Sevoflurane Postconditioning-Induced Anti-Inflammation via Inhibition of the Toll-Like Receptor-4/Nuclear Factor Kappa B Pathway Contributes to Neuroprotection against Transient Global Cerebral Ischemia in Rats
Abstract
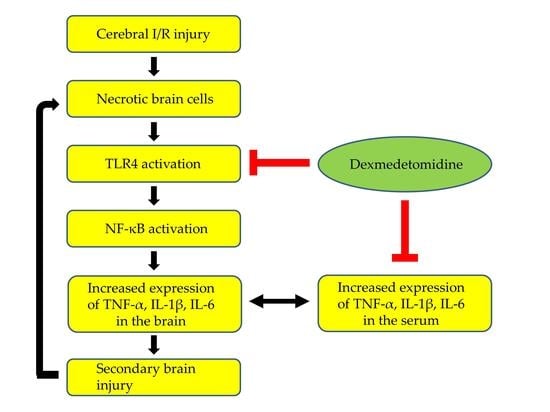
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Hemodynamics
2.2. Neurologic Deficit Score
2.3. Histological Exams
2.4. Western Blots
2.5. Serum Levels of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| I/R | ischemia/reperfusion |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| IL | interleukin |
| TLR | toll-like receptors |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa B |
| CCA | common carotid artery |
| CBF | cerebral blood flow |
| MAP | mean arterial pressure |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| TUNEL | terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end-labeling |
References
- Kim, H.C.; Kim, E.; Bae, J.I.; Lee, K.H.; Jeon, Y.T.; Hwang, J.W.; Lim, Y.J.; Min, S.W.; Park, H.P. Sevoflurane Postconditioning Reduces Apoptosis by Activating the JAK-STAT Pathway After Transient Global Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2017, 29, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Z.; Zhang, L.; Su, J.; Cai, D.; Xu, Q. Sevoflurane postconditioning improves long-term learning and memory of neonatal hypoxia-ischemia brain damage rats via the PI3K/Akt-mPTP pathway. Brain Res. 2016, 1630, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.H.; Park, H.P.; Jeon, Y.T.; Lim, Y.J.; Nam, K.; Hwang, J.W. Combined treatment with celecoxib and sevoflurane after global cerebral ischaemia has no additive neuroprotective effects in rats. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 110, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.T.; Hwang, J.W.; Lim, Y.J.; Kim, A.N.; Park, H.P. A combination of sevoflurane postconditioning and albumin increases BCL-2 expression after transient global cerebral ischemia compared with either sevoflurane postconditioning or albumin alone. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2013, 25, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Park, Y.H.; Jeon, Y.T.; Hwang, J.W.; Lim, Y.J.; Kim, E.; Park, S.Y.; Park, H.P. Sevoflurane post-conditioning increases nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor and haemoxygenase-1 expression via protein kinase C pathway in a rat model of transient global cerebral ischaemia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 114, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.K.; Wu, H.F.; Zhou, H.; Yang, B.; Liu, X.Z. Postconditioning with sevoflurane protects against focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury involving mitochondrial ATP-dependent potassium channel and mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Neurol. Res. 2015, 37, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, P.; Xu, N.; Zhu, L.; Cai, M.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y. Paradigms and mechanisms of inhalational anesthetics mediated neuroprotection against cerebral ischemic stroke. Med. Gas Res. 2016, 6, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.F.; Xu, H.; Sun, Y.; Hu, R.; Jiang, H. Induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase by isoflurane post-conditioning via hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha during tolerance against ischemic neuronal injury. Brain Res. 2012, 1451, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vartanian, K.B.; Stenzel-Poore, M.P. Toll-Like Receptor Tolerance as a Mechanism for Neuroprotection. Transl. Stroke Res. 2010, 1, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Fang, X.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Yao, L.J.; Li, J.P.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y. Toll-like receptor 4-mediated myeloid differentiation factor 88-dependent signaling pathway is activated by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in hippocampal CA1 region in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, F.; Tang, H.; Wang, J.; Prunty, M.C.; Hua, X.; Sayeed, I.; Stein, D.G. TAK-242, an antagonist for Toll-like receptor 4, protects against acute cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, S.; Ryu, H.G.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, Y.J.; Park, H.P. Dexmedetomidine confers neuroprotection against transient global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting inflammation through inactivation of the TLR-4/NF-κB pathway. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 649, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Deng, B.; Zhao, X.; Gao, C.; Yang, L.; Zhao, H.; Yu, D.; Zhang, F.; Xu, L.; Chen, L.; et al. Isoflurane preconditioning provides neuroprotection against stroke by regulating the expression of the TLR4 signalling pathway to alleviate microglial activation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, I.M.; Macrae, I.M.; Di Napoli, M. Neuroinflammation and neuroprotective strategies in acute ischaemic stroke - from bench to bedside. Curr. Mol. Med. 2009, 9, 336–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidale, S.; Consoli, A.; Arnaboldi, M.; Consoli, D. Postischemic Inflammation in Acute Stroke. J. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridder, D.A.; Schwaninger, M. NF-κB signaling in cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caso, J.R.; Pradillo, J.M.; Hurtado, O.; Lorenzo, P.; Moro, M.A.; Lizasoain, I. Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in brain damage and inflammation after experimental stroke. Circulation 2007, 115, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Ye, T.; Tang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, H.; Jiang, Y. Exercise Preconditioning Regulates the Toll-Like Receptor 4/Nuclear Factor-κB Signaling Pathway and Reduces Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Inflammatory Injury: A Study in Rats. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 2770–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, P.; Chen, M.; Peng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Dong, N. Remote Ischaemic Preconditioning and Sevoflurane Postconditioning Synergistically Protect Rats from Myocardial Injury Induced by Ischemia and Reperfusion Partly via Inhibition TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Gonzalez, R.; Baluja, A.; Veiras Del Rio, S.; Rodriguez, A.; Rodriguez, J.; Taboada, M.; Brea, D.; Alvarez, J. Effects of sevoflurane postconditioning on cell death, inflammation and TLR expression in human endothelial cells exposed to LPS. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Gao, J.; Cui, Y.; Li, M.; Li, R.; Cui, C.; Cui, J. Neuroprotective Effects of Resatorvid Against Traumatic Brain Injury in Rat: Involvement of Neuronal Autophagy and TLR4 Signaling Pathway. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.C.; Wang, P.F.; Fang, H.; Chen, J.; Xiong, X.Y.; Yang, Q.W. Toll-like receptor 4 antagonist attenuates intracerebral hemorrhage-induced brain injury. Stroke 2013, 44, 2545–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zuo, G.; Shi, X.Y.; Zhang, J.; Fang, Q.; Chen, G. Progesterone administration modulates cortical TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage in male rats. Mediat. Inflamm. 2011, 2011, 848309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Hu, Y.Y.; Dong, X.Q.; Xu, Q.P.; Yu, W.H.; Zhang, Z.Y. The protective role of oxymatrine on neuronal cell apoptosis in the hemorrhagic rat brain. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 143, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.J.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, D.J.; Wang, T.J.; Li, Y.Y. The role of TNF-alpha, IL-6, IL-10, and GDNF in neuronal apoptosis in neonatal rat with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Che, L.H.; Ji, T.F.; Shi, L.; Yu, J.L. Effects of the TLR4 signaling pathway on apoptosis of neuronal cells in diabetes mellitus complicated with cerebral infarction in a rat model. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broughton, B.R.; Reutens, D.C.; Sobey, C.G. Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke 2009, 40, e331–e339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, K.I.; Marini, A.M. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition protects cultured cerebellar granule neurons from glutamate-mediated cell death. J. Neurotrauma 2002, 19, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamczyk, S.; Robin, E.; Simerabet, M.; Kipnis, E.; Tavernier, B.; Vallet, B.; Bordet, R.; Lebuffe, G. Sevoflurane pre- and post-conditioning protect the brain via the mitochondrial K ATP channel. Br. J. Anaesth. 2010, 104, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, N.; Tsuchimori, N.; Matsumoto, T.; Ii, M. TAK-242 (resatorvid), a small-molecule inhibitor of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 signaling, binds selectively to TLR4 and interferes with interactions between TLR4 and its adaptor molecules. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 79, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsberg, M.D.; Busto, R. Rodent models of cerebral ischemia. Stroke 1989, 20, 1627–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, G.; Harhausen, D.; Schepers, C.; Hoffmann, O.; Rohr, C.; Prinz, V.; Konig, J.; Lehrach, H.; Nietfeld, W.; Trendelenburg, G. TLR2 has a detrimental role in mouse transient focal cerebral ischemia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 359, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehnardt, S.; Lehmann, S.; Kaul, D.; Tschimmel, K.; Hoffmann, O.; Cho, S.; Krueger, C.; Nitsch, R.; Meisel, A.; Weber, J.R. Toll-like receptor 2 mediates CNS injury in focal cerebral ischemia. J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 190, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, L.; Ebmeyer, U.; Safar, P.; Radovsky, A.; Neumar, R. Outcome model of asphyxial cardiac arrest in rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1995, 15, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, J.-W.; Jeon, Y.-T.; Lim, Y.-J.; Park, H.-P. Sevoflurane Postconditioning-Induced Anti-Inflammation via Inhibition of the Toll-Like Receptor-4/Nuclear Factor Kappa B Pathway Contributes to Neuroprotection against Transient Global Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112347
Hwang J-W, Jeon Y-T, Lim Y-J, Park H-P. Sevoflurane Postconditioning-Induced Anti-Inflammation via Inhibition of the Toll-Like Receptor-4/Nuclear Factor Kappa B Pathway Contributes to Neuroprotection against Transient Global Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(11):2347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112347
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Jung-Won, Young-Tae Jeon, Young-Jin Lim, and Hee-Pyoung Park. 2017. "Sevoflurane Postconditioning-Induced Anti-Inflammation via Inhibition of the Toll-Like Receptor-4/Nuclear Factor Kappa B Pathway Contributes to Neuroprotection against Transient Global Cerebral Ischemia in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 11: 2347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112347
APA StyleHwang, J. -W., Jeon, Y. -T., Lim, Y. -J., & Park, H. -P. (2017). Sevoflurane Postconditioning-Induced Anti-Inflammation via Inhibition of the Toll-Like Receptor-4/Nuclear Factor Kappa B Pathway Contributes to Neuroprotection against Transient Global Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112347