Ruscogenin Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction by Suppressing TXNIP/NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and the MAPK Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Ruscogenin Decreased MCAO/R-Induced Brain Infarct Volume and Edema, and Improved Behavioral Outcomes
2.2. Ruscogenin Ameliorated Histopaological Damage and Cerebral Blood Flow Following MCAO/R
2.3. Ruscogenin Reduced the Evans Blue Leakage and Up-Regulates the Expression of Tight Junction Proteins Following MCAO/R
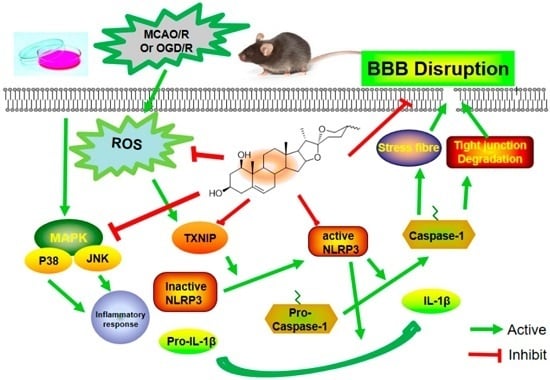
2.4. Ruscogenin Inhibited the Expression of IL-1β and Caspase-1 and Modulated the TXNIP/NLRP3 Pathway Following MCAO/R
2.5. Ruscogenin Increased the Cell Viability and Reverted the Barrier Leakage in bEnd.3 Cells Subjected to OGD/R
2.6. Ruscogenin Attenuated the Expression of Tight Junction Proteins and Actin Cytoskeleton Rearrangement in bEnd.3 Cells Subjected to OGD/R
2.7. Ruscogenin Inhibited the Expression of IL-Iβ and Caspase-1, and Modulated the TXNIP/NLRP3 Pathway in bEnd.3 Cells Subjected to OGD/R
2.8. Ruscogenin Inhibited the Production of ROS, and Regulated the MAPK Pathway in bEnd.3 Cells Subjected to OGD/R
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Reagents
4.3. Animals and Treatment
4.4. Focal Cerebral Ischemia
4.5. Cell Culture
4.6. Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation and Drug Treatment
4.7. Evaluation of Infarct Volume, Neurological Deficits, and Cerebral Water Content
4.8. Histomorphological Analysis and Cerebral Blood Flow
4.9. Evaluation of BBB Permeability
4.10. Cell Viability and Trans-Endothelial Electrical Resistance Assay
4.11. Measurement of Fluorescein Sodium Permeability
4.12. Detection of ROS Production
4.13. Western Blot Analysis
4.14. Immunofluoresence Analysis
4.15. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BBB | Blood-brain barrier |
| CBF | Cerebral blood flow |
| EB | Evans Blue |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| NLRP3 | Nucleotide-binding domain (NOD)-like receptor family, pyrin domain containing 3 |
| PKA | Protein kinase A |
| PDTC | Pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate |
| PRRs | Pattern recognition receptors |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TJs | Tight junctions |
| TXNIP | Thiredoxin-interactive protein |
| ZO-1 | Zonula occludens-1 |
References
- Fisher, M.; Saver, J.L. Future directions of acute ischaemic stroke therapy. Lancet. Neurol. 2015, 14, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, K.M.; Lal, B.K.; Meschia, J.F. Stroke: Advances in medical therapy and acute stroke intervention. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretti, R.; Pansiot, J.; Bettati, D.; Strazielle, N.; Ghersi-Egea, J.F.; Damante, G.; Fleiss, B.; Titomanlio, L.; Gressens, P. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in disorders of the developing brain. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, R.; Carmichael, S.T. Blood-brain barrier breakdown and neovascularization processes after stroke and traumatic brain injury. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2015, 28, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, M.; Bechmann, I.; Immig, K.; Reichenbach, A.; Hartig, W.; Michalski, D. Blood-brain barrier breakdown involves four distinct stages of vascular damage in various models of experimental focal cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabori, M.; Yenari, M.A. Inflammatory responses in brain ischemia. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 1258–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Pecoraro, R.; Pinto, A. Studies of selective TNF inhibitors in the treatment of braininjury from stroke and trauma: A review of the evidence to date. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2014, 8, 2221–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Pecoraro, R.; Di Raimondo, D.; Di Sciacca, R.; Canino, B.; Arnao, V.; Butta, C.; Della Corte, V.; Maida, C.; Licata, G.; Pinto, A. Immune-inflammatory markers and arterial stiffness indexes in subjects with acute ischemic stroke with and without metabolic syndrome. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Fonseca, A.C.; Matias, D.; Garcia, C.; Amaral, R.; Geraldo, L.H.; Freitas, C.; Lima, F.R. The impact of microglial activation on blood-brain barrier in brain diseases. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2014, 8, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, C.; Ling, E.A. Blood brain barrier in hypoxic-ischemic conditions. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2008, 5, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amantea, D.; Micieli, G.; Tassorelli, C.; Cuartero, M.I.; Ballesteros, I.; Certo, M.; Moro, M.A.; Lizasoain, I.; Bagetta, G. Rational modulation of the innate immune system for neuroprotection in ischemic stroke. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Ding, Z.H.; Zhan, F.X.; Cai, L.; Yin, X.; Ling, J.L.; Ye, J.J.; Hou, S.Y.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Z.H.; et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome and stroke. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 4787–4794. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, I.N.; Ishrat, T.; Fagan, S.C.; El-Remessy, A.B. Role of inflammasome activation in the pathophysiology of vascular diseases of the neurovascular unit. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 1188–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Xue, J.; Yu, J.; Kang, N.; Wang, X. Chrysophanol inhibits NALP3 inflammasome activation and ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in mice. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 370530–370542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W. Therapeutics targeting the inflammasome after central nervous system injury. Transl. Res. 2016, 167, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishrat, T.; Mohamed, I.N.; Pillai, B.; Soliman, S.; Fouda, A.Y.; Ergul, A.; El-Remessy, A.B.; Fagan, S.C. Thioredoxin-interacting protein: A novel target for neuroprotection in experimental thromboembolic stroke in mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 51, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Fu, Q.; Ma, S. Curcumin attenuates glutamate neurotoxicity in the hippocampus by suppression of ER stress-associated TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation in a manner dependent on AMPK. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 286, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nito, C.; Kamada, H.; Endo, H.; Niizuma, K.; Myer, D.J.; Chan, P.H. Role of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/cytosolic phospholipase A2 signaling pathway in blood-brain barrier disruption after focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. J. Cereb Blood Flow. Metab. 2008, 28, 1686–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, J.; Sun, Y.; Lin, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Zheng, W.; Yu, B.; Xu, Q. Anti-inflammatory activities of aqueous extract from Radix Ophiopogon japonicus and its two constituents. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 1234–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.L.; Kou, J.P.; Ma, L.; Song, J.X.; Yu, B.Y. Possible mechanism of the anti-inflammatory activity of ruscogenin: Role of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and nuclear factor-κB. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 108, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.J.; Tzeng, T.F.; Liou, S.S.; Da Lin, S.; Wu, M.C.; Liu, I.M. Ruscogenin ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by its anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.N.; Jia, R.; Liu, Y.H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.L.; Kou, J.P.; Yu, B.Y. Ruscogenin suppresses mouse neutrophil activation: Involvement of protein kinase A pathway. J. Steroid Biochem. 2015, 154, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, T.; Liu, Q.; Qian, Y.; Yang, H.; Kong, J.; Kou, J.; Yu, B. Ruscogenin reduces cerebral ischemic injury via NF-κB-mediated inflammatory pathway in the mouse model of experimental stroke. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 714, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norrving, B.; Davis, S.M.; Feigin, V.L.; Mensah, G.A.; Sacco, R.L.; Varghese, C. Stroke prevention worldwide-what could make it work. Neuroepidemiology 2015, 45, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hankey, G.J. The benefits of aspirin in early secondary stroke prevention. Lancet 2016, 388, 312–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Dar, N.J.; Bhat, Z.S.; Hussain, A.; Shah, A.; Liu, H.; Graham, S.H. Inflammation in ischemic stroke: Mechanisms, consequences and possible drug targets. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 13, 1378–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzanero, S.; Santro, T.; Arumugam, T.V. Neuronal oxidative stress in acute ischemic stroke: Sources and contribution to cell injury. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, B.; Liebner, S. Novel insights into the development and maintenance of the blood-brain barrier. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 355, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval, K.E.; Witt, K.A. Blood-brain barrier tight junction permeability and ischemic stroke. Neurobiol. Dis. 2008, 32, 200–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Yang, X.; Tao, Y.; Lan, L.; Zheng, L.; Sun, J. Tight junction disruption of blood-brain barrier in white matter lesions in chronic hypertensive rats. Neuroreport 2015, 26, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziedzic, T. Systemic inflammation as a therapeutic target in acute ischemic stroke. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2015, 15, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, J.; You, X.; Fu, Q. Inflammation in the pathogenesis of ischemic stroke. Front. Biosci. 2015, 20, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Kastin, A.J. Tumor necrosis factor and stroke: Role of the blood-brain barrier. Prog. Neurobiol. 2007, 83, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trendelenburg, G. Molecular regulation of cell fate in cerebral ischemia: Role of the inflammasome and connected pathways. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 1857–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fann, D.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Manzanero, S.; Chunduri, P.; Sobey, C.G.; Arumugam, T.V. Pathogenesis of acute stroke and the role of inflammasomes. Ageing Res. Rev. 2013, 12, 941–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denes, A.; Coutts, G.; Lenart, N.; Cruickshank, S.M.; Pelegrin, P.; Skinner, J.; Rothwell, N.; Allan, S.M.; Brough, D. AIM2 and NLRC4 inflammasomes contribute with ASC to acute brain injury independently of NLRP3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4050–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fann, D.Y.; Santro, T.; Manzanero, S.; Widiapradja, A.; Cheng, Y.L.; Lee, S.Y.; Chunduri, P.; Jo, D.G.; Stranahan, A.M.; Mattson, M.P.; et al. Intermittent fasting attenuates inflammasome activity in ischemic stroke. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 257, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Wang, Z.; Wei, X.; Han, H.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W.; Li, F.; Xin, T.; Pang, Q.; Yi, F. NLRP3 deficiency ameliorates neurovascular damage in experimental ischemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fann, D.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Manzanero, S.; Tang, S.C.; Gelderblom, M.; Chunduri, P.; Bernreuther, C.; Glatzel, M.; Cheng, Y.L.; Thundyil, J.; et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin suppresses NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuronal death in ischemic stroke. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, N.; Zu, G.; Li, Z.; Zhou, J.; Gao, D.; Lv, L.; Tian, X.; et al. New insights into salvianolic acid A action: Regulation of the TXNIP/NLRP3 and TXNIP/ChREBP pathways ameliorates HFD-induced NAFLD in rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28734–28746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, R.; Wang, X.; Fu, Q.; Ma, S. Umbelliferone ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via upregulating the PPAR gamma expression and suppressing TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 600, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, D.F.; Abderrazak, A.; El Hadri, K.; Simmet, T.; Rouis, M. The thioredoxin system as a therapeutic target in human health and disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1266–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Lu, C.; Li, C.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Z.; Liu, L. Overexpression of HSPA12B protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via a PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1832, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, C.L.; Bayraktutan, U. Antioxidants attenuate hyperglycaemia-mediated brain endothelial cell dysfunction and blood-brain barrier hyperpermeability. Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 2009, 11, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.S.; Chen, H.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, F.; Liu, C.H.; Xiang, X.; Qi, J.; Chai, C.Z.; Kou, J.P.; Yu, B.Y. YiQiFuMai Powder Injection ameliorates the oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced brain microvascular endothelial barrier dysfunction associated with the NF-κB and ROCK1/MLC signaling pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 183, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longa, E.Z.; Weinstein, P.R.; Carlson, S.; Cummins, R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 1989, 20, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; Ye, X.; Xu, Y.; Yin, M.; Chen, H.; Kou, J.; Yu, B. YiQiFuMai powder injection ameliorates blood-brain barrier dysfunction and brain edema after focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Drug. Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 315–325. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Q.; Gu, Y.; Hua, Y.; Liu, W.; Keep, R.F.; Xi, G. Deferoxamine attenuates white matter injury in a piglet intracerebral hemorrhage model. Stroke 2014, 45, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.G.; Wang, L.; Gautam, S.C.; Xu, Y.X.; Katakowski, M.; Zhang, L.J.; Lu, M.; Janakiraman, N.; et al. Human marrow stromal cell therapy for stroke in rat: Neurotrophins and functional recovery. Neurology 2002, 59, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Cao, G.; Yang, H.; Zhou, H.; Li, L.; Cao, Z.; Yu, B.; Kou, J. A combination of four active compounds alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in correlation with inhibition of autophagy and modulation of AMPK/mTOR and JNK pathways. J. Neurosci. Res. 2014, 92, 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y.; Tang, G.; Yang, G.Y.; Wang, Y. CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 protects blood-brain barrier integrity and reduces inflammatory response after focal ischemia in mice. Stroke 2013, 44, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, M.; Ahishali, B. Assessment of permeability in barrier type of endothelium in brain using tracers: Evans blue, sodium fluorescein, and horseradish peroxidase. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 763, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, M.H.; Wang, Q.; Qin, M.J.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X.Q.; Liu, B.L.; Wen, X.D. Ilexgenin A inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress and ameliorates endothelial dysfunction via suppression of TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation in an AMPK dependent manner. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 99, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, N.; Han, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, J.; Kou, J.; Yu, B. YiQiFuMai powder injection ameliorates cerebral ischemia by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated neuronal apoptosis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5493279–5493293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, C.; Chen, T.; Fang, Y.; Shi, X.; Pang, T.; Zhang, L.; Liao, H. Nafamostat mesilate protects against acute cerebral ischemia via blood-brain barrier protection. Neuropharmacology 2016, 105, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, G.; Jiang, N.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Yin, M.; Ma, X.; Zhou, K.; Qi, J.; Yu, B.; et al. Ruscogenin Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction by Suppressing TXNIP/NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and the MAPK Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091418
Cao G, Jiang N, Hu Y, Zhang Y, Wang G, Yin M, Ma X, Zhou K, Qi J, Yu B, et al. Ruscogenin Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction by Suppressing TXNIP/NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and the MAPK Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(9):1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091418
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Guosheng, Nan Jiang, Yang Hu, Yuanyuan Zhang, Guangyun Wang, Mingzhu Yin, Xiaonan Ma, Kecheng Zhou, Jin Qi, Boyang Yu, and et al. 2016. "Ruscogenin Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction by Suppressing TXNIP/NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and the MAPK Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 9: 1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091418
APA StyleCao, G., Jiang, N., Hu, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, G., Yin, M., Ma, X., Zhou, K., Qi, J., Yu, B., & Kou, J. (2016). Ruscogenin Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction by Suppressing TXNIP/NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and the MAPK Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(9), 1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091418