Influence of Parathyroid Hormone-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles in Porous Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results
2.1.1. PTH-Loaded Nanoparticles (NPTH)
Morphological Analysis of NPTHs


| Sample | PTH Loading (%) | Encapsulation Efficiency (%) | Surface Adsorbed (%) | Entrapped (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPTH_01 (1 mg PTH + 9 mg BSA) | 2.6 ± 0.4 | 25.5 ± 1.5 | 77.9 ± 2.5 | 22.1 ± 2.5 |
| NPTH_02 (2 mg PTH + 8 mg BSA) | 6.7 ± 0.5 | 33.5 ± 0.8 | 89.2 ± 3.7 | 10.8 ± 3.7 |
| NPTH_03 (3 mg PTH + 7 mg BSA) | 7.1 ± 0.8 | 23.6 ± 0.9 | 86.3 ± 3.6 | 13.7 ± 3.6 |
Release Studies from Nanoparticles


Cell Viability Test

In Vitro Bioactivity Assay for PTH (1–34) from Nanoparticles


2.1.2. CH-G Scaffolds Embedded with NPTHs
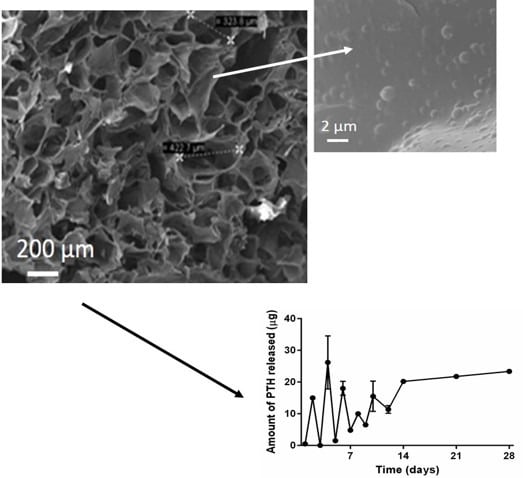
Scaffold Morphology

Dissolution Tests on NPTH-Loaded Scaffold

Release Studies from NPTH-Loaded Scaffolds

Cell Attachment and Viability Test

In Vitro Biomineralization Test

2.2. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation and Characterisation of PTH (Parathyroid Hormone) Loaded PLGA (Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) Nanoparticles (NPTH)
3.2.1. Synthesis of NPTHs
3.2.2. Characterisation of NPTHs
NPTH Morphology
PTH (1–34) Loading and Encapsulation Efficiency
In Vitro PTH (1–34) Release Studies
Tris-Tricine Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
Cell Viability Studies
In Vitro Bioactivity Assay for PTH (1–34)
In Vitro Bio-Mineralization Test on PTH-Loaded Nanoparticles
3.3. Incorporation of NPTH within CH-G Scaffolds
3.3.1. Dissolution Tests
3.3.2. PTH Release from Scaffolds
3.3.3. hFOB Cell Seeding, Attachment and Viability on CH-G Scaffold
3.3.4. In Vitro Bio-Mineralization Test
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borenstein, J.T.; Weinberg, E.J.; Orrick, B.K.; Sundback, C.; Kaazempur-Mofrad, M.R.; Vacanti, J.P. Microfabrication of three-dimensional engineered scaffolds. Tissue Eng. 2007, 13, 1837–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobsa, S.; Saltzman, W.M. Bioengineering approaches to controlled protein delivery. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 63, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; Yuk, S.H. Polymeric protein delivery systems. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 669–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Shin, H. Matrices and scaffolds for delivery of bioactive molecules in bone and cartilage tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 339–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasita, R.; Katti, D.S. Growth factor-delivery systems for tissue engineering: A materials perspective. Expert Rev. Med. Device 2006, 3, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zisch, A.H.; Lutolf, M.P.; Hubbell, J.A. Biopolymeric delivery matrices for angiogenic growth factors. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2003, 12, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, A.; Nishikawa, Y.; Nishino, M.; Kaneko, S.; Tanabe, T.; Yamauchi, K. Modified keratin sponge: Binding of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and osteoblast differentiation. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 102, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonadio, J.; Smiley, E.; Patil, P.; Goldstein, S. Localized, direct plasmid gene delivery in vivo: Prolonged therapy results in reproducible tissue regeneration. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Yu, M.; Zong, X.H.; Chiu, J.; Fang, D.F.; Seo, Y.S.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B.; Hadjiargyrou, M. Control of degradation rate and hydrophilicity in electrospun non-woven poly(d,l-lactide) nanofiber scaffolds for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4977–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahon, E.; Salvati, A.; Bombelli, F.B.; Lynch, I.; Dawson, K.A. Designing the nanoparticle-biomolecule interface for “targeting and therapeutic delivery”. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.P.; Hu, J.L.; Park, H.; Lee, M. Chitosan-based nanoparticles as a sustained protein release carrier for tissue engineering applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2012, 100A, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, P.X. Biomimetic materials for tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandagiri, V.K.; Gentile, P.; Chiono, V.; Tonda-Turo, C.; Matsiko, A.; Ramtoola, Z.; Montevecchi, F.M.; Ciardelli, G. Incorporation of PLGA nanoparticles into porous chitosan-gelatin scaffolds: Influence on the physical properties and cell behavior. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2011, 4, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madihally, S.V.; Matthew, H.W.T. Porous chitosan scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Baek, S.D.; Venkatesan, J.; Bhatnagar, I.; Chang, H.K.; Kim, H.T.; Kim, S.K. In vivo study of chitosan-natural nano hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 67, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VandeVord, P.J.; Matthew, H.W.T.; DeSilva, S.P.; Mayton, L.; Wu, B.; Wooley, P.H. Evaluation of the biocompatibility of a chitosan scaffold in mice. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 59, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.K. Chitosan composites for bone tissue engineering-an overview. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2252–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonda-Turo, C.; Gentile, P.; Saracino, S.; Chiono, V.; Nandagiri, V.K.; Muzio, G.; Canuto, R.A.; Ciardelli, G. Comparative analysis of gelatin scaffolds crosslinked by genipin and silane coupling agent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, D.S.; Li, T.Y.; Ding, J.X.; Liu, J.G.; Li, B.S.; Chen, X.S. Gelatin tight-coated poly(lactide-co-glycolide) scaffold incorporating rhbmp-2 for bone tissue engineering. Materials 2015, 8, 1009–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiono, V.; Pulieri, E.; Vozzi, G.; Ciardelli, G.; Ahluwalia, A.; Giusti, P. Genipin-crosslinked chitosan/gelatin blends for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Mater. 2008, 19, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, P.; Mattioli-Belmonte, M.; Chiono, V.; Ferretti, C.; Baino, F.; Tonda-Turo, C.; Vitale-Brovarone, C.; Pashkuleva, I.; Reis, R.L.; Ciardelli, G. Bioactive glass/polymer composite scaffolds mimicking bone tissue. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2012, 100A, 2654–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codrons, V.; Vanderbist, F.; Verbeeck, R.K.; Arras, M.; Lison, D.; Preat, V.; Vanbever, R. Systemic delivery of parathyroid hormone (1–34) using inhalation dry powders in rats. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 92, 938–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Gegg, C.A.; Hu, J.C.; Reddi, A.H.; Athanasiou, K.A. Thyroid hormones enhance the biomechanical functionality of scaffold-free neocartilage. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Pettway, G.J.; McCauley, L.K.; Ma, P.X. Pulsatile release of parathyroid hormone from an implantable delivery system. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4124–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Nagase, Y.; Iga, K.; Kawase, M.; Oka, M.; Yanai, S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Nakagawa, S.; Fukuda, T.; Adachi, H.; et al. Prevention of bone loss in ovariectomized rats by pulsatile transdermal iontophoretic administration of human PTH (1–34). J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukayama, S.; Royo, M.; Sugita, M.; Imrich, A.; Chorev, M.; Suva, L.J.; Rosenblatt, M.; Tashjian, A.H. New insights into interactions between the human PTH/PTHrP receptor and agonist/antagonist binding. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metabol. 1998, 274, E297–E303. [Google Scholar]
- Bellows, C.G.; Ishida, H.; Aubin, J.E.; Heersche, J.N.M. Parathyroid-hormone reversibly suppresses the differentiation of osteoprogenitor cells into functional osteoblasts. Endocrinology 1990, 127, 3111–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, M. Skeletal remodeling in health and disease. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neer, R.M.; Arnaud, C.D.; Zanchetta, J.R.; Prince, R.; Gaich, G.A.; Reginster, J.Y.; Hodsman, A.B.; Eriksen, E.F.; Ish-Shalom, S.; Genant, H.K.; et al. Effect of parathyroid hormone (1–34) on fractures and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1434–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabari, R.M.; Ryan, B.; Ahmad, W.; Ramtoola, Z. Physical and structural stability of the monoclonal antibody, trastuzumab (Herceptin®), intravenous solutions. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2013, 14, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aleksyniene, R.; Thomsen, J.S.; Eckardt, H.; Bundgaard, K.G.; Lind, M.; Hvid, I. Parathyroid hormone PTH (1–34) increases the volume, mineral content, and mechanical properties of regenerated mineralizing tissue after distraction osteogenesis in rabbits. Acta Orthop. 2009, 80, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OʼBrien, C.A.; Jilka, R.L.; Fu, O.; Stewart, S.; Weinstein, R.S.; Manolagas, S.C. IL-6 is not required for parathyroid hormone stimulation of RANKL expression, osteoclast formation, and bone loss in mice. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2004, 19, S335–S335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, K.E.S.; Reeve, J. Parathyroid hormone—A bone anabolic and catabolic agent. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2005, 5, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.B.; Pettway, G.J.; McCauley, L.K.; Ma, P.X. The release profiles and bioactivity of parathyroid hormone from poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosman, F. Parathyroid hormone treatment for osteoporosis. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. 2008, 15, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosman, F.; Lindsay, R. Treatment with PTH Peptides. In Osteoporosis, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 1793–1808. [Google Scholar]
- Cranney, A.; Adachi, J.D.; Guyatt, G.; Papaioannou, A.; Robinson, V.A.; Shea, B.J.; Tugwell, P.; Waldegger, L.M.; Weaver, B.; Wells, G.; et al. Risedronate for the prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. (Withdrawn Paper. 2003 art no. CD004523). Cochrane Libr. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grey, A. Emerging pharmacologic therapies for osteoporosis. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2007, 12, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perets, A.; Baruch, Y.; Weisbuch, F.; Shoshany, G.; Neufeld, G.; Cohen, S. Enhancing the vascularization of three-dimensional porous alginate scaffolds by incorporating controlled release basic fibroblast growth factor microspheres. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2003, 65A, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, M.; Wirth, M.; Pittner, F.; Gabor, F. Stabilisation and determination of the biological activity of l-asparaginase in poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) nanospheres. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 256, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinel, L.; Illi, O.E.; Zapf, J.; Malfanti, M.; Merkle, H.P.; Gander, B. Stabilizing insulin-like growth factor-I in poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres. J. Control. Release 2001, 70, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilati, U.; Allemann, E.; Doelker, E. Strategic approaches for overcoming peptide and protein instability within biodegradable nano- and microparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2005, 59, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilati, U.; Allemann, E.; Doelker, E. Poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) protein-loaded nanoparticles prepared by the double emulsion method-processing and formulation issues for enhanced entrapment efficiency. J. Microencapsul. 2005, 22, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanello, M.; Moro, L.; Pirulli, D.; Crovella, S.; DʼAndrea, P. Effects of cAMP on intercellular coupling and osteoblast differentiation. Biochem. Biophs. Res. Commun. 2001, 282, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Raggatt, L.J.; Partridge, N.C. Parathyroid hormone: A double-edged sword for bone metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 15, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proos, E.R.; Prescott, J.H.; Staples, M.A. Long-term stability and in vitro release of hPTH (1–34) from a multi-reservoir array. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivadas, N.; O’Rourke, D.; Tobin, A.; Buckley, V.; Ramtoola, Z.; Kelly, J.G.; Hickey, A.J.; Cryan, S.A. A comparative study of a range of polymeric microspheres as potential carriers for the inhalation of proteins. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 358, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoyele, S.A.; Sivadas, N.; Cryan, S.A. The effects of excipients and particle engineering on the biophysical stability and aerosol performance of parathyroid hormone (1–34) prepared as a dry powder for inhalation. AAPS Pharmscitech 2011, 12, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gentile, P.; Nandagiri, V.K.; Pabari, R.; Daly, J.; Tonda-Turo, C.; Ciardelli, G.; Ramtoola, Z. Influence of Parathyroid Hormone-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles in Porous Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 20492-20510. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160920492
Gentile P, Nandagiri VK, Pabari R, Daly J, Tonda-Turo C, Ciardelli G, Ramtoola Z. Influence of Parathyroid Hormone-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles in Porous Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(9):20492-20510. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160920492
Chicago/Turabian StyleGentile, Piergiorgio, Vijay Kumar Nandagiri, Ritesh Pabari, Jacqueline Daly, Chiara Tonda-Turo, Gianluca Ciardelli, and Zebunnissa Ramtoola. 2015. "Influence of Parathyroid Hormone-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles in Porous Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 9: 20492-20510. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160920492
APA StyleGentile, P., Nandagiri, V. K., Pabari, R., Daly, J., Tonda-Turo, C., Ciardelli, G., & Ramtoola, Z. (2015). Influence of Parathyroid Hormone-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles in Porous Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(9), 20492-20510. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160920492