Influence of Pre-Freezing Temperature on the Corneal Endothelial Cytocompatibility and Cell Delivery Performance of Porous Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Carriers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Porous Structure



2.2. Glucose Permeation Studies

2.3. In Vitro Biocompatibility Studies


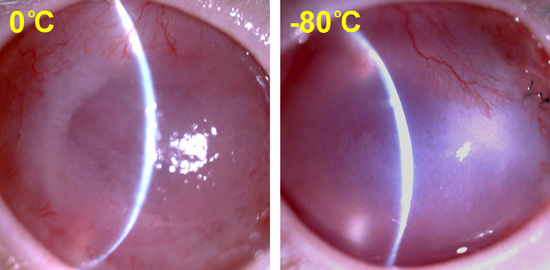
2.4. In Vivo Transplantation Studies


3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Porous HA Carriers
3.3. Characterization of Porous Structure
3.4. Glucose Permeation Studies
3.5. In Vitro Biocompatibility Studies
3.6. In Vivo Transplantation Studies
| Parameter | Ocular Score | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Corneal edema | None | Mild | Moderate | Severe | N/A a |
| Corneal cloudiness severity | Normal | Mild | Moderate | Severe | N/A a |
| Corneal neovascularization | None | Mild | Moderate | Severe | N/A a |
3.7. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kharkar, P.M.; Kiick, K.L.; Kloxin, A.M. Designing degradable hydrogels for orthogonal control of cell microenvironments. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7335–7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, W.; Dong, Y.; Wang, W. Encapsulation and 3D culture of human adipose-derived stem cells in an in-situ crosslinked hybrid hydrogel composed of PEG-based hyperbranched copolymer and hyaluronic acid. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2013, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, A.T.; Mancino, R.J.; Bowles, R.D.; Brunger, J.M.; Tainter, D.M.; Chen, Y.T.; Richardson, W.J.; Guilak, F.; Setton, L.A. Injectable laminin-functionalized hydrogel for nucleus pulposus regeneration. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7381–7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xu, H.H.K.; Zhou, H.; Weir, M.D.; Chen, Q.; Trotman, C.A. Human umbilical cord stem cell encapsulation in novel macroporous and injectable fibrin for muscle tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 4688–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeng, B.H.; Hoyt, C.S.; McLeod, S.D. Completion rate of continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis in pediatric cataract surgery using different viscoelastic materials. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2004, 30, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimmura, S.; Shimazaki, J.; Omoto, M.; Teruya, A.; Ishioka, M.; Tsubota, K. Deep lamellar keratoplasty (DLKP) in keratoconus patients using viscoadaptive viscoelastics. Cornea 2005, 24, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.Y.; Tu, I.H. Adhesion, phenotypic expression, and biosynthetic capacity of corneal keratocytes on surfaces coated with hyaluronic acid of different molecular weights. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1068–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.Y. Biofunctionalization of gelatin microcarrier with oxidized hyaluronic acid for corneal keratocyte cultivation. Colloid Surf. B 2014, 122, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.L.; Lai, J.Y.; Ma, D.H.K.; Hsiue, G.H. Carbodiimide cross-linked hyaluronic acid hydrogels as cell sheet delivery vehicles: Characterization and interaction with corneal endothelial cells. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2008, 19, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.Y.; Ma, D.H.K.; Cheng, H.Y.; Sun, C.C.; Huang, S.J.; Li, Y.T.; Hsiue, G.H. Ocular biocompatibility of carbodiimide cross-linked hyaluronic acid hydrogels for cell sheet delivery carriers. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2010, 21, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.Y. Solvent composition is critical for carbodiimide cross-linking of hyaluronic acid as an ophthalmic biomaterial. Materials 2012, 5, 1986–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.Y.; Li, Y.T. Functional assessment of cross-linked porous gelatin hydrogels for bioengineered cell sheet carriers. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.N.; Park, J.C.; Kim, H.O.; Song, M.J.; Suh, H. Characterization of porous collagen/hyaluronic acid scaffold modified by 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide cross-linking. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaghiele, M.; Sannino, A.; Yannas, I.V.; Spector, M. Collagen-based matrices with axially oriented pores. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 85, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Tsuru, K.; Hayakawa, S.; Osaka, A. Novel approach to fabricate porous gelatin-siloxane hybrids for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4765–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vlierberghe, S.; Cnudde, V.; Dubruel, P.; Masschaele, B.; Cosijns, A.; de Paepe, I.; Jacobs, P.J.S.; van Hoorebeke, L.; Remon, J.P.; Schacht, E. Porous gelatin hydrogels: 1. Cryogenic formation and structure analysis. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Yin, J.; Yan, S.; Cui, L.; Chen, X.; Xie, Y. Porous scaffolds based on cross-linking of poly(l-glutamic acid). Macromol. Biosci. 2011, 11, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, T.W.; Yang, J.; Akaike, T.; Cho, K.Y.; Nah, J.W.; Kim, S.I.; Cho, C.S. Preparation of alginate/galactosylated chitosan scaffold for hepatocyte attachment. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 2827–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamatsu, J.; Torres, F.G.; Troncoso, O.P.; Min-Lin, Y.; Boccaccini, A.R. Processing and characterization of porous structures from chitosan and starch for tissue engineering scaffolds. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 3345–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Shang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, J. Preparation and characterization of chitosan/galactosylated hyaluronic acid scaffolds for primary hepatocytes culture. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, Y.G.; Kawazoe, N.; Tateishi, T.; Chen, G. Preparation of chitosan scaffolds with a hierarchical porous structure. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2010, 93, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N.; Li, M.G.; Cooper, D.; Chen, X.B. Development of novel hybrid poly(l-lactide)/chitosan scaffolds using the rapid freeze prototyping technique. Biofabrication 2011, 3, 034105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellgren, K.L.; Ma, T. Perfusion conditioning of hydroxyapatite-chitosan-gelatin scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration from human mesenchymal stem cells. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2012, 6, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.W.; Tabata, Y.; Ikada, Y. Fabrication of porous gelatin scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Koh, C.G.; Lee, L.J. A novel 3-D model for cell culture and tissue engineering. Biomed. Microdevices 2009, 11, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.S.; Zhao, L.G.; Yin, Y.J.; Yao, K.D. Structure and properties of bilayer chitosan-gelatin scaffolds. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.X.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, G.; Franceschi, R. Engineering new bone tissue in vitro on highly porous poly(α-hydroxyl acids)/hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 54, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.Y.; Ma, D.H.K.; Lai, M.H.; Li, Y.T.; Chang, R.J.; Chen, L.M. Characterization of cross-linked porous gelatin carriers and their interaction with corneal endothelium: Biopolymer concentration effect. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, N.C. Proliferative capacity of the corneal endothelium. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2003, 22, 359–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.Y.; Chen, K.H.; Hsiue, G.H. Tissue-engineered human corneal endothelial cell sheet transplantation in a rabbit model using functional biomaterials. Transplantation 2007, 84, 1222–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.Y.; Hsieh, A.C. A gelatin-g-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) biodegradable in situ gelling delivery system for the intracameral administration of pilocarpine. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2372–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Fei, L.; Cui, F.; Tang, C.; Yin, C. Superporous hydrogels containing poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide)/O-carboxymethyl chitosan interpenetrating polymer networks. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.Y. Relationship between structure and cytocompatibility of divinyl sulfone cross-linked hyaluronic acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, J.-Y. Influence of Pre-Freezing Temperature on the Corneal Endothelial Cytocompatibility and Cell Delivery Performance of Porous Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Carriers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 18796-18811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818796
Lai J-Y. Influence of Pre-Freezing Temperature on the Corneal Endothelial Cytocompatibility and Cell Delivery Performance of Porous Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Carriers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(8):18796-18811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818796
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Jui-Yang. 2015. "Influence of Pre-Freezing Temperature on the Corneal Endothelial Cytocompatibility and Cell Delivery Performance of Porous Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Carriers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 8: 18796-18811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818796
APA StyleLai, J. -Y. (2015). Influence of Pre-Freezing Temperature on the Corneal Endothelial Cytocompatibility and Cell Delivery Performance of Porous Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Carriers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(8), 18796-18811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818796