EGFR and KRAS Mutations Predict the Incidence and Outcome of Brain Metastases in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient and Tumor Characteristics
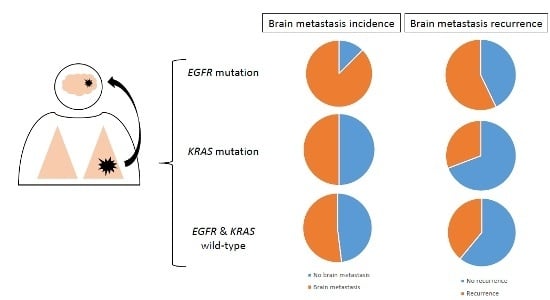
2.2. Association between Mutation Status and Brain Metastases (BM) Incidence and Recurrence
2.3. Association between Mutations Status, BM and Survival
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Patients and Data Collection
4.2. Molecular Testing
4.2.1. Pre-analytical Stage
4.2.2. High Resolution Melting (HRM)
4.3. Sequencing
4.4. Treatment
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussbaum, E.S.; Djalilian, H.R.; Cho, K.H.; Hall, W.A. Brain metastases. Histology, multiplicity, surgery, and survival. Cancer 1996, 78, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taillibert, S.; Le Rhun, É. Epidemiology of brain metastases. Cancer Radiother. 2015, 19, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimm, S.; Wampler, G.L.; Stablein, D.; Hazra, T.; Young, H.F. Intracerebral metastases in solid-tumor patients: Natural history and results of treatment. Cancer 1981, 48, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, Y.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Kang, Y.N.; Jang, J.S.; Kang, J.-H.; Jung, S.-L.; Sung, S.Y.; Jo, I.Y.; Park, H.H.; Lee, D.-S.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2015, 33, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besse, B.; Le Moulec, S.; Mazières, J.; Senellart, H.; Barlesi, F.; Chouaid, C.; Dansin, E.; Bérard, H.; Falchero, L.; Gervais, R.; et al. Bevacizumab in Patients with Nonsquamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Asymptomatic, Untreated Brain Metastases (BRAIN): A Nonrandomized, Phase II Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1896–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosell, R.; Carcereny, E.; Gervais, R.; Vergnenegre, A.; Massuti, B.; Felip, E.; Palmero, R.; Garcia-Gomez, R.; Pallares, C.; Sanchez, J.M.; et al. Spanish Lung Cancer Group in collaboration with Groupe Français de Pneumo-Cancérologie and Associazione Italiana Oncologia Toracica Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.-L.; Thongprasert, S.; Yang, C.-H.; Chu, D.-T.; Saijo, N.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Han, B.; Margono, B.; Ichinose, Y.; et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequist, L.V.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Yamamoto, N.; O’Byrne, K.; Hirsh, V.; Mok, T.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Tsai, C.-M.; Boyer, M.; et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Kim, D.-W.; Nakagawa, K.; Seto, T.; Crinó, L.; Ahn, M.-J.; de Pas, T.; Besse, B.; Solomon, B.J.; Blackhall, F.; et al. Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, D.B.; Shaw, A.T.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Solomon, B.J.; Riely, G.J.; Ahn, M.-J.; Zhou, C.; Shreeve, S.M.; Selaru, P.; Polli, A.; et al. Clinical experience with crizotinib in patients with advanced ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer and brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuler, M.; Wu, Y.-L.; Hirsh, V.; O’Byrne, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Mok, T.; Popat, S.; Sequist, L.V.; Massey, D.; Zazulina, V.; et al. First-line afatinib versus chemotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and common epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations and brain metastases. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crinò, L.; Ahn, M.-J.; De Marinis, F.; Groen, H.J.M.; Wakelee, H.; Hida, T.; Mok, T.; Spigel, D.; Felip, E.; Nishio, M.; et al. Multicenter phase II study of whole-body and intracranial activity with ceritinib in patients with ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with chemotherapy and crizotinib: Results from ASCEND-2. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2866–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeken, J.F.; Löscher, W. The blood-brain barrier and cancer: Transporters, treatment, and Trojan horses. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1663–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrobel, J.K.; Toborek, M. Blood-brain barrier remodeling during brain metastasis formation. Mol. Med. Camb. Mass 2016, 22, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Roca, C.; Raynaud, C.M.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Mercier, O.; Commo, F.; Morat, L.; Sabatier, L.; Dartevelle, P.; Taranchon, E.; Besse, B.; et al. Differential expression of biomarkers in primary non-small cell lung cancer and metastatic sites. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2009, 4, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanibuchi, M.; Kim, S.-J.; Fidler, I.J.; Nishioka, Y. The molecular biology of lung cancer brain metastasis: an overview of current comprehensions and future perspectives. J. Med. Investig. JMI 2014, 61, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascaux, C.; Iannino, N.; Martin, B.; Paesmans, M.; Berghmans, T.; Dusart, M.; Haller, A.; Lothaire, P.; Meert, A.-P.; Noel, S.; et al. The role of RAS oncogene in survival of patients with lung cancer: A systematic review of the literature with meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guibert, N.; Ilie, M.; Long, E.; Hofman, V.; Bouhlel, L.; Brest, P.; Mograbi, B.; Marquette, C.H.; Didier, A.; Mazieres, J.; et al. KRAS mutations in lung adenocarcinoma: Molecular and epidemiological characteristics, methods for detection, and therapeutic strategy perspectives. Curr. Mol. Med. 2015, 15, 418–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramlau, R.; Cufer, T.; Berzinec, P.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Olszewski, W.; Popper, H.; Bajcic, P.; Dušek, L.; Zbozinkova, Z.; Pirker, R.; INSIGHT study team. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer in the real-world setting in central Europe: The INSIGHT study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1370–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.-Y.; Na, I.I.; Kim, C.H.; Park, S.; Baek, H.; Yang, S.H. EGFR mutation and brain metastasis in pulmonary adenocarcinomas. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J.; Chen, M.; Xiao, N.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Yang, M.; Liu, L.; Chen, L. EGFR mutations are associated with higher incidence of distant metastases and smaller tumor size in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer based on PET/CT scan. Med. Oncol. Northwood Lond. Engl. 2016, 33, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, M.Y.; Ahn, H.K.; Park, K.R.; Park, H.-S.; Kang, S.M.; Park, I.; Kim, Y.S.; Hong, J.; Sym, S.J.; Park, J.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation and pattern of brain metastasis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2016, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renaud, S.; Seitlinger, J.; Falcoz, P.-E.; Schaeffer, M.; Voegeli, A.-C.; Legrain, M.; Beau-Faller, M.; Massard, G. Specific KRAS amino acid substitutions and EGFR mutations predict site-specific recurrence and metastasis following non-small-cell lung cancer surgery. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriks, L.E.L.; Smit, E.F.; Vosse, B.A.H.; Mellema, W.W.; Heideman, D.A.M.; Bootsma, G.P.; Westenend, M.; Pitz, C.; de Vries, G.J.; Houben, R.; et al. EGFR mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients: More prone to development of bone and brain metastases? Lung Cancer Amst. Neth. 2014, 84, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.T.; Lou, E.; Hsu, M.; Yu, H.A.; Naidoo, J.; Zauderer, M.G.; Sima, C.; Johnson, M.L.; Daras, M.; DeAngelis, L.M.; et al. Serum biomarkers associated with clinical outcomes fail to predict brain metastases in patients with stage IV non-small cell lung cancers. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Sun, S.-Z.; Yang, M.; Shi, J.-L.; Xu, W.; Wang, X.-F.; Song, M.-M.; Chen, H.-M. The correlation between EGFR mutation status and the risk of brain metastasis in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. J. Neurooncol. 2015, 124, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, S.; D’Argento, E.; Basso, M.; Strippoli, A.; Dadduzio, V.; Cerchiaro, E.; Martini, M.; Cassano, A.; Barone, C. Different EGFR gene mutations in Exon 18, 19 and 21 as prognostic and predictive markers in NSCLC: A single institution analysis. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2016, 20, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.M.; Cooper, B.T.; Chachoua, A.; Butler, J.; Donahue, B.; Silverman, J.S.; Kondziolka, D. Survival but not brain metastasis response relates to lung cancer mutation status after radiosurgery. J. Neurooncol. 2016, 126, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Cao, J.; Su, P.; Lian, J.; Song, X.; Yang, W.; Han, S.; Xi, Y.; Wang, Y. Exon 19 deletion of epidermal growth factor receptor is associated with prolonged survival in brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2015, 36, 9251–9258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Trevino, J.; Bora-Singhal, N.; Coppola, D.; Haura, E.; Altiok, S.; Chellappan, S.P. EGFR/Src/Akt signaling modulates Sox2 expression and self-renewal of stem-like side-population cells in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2012, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, G.L.; Vattimo, E.F.D.Q.; Junior, G.D. Identifying activating mutations in the EGFR gene: Prognostic and therapeutic implications in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2015, 41, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Z. Meta-analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor and KRAS gene status between primary and corresponding metastatic tumours of non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 27, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, P.; Yates, J.W.; Yang, Z.; Kim, D.-W.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Cantarini, M.; Pickup, K.; Jordan, A.; Hickey, M.; Grist, M.; et al. Preclinical comparison of osimertinib with other EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Brain metastases models, and early evidence of clinical brain metastases activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5130–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyokawa, G.; Seto, T.; Takenoyama, M.; Ichinose, Y. Insights into brain metastasis in patients with ALK+ lung cancer: Is the brain truly a sanctuary? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015, 34, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstraw, P.; Crowley, J.; Chansky, K.; Giroux, D.J.; Groome, P.A.; Rami-Porta, R.; Postmus, P.E.; Rusch, V.; Sobin, L. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer International Staging Committee; Participating Institutions The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals for the revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM Classification of malignant tumours. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2007, 2, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer Oxf. Engl. 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacot, W.; Lopez-Crapez, E.; Thezenas, S.; Senal, R.; Fina, F.; Bibeau, F.; Romieu, G.; Lamy, P.-J. Lack of EGFR-activating mutations in European patients with triple-negative breast cancer could emphasise geographic and ethnic variations in breast cancer mutation profiles. Breast Cancer Res. BCR 2011, 13, R133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masters, G.A.; Temin, S.; Azzoli, C.G.; Giaccone, G.; Baker, S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Ellis, P.M.; Gajra, A.; Rackear, N.; Schiller, J.H.; et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Systemic Therapy for Stage IV Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3488–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Popat, S.; Reinmuth, N.; de Ruysscher, D.; Kerr, K.M.; Peters, S.; ESMO Guidelines Working Group. Metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, iii27–iii39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soffietti, R.; Cornu, P.; Delattre, J.Y.; Grant, R.; Graus, F.; Grisold, W.; Heimans, J.; Hildebrand, J.; Hoskin, P.; Kalljo, M.; et al. EFNS Guidelines on diagnosis and treatment of brain metastases: Report of an EFNS Task Force. Eur. J. Neurol. 2006, 13, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Rhun, É.; Dhermain, F.; Noël, G.; Reyns, N.; Carpentier, A.; Mandonnet, E.; Taillibert, S.; Metellus, P.; ANOCEF. l’Association des neuro-oncologues d’expression franc¸aise ANOCEF guidelines for the management of brain metastases. Cancer Radiothérapie J. Société Fr. Radiothérapie Oncol. 2015, 19, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Total n (%) | EGFR Mutant n (%) | KRAS Mutant n (%) | EGFR and KRAS WT n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall n (%) | 142 (100.00) | 16 (11.27) | 47 (33.10) | 79 (55.63) | |
| Patients’ Characteristics | |||||
| Median age (years) | 62 (31–88) | 62 (45–87) | 60 (37–76) | 63 (31–88) | 0.338 |
| Sex F/M | 48/94 | 7/9 | 16/31 | 25/54 | 0.46 |
| Ethnicity | 0.006 * | ||||
| Caucasian | 140 (98.59) | 16 (100.00) | 47 (100.00) | 77 (97.47) | |
| Asian | 2 (1.41) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 2 (2.53) | |
| Smoking history | |||||
| Smoker | 108 (76.06) | 7 (43.75) | 42 (89.36) | 59 (74.68) | <0.001 * |
| Non-smoker | 31 (21.83) | 9 (56.25) | 3 (6.38) | 19 (24.05) | |
| ECOG PS | |||||
| 0–1 | 123 (86.62) | 14 (87.50) | 37 (78.72) | 72 (91.14) | 0.131 |
| ≥2 | 19 (13.38) | 2 (12.50) | 10 (21.28) | 7 (8.86) | |
| Disease Characteristics | |||||
| Pathology | |||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 127 (89.44) | 14 (87.50) | 46 (97.87) | 67 (84.81) | 0.050 * |
| Other | 15 (10.56) | 2 (12.50) | 1 (2.13) | 12 (15.19) | |
| Number of metastases | |||||
| 1 | 90 (63.38) | 10 (62.50) | 27 (57.45) | 53 (67.09) | 0.553 |
| ≥2 | 52 (36.62) | 6 (37.50) | 20 (42.55) | 26 (32.91) | |
| BM Characteristics | Total n (%) | EGFR Mutant n (%) | KRAS Mutant n (%) | EGFR and KRAS WT n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM Incidence | |||||
| Brain Metastasis | 0.031 * | ||||
| Yes | 81 (57.04) | 14 (87.50) | 26 (55.32) | 41 (51.90) | |
| No | 61 (42.96) | 2 (12.50) | 21 (44.68) | 38 (48.10) | |
| Synchronous | 52 (64.20) | 8 (57.14) | 18 (69.23) | 26 (63.41) | 0.741 |
| Metachronous | 29 (35.80) | 6 (42.86) | 8 (30.77) | 15 (26.59) | |
| Brain Metastasis Related Death | 0.528 | ||||
| Yes | 31 (42.26) | 7 (50.00) | 11 (44.00) | 13 (34.21) | |
| No | 46 (59.74) | 7 (50.00) | 14 (56.00) | 25 (65.79) | |
| BM Recurrence | |||||
| Recurrence | 0.047 * | ||||
| Yes n (%) | 41 (50.62) | 8 (57.14) | 8 (30.77) | 25 (60.98) | |
| No n (%) | 40 (49.38) | 6 (42.86) | 18 (69.23) | 16 (39.02) | |
| Time to Recurrence | 1.000 | ||||
| ≤12 months n (%) | 29 (70.73) | 6 (75.00) | 6 (75.00) | 17 (68.00) | |
| >12 months n (%) | 12 (29.27) | 2 (25.00) | 2 (25.00) | 8 (32.00) | |
| Characteristics | Univariate Analyses | Multivariate Analyses | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| BM Incidence | ||||||
| Age | 0.996 | 0.965–1.027 | 0.799 | 0.998 | 0.965–1.032 | 0.897 |
| Sex | 1.193 | 0.592–2.404 | 0.621 | 0.988 | 0.440–2.219 | 0.977 |
| ECOG PS | 1.041 | 0.391–2.769 | 0.936 | NA | NA | NA |
| Smoking status | 0.767 | 0.345–1.706 | 0.515 | 0.489 | 0.178–1.339 | 0.164 |
| Primary tumor local treatment | 1.384 | 0.541–3.545 | 0.498 | NA | NA | NA |
| Mutation status | 0.060 | 0.031 * | ||||
| EGFR mutant versus EGFR WT | 6.488 | 1.383–30.443 | 0.018 * | 8.745 | 1.743–43.881 | 0.008 * |
| KRAS mutant versus KRAS WT | 1.148 | 0.556–2.369 | 0.710 | 1.082 | 0.505–2.318 | 0.840 |
| BM Recurrence after Local Treatment | ||||||
| Age | 0.987 | 0.944–1.032 | 0.562 | 0.975 | 0.929–1.023 | 0.296 |
| Sex | 1.037 | 0.408–2.636 | 0.939 | 0.983 | 0.322–3.000 | 0.976 |
| ECOG PS | 0.510 | 0.137–1.898 | 0.315 | NA | NA | NA |
| Smoking status | 0.939 | 0.314–2.810 | 0.911 | 0.626 | 0.153–2.565 | 0.515 |
| Mutation status | 0.054 | 0.029 * | ||||
| EGFR mutant versus EGFR WT | 0.853 | 0.249–2.921 | 0.801 | 0.970 | 0.245–3.845 | 0.966 |
| KRAS mutant versus KRAS WT | 0.284 | 0.100–0.807 | 0.018 * | 0.234 | 0.078–0.699 | 0.009 * |
| Synchronous or metachronous BM | 1.786 | 0.712–4.480 | 0.216 | NA | NA | NA |
| BM local treatment | 0.709 | 0.236–2.133 | 0.541 | NA | NA | NA |
| Number of metastases | 0.962 | 0.390–2.370 | 0.932 | NA | NA | NA |
| Population | EGFR Mutant | KRAS Mutant | EGFR and KRAS WT | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFS and OS | ||||
| All patients n (%) Median OS (months) | 16 (11.27) 22 (4.36–39.64) | 47 (33.10) 9 (7.12–10.88) | 79 (55.63) 18 (12.30–23.70) | 0.196 |
| Patients with BM n (%) | 14 (17.28) | 26 (32.10) | 41 (50.62) | |
| Surgery and/or SRS | ||||
| Median PFS (months) Median OS (months) | 7 (6.12–7.88) 30 (4.24–55.77) | 9 (5.67–12.33) 22 (7.58–36.42) | 8 (5.08–9.16) 25 (20.44–29.56) | 0.227 0.822 |
| WBRT only | ||||
| Median PFS (months) Median OS (months) | 11 (0.00–23.88) 28 (0.00–73.09) | 9 (1.30–16.70) 7 (1.87–12.13) | 6 (5.08–6.92) 12 (5.36–18.65) | 0.272 0.208 |
| No local treatment | ||||
| Median PFS (months) Median OS (months) | 10 (8.40–11.60) 19 (1.85–36.15) | 5 (1.80–8.20) 5 (0.00–12.85) | 6 (3.23–8.77) 14 (12.22–14.78) | 0.229 0.010 * |
| Characteristics | Univariate Analyses | Multivariate Analyses | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| OS of Patients with Untreated BM | ||||||
| Age | 1.018 | 0.968–1.071 | 0.484 | NA | NA | NA |
| Sex | 1.41 | 0.310–6.044 | 0.657 | NA | NA | NA |
| ECOG PS | 8.366 | 1.643–42.606 | 0.011 * | 8.768 | 0.493–155.954 | 0.139 |
| Smoking status | 0.951 | 0.203–4.449 | 0.949 | NA | NA | NA |
| Mutation status | 0.010 * | 0.698 | ||||
| EGFR mutant versus EGFR WT | 0.536 | 0.136–2.115 | 0.374 | 0.589 | 0.134–2.581 | 0.482 |
| KRAS mutant versus KRAS WT | 7.130 | 1.240–41.012 | 0.028 * | 0.356 | 0.015–8.224 | 0.519 |
| Synchronous or metachronous BM | 1.017 | 0.339–3.047 | 0.976 | NA | NA | NA |
| Number of metastases | 11.548 | 2236–59.640 | 0.003 * | 6.669 | 1.022–43.541 | 0.047 * |
| References | Patients Number | Ethnicity | Pathology | NSCLC Stage | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [22] | 314 | Asian | ADC | All | Association between EGFR mutation and BM incidence |
| [23] | 401 | Asian | NSCLC | All | Association between EGFR mutation and BM incidence |
| [24] | 259 | Asian | NSCLC | Advanced | Association between EGFR mutation and synchronous BM and longer median BM-OS |
| [25] | 481 | Caucasian | NSCLC | Early | EGFR mutations predict BM, KRAS mutations predict pleuro-pericardial metastases |
| [26] | 189 | Caucasian | NSCLC | All | No association between EGFR and KRAS mutation status and BM incidence |
| [27] | 118 | NA | NSCLC | IV | No association between EGFR mutation status and BM incidence |
| [28] | 100 | Asian | EGFR-mutant ADC | All | Association between EGFR exon 19 deletion and BM incidence |
| [29] | 55 | Caucasian | EGFR-mutant NSCLC | All | Association between EGFR exon 19 deletion and BM incidence |
| [30] | 236 | NA | NSCLC | IV (BM) | Patients with EGFR mutant BM had improved survival |
| [31] | 106 | Asian | NSCLC | IV (BM) | Exon 19 deletion is an independent prognostic factor in BM from NSCLC |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomasini, P.; Serdjebi, C.; Khobta, N.; Metellus, P.; Ouafik, L.; Nanni, I.; Greillier, L.; Loundou, A.; Fina, F.; Mascaux, C.; et al. EGFR and KRAS Mutations Predict the Incidence and Outcome of Brain Metastases in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122132
Tomasini P, Serdjebi C, Khobta N, Metellus P, Ouafik L, Nanni I, Greillier L, Loundou A, Fina F, Mascaux C, et al. EGFR and KRAS Mutations Predict the Incidence and Outcome of Brain Metastases in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(12):2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122132
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomasini, Pascale, Cindy Serdjebi, Nataliya Khobta, Philippe Metellus, L’Houcine Ouafik, Isabelle Nanni, Laurent Greillier, Anderson Loundou, Frederic Fina, Celine Mascaux, and et al. 2016. "EGFR and KRAS Mutations Predict the Incidence and Outcome of Brain Metastases in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 12: 2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122132
APA StyleTomasini, P., Serdjebi, C., Khobta, N., Metellus, P., Ouafik, L., Nanni, I., Greillier, L., Loundou, A., Fina, F., Mascaux, C., & Barlesi, F. (2016). EGFR and KRAS Mutations Predict the Incidence and Outcome of Brain Metastases in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(12), 2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122132