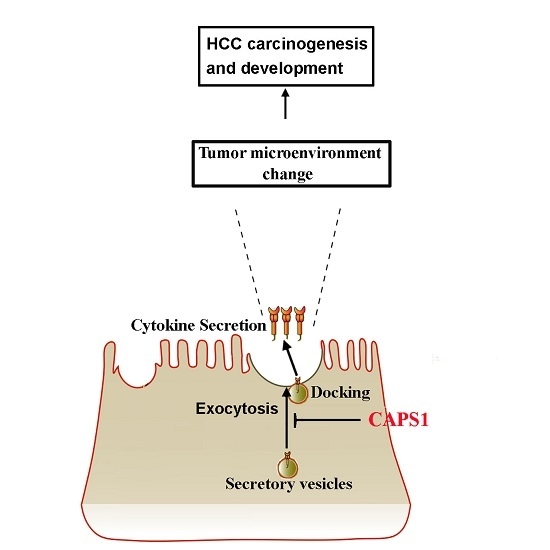
CAPS1 Negatively Regulates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development through Alteration of Exocytosis-Associated Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Reduced CAPS1 Expression in HCC Tissues and HCC Cells
2.2. Decreased CAPS1 Expression Was Associated with Aggressive Tumor Phenotypes in HCC Patients
2.3. Decreased CAPS1 Expression Correlated with Poor Prognosis of HCC
2.4. Overexpression of CAPS1 Inhibited Cell Growth and Migration, Decreased the Number of Membrane-Enclosed Vesicles and Altered Tumor Microenvironment in HCC Cell Lines
2.5. Overexpression of CAPS1 Reduces Tumor Growth in Xenograft-Bearing Nude Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Western Blotting
4.3. Immunohistochemistry and Evaluation
4.4. Establishment of Stable CAPS1 Overexpression Clones
4.5. Cell Proliferation, Growth and Migration Assay
4.6. ELISA for Cytokine
4.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.8. Xenografted Tumor Model
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perz, J.F.; Armstrong, G.L.; Farrington, L.A.; Hutin, Y.J.; Bell, B.P. The contributions of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections to cirrhosis and primary liver cancer worldwide. J. Hepatol. 2006, 45, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrero, J.A.; Kudo, M.; Bronowicki, J.P. The challenge of prognosis and staging for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncologist 2010, 15 (Suppl. S4), 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walent, J.H.; Porter, B.W.; Martin, T.F. A novel 145 kd brain cytosolic protein reconstitutes Ca2+-regulated secretion in permeable neuroendocrine cells. Cell 1992, 70, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.C.; Nestvogel, D.; Ratai, O.; Schirra, C.; Stevens, D.R.; Brose, N.; Rhee, J.; Rettig, J. Secretory vesicle priming by CAPS is independent of its SNARE-binding MUN domain. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 902–909. [Google Scholar]
- Sadakata, T.; Washida, M.; Furuichi, T. Alternative splicing variations in mouse CAPS2: Differential expression and functional properties of splicing variants. BMC Neurosci. 2007, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speidel, D.; Varoqueaux, F.; Enk, C.; Nojiri, M.; Grishanin, R.N.; Martin, T.F.; Hofmann, K.; Brose, N.; Reim, K. A family of Ca2+-dependent activator proteins for secretion: Comparative analysis of structure, expression, localization, and function. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 52802–52809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ann, K.; Kowalchyk, J.A.; Loyet, K.M.; Martin, T.F. Novel Ca2+-binding protein (CAPS) related to UNC-31 required for Ca2+-activated exocytosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 19637–19640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizaki, T.; Walent, J.H.; Kowalchyk, J.A.; Martin, T.F. A key role for a 145-kDa cytosolic protein in the stimulation of Ca2+-dependent secretion by protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 23972–23981. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller, S.; Rogers, H.A.; Lyon, P.; Rand, V.; Adamowicz-Brice, M.; Clifford, S.C.; Hayden, J.T.; Dyer, S.; Pfister, S.; Korshunov, A.; et al. Genome-wide molecular characterization of central nervous system primitive neuroectodermal tumor and pineoblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2011, 13, 866–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Xue, R.; Huang, X.; Zhang, D.; Dong, L.; Wu, H.; Shen, X. Proteomic profiling of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma with magnetic bead-based matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2011, 43, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.Y.; Ye, S.L.; Liu, Y.K.; Qin, L.X.; Sun, H.C.; Ye, Q.H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, S.J.; Li, Y.; et al. A decade’s studies on metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 130, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Cancer Genome Consortium Data Portal, CADPS Entry. Available online: https://dcc.icgc.org/genes/ENSG00000163618 (accessed on 1 September 2016).
- Farina, M.; van de Bospoort, R.; He, E.; Persoon, C.M.; van Weering, J.R.; Broeke, J.H.; Verhage, M.; Toonen, R.F. CAPS-1 promotes fusion competence of stationary dense-core vesicles in presynaptic terminals of mammalian neurons. eLife 2015, 4, e05438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nojiri, M.; Loyet, K.M.; Klenchin, V.A.; Kabachinski, G.; Martin, T.F. CAPS activity in priming vesicle exocytosis requires CK2 phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 18707–18714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Gea, V.; Toffanin, S.; Friedman, S.L.; Llovet, J.M. Role of the microenvironment in the pathogenesis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.W.; Karin, M. A cytokine-mediated link between innate immunity, inflammation, and cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Z.Z.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Q.; Yang, G.H.; Ding, Z.B.; Fan, J.; Zhou, J. High expressions of vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor predict poor prognosis in alpha-fetoprotein-negative hepatocellular carcinoma patients after curative resection. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 135, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeini, A.; Cornella, H.; Villanueva, A. Emerging signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2012, 1, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgoyne, R.D.; Morgan, A. Secretory granule exocytosis. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 581–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, D.J.; Kowalchyk, J.; Daily, N.; Petrie, M.; Martin, T.F. CAPS drives trans-SNARE complex formation and membrane fusion through syntaxin interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17308–17313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grishanin, R.N.; Klenchin, V.A.; Loyet, K.M.; Kowalchyk, J.A.; Ann, K.; Martin, T.F. Membrane association domains in Ca2+-dependent activator protein for secretion mediate plasma membrane and dense-core vesicle binding required for Ca2+-dependent exocytosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 24, 22025–22034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, T.; Beppu, T.; Okabe, H.; Nitta, H.; Imai, K.; Hayashi, H.; Chikamoto, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Ikeshima, S.; Kuramoto, M.; et al. Predictive factors of pathological vascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma within 3 cm and 3 nodules without radiological vascular invasion. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Hu, L.; Zhai, L.; Xue, R.; Ye, J.; Chen, L.; Cheng, G.; Mruk, J.; Kunapuli, S.P.; et al. Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 2 receptor is expressed in platelets and enhances platelet activation and thrombosis. Circulation 2015, 131, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Xue, R.; Weng, S.; Wu, J.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ji, L.; Hu, T.; Liu, T.; Huang, X.; et al. BIRC6 promotes hepatocellular carcinogenesis: Interaction of BIRC6 with p53 facilitating p53 degradation. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E475–E487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Fu, D.; Tang, W.; Cai, Y.; Ma, D.; Wang, H.; Xue, R.; Liu, T.; Huang, X.; Dong, L.; et al. Ubiquitin C-terminal Hydrolase 37, a novel predictor for hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence, promotes cell migration and invasion via interacting and deubiquitinating PRP19. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Feng, X.; Zhang, S.; Ren, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, B.; Lv, B.; Cai, Y.; Xia, J.; Ge, N. Caveolin-1 Confers Resistance of Hepatoma Cells to Anoikis by Activating IGF-1 Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 1223–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Characteristics | CAPS1 Expression in Tumor Tissue | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | p Value | |
| Patients | 121 | 20 | |
| Gender | |||
| Female | 19 | 2 | 0.746 |
| Male | 102 | 18 | |
| Age (years) | |||
| ≤52 | 67 | 11 | 0.975 |
| >52 | 54 | 9 | |
| HBsAg | |||
| Negative | 16 | 0 | 0.178 |
| Positive | 105 | 20 | |
| HCV | |||
| Negative | 119 | 20 | 1.000 |
| Positive | 2 | 0 | |
| ALT (units/L) | |||
| ≤75 | 99 | 20 | 0.081 |
| >75 | 22 | 0 | |
| Preoperative AFP, ng/mL | |||
| ≤20 | 55 | 8 | 0.649 |
| >20 | 66 | 12 | |
| Liver cirrhosis | |||
| No | 22 | 2 | 0.561 |
| Yes | 99 | 18 | |
| BCLC stage | |||
| A | 33 | 5 | 0.832 |
| B/C | 88 | 15 | |
| Tumor size (cm) | |||
| ≤5 | 60 | 9 | 0.704 |
| >5 | 61 | 11 | |
| Tumor number | |||
| Single | 90 | 19 | 0.080 |
| Multiple | 31 | 1 | |
| Tumor encapsulation | |||
| No | 77 | 7 | 0.016 |
| Complete | 44 | 13 | |
| Vascular invasion | |||
| No | 82 | 15 | 0.518 |
| Yes | 39 | 5 | |
| TNM stage | |||
| I | 67 | 18 | 0.003 |
| II–III | 54 | 2 | |
| Tumor differentiation | |||
| I–II | 114 | 19 | 1.000 |
| III–IV | 7 | 1 | |
| Variables | OS | TTR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p | |
| Gender (female vs. male) | 0.930 | 0.841 | 0.842 | 0.571 |
| (0.456–1.894) | (0.464–1.528) | |||
| Age, years (≤52 vs. >52) | 0.939 | 0.813 | 0.909 | 0.677 |
| (0.558–1.581) | (0.581–1.423) | |||
| HBsAg (positive vs. negative) | 0.957 | 0.918 | 0.716 | 0.349 |
| (0.410–2.232) | (0.356–1.414) | |||
| HCV (positive vs. negative) | 1.276 | 0.810 | 2.300 | 0.247 |
| (0.176–9.262) | (0.562–9.416) | |||
| BCLC stage (A vs. B/C) | 3.653 | 0.003 | 1.618 | 0.080 |
| (1.568–8.512) | (0.944–2.775) | |||
| Liver cirrhosis (no vs. yes) | 1.609 | 0.272 | 1.463 | 0.262 |
| (0.689–3.757) | (0.752–2.846) | |||
| ALT, units/L (≤75 vs. >75) | 1.192 | 0.629 | 1.542 | 0.147 |
| (0.584–2.430) | (0.858–2.768) | |||
| AFP, ng/mL (≤20 vs. >20) | 1.755 | 0.043 | 1.129 | 0.592 |
| (1.019–3.022) | (0.724–1.761) | |||
| Tumor differentiation (I–II vs. III–IV) | 1.007 | 0.989 | 2.005 | 0.081 |
| (0.364–2.786) | (0.919–4.374) | |||
| Tumor encapsulation (complete vs. none) | 0.693 | 0.185 | 0.570 | 0.020 |
| (0.403–1.192) | (0.356–0.914) | |||
| Tumor size, cm (≤5 vs. >5) | 2.755 | 0.001 | 2.152 | 0.001 |
| (1.527–4.968) | (1.351–3.428) | |||
| Tumor number (single vs. multiple) | 1.282 | 0.398 | 1.450 | 0.148 |
| (0.721–2.282) | (0.877–2.399) | |||
| TNM stage (I vs. II–III) | 2.776 | 0.000 | 2.147 | 0.001 |
| (1.632–4.722) | (1.377–3.348) | |||
| Vascular invasion (no vs. yes) | 1.837 | 0.022 | 1.887 | 0.006 |
| (1.019–3.092) | (1.196–2.979) | |||
| CAPS1 in tumor tissue (negative vs. positive) | 0.276 | 0.014 | 0.373 | 0.019 |
| (0.099–0.767) | (0.198–0.864) | |||
| Variables | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p Values |
|---|---|---|
| † OS | ||
| BCLC stage (A vs. B/C) | 1.998 (0.710–5.627) | 0.190 |
| AFP, ng/mL (≤20 vs. >20) | 1.791 (1.005–3.189) | 0.048 |
| Tumor size, cm (≤5 vs. >5) | 1.877 (0.915–3.852) | 0.086 |
| TNM stage (I vs. II–III) | 1.468 (0.805–2.678) | 0.210 |
| Vascular invasion (no vs. yes) | 1.195 (0.692–2.063) | 0.523 |
| CAPS1 expression in tumor tissue (negative vs. positive) | 0.209 (0.064–0.682) | 0.010 |
| ‡ TTR | ||
| Tumor encapsulation (complete vs. none) | 0.586 (0.355–0.968) | 0.037 |
| Tumor size, cm (≤5 vs. >5) | 1.942 (1.145–3.294) | 0.014 |
| TNM stage (I vs. II–III) | 1.319 (0.795–2.191) | 0.284 |
| Vascular invasion (no vs. yes) | 1.401 (0.863–2.740) | 0.173 |
| CAPS1 expression in tumor tissue (negative vs. positive) | 0.324 (0.143–0.733) | 0.007 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, R.; Tang, W.; Dong, P.; Weng, S.; Ma, L.; Chen, S.; Liu, T.; Shen, X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. CAPS1 Negatively Regulates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development through Alteration of Exocytosis-Associated Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101626
Xue R, Tang W, Dong P, Weng S, Ma L, Chen S, Liu T, Shen X, Huang X, Zhang S, et al. CAPS1 Negatively Regulates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development through Alteration of Exocytosis-Associated Tumor Microenvironment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(10):1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101626
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Ruyi, Wenqing Tang, Pingping Dong, Shuqiang Weng, Lijie Ma, She Chen, Taotao Liu, Xizhong Shen, Xiaowu Huang, Si Zhang, and et al. 2016. "CAPS1 Negatively Regulates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development through Alteration of Exocytosis-Associated Tumor Microenvironment" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 10: 1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101626
APA StyleXue, R., Tang, W., Dong, P., Weng, S., Ma, L., Chen, S., Liu, T., Shen, X., Huang, X., Zhang, S., & Dong, L. (2016). CAPS1 Negatively Regulates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development through Alteration of Exocytosis-Associated Tumor Microenvironment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(10), 1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101626