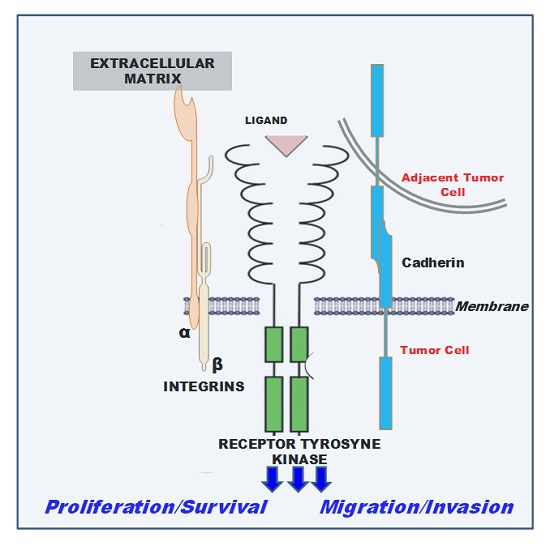
Guidance of Signaling Activations by Cadherins and Integrins in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cadherin-Associated Signaling Activation
2.1. E-cadh
2.2. P-cadh
3. Integrin-Associated Signaling Activation
3.1. Integrins and Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTKs)
3.1.1. EGFR
3.1.2. c-MET
3.1.3. VEGFR Family
3.1.4. Axl
3.2. Integrins and RNAseT2
4. Targeting Cell Adhesion Using Peptidomimetic Ligands
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jelovac, D.; Armstrong, D.K. Recent progress in the diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, L.A.; Huang, B.; Miller, R.W.; Tucker, T.; Goodrich, S.T.; Podzielinski, I.; DeSimone, C.P.; Ueland, F.R.; van Nagell, J.R.; Seamon, L.G. Ten-year relative survival for epithelial ovarian cancer. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 120, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayson, G.C.; Kohn, E.C.; Kitchener, H.C.; Ledermann, J.A. Ovarian cancer. Lancet 2014, 384, 1376–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, S.; Coward, J.I.; Bast, R.C., Jr.; Berchuck, A.; Berek, J.S.; Brenton, J.D.; Coukos, G.; Crum, C.C.; Drapkin, R.; Etemadmoghadam, D.; et al. Rethinking ovarian cancer: Recommendations for improving outcomes. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tothill, R.W.; Tinker, A.V.; George, J.; Brown, R.; Fox, S.B.; Lade, S.; Johnon, D.S.; Trivett, M.K.; Etemadmoghadam, D.; Locandro, B.; et al. Novel molecular subtypes of serous and endometrioid ovarian cancer linked to clinical outcome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5198–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Database. 2012. Available online: https://tcga-data.nci.nih.gov/ (accessed on 30 June 2011).
- Sieh, W.; Salvador, S.; McGuire, V.; Weber, R.P.; Terry, K.L.; Rossing, M.A.; Risch, H.; Wu, A.H.; Webb, P.M.; Moysich, K.; et al. Tubal ligation and risk of ovarian cancer subtypes: A pooled analysis of case-control studies. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munksgaard, P.S.; Blaakaer, J. The association between endometriosis and ovarian cancer: A review of histological, genetic and molecular alterations. Gynecol. Oncol. 2012, 124, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurman, R.J.; Shih, I.M. Pathogenesis of ovarian cancer: Lessons from morphology and molecular biology and their clinical implications. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 2008, 27, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorn, K.K.; Bonome, T.; Gangi, L.; Chandramouli, G.V.; Awtrey, C.S.; Gardner, G.J.; Barrett, J.C.; Boyd, J.; Birrer, M.J. Gene expression profiles of serous, endometrioid, and clear cell subtypes of ovarian and endometrial cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 6422–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowtell, D.D.; Bohm, S.; Ahmed, A.A.; Aspuria, P.J.; Bast, R.C., Jr.; Beral, V.; Berek, J.S.; Birrer, M.J.; Blagden, S.; Bookman, M.A.; et al. Rethinking ovarian cancer II: Reducing mortality from high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipps, E.; Tan, D.S.; Kaye, S.B. Meeting the challenge of ascites in ovarian cancer: New avenues for therapy and research. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.; Stenvers, K.L. Getting to know ovarian cancer ascites: Opportunities for targeted therapy-based translational research. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.S.; Agarwal, R.; Kaye, S.B. Mechanisms of transcoelomic metastasis in ovarian cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, R.S.; Deavers, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, E. Peritoneal inflammation—A microenvironment for Epithelial Ovarian Cancer (EOC). J. Transl. Med. 2004, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pradeep, S.; Kim, S.W.; Wu, S.Y.; Nishimura, M.; Chaluvally-Raghavan, P.; Miyake, T.; Pecot, C.V.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, H.J.; Bischoff, F.Z.; et al. Hematogenous metastasis of ovarian cancer: Rethinking mode of spread. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birbeck, M.S.; Wheatley, D.N. An electron microscopy study of the invasion of ascites tumor cells into the abdominal wall. Cancer Res. 1965, 25, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shield, K.; Riley, C.; Quinn, M.A.; Rice, G.E.; Ackland, M.L.; Ahmed, N. α2β1 Integrin affects metastatic potential of ovarian carcinoma spheroids by supporting disaggregation and proteolysis. J. Carcinog. 2007, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burleson, K.M.; Hansen, L.K.; Skubitz, A.P. Ovarian carcinoma spheroids disaggregate on type I collagen and invade live human mesothelial cell monolayers. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2004, 21, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwanicki, M.P.; Davidowitz, R.A.; Ng, M.R.; Besser, A.; Muranen, T.; Merritt, M.; Danuser, G.; Ince, T.A.; Brugge, J.S. Ovarian cancer spheroids use myosin-generated force to clear the mesothelium. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbolina, M.V.; Moss, N.M.; Westfall, S.D.; Liu, Y.; Burkhalter, R.J.; Marga, F.; Forgacs, G.; Hudson, L.G.; Stack, M.S. Microenvironmental regulation of ovarian cancer metastasis. Cancer Treat. Res. 2009, 149, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Davidson, B.; Henning, R.; Wang, J.; Yu, M.; Annunziata, C.; Hetland, T.; Kohn, E.C. Adhesion molecule protein signature in ovarian cancer effusions is prognostic of patient outcome. Cancer 2012, 118, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeichi, M. Dynamic contacts: Rearranging adherens junctions to drive epithelial remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, L.; Fannon, A.M.; Kwong, P.D.; Thompson, A.; Lehmann, M.S.; Grübel, G.; Legrand, J.-F.; Als-Nielsen, J.; Colman, D.R.; Hendrickson, W.A. Structural basis of cell-cell adhesion by cadherins. Nature 1995, 374, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, E.M.; Ali, R.G.; McCormack, A.J.; Yap, A.S. E-cadherin homophilic ligation directly signals through Rac and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to regulate adhesive contacts. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 6708–6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, A.; Goodwin, M.; Verma, S.; Yap, A.S.; Ali, R.G. Rac is a dominant regulator of cadherin-directed actin assembly that is activated by adhesive ligation independently of Tiam1. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C1061–C1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, M.; Fukata, M.; Yamaga, M.; Itoh, N.; Kaibuchi, K. Recruitment and activation of Rac1 by the formation of E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion sites. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 1829–1838. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamada, S.; Nelson, W.J. Localized zones of Rho and Rac activities drive initiation and expansion of epithelial cell-cell adhesion. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 178, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Li, Z.; Sacks, D.B. E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell attachment activates Cdc42. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 36999–37005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukata, M.; Kaibuchi, K. Rho-family GTPases in cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheelock, M.J.; Johnson, K.R. Cadherin-mediated cellular signaling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2003, 15, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, H.; Takeichi, M. Evolution: Structural and functional diversity of cadherin at the adherens junction. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 193, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miow, Q.H.; Tan, T.Z.; Ye, J.; Lau, J.A.; Yokomizo, T.; Thiery, J.P.; Mori, S. Epithelial-mesenchymal status renders differential responses to cisplatin in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 2014, 34, 1899–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiery, J.P.; Lim, C.T. Tumor dissemination: An EMT affair. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 272–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheldof, A.; Berx, G. Cadherins and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2013, 116, 317–336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.S.; Gumbiner, B.M. Adhesion-independent mechanism for suppression of tumor cell invasion by E-cadherin. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 161, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qian, X.; Karpova, T.; Sheppard, A.M.; McNally, J.; Lowy, D.R. E-cadherin-mediated adhesion inhibits ligand-dependent activation of diverse receptor tyrosine kinases. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andl, C.D.; Rustgi, A.K. No one-way street: Cross-talk between e-cadherin and receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling: A mechanism to regulate RTK activity. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2005, 4, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.R.; Durrans, A.; Lee, S.; Sheng, J.; Li, F.; Wong, S.T.; Choi, H.; El, R.T.; Ryu, S.; Troeger, J.; et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is not required for lung metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance. Nature 2015, 527, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Carstens, J.L.; Kim, J.; Scheible, M.; Kaye, J.; Sugimoto, H.; Wu, C.C.; LeBleu, V.S.; Kalluri, R. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is dispensable for metastasis but induces chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 527, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertos, N.R.; Park, M. Breast cancer—One term, many entities? J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3789–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colpaert, C.G.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Benoy, I.; Soubry, A.; Van, R.F.; van, B.P.; Goovaerts, G.; Dirix, L.Y.; van, D.P.; Fox, S.B.; et al. Inflammatory breast cancer shows angiogenesis with high endothelial proliferation rate and strong E-cadherin expression. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, K.J.; Gabrielson, E.; Werb, Z.; Ewald, A.J. Collective invasion in breast cancer requires a conserved basal epithelial program. Cell 2013, 155, 1639–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen-Ngoc, K.V.; Cheung, K.J.; Brenot, A.; Shamir, E.R.; Gray, R.S.; Hines, W.C.; Yaswen, P.; Werb, Z.; Ewald, A.J. ECM microenvironment regulates collective migration and local dissemination in normal and malignant mammary epithelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2595–E2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darai, E.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Walker-Combrouze, F.; Mlika-Cabanne, N.; Feldmann, G.; Madelenat, P.; Potet, F. Expression of cadherins in benign, borderline, and malignant ovarian epithelial tumors: A clinicopathologic study of 60 cases. Hum. Pathol. 1997, 28, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, B.R.; Worsley, S.D.; Ponder, B.A. Expression of E-cadherin, α-catenin and β-catenin in normal ovarian surface epithelium and epithelial ovarian cancers. Histopathology 1998, 32, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundfeldt, K.; Piontkewitz, Y.; Ivarsson, K.; Nilsson, O.; Hellberg, P.; Brannstrom, M.; Janson, P.O.; Enerback, S.; Hedin, L. E-cadherin expression in human epithelial ovarian cancer and normal ovary. Int. J. Cancer 1997, 74, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, T.; Horiuchi, A.; Shiozawa, T.; Osada, R.; Kikuchi, N.; Ohira, S.; Oka, K.; Konishi, I. Elevated expression of E-cadherin and α-, β-, and γ-catenins in metastatic lesions compared with primary epithelial ovarian carcinomas. Hum. Pathol. 2004, 35, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsia, D.A.; Mitra, S.K.; Hauck, C.R.; Streblow, D.N.; Nelson, J.A.; Ilic, D.; Huang, S.; Li, E.; Nemerow, G.R.; Leng, J.; et al. Differential regulation of cell motility and invasion by FAK. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 160, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomassetti, A.; de Santis, G.; Castellano, G.; Miotti, S.; Mazzi, M.; Tomasoni, D.; van Roy, F.; Carcangiu, M.L.; Canevari, S. Variant HNF1 modulates epithelial plasticity of normal and transformed ovary cells. Neoplasia 2008, 10, 1481–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, R.; Li, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.; Beyer, I.; Persson, J.; Sova, P.; Moller, T.; Pesonen, S.; Hemminki, A.; Hamerlik, P.; et al. Analysis of epithelial and mesenchymal markers in ovarian cancer reveals phenotypic heterogeneity and plasticity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yang, Y.; Dong, L.; Qiu, W.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, L. Construction and characteristics of an E-cadherin-related three-dimensional suspension growth model of ovarian cancer. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P.; Liu, L.; Ren, C.; Lindgren, P.; Boman, K.; Shen, Y.; Lundin, E.; Ottander, U.; Rytinki, M.; Liu, K. Formation of E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion activates AKT and mitogen activated protein kinase via phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase and ligand-independent activation of epidermal growth factor receptor in ovarian cancer cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 19, 2564–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, M.A.; Kraut, N.; Beug, H. Molecular requirements for epithelial-mesenchymal transition during tumor progression. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2005, 17, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.L.; Liu, L.; Ma, C.H.; Li, J.S.; Du, C.; Xu, S.; Han, L.H.; Li, L.; Wang, X.W. E-cadherin promotes proliferation of human ovarian cancer cells in vitro via activating MEK/ERK pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.A.; Ireton, R.C.; Reynolds, A.B. A core function for p120-catenin in cadherin turnover. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 163, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maretzky, T.; Reiss, K.; Ludwig, A.; Buchholz, J.; Scholz, F.; Proksch, E.; de Strooper, B.; Hartmann, D.; Saftig, P. ADAM10 mediates E-cadherin shedding and regulates epithelial cell-cell adhesion, migration, and β-catenin translocation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9182–9187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noe, V.; Fingleton, B.; Jacobs, K.; Crawford, H.C.; Vermeulen, S.; Steelant, W.; Bruyneel, E.; Matrisian, L.M.; Mareel, M. Release of an invasion promoter E-cadherin fragment by matrilysin and stromelysin-1. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marambaud, P.; Shioi, J.; Serban, G.; Georgakopoulos, A.; Sarner, S.; Nagy, V.; Baki, L.; Wen, P.; Efthimiopoulos, S.; Shao, Z.; et al. A presenilin-1/γ-secretase cleavage releases the E-cadherin intracellular domain and regulates disassembly of adherens junctions. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 1948–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogali, A.; Charalabopoulos, K.; Zampira, I.; Konstantinidis, A.K.; Tachmazoglou, F.; Daskalopoulos, G.; Constantopoulos, S.H.; Dalavanga, Y. Soluble adhesion molecules E-cadherin, intercellular adhesion molecule-1, and E-selectin as lung cancer biomarkers. Chest 2010, 138, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowden Dahl, K.D.; Symowicz, J.; Ning, Y.; Gutierrez, E.; Fishman, D.A.; Adley, B.P.; Stack, M.S.; Hudson, L.G. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 is a mediator of epidermal growth factor-dependent E-cadherin loss in ovarian carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4606–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symowicz, J.; Adley, B.P.; Gleason, K.J.; Johnson, J.J.; Ghosh, S.; Fishman, D.A.; Hudson, L.G.; Stack, M.S. Engagement of collagen-binding integrins promotes matrix metalloproteinase-9-dependent E-cadherin ectodomain shedding in ovarian carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2030–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trillsch, F.; Kuerti, S.; Eulenburg, C.; Burandt, E.; Woelber, L.; Prieske, K.; Eylmann, K.; Oliveira-Ferrer, L.; Milde-Langosch, K.; Mahner, S. E-Cadherin fragments as potential mediators for peritoneal metastasis in advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boer, C.J.; van, D.E.; van, K.H.; van Jansen Rhijn, C.M.; Warnaar, S.O.; Fleuren, G.J.; Litvinov, S.V. Changing roles of cadherins and catenins during progression of squamous intraepithelial lesions in the uterine cervix. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.; Biddlestone, L.; Shepherd, N.; Barr, H.; Warner, P.; Jankowski, J. Altered cadherin and catenin complexes in the Barrett’s esophagus-dysplasia-adenocarcinoma sequence: Correlation with disease progression and dedifferentiation. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 152, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peralta, S.A.; Knudsen, K.A.; Salazar, H.; Han, A.C.; Keshgegian, A.A. P-cadherin expression in breast carcinoma indicates poor survival. Cancer 1999, 86, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, R.G.; Tselepis, C.; Hoyland, J.; Wallis, Y.; Pretlow, T.P.; Talbot, I.; Sanders, D.S.; Matthews, G.; Morton, D.; Jankowski, J.A. Aberrant P-cadherin expression is an early event in hyperplastic and dysplastic transformation in the colon. Gut 2002, 50, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, I.S.; Madan, P.; Getsios, S.; Bertrand, M.A.; MacCalman, C.D. Cadherin switching in ovarian cancer progression. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 106, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, L.W.; Leung, P.C.; Wong, A.S. Cadherin switching and activation of p120 catenin signaling are mediators of gonadotropin-releasing hormone to promote tumor cell migration and invasion in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 2427–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, L.W.; Mak, A.S.; Cheung, A.N.; Ngan, H.Y.; Leung, P.C.; Wong, A.S. P-cadherin cooperates with insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor to promote metastatic signaling of gonadotropin-releasing hormone in ovarian cancer via p120 catenin. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2964–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, L.W.; Yung, S.; Chan, T.M.; Leung, P.C.; Wong, A.S. Targeting gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor inhibits the early step of ovarian cancer metastasis by modulating tumor-mesothelial adhesion. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usui, A.; Ko, S.Y.; Barengo, N.; Naora, H. P-cadherin promotes ovarian cancer dissemination through tumor cell aggregation and tumor-peritoneum interactions. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ip, C.K.; Yung, S.; Chan, T.M.; Tsao, S.W.; Wong, A.S. p70 S6 kinase drives ovarian cancer metastasis through multicellular spheroid-peritoneum interaction and P-cadherin/β1 integrin signaling activation. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 9133–9149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barczyk, M.; Carracedo, S.; Gullberg, D. Integrins. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 339, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruoslahti, E. RGD and other recognition sequences for integrins. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1996, 12, 697–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Guan, J.L. Focal adhesion kinase and its signaling pathways in cell migration and angiogenesis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaepfer, D.D.; Hanks, S.K.; Hunter, T.; van der, G.P. Integrin-mediated signal transduction linked to Ras pathway by GRB2 binding to focal adhesion kinase. Nature 1994, 372, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.K.; Schlaepfer, D.D. Integrin-regulated FAK-Src signaling in normal and cancer cells. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2006, 18, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyman, L.; Leroy-Dudal, J.; Fernandes, J.; Seyer, D.; Dutoit, S.; Carreiras, F. Mesothelial vitronectin stimulates migration of ovarian cancer cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2010, 34, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, K.; Mitra, A.K.; Radjabi, A.R.; Bhaskar, V.; Kistner, E.O.; Tretiakova, M.; Jagadeeswaran, S.; Montag, A.; Becker, A.; Kenny, H.A.; et al. Loss of E-cadherin promotes ovarian cancer metastasis via α 5-integrin, which is a therapeutic target. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2329–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.; Pansino, F.; Clyde, R.; Murthi, P.; Quinn, M.A.; Rice, G.E.; Agrez, M.V.; Mok, S.; Baker, M.S. Overexpression of αvβ6 integrin in serous epithelial ovarian cancer regulates extracellular matrix degradation via the plasminogen activation cascade. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carduner, L.; Picot, C.R.; Leroy-Dudal, J.; Blay, L.; Kellouche, S.; Carreiras, F. Cell cycle arrest or survival signaling through αv integrins, activation of PKC and ERK1/2 lead to anoikis resistance of ovarian cancer spheroids. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 320, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carduner, L.; Leroy-Dudal, J.; Picot, C.R.; Gallet, O.; Carreiras, F.; Kellouche, S. Ascites-induced shift along epithelial-mesenchymal spectrum in ovarian cancer cells: Enhancement of their invasive behavior partly dependant on αv integrins. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2014, 31, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, A.; Howell, V.M.; Colvin, E.K. The Extracellular matrix in epithelial ovarian cancer—A piece of a Puzzle. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kenny, H.A.; Chiang, C.Y.; White, E.A.; Schryver, E.M.; Habis, M.; Romero, I.L.; Ladanyi, A.; Penicka, C.V.; George, J.; Matlin, K.; et al. Mesothelial cells promote early ovarian cancer metastasis through fibronectin secretion. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4614–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousif, N.G. Fibronectin promotes migration and invasion of ovarian cancer cells through up-regulation of FAK-PI3K/Akt pathway. Cell Biol. Int. 2014, 38, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, F.E.; Von, G.R.; Zygmunt, M.; Munstedt, K. Association between fibronectin expression and prognosis in ovarian carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2003, 23, 4261–4267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Desgrosellier, J.S.; Cheresh, D.A. Integrins in cancer: Biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivaska, J.; Heino, J. Cooperation between integrins and growth factor receptors in signaling and endocytosis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 27, 291–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regad, T. Targeting RTK signaling pathways in cancer. Cancers 2015, 7, 1758–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Ou, W.; Meng, F.; Zhou, H.; Wang, A. Targeting HSP90 in ovarian cancers with multiple receptor tyrosine kinase coactivation. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citri, A.; Yarden, Y. EGF-ERBB signalling: Towards the systems level. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, L.; Venturino, M.; Bozzo, C.; Silengo, L.; Altruda, F.; Beguinot, L.; Tarone, G.; Defilippi, P. Integrins induce activation of EGF receptor: Role in MAP kinase induction and adhesion-dependent cell survival. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 6622–6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotti, A.; Kedeshian, P.A.; Dans, M.; Curatola, A.M.; Gagnoux-Palacios, L.; Giancotti, F.G. EGF-R signaling through Fyn kinase disrupts the function of integrin α6β4 at hemidesmosomes: Role in epithelial cell migration and carcinoma invasion. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, L.; Dolce, L.; Cabodi, S.; Bergatto, E.; Boeri, E.E.; Smeriglio, M.; Turco, E.; Retta, S.F.; Giuffrida, M.G.; Venturino, M.; et al. Integrin-induced epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor activation requires c-Src and p130Cas and leads to phosphorylation of specific EGF receptor tyrosines. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 9405–9414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabodi, S.; Moro, L.; Bergatto, E.; Boeri, E.E.; Di, S.P.; Turco, E.; Tarone, G.; Defilippi, P. Integrin regulation of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor and of EGF-dependent responses. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2004, 32, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, T.; Shen, K. The epidermal growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2012, 36, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafky, J.M.; Wilken, J.A.; Baron, A.T.; Maihle, N.J. Clinical implications of the ErbB/epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor family and its ligands in ovarian cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1785, 232–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, C.; Pinciroli, P.; Valeri, B.; Ferri, R.; Ditto, A.; Umezawa, K.; Sensi, M.; Canevari, S.; Tomassetti, A. Ligand-dependent EGFR activation induces the co-expression of IL-6 and PAI-1 via the NFκB pathway in advanced-stage epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncogene 2012, 31, 4139–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alper, O.; Bergmann-Leitner, E.S.; Bennett, T.A.; Hacker, N.F.; Stromberg, K.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling and the invasive phenotype of ovarian carcinoma cells. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Y.; Zeineldin, R.; Liu, Y.; Rosenberg, M.; Stack, M.S.; Hudson, L.G. Down-regulation of integrin α2 surface expression by mutant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFRvIII) induces aberrant cell spreading and focal adhesion formation. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9280–9286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comoglio, P.M. Pathway specificity for Met signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, E161–E162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, K.; Radjabi, A.R.; Shinomiya, N.; Kistner, E.; Kenny, H.; Becker, A.R.; Turkyilmaz, M.A.; Salgia, R.; Yamada, S.D.; Vande Woude, G.F.; et al. c-Met overexpression is a prognostic factor in ovarian cancer and an effective target for inhibition of peritoneal dissemination and invasion. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1670–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.K.; Sawada, K.; Tiwari, P.; Mui, K.; Gwin, K.; Lengyel, E. Ligand-independent activation of c-Met by fibronectin and α5β1-integrin regulates ovarian cancer invasion and metastasis. Oncogene 2011, 30, 1566–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.; Smith, B.D.; Zhou, Y.; Kaufman, M.D.; Godwin, A.K. Effective inhibition of c-MET-mediated signaling, growth and migration of ovarian cancer cells is influenced by the ovarian tissue microenvironment. Oncogene 2015, 34, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran-Jones, K.; Brown, L.M.; Samimi, G. INC280, an orally available small molecule inhibitor of c-MET, reduces migration and adhesion in ovarian cancer cell models. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N.; Hillan, K.J.; Gerber, H.P.; Novotny, W. Discovery and development of bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody for treating cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, J.; Abe, Y.; Tsutsui, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Tai, X.G.; Niwa, O.; Tsujimura, T.; Sato, B.; Terano, H.; Fujiwara, H.; et al. Inhibition of growth and metastasis of ovarian carcinoma by administering a drug capable of interfering with vascular endothelial growth factor activity. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1996, 87, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Konishi, I.; Mandai, M.; Kuroda, H.; Komatsu, T.; Nanbu, K.; Sakahara, H.; Mori, T. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in epithelial ovarian neoplasms: Correlation with clinicopathology and patient survival, and analysis of serum VEGF levels. Br. J. Cancer 1997, 76, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serini, G.; Napione, L.; Arese, M.; Bussolino, F. Besides adhesion: New perspectives of integrin functions in angiogenesis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 78, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.J.; Landen, C.N.; Lin, Y.G.; Mangala, L.S.; Lu, C.; Nick, A.M.; Stone, R.L.; Merritt, W.M.; rmaiz-Pena, G.; Jennings, N.B.; et al. Combined anti-angiogenic therapy against VEGF and integrin αvβ3 in an orthotopic model of ovarian cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 2263–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landen, C.N.; Kim, T.J.; Lin, Y.G.; Merritt, W.M.; Kamat, A.A.; Han, L.Y.; Spannuth, W.A.; Nick, A.M.; Jennnings, N.B.; Kinch, M.S.; et al. Tumor-selective response to antibody-mediated targeting of αvβ3 integrin in ovarian cancer. Neoplasia 2008, 10, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.; Black, J.R.; Sharma, R.; Stebbing, J.; Pinato, D.J. Gene of the month: Axl. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 69, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lee, J.C.; Lin, L.; Olivas, V.; Au, V.; LaFramboise, T.; bdel-Rahman, M.; Wang, X.; Levine, A.D.; Rho, J.K.; et al. Activation of the AXL kinase causes resistance to EGFR-targeted therapy in lung cancer. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byers, L.A.; Diao, L.; Wang, J.; Saintigny, P.; Girard, L.; Peyton, M.; Shen, L.; Fan, Y.; Giri, U.; Tumula, P.K.; et al. An epithelial-mesenchymal transition gene signature predicts resistance to EGFR and PI3K inhibitors and identifies Axl as a therapeutic target for overcoming EGFR inhibitor resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linger, R.M.; Keating, A.K.; Earp, H.S.; Graham, D.K. TAM receptor tyrosine kinases: Biologic functions, signaling, and potential therapeutic targeting in human cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2008, 100, 35–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Korshunov, V.A. Axl-dependent signalling: A clinical update. Clin. Sci. 2012, 122, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Fujimoto, J.; Tamaya, T. Coexpression of Gas6/Axl in human ovarian cancers. Oncology 2004, 66, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buehler, M.; Tse, B.; Leboucq, A.; Jacob, F.; Caduff, R.; Fink, D.; Goldstein, D.R.; Heinzelmann-Schwarz, V. Meta-analysis of microarray data identifies GAS6 expression as an independent predictor of poor survival in ovarian cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 238284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- tRankin, E.B.; Fuh, K.C.; Taylor, T.E.; Krieg, A.J.; Musser, M.; Yuan, J.; Wei, K.; Kuo, C.J.; Longacre, T.A.; Giaccia, A.J. Axl is an essential factor and therapeutic target for metastatic ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7570–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rea, K.; Pinciroli, P.; Sensi, M.; Alciato, F.; Bisaro, B.; Lozneanu, L.; Raspagliesi, F.; Centritto, F.; Cabodi, S.; Defilippi, P.; et al. Novel Axl-driven signaling pathway and molecular signature characterize high-grade ovarian cancer patients with poor clinical outcome. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 30859–30875. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Acquati, F.; Morelli, C.; Cinquetti, R.; Bianchi, M.G.; Porrini, D.; Varesco, L.; Gismondi, V.; Rocchetti, R.; Talevi, S.; Possati, L.; et al. Cloning and characterization of a senescence inducing and class II tumor suppressor gene in ovarian carcinoma at chromosome region 6q27. Oncogene 2001, 20, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acquati, F.; Possati, L.; Ferrante, L.; Campomenosi, P.; Talevi, S.; Bardelli, S.; Margiotta, C.; Russo, A.; Bortoletto, E.; Rocchetti, R.; et al. Tumor and metastasis suppression by the human RNASET2 gene. Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 26, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acquati, F.; Lualdi, M.; Bertilaccio, S.; Monti, L.; Turconi, G.; Fabbri, M.; Grimaldi, A.; Anselmo, A.; Inforzato, A.; Collotta, A.; et al. Loss of function of Ribonuclease T2, an ancient and phylogenetically conserved RNase, plays a crucial role in ovarian tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8140–8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lualdi, M.; Pedrini, E.; Rea, K.; Monti, L.; Scaldaferri, D.; Gariboldi, M.; Camporeale, A.; Ghia, P.; Monti, E.; Tomassetti, A.; et al. Pleiotropic modes of action in tumor cells of RNASET2, an evolutionary highly conserved extracellular RNase. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7851–7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnoff, P.; Roiz, L.; Angelkovitch, B.; Schwartz, B.; Shoseyov, O. A recombinant human RNASET2 glycoprotein with antitumorigenic and antiangiogenic characteristics: Expression, purification, and characterization. Cancer 2006, 107, 2760–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesiel-Nuttman, L.; Schwartz, B.; Shoseyov, O. Human recombinant truncated RNASET2, devoid of RNase activity; A potential cancer therapeutic agent. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 11464–11478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Li, G.; Zheng, L.; Li, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, L. Downregulation of tumor suppressor gene ribonuclease T2 and gametogenetin binding protein 2 is associated with drug resistance in ovarian cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eke, I.; Cordes, N. Focal adhesion signaling and therapy resistance in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 31, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seguin, L.; Desgrosellier, J.S.; Weis, S.M.; Cheresh, D.A. Integrins and cancer: Regulators of cancer stemness, metastasis, and drug resistance. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzardo, S.; Conti, L.; Brioschi, C.; Bartolomeo, M.P.; Arosio, D.; Belvisi, L.; Manzoni, L.; Maiocchi, A.; Maisano, F.; Forni, G. A new optical imaging probe targeting αvβ3 integrin in glioblastoma xenografts. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2011, 6, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoni, L.; Belvisi, L.; Arosio, D.; Bartolomeo, M.P.; Bianchi, A.; Brioschi, C.; Buonsanti, F.; Cabella, C.; Casagrande, C.; Civera, M.; et al. Synthesis of Gd and 68Ga complexes in conjugation with a conformationally optimized RGD sequence as potential MRI and PET tumor-imaging probes. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilkington-Miksa, M.; Arosio, D.; Battistini, L.; Belvisi, L.; De, M.M.; Vasile, F.; Burreddu, P.; Carta, P.; Rassu, G.; Perego, P.; et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel cRGD-paclitaxel conjugates for integrin-assisted drug delivery. Bioconjug. Chem. 2012, 23, 1610–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, R.; Mingozzi, M.; Belvisi, L.; Arosio, D.; Piarulli, U.; Carenini, N.; Perego, P.; Zaffaroni, N.; de, C.M.; Castiglioni, V.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation (in vitro and in vivo) of cyclic arginine-glycine-aspartate (RGD) peptidomimetic-paclitaxel conjugates targeting integrin αvβ3. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 10460–10474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sawada, K.; Ohyagi-Hara, C.; Kimura, T.; Morishige, K. Integrin inhibitors as a therapeutic agent for ovarian cancer. J. Oncol. 2012, 2012, 915140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Gorlia, T.; Erridge, S.C.; Perry, J.; Hong, Y.K.; Aldape, K.D.; Lhermitte, B.; Pietsch, T.; Grujicic, D.; et al. Cilengitide combined with standard treatment for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma with methylated MGMT promoter (CENTRIC EORTC 26071–22072 study): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merck Press Release on Cilengitide Studies. Available online: http://www.merck.de/de/press/extNewsDetail.html?newsId=C47977D13865FCB9C1257B1D001EF9CA&newsType=1 (accessed on 30 June 2016).
- Arosio, D.; Casagrande, C. Advancement in integrin facilitated drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 97, 111–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaschuk, O.W. Discovery and development of N-cadherin antagonists. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 348, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustine, C.K.; Yoshimoto, Y.; Gupta, M.; Zipfel, P.A.; Selim, M.A.; Febbo, P.; Pendergast, A.M.; Peters, W.P.; Tyler, D.S. Targeting N-cadherin enhances antitumor activity of cytotoxic therapies in melanoma treatment. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 3777–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beasley, G.M.; Riboh, J.C.; Augustine, C.K.; Zager, J.S.; Hochwald, S.N.; Grobmyer, S.R.; Peterson, B.; Royal, R.; Ross, M.I.; Tyler, D.S. Prospective Multicenter Phase II trial of systemic ADH-1 in combination with melphalan via isolated limb infusion in patients with advanced extremity melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perotti, A.; Sessa, C.; Mancuso, A.; Noberasco, C.; Cresta, S.; Locatelli, A.; Carcangiu, M.L.; Passera, K.; Braghetti, A.; Scaramuzza, D.; et al. Clinical and pharmacological phase I evaluation of Exherin (ADH-1), a selective anti-N-cadherin peptide in patients with N-cadherin-expressing solid tumours. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turley, R.S.; Tokuhisa, Y.; Toshimitsu, H.; Lidsky, M.E.; Padussis, J.C.; Fontanella, A.; Deng, W.; Augustine, C.K.; Beasley, G.M.; Davies, M.A.; et al. Targeting N-cadherin increases vascular permeability and differentially activates AKT in melanoma. Ann. Surg. 2015, 261, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doro, F.; Colombo, C.; Alberti, C.; Arosio, D.; Belvisi, L.; Casagrande, C.; Fanelli, R.; Manzoni, L.; Parisini, E.; Piarulli, U.; et al. Computational design of novel peptidomimetic inhibitors of cadherin homophilic interactions. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 2570–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardone, V.; Lucarelli, A.P.; Dalle, V.A.; Fanelli, R.; Tomassetti, A.; Belvisi, L.; Civera, M.; Parisini, E. Crystal structure of human E-Cadherin-EC1EC2 in complex with a peptidomimetic competitive inhibitor of cadherin homophilic interaction. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 5089–5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dechantsreiter, M.A.; Planker, E.; Matha, B.; Lohof, E.; Holzemann, G.; Jonczyk, A.; Goodman, S.L.; Kessler, H. N-Methylated cyclic RGD peptides as highly active and selective αVβ3 integrin antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 3033–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arap, W.; Pasqualini, R.; Ruoslahti, E. Cancer treatment by targeted drug delivery to tumor vasculature in a mouse model. Science 1998, 279, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoni, L.; Belvisi, L.; Arosio, D.; Civera, M.; Pilkington-Miksa, M.; Potenza, D.; Caprini, A.; Araldi, E.M.; Monferini, E.; Mancino, M.; et al. Cyclic RGD-containing functionalized azabicycloalkane peptides as potent integrin antagonists for tumor targeting. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, P.; Ning, Q.; Meng, M.; Liu, C. Antitumor activity of antimicrobial peptides containing CisoDGRC in CD13 negative breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panzeri, S.; Zanella, S.; Arosio, D.; Vahdati, L.; Dal, C.A.; Pignataro, L.; Paolillo, M.; Schinelli, S.; Belvisi, L.; Gennari, C.; et al. Cyclic isoDGR and RGD peptidomimetics containing bifunctional diketopiperazine scaffolds are integrin antagonists. Chemistry 2015, 21, 6265–6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Gray, B.P.; McGuire, M.J.; Brown, K.C. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a peptide-paclitaxel conjugate which targets the integrin αvβ6. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 5480–5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shintani, Y.; Fukumoto, Y.; Chaika, N.; Grandgenett, P.M.; Hollingsworth, M.A.; Wheelock, M.J.; Johnson, K.R. ADH-1 suppresses N-cadherin-dependent pancreatic cancer progression. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Integrins | Ligands | Chemical Scaffold | Tumor Cell Model 1 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| αvβ3 | cRGDfV 2 | Cyclopentapeptide | GBM | [147] |
| RGD4C | Cyclopentapeptide | BC | [148] | |
| cAbaRGD | Azabicycloalkane | EOC | [149] | |
| (DKP)-RGD | Dichetopiperazine | EOC | [135] | |
| CisoDGR | CDAK 22-mer peptide | BC | [150] | |
| Cyclo[DKP-isoDGR] | Dichetopiperazine/CDAK | GBM | [151] | |
| α5β3 | H2009.1 | 20-mer peptide | NSCL-C | [152] |
| Cadherins | ||||
| N-cadh | N-Ac-CHAVC-NH2 3 | Disulphade-linked cyclic peptide | PC | [153] |
| N- and E-cadh | Compound 3 | Benzyl ring | EOC | [145] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roggiani, F.; Mezzanzanica, D.; Rea, K.; Tomassetti, A. Guidance of Signaling Activations by Cadherins and Integrins in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091387
Roggiani F, Mezzanzanica D, Rea K, Tomassetti A. Guidance of Signaling Activations by Cadherins and Integrins in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(9):1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091387
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoggiani, Francesca, Delia Mezzanzanica, Katia Rea, and Antonella Tomassetti. 2016. "Guidance of Signaling Activations by Cadherins and Integrins in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 9: 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091387
APA StyleRoggiani, F., Mezzanzanica, D., Rea, K., & Tomassetti, A. (2016). Guidance of Signaling Activations by Cadherins and Integrins in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(9), 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091387