LRP-1: Functions, Signaling and Implications in Kidney and Other Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL)-Related Protein-1 (LRP-1) Signaling in Kidneys

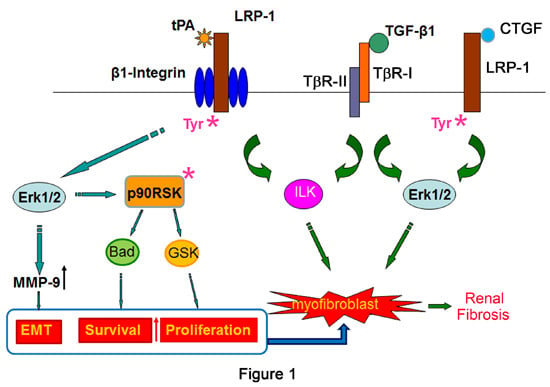
2.1. Tissue Plasminogen Activator (tPA)/LRP-1 Signaling
2.2. Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF)/LRP-1 Signaling
3. LRP-1 Signaling in Nervous System
3.1. LRP-1 and Central Nervous System
3.2. LRP-1 and Peripheral Nervous System
4. LRP-1 Signaling in Cardiovascular Disease
4.1. LRP-1 Signaling in Macrophages
4.2. LRP-1 Signaling in Muscle Cells
4.3. LRP-1 Signaling in Fibroblasts
5. LRP-1 Signaling in Cancer
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herz, J.; Strickland, D.K. LRP: A multifunctional scavenger and signaling receptor. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillis, A.P.; van Duyn, L.B.; Murphy-Ullrich, J.E.; Strickland, D.K. LDL receptor-related protein 1: Unique tissue-specific functions revealed by selective gene knockout studies. Physiol Rev. 2008, 88, 887–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, G.; Williams, S.; Strickland, D.K.; Schwartz, A.L. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein/α2-macroglobulin receptor is an hepatic receptor for tissue-type plasminogen activator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 7427–7431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herz, J.; Hamann, U.; Rogne, S.; Myklebost, O.; Gausepohl, H.; Stanley, K.K. Surface location and high affinity for calcium of a 500-kd liver membrane protein closely related to the LDL-receptor suggest a physiological role as lipoprotein receptor. EMBO J. 1988, 7, 4119–4127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Strickland, D.K.; Ashcom, J.D.; Williams, S.; Burgess, W.H.; Migliorini, M.; Argraves, W.S. Sequence identity between the α2-macroglobulin receptor and low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein suggests that this molecule is a multifunctional receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 17401–17404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, T.; Moestrup, S.K.; Gliemann, J.; Bendtsen, L.; Sand, O.; Sottrup-Jensen, L. Evidence that the newly cloned low-density-lipoprotein receptor related protein (LRP) is the α2-macroglobulin receptor. FEBS Lett. 1990, 276, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.S.; Ling, T.Y.; Tseng, W.F.; Huang, Y.H.; Tang, F.M.; Leal, S.M.; Huang, J.S. Cellular growth inhibition by IGFBP-3 and TGF-β1 requires LRP-1. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 2068–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, P.; Herz, J. Signaling through LRP1: Protection from atherosclerosis and beyond. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 81, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickland, D.K.; Ranganathan, S. Diverse role of LDL receptor-related protein in the clearance of proteases and in signaling. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 1, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonias, S.L.; Campana, W.M. LDL receptor-related protein-1: A regulator of inflammation in atherosclerosis, cancer, and injury to the nervous system. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herz, J.; Kowal, R.C.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. Proteolytic processing of the 600 kd low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) occurs in a trans-Golgi compartment. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 1769–1776. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.M. Structural, biochemical and signaling properties of the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene family. Front. Biosci. 2001, 6, D417–D428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Bu, G.; Mars, W.M.; Reeves, W.B.; Tanaka, S.; Hu, K. tPA activates LDL receptor-related protein 1-mediated mitogenic signaling involving the p90RSK and GSK3β pathway. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Yang, J.; Tanaka, S.; Gonias, S.L.; Mars, W.M.; Liu, Y. Tissue-type plasminogen activator acts as a cytokine that triggers intracellular signal transduction and induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 2120–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hance, M.W.; Dole, K.; Gopal, U.; Bohonowych, J.E.; Jezierska-Drutel, A.; Neumann, C.A.; Liu, H.; Garraway, I.P.; Isaacs, J.S. Secreted Hsp90 is a novel regulator of the epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in prostate cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 37732–37744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkawi, S.; Nassar, T.; Tarshis, M.; Cines, D.B.; Higazi, A.A. LRP and αvβ3 mediate tPA activation of smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 291, H1351–H1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Lawrence, D.A.; Li, Y.; von Arnim, C.A.; Herz, J.; Su, E.J.; Makarova, A.; Hyman, B.T.; Strickland, D.K.; Zhang, L. Endocytic receptor LRP together with tPA and PAI-1 coordinates Mac-1-dependent macrophage migration. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 1860–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopal, U.; Bohonowych, J.E.; Lema-Tome, C.; Liu, A.; Garrett-Mayer, E.; Wang, B.; Isaacs, J.S. A novel extracellular Hsp90 mediated co-receptor function for LRP1 regulates EphA2 dependent glioblastoma cell invasion. PLoS One 2011, 6, e17649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Lin, L.; Tan, X.; Yang, J.; Bu, G.; Mars, W.M.; Liu, Y. tPA protects renal interstitial fibroblasts and myofibroblasts from apoptosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Wu, C.; Mars, W.M.; Liu, Y. Tissue-type plasminogen activator promotes murine myofibroblast activation through LDL receptor-related protein 1-mediated integrin signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 3821–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loukinova, E.; Ranganathan, S.; Kuznetsov, S.; Gorlatova, N.; Migliorini, M.M.; Loukinov, D.; Ulery, P.G.; Mikhailenko, I.; Lawrence, D.A.; Strickland, D.K. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP). Evidence for integrated co-receptor function betwenn LRP and the PDGF. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 15499–15506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantuano, E.; Jo, M.; Gonias, S.L.; Campana, W.M. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP1) regulates Rac1 and RhoA reciprocally to control Schwann cell adhesion and migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 14259–14266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Mantuano, E.; Inoue, G.; Campana, W.M.; Gonias, S.L. Ligand binding to LRP1 transactivates Trk receptors by a Src family kinase-dependent pathway. Sci. Signal. 2009, 2, ra18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Huang, H.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Wang, H. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the LDL receptor-related protein (LRP) and activation of the ERK pathway are required for connective tissue growth factor to potentiate myofibroblast differentiation. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1920–1921. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gonias, S.L.; Gaultier, A.; Jo, M. Regulation of the urokinase receptor (uPAR) by LDL receptor-related protein-1 (LRP1). Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 1962–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, D.J.; Nguyen, D.H.; Gonias, S.L. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase functions in the urokinase receptor-dependent pathway by which neutralization of low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein promotes fibrosarcoma cell migration and matrigel invasion. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mantuano, E.; Lam, M.S.; Gonias, S.L. LRP1 assembles unique co-receptor systems to initiate cell signaling in response to tissue-type plasminogen activator and myelin-associated glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 34009–34018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Strickland, D.K.; Hyman, B.T.; Rebeck, G.W. Elevation of LDL receptor-related protein levels via ligand interactions in Alzheimer disease and in vitro. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 60, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Donahue, J.E.; Flaherty, S.L.; Johanson, C.E.; Duncan, J.A., 3rd; Silverberg, G.D.; Miller, M.C.; Tavares, R.; Yang, W.; Wu, Q.; Sabo, E.; et al. RAGE, LRP-1, and amyloid-β protein in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2006, 112, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, L.A.; Hegg, R.; Freitas, F.R.; Tavares, E.R.; Almeida, C.P.; Baracat, E.C.; Maranhao, R.C. Effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor and LDL receptor-related protein 1 (LRP-1) receptor in locally advanced breast cancer. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2012, 45, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGarvey, T.; Hussain, M.M.; Stearns, M.E. In situ hybridization studies of α2-macroglobulin receptor and receptor-associated protein in human prostate carcinoma. Prostate 1996, 28, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrickx, D.A.; Koning, N.; Schuurman, K.G.; van Strien, M.E.; van Eden, C.G.; Hamann, J.; Huitinga, I. Selective upregulation of scavenger receptors in and around demyelinating areas in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 72, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barcelona, P.F.; Luna, J.D.; Chiabrando, G.A.; Juarez, C.P.; Bhutto, I.A.; Baba, T.; McLeod, D.S.; Sanchez, M.C.; Lutty, G.A. Immunohistochemical localization of low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 and α2-Macroglobulin in retinal and choroidal tissue of proliferative retinopathies. Exp. Eye Res. 2010, 91, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cal, R.; Juan-Babot, O.; Brossa, V.; Roura, S.; Galvez-Monton, C.; Portoles, M.; Rivera, M.; Cinca, J.; Badimon, L.; Llorente-Cortes, V. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 expression correlates with cholesteryl ester accumulation in the myocardium of ischemic cardiomyopathy patients. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Isaac, L.; Florido, M.P.; Fecchio, D.; Singer, L.M. Murine α2-macroglobulin increase during inflammatory responses and tumor growth. Inflamm. Res. 1999, 48, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, O.; Chavey, C.; Dray, C.; Meulle, A.; Daviaud, D.; Quilliot, D.; Muller, C.; Valet, P.; Liaudet-Coopman, E. LRP1 receptor controls adipogenesis and is up-regulated in human and mouse obese adipose tissue. PLoS One 2009, 4, e7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Polavarapu, R.; She, H.; Mao, Z.; Yepes, M. Tissue-type plasminogen activator and the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein mediate cerebral ischemia-induced nuclear factor-κB pathway activation. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yepes, M.; Sandkvist, M.; Moore, E.G.; Bugge, T.H.; Strickland, D.K.; Lawrence, D.A. Tissue-type plasminogen activator induces opening of the blood-brain barrier via the LDL receptor-related protein. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.F.; Tsirka, S.E.; Strickland, S.; Stieg, P.E.; Soriano, S.G.; Lipton, S.A. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) increases neuronal damage after focal cerebral ischemia in wild-type and tPA-deficient mice. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoi, H.; Mukoyama, M.; Nagae, T.; Mori, K.; Suganami, T.; Sawai, K.; Yoshioka, T.; Koshikawa, M.; Nishida, T.; Takigawa, M.; et al. Reduction in connective tissue growth factor by antisense treatment ameliorates renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabello-Verrugio, C.; Santander, C.; Cofre, C.; Acuna, M.J.; Melo, F.; Brandan, E. The internal region leucine-rich repeat 6 of decorin interacts with low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1, modulates transforming growth factor (TGF)-β-dependent signaling, and inhibits TGF-β-dependent fibrotic response in skeletal muscles. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 6773–6787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabello-Verrugio, C.; Brandan, E. A novel modulatory mechanism of transforming growth factor-β signaling through decorin and LRP-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 18842–18850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Hu, K. Tissue plasminogen activator and chronic kidney disease: More than a simple protease. In Plasminogen Activator: Genetic Factors, Functions and Clinical Applications; Rutherford, J.M., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 53–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Jin, Y.; Mars, W.M.; Reeves, W.B.; Hu, K. Myeloid-derived tissue-type plasminogen activator promotes macrophage motility through FAK, Rac1, and NF-κB Pathways. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 2757–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, H.; Ackermann, E.J.; van der Geer, P. v-Src induces Shc binding to tyrosine 63 in the cytoplasmic domain of the LDL receptor-related protein 1. Oncogene 2003, 22, 3589–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, H.; Larsen, B.; Tyers, M.; van Der Geer, P. Tyrosine-phosphorylated low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (Lrp1) associates with the adaptor protein SHC in SRC-transformed cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 19119–19125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickland, D.K.; Gonias, S.L.; Argraves, W.S. Diverse roles for the LDL receptor family. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 13, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Tan, R.; Xiong, M.; He, W.; Fang, L.; Wen, P.; Jiang, L.; Yang, J. Mice lacking the matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene reduce renal interstitial fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2010, 299, F973–F982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande, M.T.; Lopez-Novoa, J.M. Fibroblast activation and myofibroblast generation in obstructive nephropathy. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2009, 5, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.C.; Neilson, E.G. Toward a unified theory of renal progression. Annu. Rev. Med. 2006, 57, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. Renal fibrosis: New insights into the pathogenesis and therapeutics. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strutz, F.; Zeisberg, M. Renal fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2992–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisberg, M.; Neilson, E.G. Mechanisms of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1819–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, R.; Blenis, J. The RSK family of kinases: Emerging roles in cellular signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carriere, A.; Ray, H.; Blenis, J.; Roux, P.P. The RSK factors of activating the Ras/MAPK signaling cascade. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 4258–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Roux, P.P. Regulation and function of the RSK family of protein kinases. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Hu, K. tPA promotes M1 macrophage survival through p90RSK and p38 MAPK pathway. In Proceedings of 47th Annual Meeting of American Society of Nephrology, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 11–16 November 2014.
- Lin, L.; Hu, K. Tissue plasminogen activator and inflammation: From phenotype to signaling mechanisms. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 3, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schaller, M.D. Cellular functions of FAK kinases: Insight into molecular mechanisms and novel functions. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, C.E.; Brown, M.C.; Perrotta, J.A.; Riedy, M.C.; Nikolopoulos, S.N.; McDonald, A.R.; Bagrodia, S.; Thomas, S.; Leventhal, P.S. Paxillin LD4 motif binds PAK and PIX through a novel 95-kD ankyrin repeat, ARF-GAP protein: A role in cytoskeletal remodeling. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 145, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, S.R.; Hansen, S.H. The PIX–GIT complex: A G protein signaling cassette in control of cell shape. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2008, 19, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, F.; Lemmon, C.A.; Park, D.; Romer, L.H. FAK potentiates Rac1 activation and localization to matrix adhesion sites: A role for βPIX. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, P.; Li, W.P.; Matz, R.L.; Takayama, Y.; Auwerx, J.; Anderson, R.G.; Herz, J. LRP1 functions as an atheroprotective integrator of TGFβ and PDFG signals in the vascular wall: Implications for Marfan syndrome. PLoS One 2007, 2, e448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muratoglu, S.C.; Belgrave, S.; Lillis, A.P.; Migliorini, M.; Robinson, S.; Smith, E.; Zhang, L.; Strickland, D.K. Macrophage LRP1 suppresses neo-intima formation during vascular remodeling by modulating the TGF-β signaling pathway. PLoS One 2011, 6, e28846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickland, D.K.; Au, D.T.; Cunfer, P.; Muratoglu, S.C. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1: Role in the regulation of vascular integrity. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segarini, P.R.; Nesbitt, J.E.; Li, D.; Hays, L.G.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Carmichael, D.F. The low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein/α2-macroglobulin receptor is a receptor for connective tissue growth factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 40659–40667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lee, S.R.; Arai, K.; Tsuji, K.; Rebeck, G.W.; Lo, E.H. Lipoprotein receptor-mediated induction of matrix metalloproteinase by tissue plasminogen activator. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asahi, M.; Wang, X.; Mori, T.; Sumii, T.; Jung, J.C.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Fini, M.E.; Lo, E.H. Effects of matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene knock-out on the proteolysis of blood-brain barrier and white matter components after cerebral ischemia. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 7724–7732. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Kaul, M.; Yan, B.; Kridel, S.J.; Cui, J.; Strongin, A.; Smith, J.W.; Liddington, R.C.; Lipton, S.A. S-nitrosylation of matrix metalloproteinases: Signaling pathway to neuronal cell death. Science 2002, 297, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanekiyo, T.; Liu, C.C.; Shinohara, M.; Li, J.; Bu, G. LRP1 in brain vascular smooth muscle cells mediates local clearance of Alzheimer's amyloid-β. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 16458–16465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knauer, M.F.; Orlando, R.A.; Glabe, C.G. Cell surface APP751 forms complexes with protease nexin 2 ligands and is internalized via the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP). Brain Res. 1996, 740, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrzik, C.U.; Busse, T.; Merriam, D.E.; Weggen, S.; Koo, E.H. The cytoplasmic domain of the LDL receptor-related protein regulates multiple steps in APP processing. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 5691–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spuch, C.; Ortolano, S.; Navarro, C. LRP-1 and LRP-2 receptors function in the membrane neuron. Trafficking mechanisms and proteolytic processing in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deane, R.; Wu, Z.; Zlokovic, B.V. RAGE (yin) versus LRP (yang) balance regulates alzheimer amyloid β-peptide clearance through transport across the blood-brain barrier. Stroke 2004, 35, 2628–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deane, R.; Wu, Z.; Sagare, A.; Davis, J.; du Yan, S.; Hamm, K.; Xu, F.; Parisi, M.; LaRue, B.; Hu, H.W.; et al. LRP/amyloid β-peptide interaction mediates differential brain efflux of Aβ isoforms. Neuron 2004, 43, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.L.; Yu, W.M.; Strickland, S. Peripheral regeneration. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 30, 209–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campana, W.M.; Li, X.; Dragojlovic, N.; Janes, J.; Gaultier, A.; Gonias, S.L. The low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein is a pro-survival receptor in Schwann cells: Possible implications in peripheral nerve injury. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 11197–11207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantuano, E.; Inoue, G.; Li, X.; Takahashi, K.; Gaultier, A.; Gonias, S.L.; Campana, W.M. The hemopexin domain of matrix metalloproteinase-9 activates cell signaling and promotes migration of schwann cells by binding to low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 11571–11582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orita, S.; Henry, K.; Mantuano, E.; Yamauchi, K.; de Corato, A.; Ishikawa, T.; Feltri, M.L.; Wrabetz, L.; Gaultier, A.; Pollack, M.; et al. Schwann cell LRP1 regulates remak bundle ultrastructure and axonal interactions to prevent neuropathic pain. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 5590–5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.M.; Kuhlmann, C.; Trossbach, S.; Jaeger, S.; Waldron, E.; Roebroek, A.; Luhmann, H.J.; Laatsch, A.; Weggen, S.; Lessmann, V.; et al. The functional role of the second NPXY motif of the LRP1 β-chain in tissue-type plasminogen activator-mediated activation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 12004–12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, P.; Rohlmann, A.; Bock, H.H.; Zurhove, K.; Marth, J.D.; Schomburg, E.D.; Noebels, J.L.; Beffert, U.; Sweatt, J.D.; Weeber, E.J.; et al. Neuronal LRP1 functionally associates with postsynaptic proteins and is required for normal motor function in mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 8872–8883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Boesten, L.S.; May, P.; Herz, J.; Bovenschen, N.; Huisman, M.V.; Berbee, J.F.; Havekes, L.M.; van Vlijmen, B.J.; Tamsma, J.T. Macrophage low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein deficiency enhances atherosclerosis in ApoE/LDLR double knockout mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 2710–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overton, C.D.; Yancey, P.G.; Major, A.S.; Linton, M.F.; Fazio, S. Deletion of macrophage LDL receptor-related protein increases atherogenesis in the mouse. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yancey, P.G.; Blakemore, J.; Ding, L.; Fan, D.; Overton, C.D.; Zhang, Y.; Linton, M.F.; Fazio, S. Macrophage LRP-1 controls plaque cellularity by regulating efferocytosis and Akt activation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, P.; Gotthardt, M.; Li, W.P.; Anderson, R.G.; Herz, J. LRP: Role in vascular wall integrity and protection from atherosclerosis. Science 2003, 300, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muratoglu, S.C.; Belgrave, S.; Hampton, B.; Migliorini, M.; Coksaygan, T.; Chen, L.; Mikhailenko, I.; Strickland, D.K. LRP1 protects the vasculature by regulating levels of connective tissue growth factor and HtrA1. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 2137–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, T.; Akkawi, S.; Shina, A.; Haj-Yehia, A.; Bdeir, K.; Tarshis, M.; Heyman, S.N.; Higazi, A.A. In vitro and in vivo effects of tPA and PAI-1 on blood vessel tone. Blood 2004, 103, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stouffer, G.A.; LaMarre, J.; Gonias, S.L.; Owens, G.K. Activated α2-macroglobulin and transforming growth factor-β1 induce a synergistic smooth muscle cell proliferative response. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 18340–18344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weckbach, L.T.; Gola, A.; Winkelmann, M.; Jakob, S.M.; Groesser, L.; Borgolte, J.; Pogoda, F.; Pick, R.; Pruenster, M.; Muller-Hocker, J.; et al. The cytokine midkine supports neutrophil trafficking during acute inflammation by promoting adhesion via β2 integrins (CD11/CD18). Blood 2014, 123, 1887–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaultier, A.; Hollister, M.; Reynolds, I.; Hsieh, E.H.; Gonias, S.L. LRP1 regulates remodeling of the extracellular matrix by fibroblasts. Matrix Biol. 2010, 29, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Choi, H.Y.; Li, W.P.; Xu, F.; Herz, J. LRP1 controls cPLA2 phosphorylation, ABCA1 expression and cellular cholesterol export. PLoS One 2009, 4, e6853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrand, J.; Bruban, V.; Zhou, L.; Gong, W.; El Asmar, Z.; May, P.; Zurhove, K.; Haffner, P.; Philippe, C.; Woldt, E.; et al. LRP1 controls intracellular cholesterol storage and fatty acid synthesis through modulation of Wnt signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, N.T.; Heo, K.S.; Takei, Y.; Lee, H.; Woo, C.H.; Chang, E.; McClain, C.; Hurley, C.; Wang, X.; Li, F.; et al. A crucial role for p90RSK-mediated reduction of ERK5 transcriptional activity in endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Circulation 2013, 127, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Li, Y.; Lee, J.; Schwartz, A.L.; Bu, G. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 promotes cancer cell migration and invasion by inducing the expression of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Bu, G.; Takei, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Ikematsu, S.; Muramatsu, T.; Kadomatsu, K. Midkine and LDL-receptor-related protein 1 contribute to the anchorage-independent cell growth of cancer cells. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 4009–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, B.; Koo, B.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kwon, H.J.; Kim, D.S. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 regulates infiltration of macrophages into melanoma via phosphorylation of FAK-Tyr(925). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 450, 1696–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrot, G.; Langlois, B.; Devy, J.; Jeanne, A.; Verzeaux, L.; Almagro, S.; Sartelet, H.; Hachet, C.; Schneider, C.; Sick, E.; et al. LRP-1—CD44, a new cell surface complex regulating tumor cell adhesion. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 3293–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedieu, S.; Langlois, B.; Devy, J.; Sid, B.; Henriet, P.; Sartelet, H.; Bellon, G.; Emonard, H.; Martiny, L. LRP-1 silencing prevents malignant cell invasion despite increased pericellular proteolytic activities. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 2980–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staudt, N.D.; Jo, M.; Hu, J.; Bristow, J.M.; Pizzo, D.P.; Gaultier, A.; VandenBerg, S.R.; Gonias, S.L. Myeloid cell receptor LRP1/CD91 regulates monocyte recruitment and angiogenesis in tumors. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3902–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, I.; Hemdan, N.Y.; Buchold, M.; Huse, K.; Bigl, M.; Oerlecke, I.; Ricken, A.; Gaunitz, F.; Sack, U.; Naumann, A.; et al. α2-Macroglobulin inhibits the malignant properties of astrocytoma cells by impeding β-catenin signaling. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, L.; Hu, K. LRP-1: Functions, Signaling and Implications in Kidney and Other Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 22887-22901. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151222887
Lin L, Hu K. LRP-1: Functions, Signaling and Implications in Kidney and Other Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(12):22887-22901. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151222887
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Ling, and Kebin Hu. 2014. "LRP-1: Functions, Signaling and Implications in Kidney and Other Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 12: 22887-22901. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151222887
APA StyleLin, L., & Hu, K. (2014). LRP-1: Functions, Signaling and Implications in Kidney and Other Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(12), 22887-22901. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151222887