Molecular Mechanisms to Control Post-Transplantation Hepatitis B Recurrence
Abstract
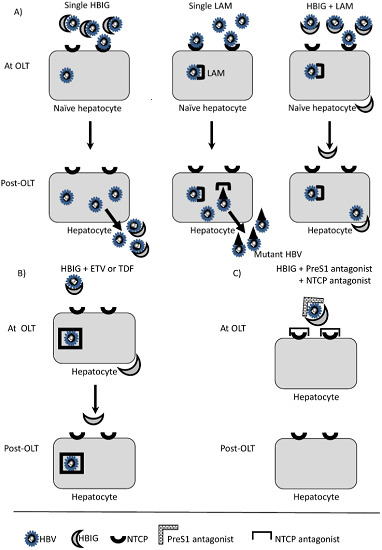
:1. Introduction
| Procedures of Post-OLT HBV Prophylaxis | Number of Patients | HBV-DNA Positivity at OLT | HBV-DNA Recurrence | Follow-up (Months) | Reference Number | Year Published | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. Lamivudine + HBIG | |||||||
| HBIG IV 10,000 IU/month | 14 | 7% | 0 | 13 | [9] | 1998 | USA |
| HBIG IM 400–800 IU/month | 141 | 76% | 4% | 62 (11–126) | [10] | 2007 | Australia |
| B. Lamivudine + HBIG (on demand) | |||||||
| HBIG IV to maintain HBsAb >200 IU/L | 21 | 38% | 9.5% | 21 (2.4–49.1) | [11] | 2001 | Germany |
| HBIG to maintain HBsAb >70 IU/L | 11 | 0% | 0 | 16 (9–22) | [12] | 2004 | Italy |
| HBIG IV to maintain HBsAb >10 IU/L | 18 | 61% | 0 | 30 (7–73) | [13] | 2007 | Japan |
| Short course (1 month) HBIG | 14 | 0% | 7% | 18 | [14] | 2003 | Spain |
| C. Lamivudine + Adefovir + HBIG | |||||||
| LAM + ADV Short course (7 days) HBIG IM 800 IU/day | 20 | 68% | 0 | 57 (27–83) | [15] | 2013 | Australia |
| One year HBIG IM 2000 IU/month LAM + ADV or TDF, TDF, ETV | 16 | 4.5% | 0 | 24 (6–40) post HBIG withdrawal | [16] | 2012 | Greece |
| D. Entecavir + HBIG | |||||||
| HBIG IM to maintain HBsAb >100 IU/L | 63 | Average 5.49 × 104 copies/mL | 0 | 41 (33–54) | [17] | 2012 | China |
| HBIG dose not specified | 61 | All cases <172 IU/mL | 0 | 18 | [18] | 2013 | Spain |
| One year HBIG IV 10,000 U/month | 29 | 52% | 3.4% | 31 | [19] | 2013 | Korea |
| E. Tenofovir + emtricitabine + perioperative HBIG | |||||||
| HBIG >6 months to maintain HBsAb >100 IU/L replaced with TDF/EMT | 21 | 56% | 0 | 31 (15–47) | [20] | 2012 | USA |
| HBIG >6 months; various protocols | 17 | 88% | 0 | 26 (4–36) | [21] | 2013 | Netherland |
| F. HBIG-free with newer NUCs | |||||||
| Entecavir | 80 | 74% | 1.2% | 26 (5–40) | [7] | 2011 | China |
| LAM + ADV (no HBIG when HBV-DNA below 3 log(10)IU/mL) | 28 | 35% | 0 | 22 (10–58) | [15] | 2013 | Australia |
| ETV, LAM + ADV, TDF, ETV + TDF (no HBIG when HBV-DNA below 3.3 log(10)IU/mL) | 75(Ent42, LAM + ADV19, TFV12, ENT + TFV2) | 31% | 8% | 21 (1–83) | [22] | 2013 | India |
2. Mechanisms of HBV-Related Hepatitis
3. Clinical Characteristics of Post-OLT HBV Recurrence
4. Past and Present Control of Post-OLT HBV Recurrence with Combination HBIG and NA
5. Mechanisms of Post-OLT HBV Recurrence and Protection

6. Mechanisms of Post-OLT HBV Prophylaxis Failure
7. HBV Vaccine Trial for Post-OLT Patients
7.1. HBV Vaccine Trial for Liver Cirrhosis Patients
| Pre-OLT Disease | Methods | Number of Patients | Definition of Success | Success Rate (%) | Reference Number | Year Published |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver Cirrhosis | ||||||
| Novel adjuvant MPL/QS2 vaccine for 0, 4, 16, 18 weeks | 16 | HBsAb >500 IU/L without HBIG | 80 | [72] | 2007 | |
| Experimental adjuvant vaccine for 0, 1, 2, 6, 12 months | 8 | HBsAb >500 IU/L 18 months without HBIG | 25 | [74] | 2005 | |
| 40 μg for 0, 1, 2, 6, 7, 8 months | 18 | HBsAb >500 IU/L 12 weeks after last vaccination | 0 | [70] | 2009 | |
| 10–20 μg/month with minimal immune suppression | 17 | HBsAb >100 IU/L without HBIG | 64 | [78] | 2009 | |
| 20 μg/month | 22 | HBsAb >100 IU/L 6 months without HBIG | 40 | [77] | 2012 | |
| 20 μg/month | 15 | HBsAb >100 IU/L 3 months without HBIG | 0 | [68] | 2011 | |
| 40 μg 0, 1, 2, 3, months, 20 μg 4, 5, 6 months | 50 | HBsAb >60 IU/L 3 months without HBIG | 24.6 | [75] | 2013 | |
| 40 μg 0, 7, 14, 28 days, 20 μg 2, 3, 4 months | 45 | HBsAb >60 IU/L 3 months without HBIG | 8.8 | [75] | 2013 | |
| 40 μg 0, 1, 6 months | 17 | HBsAb >10 IU/L without HBIG | 82 | [69] | 2000 | |
| 40 μg for 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 months | 52 | HBsAb >10 IU/L without HBIG | 7.7 | [73] | 2005 | |
| Acute Liver Failure | ||||||
| 20 μg/month | 5 | HBsAb >100 IU/L 6 months without HBIG | 100 | [77] | 2012 | |
| 10–20 μg/month with minimal immunosuppression | 3 | HBsAb >100 IU/L without HBIG | 66 | [78] | 2009 | |
| Experimental adjuvant vaccine for 0, 1, 2, 6, 12 months | 2 | HBsAb >500 IU/L 18 months without HBIG | 100 | [74] | 2005 | |
8. Future Perspectives to Control Post-OLT HBV Recurrence
9. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shukla, A.; Vadeyar, H.; Rela, M.; Shah, S. Liver Transplantation: East versus West. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2013, 3, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaki, A.; Yagi, T.; Yamamoto, K. Safe and cost-effective control of post-transplantation recurrence of hepatitis B. Hepatol. Res. 2015, 45, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusheiko, G. Treatment of HBeAg positive chronic hepatitis B: Interferon or nucleoside analogues. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitrinos, K.M.; Corsa, A.; Liu, Y.; Flaherty, J.; Snow-Lampart, A.; Marcellin, P.; Borroto-Esoda, K.; Miller, M.D. No detectable resistance to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate after 6 years of therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2014, 59, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenney, D.J.; Rose, R.E.; Baldick, C.J.; Pokornowski, K.A.; Eggers, B.J.; Fang, J.; Wichroski, M.J.; Xu, D.; Yang, J.; Wilber, R.B.; et al. Long-term monitoring shows hepatitis B virus resistance to entecavir in nucleoside-naive patients is rare through 5 years of therapy. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, Y.; Marusawa, H.; Kaido, T.; Ogura, Y.; Ogawa, K.; Yoshizawa, A.; Hata, K.; Fujimoto, Y.; Nishijima, N.; Chiba, T.; et al. Efficacy and safety of prophylaxis with entecavir and hepatitis B immunoglobulin in preventing hepatitis B recurrence after living-donor liver transplantation. Hepatol. Res. 2013, 43, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, B.; Samuel, D. Evolving strategies to prevent HBV recurrence. Liver Transpl. 2004, 10, S74–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, J.; Cheung, C.; Chan, S.C.; Yuen, M.F.; Chok, K.S.; Sharr, W.; Dai, W.C.; Chan, A.C.; Cheung, T.T.; Tsang, S.; et al. Entecavir monotherapy is effective in suppressing hepatitis B virus after liver transplantation. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetris, A.J.; Todo, S.; van Thiel, D.H.; Fung, J.J.; Iwaki, Y.; Sysyn, G.; Ming, W.; Trager, J.; Starzl, T.E. Evolution of hepatitis B virus liver disease after hepatic replacement. Practical and theoretical considerations. Am. J. Pathol. 1990, 137, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, A.; Gotanda, Y.; Itabashi, M.; Minegishi, K.; Kanemitsu, K.; Nishioka, K.; Japanese Red Cross NAT Screening Research Group. HBV NAT positive [corrected] blood donors in the early and late stages of HBV infection: Analyses of the window period and kinetics of HBV DNA. Vox Sang. 2005, 88, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allain, J.P.; Mihaljevic, I.; Gonzalez-Fraile, M.I.; Gubbe, K.; Holm-Harritshoj, L.; Garcia, J.M.; Brojer, E.; Erikstrup, C.; Saniewski, M.; Wernish, L.; et al. Infectivity of blood products from donors with occult hepatitis B virus infection. Transfusion 2013, 53, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowitz, J.S.; Martin, P.; Conrad, A.J.; Markmann, J.F.; Seu, P.; Yersiz, H.; Goss, J.A.; Schmidt, P.; Pakrasi, A.; Artinian, L.; et al. Prophylaxis against hepatitis B recurrence following liver transplantation using combination lamivudine and hepatitis B immune globulin. Hepatology 1998, 28, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gane, E.J.; Angus, P.W.; Strasser, S.; Crawford, D.H.; Ring, J.; Jeffrey, G.P.; McCaughan, G.W. Lamivudine plus low-dose hepatitis B immunoglobulin to prevent recurrent hepatitis B following liver transplantation. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenau, J.; Bahr, M.J.; Tillmann, H.L.; Trautwein, C.; Klempnauer, J.; Manns, M.P.; Boker, K.H.W. Lamivudine and low-dose hepatitis B immune globulin for prophylaxis of hepatitis B reinfection after liver transplantation possible role of mutations in the YMDD motif prior to transplantation as a risk factor for reinfection. J. Hepatol. 2001, 34, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrillo, R.; Buti, M.; Durand, F.; Charlton, M.; Gadano, A.; Cantisani, G.; Loong, C.C.; Brown, K.; Hu, W.; Lopez-Talavera, J.C.; et al. Entecavir and hepatitis B immune globulin in patients undergoing liver transplantation for chronic hepatitis B. Liver Transpl. 2013, 19, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.J.; Lu, M.Q.; Chen, Y.H.; Zhao, H.; Li, M.R.; Chen, G.H. Clinical study on prevention of HBV re-infection by entecavir after liver transplantation. Clin. Transpl. 2012, 26, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stravitz, R.T.; Shiffman, M.L.; Kimmel, M.; Puri, P.; Luketic, V.A.; Sterling, R.K.; Sanyal, A.J.; Cotterell, A.H.; Posner, M.P.; Fisher, R.A. Substitution of tenofovir/emtricitabine for Hepatitis B immune globulin prevents recurrence of Hepatitis B after liver transplantation. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, N.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Suh, K.S.; Cho, J.Y.; Baik, M.; Hong, G.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, W.; Kim, Y.J.; Yoon, J.H.; et al. Post-transplantation sequential entecavir monotherapy following 1-year combination therapy with hepatitis B immunoglobulin. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 1401–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cholongitas, E.; Vasiliadis, T.; Antoniadis, N.; Goulis, I.; Papanikolaou, V.; Akriviadis, E. Hepatitis B prophylaxis post liver transplantation with newer nucleos(t)ide analogues after hepatitis B immunoglobulin discontinuation. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2012, 14, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesdorp, D.J.; Knoester, M.; Braat, A.E.; Coenraad, M.J.; Vossen, A.C.; Claas, E.C.; van Hoek, B. Nucleoside plus nucleotide analogs and cessation of hepatitis B immunoglobulin after liver transplantation in chronic hepatitis B is safe and effective. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 58, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadhawan, M.; Gupta, S.; Goyal, N.; Taneja, S.; Kumar, A. Living related liver transplantation for hepatitis B-related liver disease without hepatitis B immune globulin prophylaxis. Liver Transpl. 2013, 19, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasunaka, T.; Takaki, A.; Yagi, T.; Iwasaki, Y.; Sadamori, H.; Koike, K.; Hirohata, S.; Tatsukawa, M.; Kawai, D.; Shiraha, H.; et al. Serum hepatitis B virus DNA before liver transplantation correlates with HBV reinfection rate even under successful low-dose hepatitis B immunoglobulin prophylaxis. Hepatol. Int. 2011, 5, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, S.; Bartenschlager, R.; Kubitz, R.; Zoulim, F. Strategies to inhibit entry of HBV and HDV into hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, S.; Urban, S.; Antoni, C.; Bottcher, B. Cryo-electron microscopy of hepatitis B virions reveals variability in envelope capsid interactions. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 4160–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruss, V. Hepatitis B virus morphogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glebe, D.; Urban, S.; Knoop, E.V.; Cag, N.; Krass, P.; Grun, S.; Bulavaite, A.; Sasnauskas, K.; Gerlich, W.H. Mapping of the hepatitis B virus attachment site by use of infection-inhibiting preS1 lipopeptides and tupaia hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, C.J.; Gripon, P.; Park, H.R.; Park, S.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C.; Yoo, O.J.; Hong, H.J. In vitro neutralization of hepatitis B virus by monoclonal antibodies against the viral surface antigen. J. Med. Virol. 1997, 52, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. eLife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Vee, M.; Gripon, P.; Stieger, B.; Fardel, O. Down-regulation of organic anion transporter expression in human hepatocytes exposed to the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin 1beta. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 2008, 36, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Vee, M.; Lecureur, V.; Stieger, B.; Fardel, O. Regulation of drug transporter expression in human hepatocytes exposed to the proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha or interleukin-6. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 2009, 37, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Vee, M.; Jouan, E.; Stieger, B.; Lecureur, V.; Fardel, O. Regulation of drug transporter expression by oncostatin M in human hepatocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bouezzedine, F.; Fardel, O.; Gripon, P. Interleukin 6 inhibits HBV entry through NTCP down regulation. Virology 2015, 481, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watashi, K.; Sluder, A.; Daito, T.; Matsunaga, S.; Ryo, A.; Nagamori, S.; Iwamoto, M.; Nakajima, S.; Tsukuda, S.; Borroto-Esoda, K.; et al. Cyclosporin A and its analogs inhibit hepatitis B virus entry into cultured hepatocytes through targeting a membrane transporter, sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP). Hepatology 2014, 59, 1726–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Ekins, S.; Polli, J.E. Structure-activity relationship for FDA approved drugs as inhibitors of the human sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP). Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doring, B.; Lutteke, T.; Geyer, J.; Petzinger, E. The SLC10 carrier family: Transport functions and molecular structure. Curr. Top. Membr. 2012, 70, 105–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anwer, M.S.; Stieger, B. Sodium-dependent bile salt transporters of the SLC10A transporter family: More than solute transporters. Pflugers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2014, 466, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucifora, J.; Esser, K.; Protzer, U. Ezetimibe blocks hepatitis B virus infection after virus uptake into hepatocytes. Antivir. Res. 2013, 97, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkongolo, S.; Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Kaufman, C.; Lindner, T.; Esser-Nobis, K.; Lohmann, V.; Mier, W.; Mehrle, S.; Urban, S. Cyclosporin A inhibits hepatitis B and hepatitis D virus entry by cyclophilin-independent interference with the NTCP receptor. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukuda, S.; Watashi, K.; Iwamoto, M.; Suzuki, R.; Aizaki, H.; Okada, M.; Sugiyama, M.; Kojima, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Mizokami, M.; et al. Dysregulation of retinoic acid receptor diminishes hepatocyte permissiveness to hepatitis B virus infection through modulation of sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 5673–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levrero, M.; Pollicino, T.; Petersen, J.; Belloni, L.; Raimondo, G.; Dandri, M. Control of cccDNA function in hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehermann, B.; Ferrari, C.; Pasquinelli, C.; Chisari, F.V. The hepatitis B virus persists for decades after patientsʼ recovery from acute viral hepatitis despite active maintenance of a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 1104–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, T.; Kang, J.H.; Nojima, M.; Tomonari, A.; Aoki, H.; Yamazaki, H.; Yane, K.; Tsuji, K.; Andoh, S.; Andoh, S.; et al. Reactivation of hepatitis B virus in patients with undetectable HBsAg undergoing chemotherapy for malignant lymphoma or multiple myeloma. J. Med. Virol. 2013, 85, 1900–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemoto, S.; Sugiyama, K.; Marusawa, H.; Inomata, Y.; Asonuma, K.; Egawa, H.; Kiuchi, T.; Miyake, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Chiba, T. Transmission of hepatitis B virus from hepatitis B core antibody-positive donors in living related liver transplants. Transplantation 1998, 65, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosel, M.; Quasdorff, M.; Wiegmann, K.; Webb, D.; Zedler, U.; Broxtermann, M.; Tedjokusumo, R.; Esser, K.; Arzberger, S.; Kirschning, C.J.; et al. Not interferon, but interleukin-6 controls early gene expression in hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maini, M.K.; Boni, C.; Ogg, G.S.; King, A.S.; Reignat, S.; Lee, C.K.; Larrubia, J.R.; Webster, G.J.; McMichael, A.J.; Ferrari, C.; et al. Direct ex vivo analysis of hepatitis B virus-specific CD8(+) T cells associated with the control of infection. Gastroenterology 1999, 117, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuch, A.; Hoh, A.; Thimme, R. The role of natural killer cells and CD8(+) T cells in hepatitis B virus infection. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbani, S.; Amadei, B.; Cariani, E.; Fisicaro, P.; Orlandini, A.; Missale, G.; Ferrari, C. The impairment of CD8 responses limits the selection of escape mutations in acute hepatitis C virus infection. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 7519–7529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boni, C.; Fisicaro, P.; Valdatta, C.; Amadei, B.; di Vincenzo, P.; Giuberti, T.; Laccabue, D.; Zerbini, A.; Cavalli, A.; Missale, G.; et al. Characterization of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-specific T-cell dysfunction in chronic HBV infection. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 4215–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.C.; Spengler, U.; Schraut, W.; Hoffmann, R.; Zachoval, R.; Eisenburg, J.; Eichenlaub, D.; Riethmuller, G.; Paumgartner, G.; Ziegler-Heitbrock, H.W.; et al. Hepatitis B virus antigen-specific T-cell activation in patients with acute and chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 1991, 13, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loggi, E.; Gamal, N.; Bihl, F.; Bernardi, M.; Andreone, P. Adaptive response in hepatitis B virus infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2014, 21, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumaidi, K.; Al-Jawabreh, A. Prevalence of occult HBV among hemodialysis patients in two districts in the northern part of the West Bank, Palestine. J. Med. Virol. 2014, 86, 1694–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degos, F.; Lugassy, C.; Degott, C.; Debure, A.; Carnot, F.; Theirs, V.; Tiollais, P.; Kreis, H.; Brechot, C. Hepatitis B virus and hepatitis B-related viral infection in renal transplant recipients. A prospective study of 90 patients. Gastroenterology 1988, 94, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Samuel, D.; Muller, R.; Alexander, G.; Fassati, L.; Ducot, B.; Benhamou, J.P.; Bismuth, H. Liver transplantation in European patients with the hepatitis B surface antigen. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1842–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetris, A.J.; Jaffe, R.; Sheahan, D.G.; Burnham, J.; Spero, J.; Iwatsuki, S.; van Theil, D.H.; Starzl, T.E. Recurrent hepatitis B in liver allograft recipients. Differentiation between viral hepatitis B and rejection. Am. J. Pathol. 1986, 125, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Todo, S.; Demetris, A.J.; van Thiel, D.; Teperman, L.; Fung, J.J.; Starzl, T.E. Orthotopic liver transplantation for patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver disease. Hepatology 1991, 13, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lerut, J.P.; Donataccio, M.; Ciccarelli, O.; Roggen, F.; Jamart, J.; Laterre, P.F.; Cornu, C.; Mazza, D.; Hanique, G.; Rahier, J.; et al. Liver transplantation and HBsAg-positive postnecrotic cirrhosis: Adequate immunoprophylaxis and delta virus co-infection as the significant determinants of long-term prognosis. J. Hepatol. 1999, 30, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, D.; Zignego, A.L.; Reynes, M.; Feray, C.; Arulnaden, J.L.; David, M.F.; Gigou, M.; Bismuth, A.; Mathieu, D.; Gentilini, P.; et al. Long-term clinical and virological outcome after liver transplantation for cirrhosis caused by chronic delta hepatitis. Hepatology 1995, 21, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, E.; Rahier, J.; Pucci, A.; Camby, P.; Scevens, M.; Salizzoni, M.; Otte, J.B.; Galmarini, D.; Marinucci, G.; Ottobrelli, A.; et al. Recurrence of hepatitis D (delta) in liver transplants: Histopathological aspects. Gastroenterology 1993, 104, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Di Paolo, D.; Tisone, G.; Piccolo, P.; Lenci, I.; Zazza, S.; Angelico, M. Low-dose hepatitis B immunoglobulin given “on demand” in combination with lamivudine: A highly cost-effective approach to prevent recurrent hepatitis B virus infection in the long-term follow-up after liver transplantation. Transplantation 2004, 77, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaki, A.; Yagi, T.; Iwasaki, Y.; Sadamori, H.; Matsukawa, H.; Matsuda, H.; Shinoura, S.; Umeda, Y.; Miyake, Y.; Terada, R.; et al. Short-term high-dose followed by long-term low-dose hepatitis B immunoglobulin and lamivudine therapy prevented recurrent hepatitis B after liver transplantation. Transplantation 2007, 83, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buti, M.; Mas, A.; Prieto, M.; Casafont, F.; Gonzalez, A.; Miras, M.; Herrero, J.I.; Jardi, R.; Cruz de Castro, E.; Garcia-Rey, C. A randomized study comparing lamivudine monotherapy after a short course of hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIg) and lamivudine with long-term lamivudine plus HBIg in the prevention of hepatitis B virus recurrence after liver transplantation. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, D.C.; Hu, K.Q. Update on rescue therapies in patients with lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 777–788. [Google Scholar]
- Corsa, A.C.; Liu, Y.; Flaherty, J.F.; Mitchell, B.; Fung, S.K.; Gane, E.; Miller, M.D.; Kitrinos, K.M. No Resistance to Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Through 96 Weeks of Treatment in Patients With Lamivudine-Resistant Chronic Hepatitis B. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.Y.; Kim, I.H.; Sohn, J.Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, S.O.; Lee, S.T.; Kim, D.G. Long-term efficacy of entecavir plus adefovir combination therapy versus entecavir monotherapy in adefovir refractory chronic hepatitis B patients with prior lamivudine resistance. Intervirology 2014, 57, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gane, E.J.; Patterson, S.; Strasser, S.I.; McCaughan, G.W.; Angus, P.W. Combination of lamivudine and adefovir without hepatitis B immune globulin is safe and effective prophylaxis against hepatitis B virus recurrence in hepatitis B surface antigen-positive liver transplant candidates. Liver Transpl. 2013, 19, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.K.; Seto, W.K.; Fung, J.; Ip, P.; Huang, F.Y.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Reduction of hepatitis B surface antigen and covalently closed circular DNA by nucleos(t)ide analogues of different potency. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilling, R.; Ijaz, S.; Davidoff, M.; Lee, J.Y.; Locarnini, S.; Williams, R.; Naoumov, N.V. Endocytosis of hepatitis B immune globulin into hepatocytes inhibits the secretion of hepatitis B virus surface antigen and virions. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 8882–8892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, A.U.; Phillips, S.; Levine, I.; Ijaz, S.; Dahari, H.; Eren, R.; Dagan, S.; Naoumov, N.V. Novel mechanism of antibodies to hepatitis B virus in blocking viral particle release from cells. Hepatology 2010, 52, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Frias, F.; Buti, M.; Jardi, R.; Vargas, V.; Quer, J.; Cotrina, M.; Martell, M.; Esteban, R.; Guardia, J. Genetic alterations in the S gene of hepatitis B virus in patients with acute hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis B and hepatitis B liver cirrhosis before and after liver transplantation. Liver 1999, 19, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, Y.; Marusawa, H.; Egawa, H.; Okamoto, S.; Ogura, Y.; Oike, F.; Nishijima, N.; Takada, Y.; Uemoto, S.; Chiba, T. De novo activation of HBV with escape mutations from hepatitis B surface antibody after living donor liver transplantation. Antivir. Ther. 2011, 16, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buti, M.; Tabernero, D.; Mas, A.; Homs, M.; Prieto, M.; Rodriguez-Frias, F.; Casafont, F.; Casillas, R.; Gonzalez, A.; Miras, M.; et al. Hepatitis B virus quasispecies evolution after liver transplantation in patients under long-term lamivudine prophylaxis with or without hepatitis B immune globulin. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2015, 17, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terasaka, T.; Ueta, E.; Ebara, H.; Waseda, K.; Hanayama, Y.; Takaki, A.; Kawabata, T.; Sugiyama, H.; Hidani, K.; Otsuka, F. Long-term observation of osteomalacia caused by adefovir-induced Fanconi’s syndrome. Acta Med. Okayama 2014, 68, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tamori, A.; Enomoto, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Iwai, S.; Morikawa, H.; Sakaguchi, H.; Habu, D.; Shiomi, S.; Imanishi, Y.; Kawada, N. Add-on combination therapy with adefovir dipivoxil induces renal impairment in patients with lamivudine-refractory hepatitis B virus. J. Viral Hepat. 2010, 17, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Z.; Chen, X.; Liang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, F.; Long, L.; McCrae, M.A.; Zhuang, H.; Shen, T.; Lu, F. Genetic polymorphisms of CXCR5 and CXCL13 are associated with non-responsiveness to the hepatitis B vaccine. Vaccine 2014, 32, 5316–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenau, J.; Hooman, N.; Rifai, K.; Solga, T.; Tillmann, H.L.; Grzegowski, E.; Nashan, B.; Klempnauer, J.; Strassburg, C.P.; Wedemeyer, H.; et al. Hepatitis B virus immunization with an adjuvant containing vaccine after liver transplantation for hepatitis B-related disease: Failure of humoral and cellular immune response. Transpl. Int. 2006, 19, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishigami, M.; Kamei, H.; Nakamura, T.; Katano, Y.; Ando, H.; Kiuchi, T.; Goto, H. Different effect of HBV vaccine after liver transplantation between chronic HBV carriers and non-HBV patients who received HBcAb-positive grafts. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 46, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Fueyo, A.; Rimola, A.; Grande, L.; Costa, J.; Mas, A.; Navasa, M.; Cirera, I.; Sanchez-Tapias, J.M.; Rodes, J. Hepatitis B immunoglobulin discontinuation followed by hepatitis B virus vaccination: A new strategy in the prophylaxis of hepatitis B virus recurrence after liver transplantation. Hepatology 2000, 31, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashiki, N.; Sugawara, Y.; Tamura, S.; Kaneko, J.; Matsui, Y.; Togashi, J.; Kokudo, N.; Omata, M.; Makuuchi, M. Double-dose double-phase use of second generation hepatitis B virus vaccine in patients after living donor liver transplantation: Not an effective measure in transplant recipients. Hepatol. Res. 2009, 39, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, N.K.; Forman, L.M.; Trotter, J.F. HBIg discontinuation with maintenance oral anti-viral therapy and HBV vaccination in liver transplant recipients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, T.; Gunther, M.; Bienzle, U.; Neuhaus, R.; Jilg, W. Vaccination against hepatitis B in liver transplant recipients: Pilot analysis of cellular immune response shows evidence of HBsAg-specific regulatory T cells. Liver Transpl. 2007, 13, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, C.M.; Liu, C.L.; Chan, S.C.; Lau, G.K.; Fan, S.T. Failure of hepatitis B vaccination in patients receiving lamivudine prophylaxis after liver transplantation for chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2005, 43, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starkel, P.; Stoffel, M.; Lerut, J.; Horsmans, Y. Response to an experimental HBV vaccine permits withdrawal of HBIg prophylaxis in fulminant and selected chronic HBV-infected liver graft recipients. Liver Transpl. 2005, 11, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Niu, Y.; Chen, H.; You, H.; Zang, Y.; Li, L.; Shan, S.; Tan, Y.; Jia, J.; Shen, Z. Immunogenicity of different hepatitis B virus vaccination schedules in liver transplant recipients. Hepatol. Res. 2013, 43, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S.S. Clinical management of hepatitis B virus infection correlated with liver transplantation. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis. Int. 2010, 9, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takaki, A.; Yagi, T.; Yasunaka, T.; Sadamori, H.; Shinoura, S.; Umeda, Y.; Yoshida, R.; Sato, D.; Nobuoka, D.; Utsumi, M.; et al. Which patients respond best to hepatitis B vaccination after a hepatitis B virus-related liver transplantation? J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahara, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Ishiyama, K.; Ide, K.; Shishida, M.; Irei, T.; Ushitora, Y.; Ohira, M.; Banshodani, M.; Tashiro, H.; et al. Successful hepatitis B vaccination in liver transplant recipients with donor-specific hyporesponsiveness. Transpl. Int. 2009, 22, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soejima, Y.; Ikegami, T.; Taketomi, A.; Yoshizumi, T.; Uchiyama, H.; Harada, N.; Yamashita, Y.; Maehara, Y. Hepatitis B vaccination after living donor liver transplantation. Liver Int. 2007, 27, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.B.; Kwon, C.H.; Lee, K.W.; Choi, G.S.; Kim, D.J.; Seo, J.M.; Kim, S.J.; Joh, J.W.; Lee, S.K. Hepatitis B virus vaccine switch program for prevention of de novo hepatitis B virus infection in pediatric patients. Transpl. Int. 2008, 21, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, S.; TrehanPati, N.; Patra, S.; Kottilil, S.; Pande, C.; Trivedi, S.S.; Sarin, S.K. Increased regulatory T cells and impaired functions of circulating CD8 T lymphocytes is associated with viral persistence in Hepatitis B virus-positive newborns. J. Viral Hepat. 2013, 20, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, P.T.; Sandalova, E.; Jo, J.; Gill, U.; Ushiro-Lumb, I.; Tan, A.T.; Naik, S.; Foster, G.R.; Bertoletti, A. Preserved T-cell function in children and young adults with immune-tolerant chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenau, J.; Hooman, N.; Hadem, J.; Rifai, K.; Bahr, M.J.; Philipp, G.; Tillmann, H.L.; Klempnauer, J.; Strassburg, C.P.; Manns, M.P. Failure of hepatitis B vaccination with conventional HBsAg vaccine in patients with continuous HBIG prophylaxis after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2007, 13, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wursthorn, K.; Wedemeyer, H.; Manns, M.P. Managing HBV in patients with impaired immunity. Gut 2010, 59, 1430–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumann, A.; Lindemann, M.; Valentin-Gamazo, C.; Lu, M.; Elmaagacli, A.; Dahmen, U.; Knop, D.; Broelsch, C.E.; Grosse-Wilde, H.; Roggendorf, M.; et al. Adoptive immune transfer of hepatitis B virus specific immunity from immunized living liver donors to liver recipients. Transplantation 2009, 87, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Lo, C.M.; Cheung, C.K.; Lau, G.K.; Fan, S.T.; Wong, J. Identification of hepatitis B virus-specific lymphocytes in human liver grafts from HBV-immune donors. Liver Transpl. 2007, 13, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paolo, D.; Lenci, I.; Cerocchi, C.; Tariciotti, L.; Monaco, A.; Brega, A.; Lotti, L.; Tisone, G.; Angelico, M. One-year vaccination against hepatitis B virus with a MPL-vaccine in liver transplant patients for HBV-related cirrhosis. Transpl. Int. 2010, 23, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crispe, I.N. The liver as a lymphoid organ. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Pichard, A.; Pol, S. Hepatitis B virus treatment beyond the guidelines: Special populations and consideration of treatment withdrawal. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2014, 7, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishigami, M.; Honda, T.; Ishizu, Y.; Onishi, Y.; Kamei, H.; Hayashi, K.; Ogura, Y.; Hirooka, Y.; Goto, H. Frequent incidence of escape mutants after successful hepatitis B vaccine response and stopping nucleos(t)ide analogues in liver-transplant recipients. Liver Transpl. 2014, 20, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachs, M.E.; Amend, W.J.; Ascher, N.L.; Bretan, P.N.; Emond, J.; Lake, J.R.; Melzer, J.S.; Roberts, J.P.; Tomlanovich, S.J.; Vincenti, F.; et al. The risk of transmission of hepatitis B from HBsAg(−), HBcAb(+), HBIgM(−) organ donors. Transplantation 1995, 59, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, R.C.; Everhart, J.E.; Lake, J.R.; Wei, Y.; Seaberg, E.C.; Wiesner, R.H.; Zetterman, R.K.; Pruett, T.L.; Ishitani, M.B.; Hoofnagle, J.H. Transmission of hepatitis B by transplantation of livers from donors positive for antibody to hepatitis B core antigen. The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Liver Transplantation Database. Gastroenterology 1997, 113, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.C.; Chen, C.L.; Concejero, A.; Wang, C.C.; Wang, S.H.; Liu, Y.W.; Yang, C.H.; Yong, C.C.; Lin, T.S.; Jawan, B.; et al. Active immunization to prevent de novo hepatitis B virus infection in pediatric live donor liver recipients. Am. J. Transpl. 2007, 7, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, C.H.; Suh, K.S.; Yi, N.J.; Chang, S.H.; Cho, Y.B.; Cho, J.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Seo, J.K.; Lee, K.U. Long-term protection against hepatitis B in pediatric liver recipients can be achieved effectively with vaccination after transplantation. Pediatr. Transpl. 2006, 10, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerino, A.; Bremer, C.M.; Glebe, D.; Mondelli, M.U. A human monoclonal antibody against hepatitis B surface antigen with potent neutralizing activity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takaki, A.; Yasunaka, T.; Yagi, T. Molecular Mechanisms to Control Post-Transplantation Hepatitis B Recurrence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 17494-17513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160817494
Takaki A, Yasunaka T, Yagi T. Molecular Mechanisms to Control Post-Transplantation Hepatitis B Recurrence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(8):17494-17513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160817494
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakaki, Akinobu, Tetsuya Yasunaka, and Takahito Yagi. 2015. "Molecular Mechanisms to Control Post-Transplantation Hepatitis B Recurrence" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 8: 17494-17513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160817494
APA StyleTakaki, A., Yasunaka, T., & Yagi, T. (2015). Molecular Mechanisms to Control Post-Transplantation Hepatitis B Recurrence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(8), 17494-17513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160817494