The Interactions of CPP–ACP with Saliva
Abstract
:1. Introduction
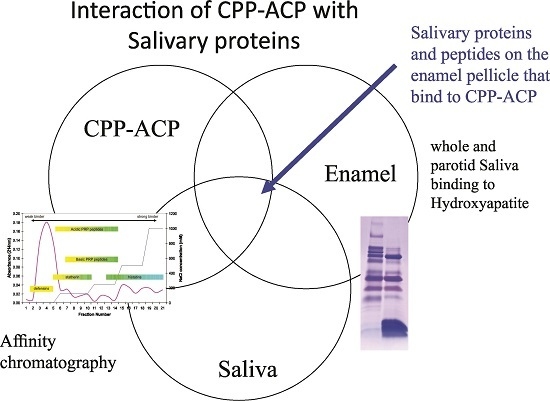
2. Results
A Diverse Range of Salivary Proteins and Peptides Bind to the Predominant Peptides of CPP–ACP
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Purification of αS1-CN (59–79) and β-CN (1–25) Peptides
4.2. Preparation of Affinity Columns Based on αS1-CN (59–79) and β-CN (1–25)
4.3. Adsorption and Elution of Salivary Proteins Bound to αS1-CN (59–79) and β-CN (1–25) Columns
4.4. Adsorption of CPP to Hydroxyapatite
4.5. Adsorption of Saliva to CPP-Coated Hydroxyapatite
4.6. Sample Preparation and SDS-PAGE
4.7. Collection of Whole and Parotid Saliva
4.8. Purification of Salivary Proteins
4.9. ELISA
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loesche, W. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol. Rev. 1986, 50, 353–380. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Featherstone, J.D.B. Dental caries: A dynamic disease process. Aust. Dent. J. 2008, 53, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, D.J.; Lynch, R.J. Diet and the microbial aetiology of dental caries: New paradigms. Int. Dent. J. 2013, 63, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merritt, J.; Qi, F.; Shi, W. Milk helps build strong teeth and promotes oral health. J. Calif. Dent. Assoc. 2006, 34, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aimutis, W.R. Bioactive properties of milk proteins with particular focus on anticariogenesis. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 989S–995S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, E.C.; Cain, C.J.; Webber, F.L.; Black, C.L.; Riley, P.F.; Johnson, I.H.; Perich, J.W. Anticariogenicity of calcium phosphate complexes of tryptic casein phosphopeptides in the rat. J. Dent. Res. 1995, 74, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, R.E.; Latour, N.G. Calcium phosphate sequestering phosphopeptide from casein. Science 1958, 128, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaisgood, H.E. Chemistry of milk protein. Dev. Dairy Chem. 1982, 1, 1–59. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, E.C.; Cai, F.; Shen, P.; Walker, G.D. Retention in plaque and remineralization of enamel lesions by various forms of calcium in a mouthrinse or sugar-free chewing gum. J. Dent. Res. 2003, 82, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, K.J.; Huq, N.L.; Palamara, J.E.; Perich, J.W.; Reynolds, E.C. Physicochemical characterization of casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate nanocomplexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 15362–15369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochrane, N.J.; Saranathan, S.; Cai, F.; Cross, K.J.; Reynolds, E.C. Enamel subsurface lesion remineralisation with casein phosphopeptide stabilised solutions of calcium, phosphate and fluoride. Caries Res. 2008, 42, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, E.C. Remineralization of enamel subsurface lesions by casein phosphopeptide-stabilized calcium phosphate solutions. J. Dent. Res. 1997, 76, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, K.J.; Huq, N.L.; Reynolds, E.C. Casein phosphopeptides in oral health—Chemistry and clinical applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, E.C.; Cai, F.; Cochrane, N.J.; Shen, P.; Walker, G.D.; Morgan, M.V.; Reynolds, C. Fluoride and casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate. J. Dent. Res. 2008, 87, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochrane, N.J.; Cai, F.; Huq, N.L.; Burrow, M.F.; Reynolds, E.C. New approaches to enhanced remineralization of tooth enamel. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, M.V.; Adams, G.G.; Bailey, D.L.; Tsao, C.E.; Fischman, S.L.; Reynolds, E.C. The anticariogenic effect of sugar-free gum containing CPP-ACP nanocomplexes on approximal caries determined using digital bitewing radiography. Caries Res. 2008, 42, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yengopal, V.; Mickenautsch, S. Caries preventive effect of casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate (CPP-ACP): A meta-analysis. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2009, 67, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochrane, N.J.; Reynolds, E.C. Calcium phosphopeptides—Mechanisms of action and evidence for clinical efficacy. Adv. Dent. Res. 2012, 24, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lendenmann, U.; Grogan, J.; Oppenheim, F.G. Saliva and dental pellicle-A review. Adv. Dent. Res. 2000, 14, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, J.N.; Custodio, W.; Hatibovic-Kofman, S.; Lee, Y.H.; Xiao, Y.; Siqueira, W.L. Proteome and peptidome of human acquired enamel pellicle on deciduous teeth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 920–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, W.L.; Zhang, W.M.; Helmerhorst, E.J.; Gygi, S.P.; Oppenheim, F.G. Identification of protein components in in vivo human acquired enamel pellicle using LC-ESI-MS/MS. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 2152–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, W.L.; Oppenheim, F.G. Small molecular weight proteins/peptides present in the in vivo formed human acquired enamel pellicle. Arch. Oral Biol. 2009, 54, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitorino, R.; Calheiros-Lobo, M.J.; Duarte, J.A.; Domingues, P.M.; Amado, F.M.L. Peptide profile of human acquired enamel pellicle using MALDI tandem MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitorino, R.; Calheiros-Lobo, M.J.; Williams, J.; Ferrer-Correia, A.J.; Tomer, K.B.; Duarte, J.A.; Domingues, P.M.; Amado, F.M. Peptidomic analysis of human acquired enamel pellicle. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2007, 21, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitorino, R.; de Morais Guedes, S.; Ferreira, R.; Lobo, M.J.; Duarte, J.; Ferrer-Correia, A.J.; Tomer, K.B.; Domingues, P.M.; Amado, F.M. Two-dimensional electrophoresis study of in vitro pellicle formation and dental caries susceptibility. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2006, 114, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitorino, R.; Lobo, M.J.; Duarte, J.; Ferrer-Correia, A.J.; Tomer, K.B.; Dubin, J.R.; Domingues, P.M.; Amado, F.M. In vitro hydroxyapatite adsorbed salivary proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 320, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Berg, E.A.; Costello, C.E.; Troxler, R.F.; Oppenheim, F.G. Identification of protein components in human acquired enamel pellicle and whole saliva using novel proteomics approaches. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 5300–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Grogan, J.; Zehnder, M.; Lendenmann, U.; Nam, B.; Wu, Z.; Costello, C.E.; Oppenheim, F.G. Compositional analysis of human acquired enamel pellicle by mass spectrometry. Arch. Oral Biol. 2001, 46, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, K.J.; Huq, N.L.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Perich, J.W.; Attard, T.J.; Reynolds, E.C. The role of multiphosphorylated peptides in mineralized tissue regeneration. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2007, 13, 479–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huq, N.L.; Cross, K.J.; Ung, M.; Myroforidis, H.; Veith, P.D.; Chen, D.; Stanton, D.; He, H.; Ward, B.R.; Reynolds, E.C. A review of the salivary proteome and peptidome and saliva-derived peptide therapeutics. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2007, 13, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rölla, G.; Ekstrand, J. Fluoride in oral fluids and dental plaque. In Fluoride in Dentistry; Fejerskov, O., Burt, B.A., Eds.; Munksgaard: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1996; pp. 215–229. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, J.L.; Lamkin, M.S.; Oppenheim, F.G. Adsorption of human salivary proteins to hydroxyapatite: A comparison between whole saliva and glandular salivary secretions. J. Dent. Res. 1992, 71, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denny, P.; Hagen, F.K.; Hardt, M.; Liao, L.; Yan, W.; Arellanno, M.; Bassilian, S.; Bedi, G.S.; Boontheung, P.; Cociorva, D.; et al. The proteomes of human parotid and submandibular/sublingual gland salivas collected as the ductal secretions. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 1994–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flora, B.; Gusman, H.; Helmerhorst, E.J.; Troxler, R.F.; Oppenheim, F.G. A new method for the isolation of histatins 1, 3, and 5 from parotid secretion using zinc precipitation. Protein Expr. Purif. 2001, 23, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Protein | Uniprot No. | Mw | pI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salivary acidic proline-rich phosphoprotein 1/2 precursor | 11,020 | 4.14 | |
| Immunoglobulin J | P01591 | 15,595 | 4.59 |
| Kallikrein-1 | P06870 | 26,406 | 4.62 |
| Salivary acidic proline-rich phosphoprotein 1/2 precursor | P02810 | 17,016 | 4.63 |
| Cystatin-S | P01036 | 14,189 | 4.83 |
| Prolactin-inducible protein | P12273 | 13,523 | 5.4 |
| Zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein | P25311 | 32,145 | 5.58 |
| Ig kappa chain C region | P01834 | 11,609 | 5.58 |
| Polymeric-immunoglobulin receptor | P01833 | 81,349 | 5.59 |
| Serum albumin | P02768 | 66,472 | 5.67 |
| Protein S100-A8 | P05109 | 13,111 | 5.71 |
| Ig alpha-1 chain C region | P01876 | 37,655 | 6.08 |
| Statherin | P02808 | 5220 | 6.25 |
| Salivary alpha-amylase | P04745 | 55,910 | 6.34 |
| Carbonic anhydrase 6 | P23280 | 33,570 | 6.41 |
| Protein S100-A9 | P06702 | 10,835 | 6.5 |
| Cystatin-SN | P01037 | 14,316 | 6.92 |
| Histatin 1 | P15515 | 4848 | 8.32 |
| Cystatin-C | P01034 | 13,347 | 8.75 |
| Lysozyme C | P61626 | 14,701 | 9.28 |
| Mucin 7 | Q8TAX7 | 36,809 | 9.3 |
| Submaxillary gland androgen-regulated protein 3 homolog B | B2R564 | 14,117 | 10 |
| Salivary acidic proline-rich phosphoprotein 1/2 precursor | 4371 | 12.01 |
| Peptide/Protein | Sequence | Mw | pI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lactotransferrin (230–243) | ESTVFEDLSDEAER | 1616.8 | 3.77 |
| Myeloperoxidase (726–741) | DFVNCSTLPALNLASW | 1746.871 | 3.8 |
| Corunlin (373–383) | EQGQTQTQPGS | 1151.57 | 4 |
| Protein S100a14 (13–26) | QEFSDVERAIETLI | 1638.78 | 4 |
| AnnexinA1 (13–26) | FIENEEQEYVQTVK | 1749 | 4.09 |
| Peroxiredoxin-5 (54–67) | APIKVGDAIPAVEV | 1370.5 | 4.37 |
| Protein S100-A8 (84–93) | FWELIGEAAK | 1160.1 | 4.53 |
| Statherin (1–9) | DSSEEKFLR | 1098.66 | 4.68 |
| Histone H2A type 1-A (102–115) | TIAQGGVLPNIQAV | 1378.6 | 5.19 |
| Protein S100-A8 (28–37) | NFHQYSVEGG | 1133.64 | 5.24 |
| Statherin (11–28) | IGRFGYGYGPYQPVPEQP | 2024.96 | 6 |
| Histone H2A type 1-D (89–104) | RNDEELNKLLGKVTIA | 1796.89 | 6.18 |
| Acidic PRP # | SPPGKPQGPPPQGGNQPQ | 1766.93 | 8.47 |
| Acidic PRP # | GPPQQGGHQQGPPPPPPGKPQ | 2067 | 8.76 |
| Con 1 # | PQGPPPQGGSKS | 1133.3 | 9.18 |
| Acidic PRP # | GGRPQGPPQGQSPQ | 1388.61 | 9.75 |
| Acidic PRP # | GPPPQGGRPQGPPQGQSPQ | 1855.92 | 9.75 |
| Acidic PRP # | GRPQGPPQQGGHQQ | 1462.5 | 9.76 |
| Acidic PRP # | GPPQQGGHPPPPQGRPQ | 1719.9 | 9.76 |
| Histatin 3 # | DSHAKRHHGYKR | 1487.7 | 10.28 |
| Histatin 3 # | DSHAKRHHGYKRKF | 1762 | 10.45 |
| Histatin 6 | DSHAKRHHGYKRKFHEKHHSHRGYR | 3191.64 | 10.62 |
| Acidic PRP | GPPQQGGHPRPPR | 1379.72 | 12 |
| Con 1 | GPPRPPQGGRPSRPPQ | 1656.8 | 12.3 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huq, N.L.; Myroforidis, H.; Cross, K.J.; Stanton, D.P.; Veith, P.D.; Ward, B.R.; Reynolds, E.C. The Interactions of CPP–ACP with Saliva. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060915
Huq NL, Myroforidis H, Cross KJ, Stanton DP, Veith PD, Ward BR, Reynolds EC. The Interactions of CPP–ACP with Saliva. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(6):915. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060915
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuq, Noorjahan Laila, Helen Myroforidis, Keith J. Cross, David P. Stanton, Paul D. Veith, Brent R. Ward, and Eric C. Reynolds. 2016. "The Interactions of CPP–ACP with Saliva" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 6: 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060915
APA StyleHuq, N. L., Myroforidis, H., Cross, K. J., Stanton, D. P., Veith, P. D., Ward, B. R., & Reynolds, E. C. (2016). The Interactions of CPP–ACP with Saliva. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(6), 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060915