Comparative Analysis for the Presence of IgG Anti-Aquaporin-1 in Patients with NMO-Spectrum Disorders
Abstract
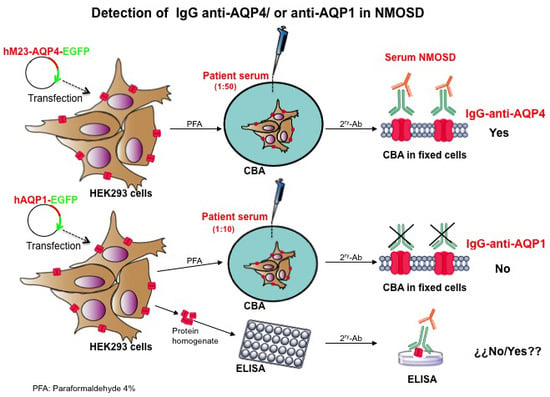
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Subjects and Serum Recollection
3.2. Plasmid Construction, Cell Culture and Cell Transfection
3.3. Immunofluorescence Assay
3.4. ELISA for AQP1 (Aquaporin-1)
3.4.1. Preparation of AQP1 Protein Homogenate
3.4.2. Adhesion of AQP1 Protein for ELISA Assay
3.4.3. Incubation with Primary and Secondary Antibodies
3.4.4. Signal Detection: Per Well, 100 μL of 3,3′,5,5′-Tetramethylbenzidine (TMB)
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Lennon, V.A.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Pittock, S.J.; Weinshenker, B.G. The spectrum of neuromyelitis optica. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzawa, A.; Mori, M.; Kuwabara, S. Neuromyelitis optica: Concept, immunology and treatment. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennon, V.A.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; Kryzer, T.J.; Pittock, S.J.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Fujihara, K.; Nakashima, I.; Weinshenker, B.G. A serum autoantibody marker of neuromyelitis optica: Distinction from multiple sclerosis. Lancet 2004, 364, 2106–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittock, S.J.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; Corboy, J.R.; Lennon, V.A. Neuromyelitis optica brain lesions localized at sites of high aquaporin 4 expression. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinshenker, B.G.; Wingerchuk, D.M. Neuromyelitis optica: Clinical syndrome and the NMO-IgG autoantibody marker. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 318, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Hoddevik, E.H.; Ottersen, O.P. Aquaporins: Multifarious roles in brain. Neuroscience 2010, 168, 859–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venero, J.L.; Vizuete, M.L.; Ilundain, A.A.; Machado, A.; Echevarria, M.; Cano, J. Detailed localization of aquaporin-4 messenger rna in the CNS: Preferential expression in periventricular organs. Neuroscience 1999, 94, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkman, A.S.; Phuan, P.W.; Asavapanumas, N.; Tradtrantip, L. Biology of AQP4 and anti-AQP4 antibody: Therapeutic implications for NMO. Brain Pathol. 2013, 23, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayrol, R.; Saikali, P.; Vincent, T. Effector functions of antiaquaporin-4 autoantibodies in neuromyelitis optica. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1173, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujihara, K. Neuromyelitis optica and astrocytic damage in its pathogenesis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 306, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchinetti, C.F.; Mandler, R.N.; McGavern, D.; Bruck, W.; Gleich, G.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Trebst, C.; Weinshenker, B.; Wingerchuk, D.; Parisi, J.E.; et al. A role for humoral mechanisms in the pathogenesis of Devic’s neuromyelitis optica. Brain 2002, 125, 1450–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Banwell, B.; Bennett, J.L.; Cabre, P.; Carroll, W.; Chitnis, T.; de Seze, J.; Fujihara, K.; Greenberg, B.; Jacob, A.; et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Neurology 2015, 85, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melamed, E.; Levy, M.; Waters, P.J.; Sato, D.K.; Bennett, J.L.; John, G.R.; Hooper, D.C.; Saiz, A.; Bar-Or, A.; Kim, H.J.; et al. Update on biomarkers in neuromyelitis optica. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 2, e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badaut, J.; Brunet, J.F.; Grollimund, L.; Hamou, M.F.; Magistretti, P.J.; Villemure, J.G.; Regli, L. Aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 4 expression in human brain after subarachnoid hemorrhage and in peritumoral tissue. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2003, 86, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oshio, K.; Binder, D.K.; Liang, Y.; Bollen, A.; Feuerstein, B.; Berger, M.S.; Manley, G.T. Expression of the aquaporin-1 water channel in human glial tumors. Neurosurgery 2005, 56, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, R.; Okuda, M.; Asai, J.; Nagashima, G.; Itokawa, H.; Matsunaga, A.; Fujimoto, T.; Suzuki, T. Astrocytes co-express aquaporin-1, -4, and vascular endothelial growth factor in brain edema tissue associated with brain contusion. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2006, 96, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tzartos, J.S.; Stergiou, C.; Kilidireas, K.; Zisimopoulou, P.; Thomaidis, T.; Tzartos, S.J. Anti-aquaporin-1 autoantibodies in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzun, E.; Tzartos, J.; Ekizoglu, E.; Stergiou, C.; Zisimopoulou, P.; Coban, A.; Shugaiv, E.; Turkoglu, R.; Kurtuncu, M.; Baykan, B.; et al. Aquaporin-1 antibody in neuromyelitis optical patients. Eur. Neurol. 2014, 72, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Shan, F.; Chen, M.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, B.; Gao, C.; Gao, Q.; Yang, N. Development of a cell-based assay for the detection of anti-aquaporin 1 antibodies in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 273, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schanda, K.; Waters, P.; Holzer, H.; Aboulenein-Djamshidian, F.; Leite, M.I.; Palace, J.; Vukusic, S.; Marignier, R.; Berger, T.; Reindl, M. Antibodies to aquaporin-1 are not present in neuromyelitis optica. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 2, e160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez Gomar, I.; Diaz Sanchez, M.; Ucles Sanchez, A.J.; Casado Chocan, J.L.; Ramirez-Lorca, R.; Serna, A.; Villadiego, J.; Toledo-Aral, J.J.; Echevarria, M. An immunoassay that distinguishes real neuromyelitis optica signals from a labeling detected in patients receiving natalizumab. BMC Neurol. 2014, 14, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Andres, C.; Guillem, A.; Rodriguez-Mahou, M.; Lopez Longo, F.J. Frequency and significance of anti-Ro (SS-A) antibodies in multiple sclerosis patients. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2001, 104, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szmyrka-Kaczmarek, M.; Pokryszko-Dragan, A.; Pawlik, B.; Gruszka, E.; Korman, L.; Podemski, R.; Wiland, P.; Szechinski, J. Antinuclear and antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with multiple sclerosis. Lupus 2012, 21, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polman, C.H.; Reingold, S.C.; Banwell, B.; Clanet, M.; Cohen, J.A.; Filippi, M.; Fujihara, K.; Havrdova, E.; Hutchinson, M.; Kappos, L.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the Mcdonald criteria. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu-Rodriguez, I.; Sanchez Silva, R.; Martins, A.P.; Soveral, G.; Toledo-Aral, J.J.; Lopez-Barneo, J.; Echevarria, M. Functional and transcriptional induction of aquaporin-1 gene by hypoxia; analysis of promoter and role of Hif-1α. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galan-Cobo, A.; Ramirez-Lorca, R.; Toledo-Aral, J.J.; Echevarria, M. Aquaporin-1 plays important role in proliferation by affecting cell cycle progression. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serna, A.; Galan-Cobo, A.; Rodrigues, C.; Sanchez-Gomar, I.; Toledo-Aral, J.J.; Moura, T.F.; Casini, A.; Soveral, G.; Echevarria, M. Functional inhibition of aquaporin-3 with a gold-based compound induces blockage of cell proliferation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 1787–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villadiego, J.; Mendez-Ferrer, S.; Valdes-Sanchez, T.; Silos-Santiago, I.; Farinas, I.; Lopez-Barneo, J.; Toledo-Aral, J.J. Selective glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor production in adult dopaminergic carotid body cells in situ and after intrastriatal transplantation. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 4091–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Diagnosis | Number of Patients (205) | Gender Female/Male | Mean Age at Inclusion ± SD (range) | AQP4+ Antibodies | AQP1+ Antibodies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. NMOSD | 8 | 7/1 | 57.14 ± 13.52 (40–80) | 6 | 0 |
| 2. MS | 94 | 66/28 | 39.87 ± 11.84 (18–76) | 0 | 0 |
| * RRMS | 85 | 59/26 | 0 | 0 | |
| * PPMS | 7 | 5/2 | 0 | 0 | |
| * SPMS | 2 | 2/0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 3. Idiopathic ON | 39 | 27/12 | 39.55 ± 13.02 (14–68) | 0 | 0 |
| * Isolated episode | 30 | 22/8 | 0 | 0 | |
| * Recurrent idiopathic ON | 9 | 5/4 | 0 | 0 | |
| 4. Idiopathic myelitis | 29 | 19/10 | 45.13 ± 13.58 (21–69) | 0 | 0 |
| * Isolated episode: | 26 | 17/9 | 0 | 0 | |
| >3 vertebral segments | 10 | 5/5 | 0 | 0 | |
| <3 vertebral segments | 16 | 12/4 | 0 | 0 | |
| * Recurrent idiopathic myelitis | 3 | 2/1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 5. OIDD of the CNS | 9 | 5/4 | 48.88 ± 10.37 (26–60) | 0 | 0 |
| * ADEM | 2 | 0/2 | 0 | 0 | |
| * Infratentorial CIS | 4 | 2/2 | 0 | 0 | |
| * RIS | 3 | 3/0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 6. Other neurology disorders | 18 | 8/10 | 51.35 ± 12.79 (26–79) | 0 | 0 |
| * Myelitis associated with lupus | 3 | 3/0 | 0 | 0 | |
| * Myelitis associated with sarcoidosis | 1 | 0/1 | 0 | 0 | |
| * ON associated with Sjögren syndrome | 1 | 1/0 | 0 | 0 | |
| * Multifocal motor neuropathy | 3 | 0/3 | 0 | 0 | |
| * CIDP | 1 | 1/0 | 0 | 0 | |
| * Hereditary spastic paraparesis | 1 | 1/0 | 0 | 0 | |
| * Spinal infraction | 2 | 1/1 | 0 | 0 | |
| * Ischemic optic neuropathy | 6 | 1/5 | 0 | 0 | |
| 7. Healthy controls | 8 | 6/2 | 36.42 ± 8.12 (27–47) | 0 | 0 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez Gomar, I.; Díaz Sánchez, M.; Uclés Sánchez, A.J.; Casado Chocán, J.L.; Suárez-Luna, N.; Ramírez-Lorca, R.; Villadiego, J.; Toledo-Aral, J.J.; Echevarría, M. Comparative Analysis for the Presence of IgG Anti-Aquaporin-1 in Patients with NMO-Spectrum Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081195
Sánchez Gomar I, Díaz Sánchez M, Uclés Sánchez AJ, Casado Chocán JL, Suárez-Luna N, Ramírez-Lorca R, Villadiego J, Toledo-Aral JJ, Echevarría M. Comparative Analysis for the Presence of IgG Anti-Aquaporin-1 in Patients with NMO-Spectrum Disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(8):1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081195
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez Gomar, Ismael, María Díaz Sánchez, Antonio José Uclés Sánchez, José Luis Casado Chocán, Nela Suárez-Luna, Reposo Ramírez-Lorca, Javier Villadiego, Juan José Toledo-Aral, and Miriam Echevarría. 2016. "Comparative Analysis for the Presence of IgG Anti-Aquaporin-1 in Patients with NMO-Spectrum Disorders" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 8: 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081195
APA StyleSánchez Gomar, I., Díaz Sánchez, M., Uclés Sánchez, A. J., Casado Chocán, J. L., Suárez-Luna, N., Ramírez-Lorca, R., Villadiego, J., Toledo-Aral, J. J., & Echevarría, M. (2016). Comparative Analysis for the Presence of IgG Anti-Aquaporin-1 in Patients with NMO-Spectrum Disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(8), 1195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081195