Ligand and Structure-Based Approaches for the Identification of Peptide Deformylase Inhibitors as Antibacterial Drugs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
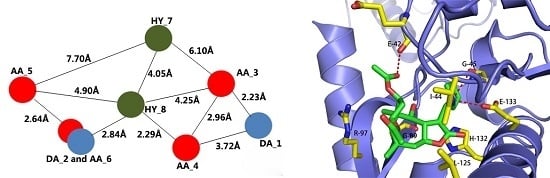
2.1. Results of Pharmacophore Mapping
2.2. Virtual Screening Analysis
2.3. Validation of Molecular Docking
2.4. Molecular Docking Analysis
2.5. Binding Mode of ZINC12660672, ZINC12652500 and ZINC08740166 in E. coli PDF
2.6. In Silico Pharmacokinetic and Toxicity Prediction
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Database Search and Calculation Method
3.2. Generation of Pharmacophore Model
3.3. High-Throughput Virtual Screening
3.4. Molecular Docking
3.5. Validation of Molecular Docking
3.6. In Silico Pharmacokinetics and Toxicity Studies
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Briers, Y.; Walmagh, M.; Grymonprez, B.; Biebl, M.; Pirnay, J.P.; Defraine, V.; Michiels, J.; Cenens, W.; Aertsen, A.; Miller, S.; et al. Art-175 is a highly efficient antibacterial against multidrug-resistant strains and persisters of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3774–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderer, O.J.; Dumont, E.; Zhu, J.; Kurtinecz, M.; Jones, L.S. Single-dose safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of the antibiotic GSK1322322, a novel peptide deformylase inhibitor. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2005–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, C.S.; Neckermann, G.; Fischer, E.; Pecanka, R.; Yu, D.; Manni, K.; Goldovitz, J.; Amaral, K.; Dzink-Fox, J.; Ryder, N.S. In vivo characterization of the peptide deformylase inhibitor LBM415 in murine infection models. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 3777–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangshetti, J.N.; Khan, F.A.; Shinde, D.B. Peptide deformylase: A new target in antibacterial, antimalarial and anticancer drug discovery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 214–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeili, M.; Moore, C.; Davis, C.J.; Cochran, J.B.; Shah, S.; Shrestha, T.B.; Zhang, Y.; Bossmann, S.H.; Benjamin, W.H.; Kutsch, O.; et al. Copper complexation screen reveals compounds with potent antibiotic properties against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3727–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.-H.; Choi, Y.-S.; Kim, W.-J.; Jeon, Y.H.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, B.-J.; Ryu, K.-S. Codon optimization enhances protein expression of human peptide deformylase in E. coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2010, 70, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopal, R.; Kim, Y.G.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.K.; Chae, J.D.; Son, B.K.; Seo, C.H.; Park, Y. Synergistic effects and antibiofilm properties of chimeric peptides against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii strains. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1622–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; van Aller, G.S.; Taylor, A.N.; Kerrigan, J.J.; Liu, W.S.; Trulli, J.M.; Lai, Z.; Holmes, D.; Aubart, K.M.; Brown, J.R.; et al. Phylogenomic and biochemical characterization of three Legionella pneumophila polypeptide deformylases. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 5249–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusmini, R.; Vecchietti, D.; Macchi, R.; Vidal-Aroca, F.; Bertoni, G. A shotgun antisense approach to the identification of novel essential genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, J.M.; Beckett, R.P.; Brown, A.; Catlin, G.; Lobell, M.; Palan, S.; Thomas, W.; Whittaker, M.; Wood, S.; Salama, S.; et al. Antibiotic activity and characterization of BB-3497, a novel peptide deformylase inhibitor. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, A.I.; Zorzet, A.; Kanth, A.; Dahlstrom, S.; Berg, O.G.; Andersson, D.I. Reducing the fitness cost of antibiotic resistance by amplification of initiator tRNA genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 6976–6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giglione, C.; Serero, A.; Pierre, M.; Boisson, B.; Meinnel, T. Identification of eukaryotic peptide deformylases reveals universality of N-terminal protein processing mechanisms. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 5916–5929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinnel, T. Peptide Deformylase of Eukaryotic Protists: A Target for new antiparasitic agents? Parasitol. Today 2000, 16, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randhawa, H.; Chikara, S.; Gehring, D.; Yildirim, T.; Menon, J.; Reindl, K. Overexpression of peptide deformylase in breast, colon, and lung cancers. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.; Chen, D.; White, R.J.; Patel, D.V.; Yuan, Z. Bacterial peptide deformylase inhibitors: A new class of antibacterial agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 1607–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.S.; Buss, A.D. Natural products—The future scaffolds for novel antibiotics? Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 71, 919–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.Z.; Patel, D.V.; Hackbarth, C.J.; Wang, W.; Dreyer, G.; Young, D.C.; Margolis, P.S.; Wu, C.; Ni, Z.J.; Trias, J.; et al. Actinonin, a naturally occurring antibacterial agent, is a potent deformylase inhibitor. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fieulaine, S.; Juillan-Binard, C.; Serero, A.; Dardel, F.; Giglione, C.; Meinnel, T.; Ferrer, J.L. The crystal structure of mitochondrial (Type 1A) peptide deformylase provides clear guidelines for the design of inhibitors specific for the bacterial forms. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 42315–42324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinnel, T.; Patiny, L.; Ragusa, S.; Blanquet, S. Design and synthesis of substrate analogue inhibitors of peptide deformylase. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 4287–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lofland, D.; Difuntorum, S.; Waller, A.; Clements, J.M.; Weaver, M.K.; Karlowsky, J.A.; Johnson, K. In vitro antibacterial activity of the peptide deformylase inhibitor BB-83698. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 53, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dwyer, K.; Hackel, M.; Hightower, S.; Hoban, D.; Bouchillon, S.; Qin, D.; Aubart, K.; Zalacain, M.; Butler, D. Comparative analysis of the antibacterial activity of a novel peptide deformylase inhibitor, GSK1322322. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2333–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerqueira, N.M.; Gesto, D.; Oliveira, E.F.; Santos-Martins, D.; Bras, N.F.; Sousa, S.F.; Fernandes, P.A.; Ramos, M.J. Receptor-based virtual screening protocol for drug discovery. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 582, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sybyl 7.1.; Tripos Associates Inc., S.H. R.: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2005.
- Pham, T.A.; Jain, A.N. Customizing scoring functions for docking. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2008, 22, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.Y.; Zhang, H.X.; Mezei, M.; Cui, M. Molecular docking: A powerful approach for structure-based drug discovery. Curr. Comput. Aided Drug Des. 2011, 7, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staker, B.L.; Buchko, G.W.; Myler, P.J. Recent contributions of structure-based drug design to the development of antibacterial compounds. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2015, 27, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cain, R.; Narramore, S.; McPhillie, M.; Simmons, K.; Fishwick, C.W. Applications of structure-based design to antibacterial drug discovery. Bioorg. Chem. 2014, 55, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, A.S.; Pati, S.P.; Kumar, P.P.; Pradeep, H.N.; Sastry, G.N. Virtual screening in drug discovery—A computational perspective. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2007, 8, 329–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Bryant, S.H. Structure-based virtual screening for drug discovery: A problem-centric review. AAPS J. 2012, 14, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wu, M.B.; Chen, Z.J.; Chen, H.; Lin, J.P.; Yang, L.R. Fragment-based drug discovery and molecular docking in drug design. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2015, 16, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, V.K.; Goel, A.; Ghate, M.; Patel, P. Ligand and structure-based approaches for the identification of SIRT1 activators. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 228, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeliger, D.; de Groot, B.L. Ligand docking and binding site analysis with PyMOL and Autodock/Vina. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2010, 24, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OSIRIS Property Explorer. Available online: http://www.organic-chemistry.org/prog/peo/ (accessed on 29 January 2016).





| Model | Specificity | N-hits a | Feats b | Energy c | Sterics d | Hbond e | Mol-Qry f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.65 | 18 | 8 | 9.03 | 690 | 181.40 | 48.51 |
| 2 | 3.65 | 18 | 8 | 9.03 | 690 | 181.40 | 48.51 |
| Compound | Total Score a | Crash b | Polar c |
|---|---|---|---|
| J | 9.41 | −2.60 | 5.75 |
| ZINC12660672 | 8.10 | −2.14 | 1.29 |
| ZINC12652500 | 8.05 | −2.58 | 6.25 |
| ZINC08740166 | 7.44 | −2.94 | 1.67 |
| A | 7.11 | −2.31 | 4.56 |
| ZINC03984371 | 6.51 | −1.79 | 1.22 |
| ZINC04992698 | 6.40 | −0.54 | 6.68 |
| ZINC12658529 | 6.21 | −2.71 | 3.32 |
| ZINC03088016 | 6.18 | −0.96 | 5.26 |
| ZINC00323509 | 6.12 | −1.18 | 2.11 |
| Parameters | ZINC12660672 | ZINC08740166 | ZINC12652500 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mutagenicity a | NO | NO | NO |
| Tumorigenicity b | NO | NO | NO |
| Irritant c | NO | NO | NO |
| Reproductive effect d | NO | NO | NO |
| Solubility e | −1.37 | −3.01 | −1.93 |
| cLogP f | −2.24 | 1.26 | −1.61 |
| Drug-likeness g | −6.68 | 4.62 | −1.86 |
| Molecular weight | 451.0 | 437.0 | 369.0 |
| Drug score h | 0.41 | 0.78 | 0.15 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, J.; Liang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Qiu, S.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L. Ligand and Structure-Based Approaches for the Identification of Peptide Deformylase Inhibitors as Antibacterial Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071141
Gao J, Liang L, Zhu Y, Qiu S, Wang T, Zhang L. Ligand and Structure-Based Approaches for the Identification of Peptide Deformylase Inhibitors as Antibacterial Drugs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(7):1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071141
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Jian, Li Liang, Yasheng Zhu, Shengzhi Qiu, Tao Wang, and Ling Zhang. 2016. "Ligand and Structure-Based Approaches for the Identification of Peptide Deformylase Inhibitors as Antibacterial Drugs" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 7: 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071141
APA StyleGao, J., Liang, L., Zhu, Y., Qiu, S., Wang, T., & Zhang, L. (2016). Ligand and Structure-Based Approaches for the Identification of Peptide Deformylase Inhibitors as Antibacterial Drugs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(7), 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071141