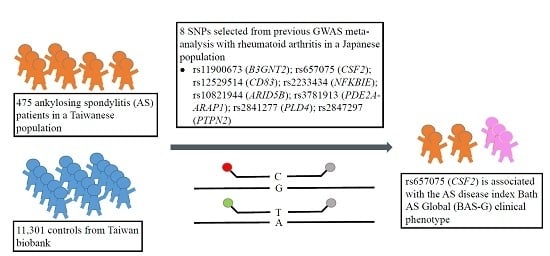
rs657075 (CSF2) Is Associated with the Disease Phenotype (BAS-G) of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Association Study between RA Polymorphisms and Susceptibility to AS
2.2. rs657075 Is Associated with the Disease Activity Index
2.3. Association Study between RA Polymorphisms and Inflammatory Biochemical Parameters of AS
2.4. Studies for Tissue Expression Quantitative Trait Loci (eQTLs) of rs657075
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Subjects
4.2. Candidate Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)
4.3. DNA Extraction
4.4. Genotyping
4.5. SNP Annotation Data Query
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braun, J.; Sieper, J. Ankylosing spondylitis. Lancet 2007, 369, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, B. Ankylosing spondylitis, a seronegative spondarthritis. Practitioner 1987, 231, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calin, A.; Brophy, S.; Blake, D. Impact of sex on inheritance of ankylosing spondylitis: A cohort study. Lancet 1999, 354, 1687–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Laval, S.H.; Brophy, S.; Calin, A. Recurrence risk modelling of the genetic susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2000, 59, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.A.; Kennedy, L.G.; MacGregor, A.J.; Darke, C.; Duncan, E.; Shatford, J.L.; Taylor, A.; Calin, A.; Wordsworth, P. Susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis in twins: The role of genes, HLA, and the environment. Arthritis Rheumatol. 1997, 40, 1823–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewerton, D.A.; Hart, F.D.; Nicholls, A.; Caffrey, M.; James, D.C.; Sturrock, R.D. Ankylosing spondylitis and HL-A 27. Lancet 1973, 1, 904–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ball, E.J. Genetic aspects of ankylosing spondylitis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2002, 16, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, W.P.; Van der Linden, S.M.; Khan, M.A.; Rentsch, H.U.; Cats, A.; Russell, A.; Thomson, G. HLA-Bw60 increases susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis in HLA-B27+ patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 1989, 32, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Pile, K.D.; Kennedy, L.G.; Calin, A.; Darke, C.; Bell, J.; Wordsworth, B.P.; Cornelis, F. HLA class I associations of ankylosing spondylitis in the white population in the United Kingdom. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1996, 55, 268–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.C.; Tsai, W.C.; Lin, H.S.; Tsai, C.Y.; Chou, C.T. HLA-B60 and B61 are strongly associated with ankylosing spondylitis in HLA-B27-negative Taiwan Chinese patients. Rheumatology 2004, 43, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.C.; Sung-Ching, H.W.; Hsu, Y.W.; Wen, Y.F.; Wang, W.C.; Wong, R.H.; Lu, H.F.; Gaalen, F.A.; Chang, W.C. Interaction between HLA-B60 and HLA-B27 as a Better Predictor of Ankylosing Spondylitis in a Taiwanese Population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gaalen, F.A.; Verduijn, W.; Roelen, D.L.; Bohringer, S.; Huizinga, T.W.; Van der Heijde, D.M.; Toes, R.E. Epistasis between two HLA antigens defines a subset of individuals at a very high risk for ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.S.; Li, C.; Lin, Z.M.; Huang, J.X.; Wei, Q.J.; Wang, X.W.; Xie, Y.Y.; Liao, Z.T.; Chao, S.Y.; Gu, J.R. Association of IL-1 gene complex members with ankylosing spondylitis in Chinese Han population. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2010, 37, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safrany, E.; Pazar, B.; Csongei, V.; Jaromi, L.; Polgar, N.; Sipeky, C.; Horvath, I.F.; Zeher, M.; Poor, G.; Melegh, B. Variants of the IL23R gene are associated with ankylosing spondylitis but not with Sjogren syndrome in Hungarian population samples. Scand. J. Immunol. 2009, 70, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.H.; Wong, R.H.; Wei, J.C.; Tsay, M.D.; Chen, W.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Shih, W.T.; Chiou, S.P.; Tu, Y.C.; Lee, H.S. Effects of genetic polymorphisms of programmed cell death 1 and its ligands on the development of ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 1809–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.H.; Wei, J.C.; Chen, C.C.; Chuang, C.S.; Chou, C.H.; Lin, Y.J.; Wang, M.F.; Wong, R.H. Associations of the PTPN22 and CTLA-4 genetic polymorphisms with Taiwanese ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol. Int. 2014, 34, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.Y.; Chang, Y.H.; Lo, M.K.; Chang, C.P.; Yang, S.C.; Yang, T.P.; Ho, K.T.; Juan, C.W.; Shiau, M.Y. Polymorphisms of cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 and cytokine genes in Taiwanese patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Tissue Antigens 2010, 75, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.C.; Yen, J.H.; Juo, S.H.; Chen, W.C.; Wang, Y.S.; Chiu, Y.C.; Hsieh, T.J.; Guo, Y.C.; Huang, C.H.; Wong, R.H.; et al. Association of ORAI1 haplotypes with the risk of HLA-B27 positive ankylosing spondylitis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.C.; Hung, K.S.; Hsu, Y.W.; Wong, R.H.; Huang, C.H.; Jan, M.S.; Wu, S.J.; Juan, Y.S.; Chang, W.C. Genetic polymorphisms of stromal interaction molecule 1 associated with the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein in HLA-B27 positive ankylosing spondylitis patients. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australo-Anglo-American Spondyloarthritis Consortium; Reveille, J.D.; Sims, A.M.; Danoy, P.; Evans, D.M.; Leo, P.; Pointon, J.J.; Jin, R.; Zhou, X.; Bradbury, L.A.; et al. Genome-wide association study of ankylosing spondylitis identifies non-MHC susceptibility loci. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, D.M.; Spencer, C.C.; Pointon, J.J.; Su, Z.; Harvey, D.; Kochan, G.; Oppermann, U.; Dilthey, A.; Pirinen, M.; Stone, M.A.; et al. Interaction between ERAP1 and HLA-B27 in ankylosing spondylitis implicates peptide handling in the mechanism for HLA-B27 in disease susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Bei, J.X.; Shen, M.; Li, Q.; Liao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Q.; Wei, Q.; Low, H.Q.; Guo, Y.M.; et al. A genome-wide association study in Han Chinese identifies new susceptibility loci for ankylosing spondylitis. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium; Australo-Anglo-American Spondylitis Consortium; Burton, P.R.; Clayton, D.G.; Cardon, L.R.; Craddock, N.; Deloukas, P.; Duncanson, A.; Kwiatkowski, D.P.; McCarthy, M.I.; et al. Association scan of 14,500 nonsynonymous SNPs in four diseases identifies autoimmunity variants. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- International Genetics of Ankylosing Spondylitis Consortium; Cortes, A.; Hadler, J.; Pointon, J.P.; Robinson, P.C.; Karaderi, T.; Leo, P.; Cremin, K.; Pryce, K.; Harris, J.; et al. Identification of multiple risk variants for ankylosing spondylitis through high-density genotyping of immune-related loci. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.M.; Ho, H.H.; Chang, S.W.; Wu, Y.J.; Lin, J.C.; Chang, P.Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.Y. ERAP1 genetic variations associated with HLA-B27 interaction and disease severity of syndesmophytes formation in Taiwanese ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.F.; Wei, J.C.; Hsu, Y.W.; Chiou, H.Y.; Wong, H.S.; Wong, R.H.; Ikegawa, S.; Chang, W.C. rs10865331 associated with susceptibility and disease severity of ankylosing spondylitis in a Taiwanese population. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.C.; Hsu, Y.W.; Hung, K.S.; Wong, R.H.; Huang, C.H.; Liu, Y.T.; Guo, Y.C.; Ikegawa, S.; Chang, W.C. Association study of polymorphisms rs4552569 and rs17095830 and the risk of ankylosing spondylitis in a Taiwanese population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e52801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firestein, G.S. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 2003, 423, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terao, C.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Gregersen, P.K. Recent Advances in Defining the Genetic Basis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2016, 17, 273–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, Y.; Terao, C.; Ikari, K.; Kochi, Y.; Ohmura, K.; Suzuki, A.; Kawaguchi, T.; Stahl, E.A.; Kurreeman, F.A.; Nishida, N.; et al. Meta-analysis identifies nine new loci associated with rheumatoid arthritis in the Japanese population. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundquist, K.; Martineus, J.C.; Li, X.; Hemminki, K.; Sundquist, J. Concordant and discordant associations between rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and ankylosing spondylitis based on all hospitalizations in Sweden between 1973 and 2004. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 1199–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemminki, K.; Li, X.; Sundquist, J.; Sundquist, K. Familial associations of rheumatoid arthritis with autoimmune diseases and related conditions. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirota, M.; Schaub, M.A.; Batzoglou, S.; Robinson, W.H.; Butte, A.J. Autoimmune disease classification by inverse association with SNP alleles. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard-Miceli, C.; Criswell, L.A. Emerging patterns of genetic overlap across autoimmune disorders. Genom. Med. 2012, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, Y.; Wu, D.; Trynka, G.; Raj, T.; Terao, C.; Ikari, K.; Kochi, Y.; Ohmura, K.; Suzuki, A.; Yoshida, S.; et al. Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis contributes to biology and drug discovery. Nature 2014, 506, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, S.D.; Steiner, A.; Garrett, S.L.; Calin, A. The Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Patient Global Score (BAS-G). Br. J. Rheumatol. 1996, 35, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zochling, J. Measures of symptoms and disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS), Ankylosing Spondylitis Quality of Life Scale (ASQoL), Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI), Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (BASFI), Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Global Score (BAS-G), Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index (BASMI), Dougados Functional Index (DFI), and Health Assessment Questionnaire for the Spondylarthropathies (HAQ-S). Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, S47–S58. [Google Scholar]
- Codarri, L.; Gyulveszi, G.; Tosevski, V.; Hesske, L.; Fontana, A.; Magnenat, L.; Suter, T.; Becher, B. RORgammat drives production of the cytokine GM-CSF in helper T cells, which is essential for the effector phase of autoimmune neuroinflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hukuda, S.; Minami, M.; Saito, T.; Mitsui, H.; Matsui, N.; Komatsubara, Y.; Makino, H.; Shibata, T.; Shingu, M.; Sakou, T.; et al. Spondyloarthropathies in Japan: Nationwide questionnaire survey performed by the Japan Ankylosing Spondylitis Society. J. Rheumatol. 2001, 28, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.T.; Pei, L.; Chang, D.M.; Lee, C.F.; Schumacher, H.R.; Liang, M.H. Prevalence of rheumatic diseases in Taiwan: A population study of urban, suburban, rural differences. J. Rheumatol. 1994, 21, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.T.; Schumacher, H.R. Human leucocyte antigens (class I and II) in central Taiwan aborigines: Can these explain the observed differences in rheumatic disease patterns compared with Han Chinese? Rheumatology 2000, 39, 1297–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Linden, S.; Valkenburg, H.A.; Cats, A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984, 27, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.T.; Tsai, Y.F.; Liu, J.; Wei, J.C.; Liao, T.S.; Chen, M.L.; Liu, L.Y. The detection of the HLA-B27 antigen by immunomagnetic separation and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay-comparison with a flow cytometric procedure. J. Immunol. Methods 2001, 255, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| SNP | Chromosome | Position (bp) | Cytoband | Candidate Gene | Context | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs11900673 | 2 | 62306165 | 2p15 | B3GNT2 | NA | 1.1 × 10−8 |
| rs657075 | 5 | 131458017 | 5q31 | CSF2 | NA | 2.8 × 10−10 |
| rs12529514 | 6 | 14204637 | 6p23 | CD83 | NA | 2.0 × 10−8 |
| rs2233434 | 6 | 44340898 | 6p21.1 | NFKBIE | Exon (Val/Ala) | 5.8 × 10−19 |
| rs10821944 | 10 | 63455095 | 10q21 | ARID5B | Intron | 5.5 × 10−18 |
| rs3781913 | 11 | 72051144 | 11q13 | PDE2A-ARAP1 | Intron | 5.8 × 10−10 |
| rs2841277 | 14 | 104462050 | 14q32 | PLD4 | Near Gene-5‘ | 1.9 × 10−14 |
| rs2847297 | 18 | 12787694 | 18p11 | PTPN2 | Intron | 2.2 × 10−8 |
| Characteristics | Patients with AS | Taiwanese Biobank Controls |
|---|---|---|
| Number of subjects | 475 | 11,301 |
| Gender: Male (%) | 323 (68.0%) | |
| Age (years) | 39.1 ± 11.3 a | |
| Range | 17~82 | |
| HLA-B27+ | 431 (90.7%) | |
| BASDAI | 4.3 ± 2.2 | |
| BASFI | 2.1 ± 2.2 | |
| BAS-G | 4.4 ± 2.8 |
| Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism | Genotype | Cases (%) (n = 475) | Control Subjects (%) (n = 11,301) | Allele | Cases (%) (n = 475) | Control Subjects (%) (n = 11,301) | Dominant p Value | Recessive p Value | Allelic p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B3GNT2 | TT | 5 (1.3) | 346 (3.0) | T | 118 (15.6) | 4008 (17.7) | 0.2993 | 0.0512 | 0.1191 |
| rs11900673 | CT | 108 (28.6) | 3316 (29.4) | C | 638 (84.4) | 18,574 (82.3) | |||
| CC | 265 (70.1) | 7629 (67.6) | |||||||
| CSF2 | AA | 27 (7.1) | 711 (6.3) | A | 185 (24.2) | 5715 (25.7) | 0.2272 | 0.5558 | 0.4579 |
| rs657075 | GA | 131 (34.2) | 4293 (38.1) | G | 581 (75.8) | 16,481 (74.3) | |||
| GG | 225 (58.7) | 6274 (55.6) | |||||||
| CD83 | CC | 28 (7.1) | 613 (5.4) | C | 199 (25.3) | 5319 (23.6) | 0.5013 | 0.1514 | 0.2731 |
| rs12529514 | TC | 143 (36.3) | 4093 (36.3) | T | 589 (74.7) | 17,251 (76.5) | |||
| TT | 223 (56.6) | 6579 (58.3) | |||||||
| NFKBIE | CC | 11 (2.5) | 12 (2.6) | C | 135 (15.1) | 151 (16.6) | 0.3533 | 0.8665 | 0.3855 |
| rs2233434 | TC | 113 (25.3) | 127 (28.0) | T | 757 (84.9) | 757 (83.4) | |||
| TT | 322 (72.2) | 315 (69.4) | |||||||
| ARID5B | GG | 32 (7.9) | 792 (7.0) | G | 209 (25.7) | 5988 (26.5) | 0.3120 | 0.5123 | 0.5901 |
| rs10821944 | TG | 145 (35.6) | 4404 (39.0) | T | 605 (74.3) | 16,588 (73.3) | |||
| TT | 230 (56.5) | 6092 (54.0) | |||||||
| PDE2A-ARAP1 | CC | 47 (10.8) | 44 (8.9) | C | 275 (31.5) | 284 (28.6) | 0.2362 | 0.3280 | 0.1731 |
| rs3781913 | AC | 181 (41.4) | 196 (39.4) | A | 599 (68.5) | 710 (74.3) | |||
| AA | 209 (47.8) | 257 (51.7) | |||||||
| PLD4 | CC | 82 (18.3) | 1954 (17.3) | C | 379 (42.4) | 9370 (41.5) | 0.7506 | 0.5730 | 0.6012 |
| rs2841277 | TC | 215 (48.1) | 5462 (48.4) | T | 515 (57.6) | 13,200 (58.5) | |||
| TT | 150 (33.6) | 3869 (34.3) | |||||||
| PTPN2 | GG | 40 (9.3) | 1053 (9.2) | G | 273 (31.7) | 6728 (29.8) | 0.1447 | 0.9848 | 0.2640 |
| rs2847297 | AG | 193 (44.8) | 4658 (41.2) | A | 589 (68.3) | 15,862 (70.2) | |||
| AA | 198 (45.9) | 5602 (49.6) |
| Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism | Genotype | BASDAI | BASFI | BAS-G |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B3GNT2 | TT | 3.1 ± 0.9 a | 0.8 ± 0.8 | 3.9 ± 3.3 |
| rs11900673 | CT | 4.3 ± 2.3 | 1.9 ± 2.1 | 4.3 ± 2.7 |
| CC | 4.3 ± 2.1 | 2.1 ± 2.3 | 4.4 ± 2.7 | |
| p value † | 0.322 | 0.262 | 0.834 | |
| q value | 0.858 | 0.699 | 0.886 | |
| CSF2 | AA | 5.1 ± 2.1 | 2.4 ± 2.2 | 6.1 ± 2.8 |
| rs657075 | GA | 4.3 ± 2.3 | 2.0 ± 2.2 | 4.4 ± 2.7 |
| GG | 4.3 ± 2.2 | 2.0 ± 2.3 | 4.2 ± 2.8 | |
| p value † | 0.452 | 0.816 | 0.011 | |
| q value | 0.858 | 0.848 | 0.088 | |
| CD83 | CC | 4.9 ± 2.2 | 2.2 ± 2.0 | 5.1 ± 2.9 |
| rs12529514 | TC | 4.3 ± 2.2 | 2.1 ± 2.3 | 4.5 ± 2.7 |
| TT | 4.4 ± 2.2 | 2.1 ± 2.2 | 4.3 ± 2.7 | |
| p value † | 0.772 | 0.848 | 0.528 | |
| q value | 0.858 | 0.848 | 0.780 | |
| NFKBIE | CC | 4.9 ± 1.8 | 1.7 ± 1.7 | 3.5 ± 2.1 |
| rs2233434 | TC | 4.4 ± 2.2 | 2.0 ± 2.2 | 4.8 ± 2.7 |
| TT | 4.3 ± 2.2 | 2.1 ± 2.3 | 4.3 ± 2.8 | |
| p value † | 0.725 | 0.759 | 0.137 | |
| q value | 0.858 | 0.848 | 0.403 | |
| ARID5B | GG | 4.3 ± 2.1 a | 2.2 ± 2.0 | 4.6 ± 3.1 |
| rs10821944 | TG | 4.5 ± 2.2 | 2.2 ± 2.3 | 4.6 ± 2.7 |
| TT | 4.3 ± 2.2 | 2.0 ± 2.2 | 4.3 ± 2.7 | |
| p value † | 0.799 | 0.674 | 0.483 | |
| q value | 0.858 | 0.848 | 0.780 | |
| PDE2A-ARAP1 | CC | 3.9 ± 2.3 | 1.7 ± 2.0 | 4.0 ± 2.8 |
| rs3781913 | AC | 4.3 ± 2.2 | 2.0 ± 2.3 | 4.4 ± 2.8 |
| AA | 4.5 ± 2.2 | 2.2 ± 2.2 | 4.5 ± 2.8 | |
| p value † | 0.239 | 0.198 | 0.585 | |
| q value | 0.858 | 0.699 | 0.780 | |
| PLD4 | CC | 4.3 ± 2.3 | 1.8 ± 1.8 | 4.3 ± 2.6 |
| rs2841277 | TC | 4.4 ± 2.1 | 2.2 ± 2.3 | 4.3 ± 2.7 |
| TT | 4.3 ± 2.2 | 2.0 ± 2.3 | 4.6 ± 3.0 | |
| p value † | 0.858 | 0.218 | 0.886 | |
| q value | 0.858 | 0.699 | 0.886 | |
| PTPN2 | GG | 4.7 ± 2.6 | 2.3 ± 2.6 | 4.8 ± 3.1 |
| rs2847297 | AG | 4.2 ± 2.2 | 2.0 ± 2.2 | 4.2 ± 2.7 |
| AA | 4.5 ± 2.1 | 2.1 ± 2.2 | 4.6 ± 2.7 | |
| p value † | 0.405 | 0.603 | 0.151 | |
| q value | 0.858 | 0.848 | 0.403 | |
| Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism | Genotype | IgA (mg/dL) | ESR (mm/h) | CRP (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B3GNT2 | TT | 263.40 ± 53.86 a | 11.60 ± 11.63 | 0.49 ± 0.27 |
| rs11900673 | CT | 307.39 ± 113.43 | 22.15 ± 18.14 | 0.93 ± 1.67 |
| CC | 317.30 ± 125.25 | 25.97 ± 20.93 | 1.22 ± 1.91 | |
| p value † | 0.500 | 0.065 | 0.180 | |
| q value | 0.571 | 0.520 | 0.720 | |
| CSF2 | AA | 371.31 ± 151.17 | 26.59 ± 20.15 | 1.52 ± 1.75 |
| rs657075 | GA | 304.23 ± 121.55 | 25.64 ± 22.61 | 1.17 ± 1.93 |
| GG | 322.66 ± 119.54 | 23.02 ± 17.98 | 0.98 ± 1.58 | |
| p value † | 0.029 | 0.541 | 0.274 | |
| q value | 0.194 | 0.845 | 0.731 | |
| CD83 | CC | 351.13 ± 163.63 | 25.57 ± 25.22 | 1.31 ± 1.98 |
| rs12529514 | TC | 330.24 ± 130.04 | 25.58 ± 18.73 | 1.08 ± 1.63 |
| TT | 312.55 ± 116.45 | 25.17 ± 22.05 | 1.20 ± 1.96 | |
| p value † | 0.087 | 0.891 | 0.827 | |
| q value | 0.194 | 0.845 | 0.945 | |
| NFKBIE | CC | 301.55 ± 116.79 | 35.30 ± 24.70 | 1.76 ± 2.16 |
| rs2233434 | TC | 301.49 ± 112.85 | 24.60 ± 22.42 | 1.16 ± 1.70 |
| TT | 330.32 ± 132.87 | 25.38 ± 20.66 | 1.15 ± 1.88 | |
| p value † | 0.176 | 0.484 | 0.594 | |
| q value | 0.235 | 0.845 | 0.945 | |
| ARID5B | GG | 369.07 ± 167.58 | 27.03 ± 25.29 | 1.33 ± 1.81 |
| rs10821944 | TG | 324.63 ± 129.37 | 25.16 ± 20.59 | 1.18 ± 2.00 |
| TT | 312.27 ± 115.63 | 25.22 ± 20.84 | 1.08 ± 1.70 | |
| p value † | 0.109 | 0.845 | 0.816 | |
| q value | 0.194 | 0.845 | 0.945 | |
| PDE2A-ARAP1 | CC | 306.59 ± 137.91 | 21.81 ± 22.15 | 1.11 ± 2.12 |
| rs3781913 | AC | 306.65 ± 107.39 | 24.65 ± 19.00 | 1.15 ± 1.82 |
| AA | 336.00 ± 132.63 | 25.64 ± 21.70 | 1.15 ± 1.76 | |
| p value † | 0.118 | 0.651 | 0.995 | |
| q value | 0.194 | 0.845 | 0.995 | |
| PLD4 | CC | 325.88 ± 142.40 | 22.71 ± 18.27 | 1.08 ± 1.92 |
| rs2841277 | TC | 310.67 ± 126.94 | 26.50 ± 23.30 | 1.15 ± 1.84 |
| TT | 338.13 ± 122.76 | 23.19 ± 18.32 | 1.09 ± 1.69 | |
| p value † | 0.121 | 0.241 | 0.788 | |
| q value | 0.194 | 0.845 | 0.945 | |
| PTPN2 | GG | 323.91 ± 140.76 | 28.00 ± 21.32 | 1.66 ± 2.55 |
| rs2847297 | AG | 318.27 ± 129.70 | 25.58 ± 22.68 | 1.15 ± 1.68 |
| AA | 322.05 ± 120.44 | 23.78 ± 18.89 | 1.03 ± 1.84 | |
| p value † | 0.788 | 0.451 | 0.162 | |
| q value | 0.788 | 0.845 | 0.720 | |
| SNP ID | Gencode ID (ENSG00000-) | Gene Symbol | p Value | Effect Size | Tissue | Actions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs657075 | 164398.8 | ACSL6 | 4.70 × 10−7 | 1.00 | Colon, sigmoid | AG > GG |
| rs3781913 | 186635.10 | ARAP1 | 1.40 × 10−8 | −0.29 | Esophagus, mucosa | TT > GT > GG |
| 214530.3 | STARD10 | 1.40 × 10−6 | 0.38 | Heart, atrial appendage | TT < GT < GG | |
| 256007.1 | ARAP1-AS1 | 3.00× 10−6 | −0.18 | Esophagus, mucosa | TT > GT > GG | |
| 214530.3 | STARD10 | 3.20 × 10−6 | 0.19 | Whole blood | TT < GT < GG | |
| 214530.3 | STARD10 | 3.30 × 10−6 | 0.20 | Cells, transformed fibroblasts | TT < GT < GG | |
| 214530.3 | STARD10 | 1.00 × 10−5 | 0.16 | Muscle, skeletal | TT < GT < GG | |
| rs2841277 | 140104.9 | C14orf79 | 1.10 × 10−8 | 0.29 | Cells, transformed fibroblasts | CC < CT < TT |
| 140104.9 | C14orf79 | 2.10 × 10−8 | 0.44 | Brain, cortex | CC < CT < TT | |
| 140104.9 | C14orf79 | 6.60 × 10−7 | 0.25 | Skin, sun-exposed (lower leg) | CC < CT < TT | |
| 140104.9 | C14orf79 | 2.30 × 10−6 | 0.47 | Brain, cerebellum | CC < CT < TT | |
| 140104.9 | C14orf79 | 8.30 × 10−6 | 0.29 | Esophagus, muscularis | CC < CT < TT | |
| rs2847297 | 267654.1 | RP11-973H7.4 | 6.60 × 10−14 | 0.45 | Whole blood | AA < AG < GG |
| 260302.1 | RP11-973H7.1 | 2.10 × 10−10 | 0.49 | Artery, tibial | AA < AG < GG | |
| 260302.1 | RP11-973H7.1 | 7.20 × 10−9 | 0.52 | Artery, aorta | AA < AG < GG | |
| 260302.1 | RP11-973H7.1 | 2.70 × 10−7 | 0.48 | Esophagus, muscularis | AA < AG < GG | |
| 260302.1 | RP11-973H7.1 | 4.10 × 10−7 | 0.40 | Lung | AA < AG < GG | |
| 260302.1 | RP11-973H7.1 | 5.00 × 10−7 | 0.25 | Whole blood | AA < AG < GG |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.-C.; Wei, J.C.-C.; Lu, H.-F.; Wong, H.S.-C.; Woon, P.Y.; Hsu, Y.-W.; Huang, J.-D.; Chang, W.-C. rs657075 (CSF2) Is Associated with the Disease Phenotype (BAS-G) of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010083
Chen W-C, Wei JC-C, Lu H-F, Wong HS-C, Woon PY, Hsu Y-W, Huang J-D, Chang W-C. rs657075 (CSF2) Is Associated with the Disease Phenotype (BAS-G) of Ankylosing Spondylitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(1):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010083
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Wei-Chiao, James Cheng-Chung Wei, Hsing-Fang Lu, Henry Sung-Ching Wong, Peng Yeong Woon, Yu-Wen Hsu, Jin-Ding Huang, and Wei-Chiao Chang. 2017. "rs657075 (CSF2) Is Associated with the Disease Phenotype (BAS-G) of Ankylosing Spondylitis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 1: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010083
APA StyleChen, W. -C., Wei, J. C. -C., Lu, H. -F., Wong, H. S. -C., Woon, P. Y., Hsu, Y. -W., Huang, J. -D., & Chang, W. -C. (2017). rs657075 (CSF2) Is Associated with the Disease Phenotype (BAS-G) of Ankylosing Spondylitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(1), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010083