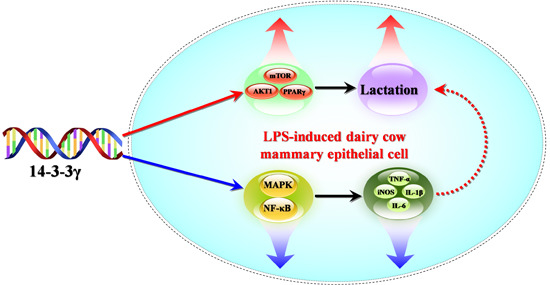
14-3-3γ Regulates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses and Lactation in Dairy Cow Mammary Epithelial Cells by Inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs and Up-Regulating mTOR Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Dairy Cow Mammary Epithelial Cells (DCMECs)

2.2. Effect of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on the Expression of 14-3-3γ mRNA

2.3. Expression of 14-3-3γ Proteins

2.4. 14-3-3γ Overexpression Inhibited Inflammatory Cytokine mRNA Expression in LPS-Induced DCMECs

2.5. 14-3-3γ Overexpression Decreased the Production of Inflammatory Cytokines in LPS-Induced DCMECs

2.6. 14-3-3γ Overexpression Inhibited the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Signal Pathway in LPS-Induced DCMECs

2.7. 14-3-3γ Overexpression Inhibited the Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB) Signaling Pathway in LPS-Induced DCMECs

2.8. 14-3-3γ Overexpression Improved the Viability and Proliferation of LPS-Induced DCMECs
| Groups | Numbers (105) | Viability (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 5.15 ± 0.21 | 95.51 ± 5.36 |
| pGCMV-IRES-EGFP-14-3-3 | 5.97 ± 0.37 * | 97.08 ± 4.99 * |
| pGCMV-IRES-EGFP | 5.39 ± 0.32 | 95.08 ± 5.87 |
| LPS | 0.64 ± 0.09 ** | 43.25 ± 2.83 ** |
| pGCMV-IRES-EGFP + LPS | 0.51 ± 0.08 ** | 41.89 ± 3.75 ** |
| pGCMV-IRES-EGFP-14-3-3γ + LPS | 1.90 ± 0.13 ## | 76.41 ± 3.97 ## |
2.9. 14-3-3γ Overexpression Promoted the Secretion of β-Casein, Triglycerides and Lactose in LPS-Induced DCMECs

2.10. 14-3-3γ Overexpression Increased the Expression of Lactation-Associated Proteins in LPS-Induced DCMECs

3. Discussion

4. Experimental Section
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Identification and Culture of DCMECs
4.3. Effect of LPS on Expression of 14-3-3γ mRNA
4.4. Transfection of pGCMV-IRES-EGFP-14-3-3γ (Expression Vectors)
4.5. Quantification of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α) and Interleukin-6 (IL-6)
4.6. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
| Gene Name | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Product Size (bp) | GenBank |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14-3-3γ | Forward: GCCGTATGTCAGGATGT | 171 | BC153255.1 |
| Reverse: GCCAGGTAGCGGTAAT | |||
| TNF-α | Forward: GCCGTATGTCAGGATGT | 140 | AC000180.1 |
| Reverse: GCCAGGTAGCGGTAAT | |||
| IL-6 | Forward: TGAGGGAAATCAGGAAAATGT | 269 | AC000161.1 |
| Reverse: CAGTGTTTGTGGCTGGAGTG | |||
| IL-1β | Forward: AGGTGGTGTCGGTCATCGT | 190 | NC019460.1 |
| Reverse: GCTCTCTGTCCTGGAGTTTGC | |||
| iNOS | Forward: CAGCCCCCGTCCAGTCCAGTGA | 186 | AC000176.1 |
| Reverse: GACTCATTCCCGTGCTTGCCCG | |||
| β-actin | Forward: CCGCAAGGACCTCTACGC | 206 | AC000182.1 |
| Reverse: CATGCCAATCTCATCTCGTTTT |
4.7. Assessment of Viability and Proliferation of DCMECs
4.8. Determination of β-Casein, Triglycerides and Lactose
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jouany, J.P. Optimizing rumen functions in the close-up transition period and early lactation to drive dry matter intake and energy balance in cows. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2006, 96, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khafipour, E.; Krause, D.O.; Plaizier, J.C. A grain-based subacute ruminal acidosis challenge causes translocation of lipopolysaccharide and triggers inflammation. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 1060–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Liang, D.; Li, F.; Li, D.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, N.; et al. Geniposide, from Gardenia jasminoides Ellis, inhibits the inflammatory response in the primary mouse macrophages and mouse models. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 14, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, T.; Natoli, G. Transcriptional regulation of macrophage polarization: Enabling diversity with identity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.J.; Wynn, T.A. Obstacles and opportunities for understanding macrophage polarization. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 89, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagan, J.C.; Medzhitov, R. Phosphoinositide-mediated adaptor recruitment controls toll-like receptor signaling. Cell 2006, 125, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldammer, T.; Zerbe, H.; Molenaar, A.; Schuberth, H.J.; Brunner, R.M.; Kata, S.R.; Seyfert, H.M. Mastitis increases mammary mRNA abundance of β-defensin 5, toll-like-receptor 2 (TLR2), and TLR4 but not TLR9 in cattle. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2004, 11, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, L.; He, J.; Jiang, H.; Xu, C.; Pu, S.; Xu, G. Bacterial endotoxin stimulates adipose lipolysis via toll-like receptor 4 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 5915–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waggoner, J.W.; Loest, C.A.; Turner, J.L.; Mathis, C.P.; Hallford, D.M. Effects of dietary protein and bacterial lipopolysaccharide infusion on nitrogen metabolism and hormonal responses of growing beef steers. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 87, 3656–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zebeli, Q.; Ametaj, B.N. Relationships between rumen lipopolysaccharide and mediators of inflammatory response with milk fat production and efficiency in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 3800–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, S.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Meyer, H.H.; Bruckmaier, R.M. Short-term changes of mRNA expression of various inflammatory factors and milk proteins in mammary tissue during LPS-induced mastitis. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2004, 26, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, A.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X. The role of TLR4-mediated PTEN/PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway in neuroinflammation in hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience 2014, 269, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butchar, J.P.; Parsa, K.V.; Marsh, C.B.; Tridandapani, S. Negative regulators of toll-like receptor 4-mediated macrophage inflammatory response. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 4143–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, D.K. The 14-3-3 proteins: Integrators of diverse signaling cues that impact cell fate and cancer development. Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosing, A.S.; Kundu, S.T.; Dalal, S.N. 14-3-3γ is required to enforce both the incomplete S phase and G2 DNA damage checkpoints. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 3171–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Nesland, J.M.; Suo, Z.; Trope, C.G.; Holm, R. The prognostic value of 14-3-3 isoforms in vulvar squamous cell carcinoma cases: 14-3-3β and epsilon are independent prognostic factors for these tumors. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Y.; Li, J.; Pober, J.S.; Min, W. RIP1-mediated AIP1 phosphorylation at a 14-3-3-binding site is critical for tumor necrosis factor-induced ASK1-JNK/p38 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 14788–14796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.G. Proteomic Analysis of the Lactation Regulation in DCMECs Treated with Different Hormones. Ph.D. Dissertation, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, L.; Dong, Y.; Hua, Y.G.; Dian, S.; Min, X.; Min, H. Protective role of 14-3-3γ in burn and LPS-induced rat myocardial injury. Chin. J. Pathophysiol. 2012, 28, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, L.; Dong, Y.; Dian, S.; Min, X.; Ming, H. The role of Bax in the 14-3-3γ protection against cardiomyocytes damage induced by LPS. Tianjin Med. J. 2012, 40, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, C.Y.; Park, K.R.; Lee, J.H.; Jeon, Y.J.; Liu, K.H.; Oh, S.; Kim, D.E.; Yea, S.S. Isoeugenol suppression of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression is mediated by down-regulation of NF-κB, ERK1/2, and p38 kinase. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 576, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, N.D. Integrating cell-signaling pathways with NF-κB and IKK function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmore, T.D. Introduction to NF-κB: Players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6680–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, L. The Rule of LRP16 in Regulating LPS Induced TLR4 Signaling Pathway and Its Mechanism. Ph.D. Dissertation, Postgraduate Medical Institute, Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Yi, B.; Liao, Z.; Tang, L.; Yin, D.; Zeng, S.; Yao, J.; He, M. 14-3-3γ protein attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiomyocytes injury through the Bcl-2 family/mitochondria pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 21, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairfield, A.M.; Plaizier, J.C.; Duffield, T.F.; Lindinger, M.I.; Bagg, R.; Dick, P.; McBride, B.W. Effects of prepartum administration of a monensin controlled release capsule on rumen pH, feed intake, and milk production of transition dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, M.J.; Hume, D.A. Endotoxin signal transduction in macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1996, 60, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blum, J.W.; Dosogne, H.; Hoeben, D.; Vangroenweghe, F.; Hammon, H.M.; Bruckmaier, R.M.; Burvenich, C. Tumor necrosis factor-α and nitrite/nitrate responses during acute mastitis induced by Escherichia coli infection and endotoxin in dairy cows. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2000, 19, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silanikove, N.; Shapiro, F.; Shamay, A.; Leitner, G. Role of xanthine oxidase, lactoperoxidase, and NO in the innate immune system of mammary secretion during active involution in dairy cows: Manipulation with casein hydrolyzates. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 38, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Zhao, R.; Chen, X.Q.; Yu, A.C. 14-3-3γ and neuroglobin are new intrinsic protective factors for cerebral ischemia. Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 41, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autieri, M.V. Inducible expression of the signal transduction protein 14-3-3 in injured arteries and stimulated human vascular smooth muscle cells. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2004, 76, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, J.; Duncan, J.A. Assessing ATP binding and hydrolysis by NLR proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1040, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.W.; Egan, L.; Li, Z.W.; Greten, F.R.; Kagnoff, M.F.; Karin, M. The two faces of IKK and NF-κB inhibition: Prevention of systemic inflammation but increased local injury following intestinal ischemia-reperfusion. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Z.; Liang, D.; Li, F.; Cao, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z. Magnolol inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response by interfering with TLR4 mediated NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 145, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleen, J.L.; Hooijer, G.A.; Rehage, J.; Noordhuizen, J.P. Subacute ruminal acidosis (SARA): A review. J. Vet. Med. A Physiol. Pathol. Clin. Med. 2003, 50, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutinaud, M.; Guinard-Flamenta, J.; Jammes, H. The number and activity of mammary epithelial cells, determining factors for milk production. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2004, 44, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, P.M.; Chugn, S.W.; Sultzer, B.M. Genes, receptors, signals and responses to lipopolysaccharide endotoxin. Scand. J. Immunol. 2000, 51, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadegowda, A.K.; Bionaz, M.; Piperova, L.S.; Erdman, R.A.; Loor, J.J. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ activation and long-chain fatty acids alter lipogenic gene networks in bovine mammary epithelial cells to various extents. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 4276–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, B.; Alcorn, J. LPS-induced inflammation downregulates mammary gland glucose, fatty acid, and l-carnitine transporter expression at different lactation stages. Res. Vet. Sci. 2010, 89, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silanikove, N.; Rauch-Cohen, A.; Shapiro, F.; Arieli, A.; Merin, U.; Leitner, G. Lipopolysaccharide challenge of the mammary gland in cows induces nitrosative stress that impairs milk oxidative stability. Animal 2012, 6, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiling, J.H.; Sabatini, D.M. Stress and mTOR ture signaling. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6373–6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bionaz, M.; Loor, J.J. Gene networks driving bovine mammary protein synthesis during the lactation cycle. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2011, 5, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bian, C.X.; Shi, Z.; Meng, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, L.Z.; Jiang, B.H. P70S6K 1 regulation of angiogenesis through VEGF and HIF-1α expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 398, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, C.H.; Watson, C.J. Making milk: A new link between STAT5 and Akt1. JAK-STAT 2013, 2, e23228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecka-Czernik, B.; Suva, L.J. Resolving the two “Bony” faces of PPAR-γ. PPAR Res. 2006, 2006, 27489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowell, B.B. PPARγ: An essential regulator of adipogenesis and modulator of fat cell function. Cell 1999, 99, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberle, D.; Hegarty, B.; Bossard, P.; Ferre, P.; Foufelle, F. SREBP transcription factors: Master regulators of lipid homeostasis. Biochimie 2004, 86, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Hou, X.; Qu, B.; Wang, J.; Gao, X.; Li, Q. Pten regulates development and lactation in the mammary glands of dairy cows. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, B.B.; Miao, J.F.; Zhu, Y.M.; Deng, Y.E.; Zou, S.X. Protective effect of retinoid against endotoxin-induced mastitis in rats. Inflamm. Res. 2009, 58, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lin, Y.; Bian, Y.; Liu, L.; Shao, L.; Lin, L.; Qu, B.; Zhao, F.; Gao, X.; Li, Q. Leucyl-tRNA synthetase regulates lactation and cell proliferation via mTOR signaling in dairy cow mammary epithelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5952–5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.M.; Wang, C.M.; Li, Q.Z.; Gao, X.J. MiR-15a decreases bovine mammary epithelial cell viability and lactation and regulates growth hormone receptor expression. Molecules 2012, 17, 12037–12048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y; Zhao, F.; Luo, C.; Zhang, X.; Si, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Gao, X. SOCS3-mediated blockade reveals major contribution of JAK2/STAT5 signaling pathway to lactation and proliferation of dairy cow mammary epithelial cells in vitro. Molecules 2013, 18, 12987–13002. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.M.; Li, Q.Z.; Huang, J.G.; Gao, X.J. Proteomic and functional analyses reveal MAPK1 regulates milk protein synthesis. Molecules 2012, 18, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Bian, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Wang, C.; Li, Q.; Gao, X. MicroRNA-152 regulates DNA methyltransferase 1 and is involved in the development and lactation of mammary glands in dairy cows. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, W.; Fu, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Xie, S.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Lv, Q.; Li, Z.; et al. IL-21 modulates release of proinflammatory cytokines in LPS-stimulated macrophages through distinct signaling pathways. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Lin, Y.; Liu, L.; Bian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Li, Q. 14-3-3γ Regulates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses and Lactation in Dairy Cow Mammary Epithelial Cells by Inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs and Up-Regulating mTOR Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 16622-16641. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160716622
Liu L, Lin Y, Liu L, Bian Y, Zhang L, Gao X, Li Q. 14-3-3γ Regulates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses and Lactation in Dairy Cow Mammary Epithelial Cells by Inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs and Up-Regulating mTOR Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(7):16622-16641. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160716622
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lixin, Ye Lin, Lili Liu, Yanjie Bian, Li Zhang, Xuejun Gao, and Qingzhang Li. 2015. "14-3-3γ Regulates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses and Lactation in Dairy Cow Mammary Epithelial Cells by Inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs and Up-Regulating mTOR Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 7: 16622-16641. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160716622
APA StyleLiu, L., Lin, Y., Liu, L., Bian, Y., Zhang, L., Gao, X., & Li, Q. (2015). 14-3-3γ Regulates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses and Lactation in Dairy Cow Mammary Epithelial Cells by Inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs and Up-Regulating mTOR Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(7), 16622-16641. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160716622