The Effects of Aquaporin-1 in Pulmonary Edema Induced by Fat Embolism Syndrome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
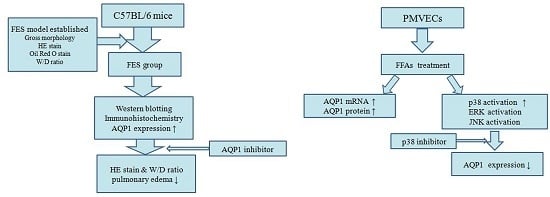
2.1. Fat Embolism Syndrome (FES) Model Was Established in the Mice
2.2. AQP1 Is Increased in FES Mice
2.3. AQP1 Is Required for the Lung Injury Induced by FES
2.4. Morphological Characterization of Rat Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells
2.5. Free Fatty Acid (FFA) Induces Up-Regulation of AQP1 in PMVECs
2.6. ERK, p38 Kinase, and JNK Activation by FFAs in PMVECs
2.7. Effects of p38 Inhibitor on FFA-Induced Up-Regulation of AQP1 in PMVECs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Mouse Models of Fat Embolism
4.3. Measurement of Wet-to-Dry (W/D) Lung Weight
4.4. Primary Cell Isolation and Culture
4.5. Immunofluorescence
4.6. FFA Treatment
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.9. Immunohistochemistry
4.10. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akhtar, S. Fat embolism. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2009, 27, 533–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulde, G.W.; Harrison, P. Fat embolism—A review. Arch. Emerg. Med. 1991, 8, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, R.E.; Kitchen, P.; Owen, D.S.; Bland, C.; Marshall, L.; Conner, A.C.; Bill, R.M.; Conner, M.T. Human aquaporins: Regulators of transcellular water flow. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 1492–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniatis, N.A.; Kotanidou, A.; Catravas, J.D.; Orfanos, S.E. Endothelial pathomechanisms in acute lung injury. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2008, 49, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkman, A.S.; Matthay, M.A.; Song, Y. Aquaporin water channels and lung physiology. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2000, 278, L867–L879. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Jayaraman, S.; Yang, B.; Matthay, M.A.; Verkman, A.S. Role of aquaporin water channels in airway fluid transport, humidification, and surface liquid hydration. J. Gen. Physiol. 2001, 117, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towne, J.E.; Harrod, K.S.; Krane, C.M.; Menon, A.G. Decreased expression of aquaporin (AQP)1 and AQP5 in mouse lung after acute viral infection. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2000, 22, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, J.; Hamil, T.; Creighton, J.; Wu, S.; Bhat, P.; McDonald, F.; Stevens, T. Structural and functional characteristics of lung macro- and microvascular endothelial cell phenotypes. Microvasc. Res. 2004, 67, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ali, K.M.; Gourlay, T. Assessment of the risk of systemic fat mobilization and fat embolism as a consequence of liposuction: Ex vivo study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 117, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, G.; Magyar, Z.; Reffy, A. The role of free fatty acids in pulmonary fat embolism. Injury 1977, 8, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borok, Z.; Verkman, A.S. Lung edema clearance: 20 years of progress: Invited review: Role of aquaporin water channels in fluid transport in lung and airways. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 93, 2199–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Huang, H.; Lu, F.; Chen, Y. Acute lung injury and change in expression of aquaporins 1 and 5 in a rat model of acute pancreatitis. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 2010, 57, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Bi, L.T.; Hou, S.P.; Zhao, X.L.; Song, Y.L.; Ma, T.H. Reduced lung water transport rate associated with downregulation of aquaporin-1 and aquaporin-5 in aged mice. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2009, 36, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabregat, G.; Garcia-de-la-Asuncion, J.; Sarria, B.; Cortijo, J.; De Andres, J.; Mata, M.; Pastor, E.; Belda, F.J. Increased expression of AQP 1 and AQP 5 in rat lungs ventilated with low tidal volume is time dependent. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Zhou, L.; Ge, Y.; Lin, S.; Du, J. Effects of different resuscitation fluids on pulmonary expression of aquaporin1 and aquaporin5 in a rat model of uncontrolled hemorrhagic shock and infection. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIff, T.E.; Poisner, A.M.; Herndon, B.; Lankachandra, K.; Schutt, S.; Haileselassie, B.; Patel, S.; Quinn, T.; Adler, F.; Molteni, A. Fat embolism: Evolution of histopathological changes in the rat lung. J. Orthop. Res. 2010, 28, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, H.; Hanagama, M.; Kamiya, M.; Shinone, K.; Nata, M. Experimental pulmonary fat embolism induced by injection of triolein in rats. Legal Med. 2008, 10, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, T.; Hata, H.; Ozawa, H.; Takata, K. Immunohistochemical localization of the aquaporins AQP1, AQP3, AQP4, and AQP5 in the mouse respiratory system. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2009, 42, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, E.P.; Umenishi, F.; Matthay, M.A.; Verkman, A.S. Developmental changes in water permeability across the alveolar barrier in perinatal rabbit lung. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, C.; Fukuda, N.; Song, Y.; Ma, T.; Matthay, M.A.; Verkman, A.S. Lung fluid transport in aquaporin-1 and aquaporin-4 knockout mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Xie, C.; He, Q.; Deng, X. Increased expression of aquaporin-1 on the pleura of rats with a tuberculous pleural effusion. Lung 2007, 185, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkman, A.S. Role of aquaporins in lung liquid physiology. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2007, 159, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Xie, C. Effects of downregulation of aquaporin1 by peptidoglycan and lipopolysaccharide via MAPK pathways in MeT-5A cells. Lung 2011, 189, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tie, L.; Lu, N.; Pan, X.Y.; Pan, Y.; An, Y.; Gao, J.W.; Lin, Y.H.; Yu, H.M.; Li, X.J. Hypoxia-induced up-regulation of aquaporin-1 protein in prostate cancer cells in a p38-dependent manner. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 29, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Du, L.; Chen, Y.; Qin, S.; Liang, Q.; Zou, X.; Liang, X.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, K.; et al. Down-regulation of Aquaporin1 (AQP1) by peptidoglycan via p38 MAPK pathways in primary rat pleural mesothelial cells. Exp. Lung Res. 2014, 40, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, L.S.; Nielsen, S.; Agre, P.; Brown, R.H. Decreased pulmonary vascular permeability in aquaporin-1-null humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Liu, H.; Ge, H.; Qian, J.; Qin, J.; Sun, L.; Chen, M.; Yan, M.; Shen, A. Lipopolysaccharide induces expression of SSeCKS in rat lung microvascular endothelial cell. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 305, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Liang, M.; Xue, Y.; Xi, C.; Zhou, M.; Jiang, W. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2/angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas axis prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells by inhibiting JNK/NF-κB pathways. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourghi, M.; Pei, J.V.; De Ieso, M.L.; Flynn, G.; Yool, A.J. Bumetanide derivatives AqB007 and AqB011 selectively block the aquaporin-1 ion channel conductance and slow cancer cell migration. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 89, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, M.D.; Schellekens, H.; Boylan, G.B.; Cryan, J.F.; Griffin, B.T. In vitro bidirectional permeability studies identify pharmacokinetic limitations of NKCC1 inhibitor bumetanide. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 770, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Xiang, Y.; Mu, S.M.; Li, T.; Yu, H.M.; Li, X.J. Effects of acetazolamide and anordiol on osmotic water permeability in AQP1-cRNA injected Xenopus oocyte. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2004, 25, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schweitzer, K.; Li, E.; Sidhaye, V.; Leitch, V.; Kuznetsov, S.; King, L.S. Accumulation of aquaporin-1 during hemolysin-induced necrotic cell death. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2008, 13, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Tian, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Shang, J.; Jiang, W.; Wang, A. The Effects of Aquaporin-1 in Pulmonary Edema Induced by Fat Embolism Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071183
Zhang Y, Tian K, Wang Y, Zhang R, Shang J, Jiang W, Wang A. The Effects of Aquaporin-1 in Pulmonary Edema Induced by Fat Embolism Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(7):1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071183
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yiwei, Kun Tian, Yan Wang, Rong Zhang, Jiawei Shang, Wei Jiang, and Aizhong Wang. 2016. "The Effects of Aquaporin-1 in Pulmonary Edema Induced by Fat Embolism Syndrome" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 7: 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071183
APA StyleZhang, Y., Tian, K., Wang, Y., Zhang, R., Shang, J., Jiang, W., & Wang, A. (2016). The Effects of Aquaporin-1 in Pulmonary Edema Induced by Fat Embolism Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(7), 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071183