imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine derivatives as inhibitors of aurora kinases: Lead optimization studies toward the identification of an orally bioavailable preclinical development candidate. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5213–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.C.; Wright, D.L. The design and docking of virtual compound libraries to structures of drug targets. Curr. Comput.-Aided Drug Des. 2005, 1, 103–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.D.; Mancera, R.L. Expanded interaction fingerprint method for analyzing ligand binding modes in docking and structure-based drug design. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2004, 44, 1942–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, J.H.; Elkin, C.; Madison, V.S.; Duca, J.S. Cross-docking of inhibitors into CDK2 structures. 2. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2008, 48, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatachalam, C.M.; Jiang, X.; Oldfield, T.; Waldman, M. LigandFit: A novel method for the shape-directed rapid docking of ligands to protein active sites. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2003, 21, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prime, M.E.; Courtney, S.M.; Brookfield, F.A.; Marston, R.W.; Walker, V.; Warne, J.; Boyd, A.E.; Kairies, N.A.; von der Saal, W.; Limberg, A.; et al. Phthalazinone pyrazoles as potent, selective, and orally bioavailable inhibitors of aurora-A kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.L.; Groom, C.R.; Alex, A. Ligand efficiency: A useful metric for lead selection. Drug Discovery Today 2004, 9, 430–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaman, M.W.; Herrgard, S.; Treiber, D.K.; Gallant, P.; Atteridge, C.E.; Campbell, B.T.; Chan, K.W.; Ciceri, P.; Davis, M.I.; Edeen, P.T.; et al. A quantitative analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rye, C.K.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, S.G.; You, H.J.; Lee, R.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, S. 3D-QSAR studies of heterocyclic quinones with inhibitory activity on vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation using pharmacophore-based alignment. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 9772–9779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khmel’nitskaya, E.Y.; Grigoriev, N.B.; Lyubchanskaya, V.M.; Mukhanova, T.I.; Granik, V.G. Investigation of the oxidation-reduction characteristics of heterocyclic quinones. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2004, 40, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- eMolecules. Available online: http://www.emolecules.com/ (accessed on 1 January 2014).
- Brooks, B.R.; Bruccoleri, R.E.; Olafson, B.D.; States, D.J.; Swaminathan, S.; Karplus, M. CHARMM: A program for macromolecular energy, minmimization, and dynamics calculations. J. Comp. Chem. 1983, 4, 187–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, A.; Kirchhoff, P.D.; Jiang, X.; Venkatachalam, C.M.; Waldman, M. LigScore: A novel scoring function for predicting binding affinities. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2005, 23, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehlhaar, D.K.; Verkhivker, G.M.; Rejto, P.A.; Sherman, C.J.; Fogel, D.B.; Fogel, L.J.; Freer, S.T. Molecular recognition of the inhibitor AG-1343 by HIV-1 protease: Conformationally flexible docking by evolutionary programming. Chem. Biol. 1995, 2, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.N. Scoring non covalent protein-ligand interactions: A continuous differentiable function tuned to compute binding affinities. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 1996, 10, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muegge, I. PMF scoring revisited. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 5895–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, H.J. Prediction of binding constants of protein ligands: A fast method for the prioritization of hits obtained from the de novo design or 3D database search programs. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 1998, 12, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-T.; Jung, S.H.; Kang, S.Y.; Ryu, C.-K.; Kang, N.S. The Discovery of Aurora Kinase Inhibitor by Multi-Docking-Based Virtual Screening. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 20403-20412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151120403
Kim J-T, Jung SH, Kang SY, Ryu C-K, Kang NS. The Discovery of Aurora Kinase Inhibitor by Multi-Docking-Based Virtual Screening. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(11):20403-20412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151120403
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jun-Tae, Seo Hee Jung, Sun Young Kang, Chung-Kyu Ryu, and Nam Sook Kang. 2014. "The Discovery of Aurora Kinase Inhibitor by Multi-Docking-Based Virtual Screening" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 11: 20403-20412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151120403
APA StyleKim, J. -T., Jung, S. H., Kang, S. Y., Ryu, C. -K., & Kang, N. S. (2014). The Discovery of Aurora Kinase Inhibitor by Multi-Docking-Based Virtual Screening. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(11), 20403-20412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151120403