Comparative Mitogenomics of the Genus Odontobutis (Perciformes: Gobioidei: Odontobutidae) Revealed Conserved Gene Rearrangement and High Sequence Variations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Mitogenome Composition

| Region | A+T | AT-skew | GC-skew | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Osi | Opl | Oya | Oin | Opo | Osi | Opl | Oya | Oin | Opo | Osi | Opl | Oya | Oin | Opo | |
| Whole genome | 58.91 | 56.87 | 55.79 | 55.33 | 55.43 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.02 | −0.30 | −0.30 | −0.31 | −0.30 | −0.30 |
| Protein-coding genes | 58.39 | 55.86 | 55.17 | 54.63 | 54.76 | 0.03 | 0.01 | −0.03 | −0.01 | −0.05 | −0.31 | −0.32 | −0.33 | −0.31 | −0.32 |
| 1st codon position | 50.96 | 48.21 | 48.43 | 48.03 | 48.42 | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.01 | −0.05 | −0.05 | −0.07 | −0.05 | −0.06 |
| 2nd codon position | 59.20 | 58.79 | 58.57 | 58.61 | 58.48 | −0.16 | −0.38 | −0.17 | −0.38 | −0.17 | −0.34 | −0.36 | −0.35 | −0.35 | −0.35 |
| 3rd codon position | 65.00 | 60.58 | 58.52 | 57.27 | 57.37 | 0.17 | 0.26 | 0.06 | 0.25 | 0.03 | −0.62 | −0.64 | −0.63 | −0.59 | −0.60 |
| tRNA genes | 56.63 | 55.35 | 55.97 | 55.11 | 55.43 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.03 | −0.15 | 0.03 | −0.14 | 0.03 |
| rrnL | 57.85 | 56.01 | 54.72 | 56.30 | 55.74 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.17 | 0.28 | 0.19 | −0.13 | −0.11 | −0.11 | −0.10 | −0.10 |
| rrnS | 54.95 | 53.80 | 53.15 | 52.00 | 52.68 | 0.17 | 0.26 | 0.13 | 0.27 | 0.12 | −0.12 | −0.14 | −0.14 | −0.16 | −0.14 |
| Control region | 68.77 | 68.28 | 64.98 | 64.79 | 64.67 | 0.19 | 0.01 | 0.20 | −0.01 | 0.19 | −0.25 | −0.15 | −0.13 | −0.13 | −0.13 |
2.2. Comparison of Protein-Coding Genes


| Gene | Osi-Opl | Osi-Oya | Osi-Opo | Osi-Oin | Opl-Oya | Opl-Opo | Opl-Oin | Oya-Opo | Oya-Oin | Opo-Oin | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| atp6 | 0.250 | 0.228 | 0.234 | 0.245 | 0.214 | 0.216 | 0.233 | 0.097 | 0.113 | 0.055 | 0.189 |
| atp8 | 0.249 | 0.262 | 0.288 | 0.291 | 0.238 | 0.266 | 0.239 | 0.130 | 0.138 | 0.045 | 0.215 |
| cox1 | 0.148 | 0.143 | 0.142 | 0.153 | 0.145 | 0.152 | 0.146 | 0.081 | 0.081 | 0.040 | 0.123 |
| cox2 | 0.168 | 0.157 | 0.170 | 0.162 | 0.123 | 0.132 | 0.128 | 0.066 | 0.063 | 0.034 | 0.120 |
| cox3 | 0.163 | 0.166 | 0.187 | 0.178 | 0.147 | 0.172 | 0.164 | 0.094 | 0.106 | 0.059 | 0.143 |
| cob | 0.213 | 0.208 | 0.192 | 0.195 | 0.176 | 0.144 | 0.128 | 0.093 | 0.098 | 0.049 | 0.150 |
| nad1 | 0.217 | 0.239 | 0.248 | 0.249 | 0.191 | 0.192 | 0.207 | 0.129 | 0.132 | 0.058 | 0.186 |
| nad2 | 0.228 | 0.250 | 0.257 | 0.258 | 0.227 | 0.243 | 0.247 | 0.170 | 0.171 | 0.063 | 0.211 |
| nad3 | 0.294 | 0.279 | 0.300 | 0.263 | 0.232 | 0.334 | 0.255 | 0.207 | 0.133 | 0.128 | 0.243 |
| nad4 | 0.268 | 0.268 | 0.267 | 0.257 | 0.229 | 0.246 | 0.241 | 0.113 | 0.118 | 0.063 | 0.207 |
| nad4L | 0.159 | 0.150 | 0.207 | 0.145 | 0.182 | 0.272 | 0.203 | 0.175 | 0.095 | 0.111 | 0.170 |
| nad5 | 1.920 | 1.819 | 1.759 | 1.860 | 0.218 | 0.237 | 0.229 | 0.125 | 0.120 | 0.062 | 0.835 |
| nad6 | 0.269 | 0.278 | 0.295 | 0.297 | 0.271 | 0.262 | 0.277 | 0.126 | 0.123 | 0.066 | 0.226 |
| Nt | 0.924 | 0.934 | 1.259 | 1.257 | 0.292 | 1.233 | 1.251 | 1.125 | 1.148 | 0.058 | 0.948 |
| AA | 1.057 | 1.051 | 1.519 | 1.523 | 0.255 | 1.483 | 1.492 | 1.450 | 1.462 | 0.040 | 1.133 |

2.3. High Variations in Control Regions
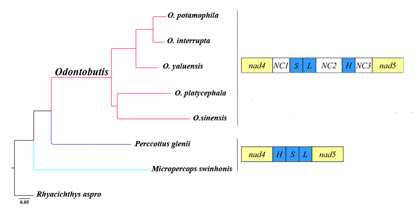
2.4. Gene Rearrangement and Possible Mechanisms



2.5. Phylogenetic Relationships

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Samples and DNA Extraction
3.2. PCR Amplification and Sequencing
3.3. Gene Annotation and Sequence Analysis
3.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, W.M. The mitochondrial genome of animals. In Molecular Evolutionary Genetics; McIntyre, R.J., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 95–130. [Google Scholar]
- Boore, J.L. Animal mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Cao, X.; Deng, W.; Luo, W.; Wang, W.M. Population genetic structure and post-establishment dispersal patterns of the red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii in China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H. Molecular systematics of Xenocyprinae (Teleotei: Cyprinidae): Taxonomy, biogeography, and coevolution of a special group restricted in East Asia. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2001, 18, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miya, M.; Takeshima, H.; Endo, H.; Ishiguro, N.B.; Inoue, J.G.; Mukai, T.; Satoh, T.P.; Shirai, S.M.; Yamaguchi, A.; Mabuchi, K.; et al. Major patterns of higher teleostean phylogenies: A new perspective based on 100 complete mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 26, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, L.Y.; Qiao, G.X. Hemipteran mitochondrial genomes: Features, structures and implications for phylogeny. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 12382–12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boore, J.L. The use of genome-level characters for phylogenetic reconstruction. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boore, J.L.; Brown, W.M. Big trees from little genomes: Mitochondrial gene orders as a phylogenetic tool. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1998, 8, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnason, E.; Rand, D.M. Heteroplasmy of short tandem repeats in mitochondrial DNA of Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua. Genetics 1992, 132, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matson, C.W.; Baker, R.J. DNA sequence variation in the mitochondrial control region of red-backed voles (Clethrionomys). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crochet, P.A.; Desmarais, E. Slow rate of evolution in the mitochondrial control region of gulls (Aves: Laridae). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 12, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, D.A.; Densmore, L.D. Repetitive sequences in the crocodilian mitochondrial control region: Poly-A sequences and heteroplasmic tandem repeats. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Shi, W.; Si, L.Z.; Wang, Z.M.; Kong, X.Y. The complete mitochondrial genome of peacock sole Pardachirus pavoninus (Pleuronectiformes: Soleidae) and comparative analysis of the control region among 13 soles. Mol. Biol. 2015, 49, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.; Bankier, A.T.; Barrell, B.G.; de Bruijn, M.H.L.; Coulson, A.R.; Drouin, J.; Eperon, I.C.; Nierlich, D.P.; Roe, B.A.; Sanger, F.; et al. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature 1981, 290, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buroker, N.E.; Brown, J.R.; Gilbert, T.A.; O’Hara, P.J.; Beckenbach, A.T.; Thomas, W.K.; Smith, M.J. Length heteroplasmy of sturgeon mitochondrial DNA: An illegitimate elongation model. Genetics 1990, 124, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Broughton, R.E.; Dowling, T.E. Length variation in mitochondrial DNA of the minnow Gyprinella spiloptera. Genetics 1994, 138, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Kong, X.Y.; Wang, Z.M.; Yu, S.S.; Chen, H.X.; de Stasio, E.A. Pause-melting misalignment: A novel model for the birth and motif indel of tandem repeats in the mitochondrial genome. BMC Genom. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macey, J.R.; Larson, A.; Anajeva, N.B.; Fang, Z.; Papenfuss, T.J. Two novel gene orders and the role of light-strand replication in rearrangement of the vertebrate mitochondrial genome. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1997, 14, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoelzel, A.R.; Hancock, J.M.; Dover, G.A. Generation of VNTRs and heteroplasmy by sequence turnover in the mitochondrial control region of two elephant seal species. J. Mol. Evol. 1993, 37, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Onorio de Meo, P.; D’Antonio, M.; Griggio, F.; Lupi, R.; Borsani, M.; Pavesi, G.; Pesole, G.; Castrignanò, T.; Gissi, C. MitoZoa 2.0: A database resource and search tools for comparative and evolutionary analyses of mitochondrial genomes in Metazoa. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1168–D1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miya, M.; Nishida, M. The mitogenomic contributions to molecular phylogenetics and evolution of fishes: A 15-year retrospect. Ichthyol. Res. 2015, 62, 29–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janke, A.; Xu, X.; Arnason, U. The complete mitochondrial genome of the wallaroo (Macropus robustus) and the phylogenetic relationship among Monotrema, Marsupialia and Eutheria. Porc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 94, 1276–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pääbo, S.; Thomas, W.K.; Whitfield, K.M.; Kumazawa, Y.; Wilson, A.C. Rearrangements of mitochondrial transfer RNA genes in marsupials. J. Mol. Evol. 1991, 33, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San Mauro, D.; Gower, D.J.; Zardoya, R.; Wilkinson, M. A hotspot of gene order rearrangement by tandem duplication and random loss in the vertebrate mitochondrial genome. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janke, A.; Arnason, U. The complete mitochondrial genome of Alligator mississippiensis and the separation between recent archosauria (birds and crocodiles). Mol. Biol. Evol. 1997, 14, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumazawa, Y.; Nishida, M. Variations in mitochondrial tRNA gene organization of reptiles as phylogenetic markers. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1995, 12, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mabuchi, K.; Miya, M.; Satoh, T.P.; Westnest, M.W.; Nishida, M. Gene rearrangements and evolution of tRNA pseudogenes in the mitochondrial genome of the parrotfish (Teleostei: Perciformes: Scaridae). J. Mol. Evol. 2004, 59, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunt, D.H.; Hyman, B.C. Animal mitochondrial DNA recombination. Nature 1997, 387, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burzynski, A.; Zbawicka, M.; Skibinski, D.O.; Wenne, R. Evidence for recombination of mtDNA in the marine mussel Mytilus trossulus from the Baltic. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraytsberg, Y.; Schwartz, M.; Brown, T.A.; Ebralidse, K.; Kunz, W.S.; Clayton, D.A.; Vissing, J.; Khrapko, K. Recombination of human mitochondrial DNA. Science 2004, 304, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boore, J.L. The duplication/random loss model for gene rearrangement exemplified by mitochondrial genomes of deuterostome animals. In Comparative Genomics; Sankoff, D., Nadeau, J., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publisher: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 1, pp. 133–147. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, J.G.; Miya, M.; Tsukamoto, K.; Nishida, M. Complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of Conger myriaster (Teleostei: Anguilliformes): Novel gene order for vertebrate mitochondrial genomes and the phylogenetic implications for anguilliform families. J. Mol. Evol. 2001, 52, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Gong, L.; Wang, S.Y.; Miao, X.G.; Kong, X.Y. Tandem duplication and random loss for mitogenome rearrangement in Symphurus (Teleost: Pleuronectiformes). BMC Genom. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavrov, D.V.; Boore, J.L.; Brown, W.M. Complete mtDNA sequences of two millipedes suggest a new model for mitochondrial gene rearrangements: Duplication and nonrandom loss. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckenbach, A.T. Mitochondrial genome sequences of Nematocera (lower Diptera): Evidence of rearrangement following a complete genome duplication in a winter crane fly. Genome Biol. Evol. 2012, 4, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gai, Y.; Song, D.; Sun, H.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, K. The complete mitochondrial genome of Symphylella sp. (Myriapoda: Symphyla): Extensive gene order rearrangement and evidence in favor of Progoneata. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 49, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Z. A novel rearrangement in the mitochondrial genome of tongue sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis: Control region translocation and a tRNA gene inversion. Genome 2009, 52, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Dong, X.L.; Wang, Z.M.; Miao, X.G.; Wang, S.Y.; Kong, X.Y. Complete mitogenome sequences of four flatfishes (Pleuronectiformes) reveal a novel gene arrangement of L-strand coding genes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, J.S. Fishes of the World, 4th ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Thacker, C.E. Molecular phylogeny of the gobioid fishes (Teleostei: Perciformes: Gobioidei). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 26, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, C.D. Morphological adaptations to special environments of gobies. In The Biology of Gobies; Patzner, R.A., van Tassell, J.L., Kovačić, M., Kapoor, B.G., Eds.; Science Publishers: Enfield, NH, USA, 2011; pp. 345–366. [Google Scholar]
- Thacker, C.E.; Hardman, M.A. Molecular phylogeny of basal gobioid fishes: Rhyacichthyidae, Odontobutidae, Xenisthmidae, Eleotridae (Teleostei: Perciformes: Gobioidei). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2005, 37, 858–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, A. Systematics of Odontobutidae. In The Biology of Gobies; Patzner, R.A., van Tassell, J.L., Kovačić, M., Kapoor, B.G., Eds.; Science Publishers: Enfield, NH, USA, 2011; pp. 61–77. [Google Scholar]
- Agorreta, A.; San Mauro, D.; Schliewen, U.; van Tassell, J.L.; Kovačić, M.; Zardoya, R.; Rüber, L. Molecular phylogenetics of Gobioidei and phylogenetic placement of European gobies. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agorreta, A.; Rüber, L. A standardized reanalysis of molecular phylogenetic hypotheses of Gobioidei. Syst. Biodivers. 2012, 10, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoese, D.F.; Gill, A.C. Phylogenetic relationships of eleotridid fishes (Perciformes: Gobioidei). Bull. Mar. Sci. 1993, 52, 415–440. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, P.J. The osteology and adaptive features of Rhyacichthys aspro (Teleostei: Gobioidei) and the higher classification of gobioid fishes. J. Zool. 1973, 171, 397–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Tsai, M.P.; Dean, J.; Lee, S.C. Molecular phylogeny of gobioid fishes (Perciformes: Gobioidei) based on mitochondrial 12S rRNA sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2001, 20, 390–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thacker, C.E. Phylogeny of Gobioidei and placement within Acanthomorpha, with a new classification and investigation of diversification and character evolution. Copeia 2009, 1, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornabene, L.; Chen, Y.; Pezold, F. Gobies are deeply divided: Phylogenetic evidence from nuclear DNA (Teleostei: Gobioidei: Gobiidae). Syst. Biodivers. 2013, 11, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Ikeo, K.; Imanishi, T.; Ono, H.; Umehara, Y.; Hamamatsu, C.; Ikeda, Y.; Sugiyama, K.; Sakamoto, K.; et al. Evolutionary aspects of gobioid fishes based upon a phylogenetic analysis of mitochondrial cytochrome b genes. Gene 2000, 259, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, G.; Zhang, Q. Molecular phylogeny of the genus Odontobutis based upon partial sequences of mitochondrial 12S rRNA genes. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2007, 31, 473–478. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ki, J.S.; Jung, S.O.; Hwang, D.S.; Lee, Y.M.; Lee, J.S. Unusual mitochondrial genome structure of the freshwater goby Odontobutis platycephala: Rearrangement on tRNAs and an additional non-coding region. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 73, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yin, S. Complete mitochondrial genome and phylogenic analysis of Odontobutis yaluensis, Perciformes, Odontobutidae. Mitochondrial DNA 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.X.; Sun, Y.N.; Wang, R.X.; Tang, D.; Zhao, S.L.; Xu, T.J. Chracteristics and phylogenetic analysis of mitochondrial genome in the gobies. Hereditas (Beijing) 2013, 35, 1391–1402. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, R. Complete mitochondrial genome of the freshwater goby Odontobutis potamophila (Perciformes: Odontobutidae). Mitochondrial DNA 2013, 26, 299–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, R.; Qiu, P. Organization of the mitochondrial genome of Odontobutis sinensis (Perciformes: Odontobutidae): Rearrangement of tRNAs and additional non-coding regions. Mitochondrial DNA 2013, 26, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, W.; Fukunaga, T.; Isagozawa, R.; Yamada, K.; Maeda, Y.; Sado, T.; Mabuchi, K.; Takeshima, H.; Miya, M.; Nishida, M. MitoFish and MitoAnnotator: A mitochondrial genome database of fish with an accurate and automatic annotation pipeline. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachtrog, D. Reduced selection for codon usage bias in Drosophila miranda. J. Mol. Evol. 2007, 64, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojala, D.; Montoya, J.; Attardi, G. tRNA punctuation model of RNA processing in human mitochondria. Nature 1981, 290, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, X.; Jin, X.; Sun, Y. The complete mitochondrial genome of Lophiogobius ocellicauda (Perciformes, Gobiidae). Mitochondrial DNA 2013, 25, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.C.; Kweon, H.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, C.B.; Gye, M.C.; Lee, W.O.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, J.S. The complete mitochondrial genome of the javeline goby Acanthogobius hasta (Perciformes, Gobiidae) and phylogenetic considerations. Gene 2004, 336, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broughton, R.E.; Milam, J.E.; Roe, B.A. The complete sequence of the zebrafish (Danio rerio) mitochondrial genome and evolutionary patterns in vertebrate mitochondrial DNA. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 1958–1967. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.F.; Su, T.J.; Luo, A.R.; Zhu, C.D.; Wu, C.S. Characterization of the complete mitochondrion genome of diurnal moth Amata emma (Butler) (Lepidoptera: Erebidae) and its phylogenetic implications. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grantham, R.; Gautier, C.; Gouy, M. Codon catalog usage and the genome hypothesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980, 8, r49–r62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meganathan, P.R.; Pagan, H.J.T.; McCulloch, E.S.; Stevens, R.D.; Ray, D.A. Complete mitochondrial genome sequences of three bats species and whole genome mitochondrial analyses reveal patterns of codon bias and lend support to a basal split in Chiroptera. Gene 2012, 492, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, C.; Koblmüller, S.; Gülly, C.; Schlötterer, C.; Sturmbauer, C.; Thallinger, G.G. Complete mitochondrial DNA sequences of the threadfin cichlid (Petrochromis trewavasae) and the blunthead cichlid (Tropheus moorii) and patterns of mitochondrial genome evolution in cichlid fishes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crozier, R.H.; Crozier, Y.C. The mitochondrial genome of the honeybee Apis mellifera: Complete sequence and genome organization. Genetics 1993, 133, 97–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chai, H.N.; Du, Y.Z. The complete mitochondrial genome of the pink stem borer, Sesamia inferens, in comparison with four other noctuid moths. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 10236–10256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Li, H.; Zhao, P.; Cai, W. Comparative mitogenomics of the assassin bug genus Peirates (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Peiratinae) reveal conserved mitochondrial genome organization of P. atromaculatus, P. fulvescens and P. turpis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Nielsen, R. Estimating synonymous and nonsynonymous substitution rates under realistic evolutionary models. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.B.; Shen, Y.Y.; Irwin, D.M.; Zhang, Y.P. Evaluating the roles of energetic functional constraints on teleost mitochondrial-encoded protein evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levinson, G.; Gutman, G.A. Slipped-strand mispairing: A major mechanism for DNA sequence evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moritz, C.; Brown, W.M. Tandem duplications in animal mitochondrial DNAs: Variation in incidence and gene content among lizards. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 7183–7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miya, M.; Kawaguchi, A.; Nishida, M. Mitogenomic exploration of higher teleostean phylogenies: A case study for moderate-scale evolutionary genomics with 38 newly determined complete mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 1993–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, I.S.; Kottelat, M.; Wu, H.L. A new genus of freshwater sleeper (Teleostei: Odontobutididae) from southern China and mainland Southeast Asia. J. Fish. Soc. Taiwan 2002, 29, 229–235. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.L.; Chen, I.S.; Chong, D.H. A new species of the genus Odontobutis (Pesces, Odontobutidae) from China. J. Shanghai Fish. Univ. 2002, 11, 6–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.H.; Wang, W.M.; Liu, X.L.; Luo, W.; Zhang, J.; Gui, Y. DNA extraction from crayfish exoskeleton. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 49, 953–957. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wyman, S.K.; Jansen, R.K.; Boore, J.L. Automatic annotation of organellar genomes with DOGMA. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 3253–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lower, T.M.; Eddy, S.R. tRNAscan-SE: A program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genome sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 955–964. [Google Scholar]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWillian, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; Thompsom, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA 5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perna, N.T.; Kocher, T.D. Patterns of nucleotide composition of four fold degenerate sites of animal mitochondrial genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 41, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A.; Hoover, P.; Rougemont, J. A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML Web-Servers. Syst. Biol. 2008, 75, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree, a graphical viewer of phylogenetic trees. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree (accesse on 24 July 2015).
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Z.; Yang, X.; Bercsenyi, M.; Wu, J.; Yu, Y.; Wei, K.; Fan, Q.; Yang, R. Comparative Mitogenomics of the Genus Odontobutis (Perciformes: Gobioidei: Odontobutidae) Revealed Conserved Gene Rearrangement and High Sequence Variations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 25031-25049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161025031
Ma Z, Yang X, Bercsenyi M, Wu J, Yu Y, Wei K, Fan Q, Yang R. Comparative Mitogenomics of the Genus Odontobutis (Perciformes: Gobioidei: Odontobutidae) Revealed Conserved Gene Rearrangement and High Sequence Variations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(10):25031-25049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161025031
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Zhihong, Xuefen Yang, Miklos Bercsenyi, Junjie Wu, Yongyao Yu, Kaijian Wei, Qixue Fan, and Ruibin Yang. 2015. "Comparative Mitogenomics of the Genus Odontobutis (Perciformes: Gobioidei: Odontobutidae) Revealed Conserved Gene Rearrangement and High Sequence Variations" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 10: 25031-25049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161025031
APA StyleMa, Z., Yang, X., Bercsenyi, M., Wu, J., Yu, Y., Wei, K., Fan, Q., & Yang, R. (2015). Comparative Mitogenomics of the Genus Odontobutis (Perciformes: Gobioidei: Odontobutidae) Revealed Conserved Gene Rearrangement and High Sequence Variations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(10), 25031-25049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161025031