The Transcription Factor OsWRKY45 Negatively Modulates the Resistance of Rice to the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Characterization of OsWRKY45
2.2. Antisense Expression of OsWRKY45
2.3. Silencing OsWRKY45 Enhances Levels of BPH-Induced Ethylene and H2O2 but Not of JA and SA
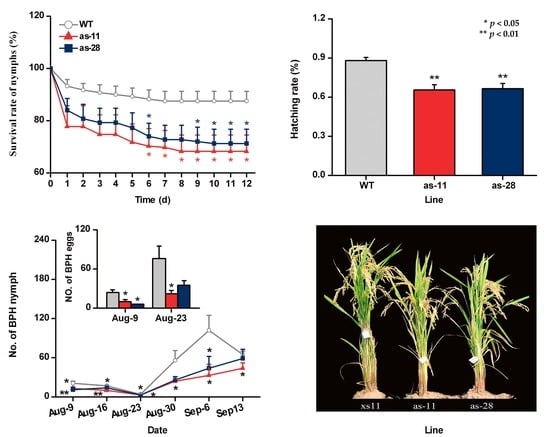
2.4. OsWRKY45 Negatively Mediates Rice Resistance to BPH
2.5. Effect of OsWRKY45 on Multitrophic Interactions in the Field
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Growth
4.2. Insects
4.3. Isolation and Characterization of OsWRKY45 cDNA
4.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.5. qRT-PCR
4.6. Generation and Characterization of Transgenic Plants
4.7. Plant Treatments
4.8. JA and SA Analysis
4.9. Hydrogen Peroxide Analysis
4.10. Ethylene Analysis
4.11. BPH Bioassays in the Laboratory
4.12. Field Experiment
4.13. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zavala, J.A.; Patankar, A.G.; Gase, K.; Baldwin, I.T. Constitutive and inducible trypsin proteinase inhibitor production incurs large fitness costs in Nicotiana attenuata. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1607–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, G.A.; Jander, G. Plant immunity to insect herbivores. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 41–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Q.; Baldwin, I.T. New insights into plant responses to the attack from insect herbivores. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2010, 44, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halitschke, R.; Schittko, U.; Pohnert, G.; Boland, W.; Baldwin, I.T. Molecular interactions between the specialist herbivore Manduca sexta (Lepidoptera, Sphingidae) and its natural host Nicotiana attenuata. III. Fatty acid-amino acid conjugates in herbivore oral secretions are necessary and sufficient for herbivore-specific plant responses. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Ju, H.P.; Zhou, G.X.; Zhu, C.S.; Erb, M.; Wang, X.P.; Wang, P.; Lou, Y.G. An ear-motif-containing ERF transcription factor affects herbivore-induced signaling, defense and resistance in rice. Plant J. 2011, 68, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, G.; Wang, Q.; Bian, W.; Erb, M.; Lou, Y. Prioritizing plant defence over growth through WRKY regulation facilitates infestation by non-target herbivores. Elife 2015, 4, e04805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Ye, M.; Li, R.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, G.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J.; Lou, Y. The rice transcription factor WRKY53 suppresses herbivore-induced defenses by acting as a negative feedback modulator of mitogen-activated protein kinase activity. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 2907–2921. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schweizer, F.; Fernandez-Calvo, P.; Zander, M.; Diez-Diaz, M.; Fonseca, S.; Glauser, G.; Lewsey, M.G.; Ecker, J.R.; Solano, R.; Reymond, P. Arabidopsis basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors MYC2, MYC3, and MYC4 regulate glucosinolate biosynthesis, insect performance, and feeding behavior. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 3117–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rushton, P.J.; Somssich, I.E.; Ringler, P.; Shen, Q.X.J. WRKY transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, P.; Reddy, M.P.; Chikara, J. WRKY: Its structure, evolutionary relationship, DNA-binding selectivity, role in stress tolerance and development of plants. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 3883–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakshi, M.; Oelmuller, R. WRKY transcription factors: Jack of many trades in plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2014, 9, e27700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.P.; Somssich, I.E. The role of WRKY transcription factors in plant immunity. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eulgem, T.; Somssich, I.E. Networks of WRKY transcription factors in defense signaling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.C.; Lai, Z.; Fan, B.; Chen, Z. Arabidopsis WRKY38 and WRKY62 transcription factors interact with histone deacetylase 19 in basal defense. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 2357–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkenbihl, R.P.; Diezel, C.; Somssich, I.E. Arabidopsis WRKY33 is a key transcriptional regulator of hormonal and metabolic responses toward Botrytis cinerea infection. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 266–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulker, B.; Shahid Mukhtar, M.; Somssich, I.E. The WRKY70 transcription factor of Arabidopsis influences both the plant senescence and defense signaling pathways. Planta 2007, 226, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimono, M.; Koga, H.; Akagi, A.; Hayashi, N.; Goto, S.; Sawada, M.; Kurihara, T.; Matsushita, A.; Sugano, S.; Jiang, C.J.; et al. Rice WRKY45 plays important roles in fungal and bacterial disease resistance. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Z.; Liu, H.; Qiu, D.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, S. A pair of allelic WRKY genes play opposite roles in rice-bacteria interactions. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Hao, J.; Chen, X.; Hao, Z.; Wang, X.; Lou, Y.; Peng, Y.; Guo, Z. Overexpression of rice WRKY89 enhances ultraviolet B tolerance and disease resistance in rice plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 65, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, D.; Xiao, J.; Ding, X.; Xiong, M.; Cai, M.; Cao, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, S. OsWRKY13 mediates rice disease resistance by regulating defense-related genes in salicylate- and jasmonate-dependent signaling. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2007, 20, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chujo, T.; Takai, R.; Akimoto-Tomiyama, C.; Ando, S.; Minami, E.; Nagamura, Y.; Kaku, H.; Shibuya, N.; Yasuda, M.; Nakashita, H.; et al. Involvement of the elicitor-induced gene OsWRKY53 in the expression of defense-related genes in rice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1769, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciolkowski, I.; Wanke, D.; Birkenbihl, R.P.; Somssich, I.E. Studies on DNA-binding selectivity of WRKY transcription factors lend structural clues into WRKY-domain function. Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 68, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skibbe, M.; Qu, N.; Galis, I.; Baldwin, I.T. Induced plant defenses in the natural environment: Nicotiana attenuata WRKY3 and WRKY6 coordinate responses to herbivory. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 1984–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.A. Rice Insect Pests; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, T.; Kitagawa, H. Photosynthesis and translocation of assimilates in rice plants following phloem feeding by the planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Homoptera: Delphacidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2000, 93, 1192–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Y.G.; Du, M.H.; Turlings, T.C.J.; Cheng, J.A.; Shan, W.F. Exogenous application of jasmonic acid induces volatile emissions in rice and enhances parasitism of Nilaparvata lugens eggs by the parasitoid Anagrus nilaparvatae. J. Chem. Ecol. 2005, 31, 1985–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.X.; Qi, J.F.; Ren, N.; Cheng, J.A.; Erb, M.; Mao, B.Z.; Lou, Y.G. Silencing OsHI-LOX makes rice more susceptible to chewing herbivores, but enhances resistance to a phloem feeder. Plant J. 2009, 60, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.F.; Zhou, G.X.; Yang, L.J.; Erb, M.; Lu, Y.H.; Sun, X.L.; Cheng, J.A.; Lou, Y.G. The chloroplast-localized phospholipases D α4 and α5 regulate herbivore-induced direct and indirect defenses in rice. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 1987–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Afsheen, S.; Xin, Z.J.; Han, X.; Lou, Y.G. OsNPR1 negatively regulates herbivore-induced JA and ethylene signaling and plant resistance to a chewing herbivore in rice. Physiol. Plant. 2013, 147, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Li, J.C.; Ju, H.P.; Liu, X.L.; Erb, M.; Wang, X.; Lou, Y.G. Contrasting effects of ethylene biosynthesis on induced plant resistance against a chewing and a piercing-sucking herbivore in rice. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 1670–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, H.; Hayashi, N.; Matsushita, A.; Liu, X.Q.; Nakayama, A.; Sugano, S.; Jiang, C.J.; Takatsuji, H. Blast resistance of CC-NB-LRR protein Pb1 is mediated by WRKY45 through protein-protein interaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9577–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimono, M.; Sugano, S.; Nakayama, A.; Jiang, C.J.; Ono, K.; Toki, S.; Takatsuji, H. Rice WRKY45 plays a crucial role in benzothiadiazole-inducible blast resistance. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2064–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, P.; Rabara, R.C.; Langum, T.J.; Boken, A.K.; Rushton, D.L.; Boomsma, D.D.; Rinerson, C.I.; Rabara, J.; Reese, R.N.; Chen, X.; et al. The WRKY transcription factor family in Brachypodium distachyon. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berri, S.; Abbruscato, P.; Faivre-Rampant, O.; Brasileiro, A.C.; Fumasoni, I.; Satoh, K.; Kikuchi, S.; Mizzi, L.; Morandini, P.; Pe, M.E.; et al. Characterization of WRKY co-regulatory networks in rice and Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2009, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Amornsiripanitch, N.; Dong, X. A genomic approach to identify regulatory nodes in the transcriptional network of systemic acquired resistance in plants. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuja, I.; Kissen, R.; Bones, A.M. Phytoalexins in defense against pathogens. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erb, M.; Meldau, S.; Howe, G.A. Role of phytohormones in insect-specific plant reactions. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, H.; Komori, T.; Uemura, S.; Kanda, Y.; Shimotani, K.; Nakai, K.; Furuichi, T.; Takebayashi, K.; Sugimoto, T.; Sano, S.; et al. Chloroplast-mediated activation of plant immune signalling in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Li, J.; Han, X.; Li, R.; Wu, J.; Yu, H.; Hu, L.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, J.; Lou, Y. Jasmonic acid carboxyl methyltransferase regulates development and herbivory-induced defense response in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Brader, G.; Kariola, T.; Palva, E.T. WRKY70 modulates the selection of signaling pathways in plant defense. Plant J. 2006, 46, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Hettenhausen, C.; Meldau, S.; Baldwin, I.T. Herbivory rapidly activates MAPK signaling in attacked and unattacked leaf regions but not between leaves of Nicotiana attenuata. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1096–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Meng, X.; Wang, R.; Mao, G.; Han, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Dual-level regulation of ACC synthase activity by MPK3/MPK6 cascade and its downstream WRKY transcription factor during ethylene induction in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Phosphorylation of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase by MPK6, a stress-responsive mitogen-activated protein kinase, induces ethylene biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 3386–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Liu, G.; Meng, X.; Liu, Y.; Ji, X.; Li, Y.; Nie, X.; Wang, Y. A WRKY gene from Tamarix hispida, ThWRKY4, mediates abiotic stress responses by modulating reactive oxygen species and expression of stress-responsive genes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 82, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutuku, J.M.; Yoshida, S.; Shimizu, T.; Ichihashi, Y.; Wakatake, T.; Takahashi, A.; Seo, M.; Shirasu, K. The WRKY45-dependent signaling pathway is required for resistance against Striga hermonthica parasitism. Plant Physiol. 2015, 168, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaloshian, I.; Walling, L.L. Hemipterans as plant pathogens. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2005, 43, 491–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takatsuji, H. Development of disease-resistant rice using regulatory components of induced disease resistance. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, S.; Sasakura-Shimoda, F.; Suetsugu, M.; Selvaraj, M.G.; Hayashi, N.; Yamazaki, M.; Ishitani, M.; Shimono, M.; Sugano, S.; Matsushita, A.; et al. Development of disease-resistant rice by optimized expression of WRKY45. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, S.; Sasakura-Shimoda, F.; Yamazaki, M.; Hayashi, N.; Suetsugu, M.; Ochiai, H.; Takatsuji, H. Development of disease-resistant rice by pathogen-responsive expression of WRKY45. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, S.; Forno, D.A.; Cock, J.H.; Gomez, K.A. Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice, 3rd ed.; International Rice Research Institute: LOS Baños, Laguna, Philippines, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.J.; Wang, X.; Lou, Y.G.; Cheng, J.A. Role of ethylene signaling in the production of rice volatiles induced by the rice brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 2457–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRRI. Standard Evaluation System for Rice, 4th ed.; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, C.; Ren, N.; Wang, X.; Sumera, A.; Cheng, J.; Lou, Y. Preference and performance of Anagrus nilaparvatae (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae): Effect of infestation duration and density by Nilaparvata lugens (Homoptera: Delphacidae). Environ. Entomol. 2008, 37, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huangfu, J.; Li, J.; Li, R.; Ye, M.; Kuai, P.; Zhang, T.; Lou, Y. The Transcription Factor OsWRKY45 Negatively Modulates the Resistance of Rice to the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060697
Huangfu J, Li J, Li R, Ye M, Kuai P, Zhang T, Lou Y. The Transcription Factor OsWRKY45 Negatively Modulates the Resistance of Rice to the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(6):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060697
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuangfu, Jiayi, Jiancai Li, Ran Li, Meng Ye, Peng Kuai, Tongfang Zhang, and Yonggen Lou. 2016. "The Transcription Factor OsWRKY45 Negatively Modulates the Resistance of Rice to the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 6: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060697
APA StyleHuangfu, J., Li, J., Li, R., Ye, M., Kuai, P., Zhang, T., & Lou, Y. (2016). The Transcription Factor OsWRKY45 Negatively Modulates the Resistance of Rice to the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(6), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060697