Molecular-Targeted Therapies for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Its Resistance Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Roles of EGFR/ERBB in Cancer
2.1. History of Discovery
2.2. EGFR/ERBB Signaling
2.3. EGFR/HER Ligands
2.4. Nuclear Localization and Functions of the EGFR/ERBB Family
3. Amplifications and Mutations in EGFR in Cancer
3.1. EGFR
3.2. HER2
3.3. HER3 and HER4
4. Cancer Therapy Targeting EGFR
4.1. TKIs Targeting EGFR
4.2. Anti-EGFR mAbs
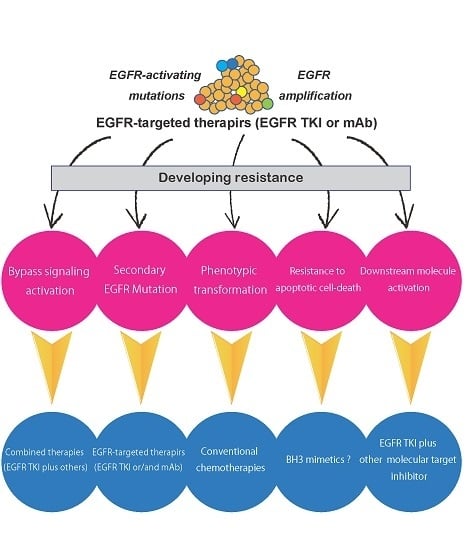
5. Mechanisms of Resistance to EGFR TKIs
5.1. Secondary Mutations in the EGFR Gene
5.2. Activation of Alternative Pathways
5.3. Phenotypic Transformation
5.4. Resistance to Apoptotic Cell Death
6. Mechanisms of Resistance to Anti-EGFR Antibodies
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| ERBB | Avian erythroblastosis oncogene B |
| HER2 | Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| SCCHN | Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck |
| PFS | Progress-free survival |
| TKI | Tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| mAb | Monoclonal antibody |
| PDGFR | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor |
| NRG | Neuregulin |
References
- Yarden, Y. The EGFR family and its ligands in human cancer. Signalling mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Eur. J. Cancer 2001, 37 (Suppl. 4), S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Geer, P.; Hunter, T.; Lindberg, R.A. Receptor protein-tyrosine kinases and their signal transduction pathways. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1994, 10, 251–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olayioye, M.A.; Neve, R.M.; Lane, H.A.; Hynes, N.E. The ErbB signaling network: Receptor heterodimerization in development and cancer. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 3159–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardiello, F.; Tortora, G. EGFR antagonists in cancer treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1160–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furnari, F.B.; Fenton, T.; Bachoo, R.M.; Mukasa, A.; Stommel, J.M.; Stegh, A.; Hahn, W.C.; Ligon, K.L.; Louis, D.N.; Brennan, C.; et al. Malignant astrocytic glioma: Genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2683–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgillo, F.; Della Corte, C.M.; Fasano, M.; Ciardiello, F. Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR-targeted drugs: Lung cancer. ESMO Open 2016, 1, e000060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misale, S.; Yaeger, R.; Hobor, S.; Scala, E.; Janakiraman, M.; Liska, D.; Valtorta, E.; Schiavo, R.; Buscarino, M.; Siravegna, G.; et al. Emergence of KRAS mutations and acquired resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in colorectal cancer. Nature 2012, 486, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowits, G.; Haddad, R.I. Overcoming resistance to EGFR inhibitor in head and neck cancer: A review of the literature. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, T.J.; Bell, D.W.; Sordella, R.; Gurubhagavatula, S.; Okimoto, R.A.; Brannigan, B.W.; Harris, P.L.; Haserlat, S.M.; Supko, J.G.; Haluska, F.G.; et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downward, J.; Yarden, Y.; Mayes, E.; Scrace, G.; Totty, N.; Stockwell, P.; Ullrich, A.; Schlessinger, J.; Waterfield, M.D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature 1984, 307, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schechter, A.L.; Stern, D.F.; Vaidyanathan, L.; Decker, S.J.; Drebin, J.A.; Greene, M.I.; Weinberg, R.A. The neu oncogene: An erb-B-related gene encoding a 185,000-Mr tumour antigen. Nature 1984, 312, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, W.J.; Arteaga, C.L.; Muthuswamy, S.K.; Siegel, P.M.; Webster, M.A.; Cardiff, R.D.; Meise, K.S.; Li, F.; Halter, S.A.; Coffey, R.J. Synergistic interaction of the Neu proto-oncogene product and transforming growth factor alpha in the mammary epithelium of transgenic mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 5726–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Fiore, P.P.; Pierce, J.H.; Kraus, M.H.; Segatto, O.; King, C.R.; Aaronson, S.A. erbB-2 is a potent oncogene when overexpressed in NIH/3T3 cells. Science 1987, 237, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphreys, R.C.; Hennighausen, L. Transforming growth factor alpha and mouse models of human breast cancer. Oncogene 2000, 19, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarden, Y.; Pines, G. The ERBB network: At last, cancer therapy meets systems biology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, Y.J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Feyereislova, A.; Chung, H.C.; Shen, L.; Sawaki, A.; Lordick, F.; Ohtsu, A.; Omuro, Y.; Satoh, T.; et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): A phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Miles, D.; Gianni, L.; Krop, I.E.; Welslau, M.; Baselga, J.; Pegram, M.; Oh, D.Y.; Dieras, V.; Guardino, E.; et al. Trastuzumab emtansine for HER2-positive advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paez, J.G.; Janne, P.A.; Lee, J.C.; Tracy, S.; Greulich, H.; Gabriel, S.; Herman, P.; Kaye, F.J.; Lindeman, N.; Boggon, T.J.; et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004, 304, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsudomi, T.; Kosaka, T.; Yatabe, Y. Biological and clinical implications of EGFR mutations in lung cancer. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 11, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, C.H.; Boggon, T.J.; Li, Y.; Woo, M.S.; Greulich, H.; Meyerson, M.; Eck, M.J. Structures of lung cancer-derived EGFR mutants and inhibitor complexes: Mechanism of activation and insights into differential inhibitor sensitivity. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarden, Y.; Sliwkowski, M.X. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrett, T.P.; McKern, N.M.; Lou, M.; Elleman, T.C.; Adams, T.E.; Lovrecz, G.O.; Kofler, M.; Jorissen, R.N.; Nice, E.C.; Burgess, A.W.; et al. The crystal structure of a truncated ErbB2 ectodomain reveals an active conformation, poised to interact with other ErbB receptors. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Telesco, S.E.; Liu, Y.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Lemmon, M.A. ErbB3/HER3 intracellular domain is competent to bind ATP and catalyze autophosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7692–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arteaga, C.L.; Engelman, J.A. ERBB receptors: From oncogene discovery to basic science to mechanism-based cancer therapeutics. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 282–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umekita, Y.; Enokizono, N.; Sagara, Y.; Kuriwaki, K.; Takasaki, T.; Yoshida, A.; Yoshida, H. Immunohistochemical studies on oncogene products (EGF-R, c-erbB-2) and growth factors (EGF, TGF-alpha) in human breast cancer: Their relationship to oestrogen receptor status, histological grade, mitotic index and nodal status. Virchows Arch. A Pathol. Anat. Histopathol. 1992, 420, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, T.; Mizushima, H.; Chinen, I.; Moribe, H.; Yagi, S.; Hoffman, R.M.; Kimura, T.; Yoshino, K.; Ueda, Y.; Enomoto, T.; et al. HB-EGF and PDGF mediate reciprocal interactions of carcinoma cells with cancer-associated fibroblasts to support progression of uterine cervical cancers. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6633–6642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.E.; Kim, H.J.; Shin, D.H.; Hwang, S.H.; Kang, C.D.; Oh, S.O. Overexpression of NRG1 promotes progression of gastric cancer by regulating the self-renewal of cancer stem cells. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prentice, L.M.; Shadeo, A.; Lestou, V.S.; Miller, M.A.; deLeeuw, R.J.; Makretsov, N.; Turbin, D.; Brown, L.A.; Macpherson, N.; Yorida, E.; et al. NRG1 gene rearrangements in clinical breast cancer: Identification of an adjacent novel amplicon associated with poor prognosis. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7281–7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, T.R.; Lee, D.Y.; Berry, L.; Shames, D.S.; Settleman, J. Neuregulin-1-mediated autocrine signaling underlies sensitivity to HER2 kinase inhibitors in a subset of human cancers. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonesaka, K.; Kudo, K.; Nishida, S.; Takahama, T.; Iwasa, T.; Yoshida, T.; Tanaka, K.; Takeda, M.; Kaneda, H.; Okamoto, I.; et al. The pan-HER family tyrosine kinase inhibitor afatinib overcomes HER3 ligand heregulin-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 33602–33611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.W.; Ali-Seyed, M.; Wu, Y.; Bartholomeusz, G.; Hsu, S.C.; Hung, M.C. Nuclear-cytoplasmic transport of EGFR involves receptor endocytosis, importin beta1 and CRM1. J. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 98, 1570–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psyrri, A.; Yu, Z.; Weinberger, P.M.; Sasaki, C.; Haffty, B.; Camp, R.; Rimm, D.; Burtness, B.A. Quantitative determination of nuclear and cytoplasmic epidermal growth factor receptor expression in oropharyngeal squamous cell cancer by using automated quantitative analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5856–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traynor, A.M.; Weigel, T.L.; Oettel, K.R.; Yang, D.T.; Zhang, C.; Kim, K.; Salgia, R.; Iida, M.; Brand, T.M.; Hoang, T.; et al. Nuclear EGFR protein expression predicts poor survival in early stage non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2013, 81, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.C.; Hung, M.C. Nuclear translocation of the epidermal growth factor receptor family membrane tyrosine kinase receptors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6484–6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, T.M.; Iida, M.; Luthar, N.; Starr, M.M.; Huppert, E.J.; Wheeler, D.L. Nuclear EGFR as a molecular target in cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 108, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.W.; Hsu, S.C.; Ali-Seyed, M.; Gunduz, M.; Xia, W.; Wei, Y.; Bartholomeusz, G.; Shih, J.Y.; Hung, M.C. Nuclear interaction of EGFR and STAT3 in the activation of the iNOS/NO pathway. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.W.; Cao, X.; Zhu, H.; Ali-Osman, F. Cyclooxygenase-2 is a novel transcriptional target of the nuclear EGFR-STAT3 and EGFRvIII-STAT3 signaling axes. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmann, K.; Mayer, C.; Fehrenbacher, B.; Schaller, M.; Raju, U.; Milas, L.; Chen, D.J.; Kehlbach, R.; Rodemann, H.P. Radiation-induced epidermal growth factor receptor nuclear import is linked to activation of DNA-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 31182–31189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmann, K.; Mayer, C.; Rodemann, H.P. Inhibition of radiation-induced EGFR nuclear import by C225 (Cetuximab) suppresses DNA-PK activity. Radiother. Oncol. 2005, 76, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Iida, M.; Dunn, E.F.; Ghia, A.J.; Wheeler, D.L. Nuclear EGFR contributes to acquired resistance to cetuximab. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3801–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, H.; Fukui, Y.; Ueyama, Y.; Tamaoki, N.; Kawamoto, T.; Taniguchi, S.; Shibuya, M. Amplification of the structurally and functionally altered epidermal growth factor receptor gene (c-erbB) in human brain tumors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1988, 8, 1816–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawa, N.; Ekstrand, A.J.; James, C.D.; Collins, V.P. Identical splicing of aberrant epidermal growth factor receptor transcripts from amplified rearranged genes in human glioblastomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 8602–8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscatello, D.K.; Holgado-Madruga, M.; Godwin, A.K.; Ramirez, G.; Gunn, G.; Zoltick, P.W.; Biegel, J.A.; Hayes, R.L.; Wong, A.J. Frequent expression of a mutant epidermal growth factor receptor in multiple human tumors. Cancer Res 1995, 55, 5536–5539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, I.; Kenyon, L.C.; Emlet, D.R.; Mori, T.; Sasaki, J.; Hirosako, S.; Ichikawa, Y.; Kishi, H.; Godwin, A.K.; Yoshioka, M.; et al. Expression of constitutively activated EGFRvIII in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2003, 94, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, R.; Ji, X.D.; Harmon, R.C.; Lazar, C.S.; Gill, G.N.; Cavenee, W.K.; Huang, H.J. A mutant epidermal growth factor receptor common in human glioma confers enhanced tumorigenicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 7727–7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reardon, D.A.; Wen, P.Y.; Mellinghoff, I.K. Targeted molecular therapies against epidermal growth factor receptor: Past experiences and challenges. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16 (Suppl. 8), viii7–viii13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, J.N.; Reardon, D.A.; Peery, T.; Dowell, J.M.; Quinn, J.A.; Penne, K.L.; Wikstrand, C.J.; Van Duyn, L.B.; Dancey, J.E.; McLendon, R.E.; et al. Phase II trial of gefitinib in recurrent glioblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsamadicy, A.A.; Chongsathidkiet, P.; Desai, R.; Woroniecka, K.; Farber, S.H.; Fecci, P.E.; Sampson, J.H. Prospect of rindopepimut in the treatment of glioblastoma. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2017, 17, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Teugels, E.; Sadones, J.; De Brakeleer, S.; Duerinck, J.; Du Four, S.; Michotte, A.; De Greve, J.; Neyns, B. Correlation of EGFR, IDH1 and PTEN status with the outcome of patients with recurrent glioblastoma treated in a phase II clinical trial with the EGFR-blocking monoclonal antibody cetuximab. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Quang, T.S.; Gracely, E.J.; Kim, J.H.; Emrich, J.G.; Yaeger, T.E.; Jenrette, J.M.; Cohen, S.C.; Black, P.; Brady, L.W. A Phase II study of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor radioimmunotherapy in the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 113, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.; Butowski, N.; Tran, D.D.; Recht, L.D.; Lim, M.; Hirte, H.; Ashby, L.; Mechtler, L.; Goldlust, S.A.; Iwamoto, F.; et al. Rindopepimut with temozolomide for patients with newly diagnosed, EGFRvIII-expressing glioblastoma (ACT IV): A randomised, double-blind, international phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederick, L.; Wang, X.Y.; Eley, G.; James, C.D. Diversity and frequency of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in human glioblastomas. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 1383–1387. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, H.; Endo, K.; Konishi, A.; Takada, M.; Kawahara, M.; Iuchi, K.; Matsumura, A.; Okumura, M.; Tanaka, H.; Kawaguchi, T.; et al. EGFR Mutation status in Japanese lung cancer patients: Genotyping analysis using LightCycler. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 2924–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, T.; Ohe, Y.; Sakamoto, H.; Tsuta, K.; Matsuno, Y.; Tateishi, U.; Yamamoto, S.; Nokihara, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Sekine, I.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations and increased copy numbers predict gefitinib sensitivity in patients with recurrent non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 6829–6837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, K.D.; Garton, A.J.; Romero, M.S.; Kahler, J.; Thomson, S.; Ross, S.; Park, F.; Haley, J.D.; Gibson, N.; Sliwkowski, M.X. Kinetic analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor somatic mutant proteins shows increased sensitivity to the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, erlotinib. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8163–8171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigematsu, H.; Lin, L.; Takahashi, T.; Nomura, M.; Suzuki, M.; Wistuba, I.I.; Fong, K.M.; Lee, H.; Toyooka, S.; Shimizu, N.; et al. Clinical and biological features associated with epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations in lung cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2005, 97, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrick, D.T.; Kittelson, J.; Winterhalder, R.; Kotantoulas, G.; Ingeberg, S.; Keith, R.L.; Kennedy, T.C.; Miller, Y.E.; Franklin, W.A.; Hirsch, F.R. Analysis of c-ErbB1/epidermal growth factor receptor and c-ErbB2/HER-2 expression in bronchial dysplasia: Evaluation of potential targets for chemoprevention of lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12 Pt 1, 2281–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, T.D.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W.; Velculescu, V.E. Somatic mutations of EGFR in colorectal cancers and glioblastomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, C.; Li, F.; Wang, X. EGFR gene copy number as a prognostic marker in colorectal cancer patients treated with cetuximab or panitumumab: A systematic review and meta analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekstrand, A.J.; Sugawa, N.; James, C.D.; Collins, V.P. Amplified and rearranged epidermal growth factor receptor genes in human glioblastomas reveal deletions of sequences encoding portions of the N- and/or C-terminal tails. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 4309–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtt, M.R.; Moossy, J.; Donovan-Peluso, M.; Locker, J. Amplification of epidermal growth factor receptor gene in gliomas: Histopathology and prognosis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1992, 51, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apicella, M.; Corso, S.; Giordano, S. Targeted therapies for gastric cancer: Failures and hopes from clinical trials. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 57654–57669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Bian, X.Y.; Ni, X.Z.; Shen, D.P.; Shen, Y.Y.; Liu, H.; Shen, Z.Y.; Liu, Q. Correlation of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 expression with clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis in gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 2171–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Parker, B.A.; Schwab, R.; Kurzrock, R. HER2 aberrations in cancer: Implications for therapy. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, P.; Hunter, C.; Bignell, G.; Edkins, S.; Davies, H.; Teague, J.; Stevens, C.; O’Meara, S.; Smith, R.; Parker, A.; et al. Lung cancer: Intragenic ERBB2 kinase mutations in tumours. Nature 2004, 431, 525–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcila, M.E.; Chaft, J.E.; Nafa, K.; Roy-Chowdhuri, S.; Lau, C.; Zaidinski, M.; Paik, P.K.; Zakowski, M.F.; Kris, M.G.; Ladanyi, M. Prevalence, clinicopathologic associations, and molecular spectrum of ERBB2 (HER2) tyrosine kinase mutations in lung adenocarcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4910–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, B.S.; Kljavin, N.M.; Stawiski, E.W.; Chan, E.; Parikh, C.; Durinck, S.; Chaudhuri, S.; Pujara, K.; Guillory, J.; Edgar, K.A.; et al. Oncogenic ERBB3 mutations in human cancers. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.; Killian, K.J.; Samuels, Y.; Rudloff, U. ERBB4 mutation analysis: Emerging molecular target for melanoma treatment. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1102, 461–480. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeng, N.; Liu, L.; McCabe, M.G.; Jones, D.T.; Ichimura, K.; Collins, V.P. Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) analysis with fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) probes reveals differential expression of the four ERBB4 juxtamembrane region variants between medulloblastoma and pilocytic astrocytoma. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2009, 35, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bareschino, M.A.; Schettino, C.; Troiani, T.; Martinelli, E.; Morgillo, F.; Ciardiello, F. Erlotinib in cancer treatment. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18 (Suppl. 6), vi35–vi41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaccone, G.; Gonzalez-Larriba, J.L.; van Oosterom, A.T.; Alfonso, R.; Smit, E.F.; Martens, M.; Peters, G.J.; van der Vijgh, W.J.; Smith, R.; Averbuch, S.; et al. Combination therapy with gefitinib, an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, gemcitabine and cisplatin in patients with advanced solid tumors. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrelli, F.; Borgonovo, K.; Cabiddu, M.; Ghilardi, M.; Barni, S. Cetuximab and panitumumab in KRAS wild-type colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2011, 26, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrelli, F.; Barni, S. Anti-EGFR-targeting agents in recurrent or metastatic head and neck carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Head Neck 2012, 34, 1657–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha-Lima, C.M.; Soares, H.P.; Raez, L.E.; Singal, R. EGFR targeting of solid tumors. Cancer Control 2007, 14, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardiello, F. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors as anticancer agents. Drugs 2000, 60 (Suppl. 1), 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slichenmyer, W.J.; Fry, D.W. Anticancer therapy targeting the erbB family of receptor tyrosine kinases. Semin. Oncol. 2001, 28 (Suppl. 16), 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.C.; Sadeghi, P.; Pinter-Brown, L.C.; Yashar, S.; Chiu, M.W. Cutaneous side effects of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors: Clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and management. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 56, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Perez-Soler, R. Skin toxicities associated with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Target Oncol. 2009, 4, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widakowich, C.; de Castro, G., Jr.; de Azambuja, E.; Dinh, P.; Awada, A. Review: Side effects of approved molecular targeted therapies in solid cancers. Oncologist 2007, 12, 1443–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotta, K.; Kiura, K.; Takigawa, N.; Yoshioka, H.; Harita, S.; Kuyama, S.; Yonei, T.; Fujiwara, K.; Maeda, T.; Aoe, K.; et al. Comparison of the incidence and pattern of interstitial lung disease during erlotinib and gefitinib treatment in Japanese Patients with non-small cell lung cancer: The Okayama Lung Cancer Study Group experience. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, V.A.; Hirsh, V.; Cadranel, J.; Chen, Y.M.; Park, K.; Kim, S.W.; Zhou, C.; Su, W.C.; Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; et al. Afatinib versus placebo for patients with advanced, metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of erlotinib, gefitinib, or both, and one or two lines of chemotherapy (LUX-Lung 1): A phase 2b/3 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, D.A.; Ashton, S.E.; Ghiorghiu, S.; Eberlein, C.; Nebhan, C.A.; Spitzler, P.J.; Orme, J.P.; Finlay, M.R.; Ward, R.A.; Mellor, M.J.; et al. AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1046–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.S.; Cho, B.C.; Soo, R.A. Next-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2016, 93, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, A.W.; Cho, H.S.; Eigenbrot, C.; Ferguson, K.M.; Garrett, T.P.; Leahy, D.J.; Lemmon, M.A.; Sliwkowski, M.X.; Ward, C.W.; Yokoyama, S. An open-and-shut case? Recent insights into the activation of EGF/ErbB receptors. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunada, H.; Magun, B.E.; Mendelsohn, J.; MacLeod, C.L. Monoclonal antibody against epidermal growth factor receptor is internalized without stimulating receptor phosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 3825–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H.; Sakai, K.; Arao, T.; Shimoyama, T.; Tamura, T.; Nishio, K. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of cetuximab against tumor cells with wild-type or mutant epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, A.S.; Liu, S.; Lee, J.J.; Alden, C.M.; Blumenschein, G.R., Jr.; Herbst, R.; Davis, S.E.; Kim, E.; Lippman, S.; Heymach, J.; et al. Clinical and biomarker outcomes of the phase II vandetanib study from the BATTLE trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 658–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, C.H.; Mengwasser, K.E.; Toms, A.V.; Woo, M.S.; Greulich, H.; Wong, K.K.; Meyerson, M.; Eck, M.J. The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Boggon, T.J.; Dayaram, T.; Janne, P.A.; Kocher, O.; Meyerson, M.; Johnson, B.E.; Eck, M.J.; Tenen, D.G.; Halmos, B. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balak, M.N.; Gong, Y.; Riely, G.J.; Somwar, R.; Li, A.R.; Zakowski, M.F.; Chiang, A.; Yang, G.; Ouerfelli, O.; Kris, M.G.; et al. Novel D761Y and common secondary T790M mutations in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung adenocarcinomas with acquired resistance to kinase inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6494–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.A.; Arcila, M.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Sima, C.S.; Zakowski, M.F.; Pao, W.; Kris, M.G.; Miller, V.A.; Ladanyi, M.; Riely, G.J. Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Isa, S.; Ando, M.; Tamiya, A.; Kubo, A.; Saka, H.; Takeo, S.; Adachi, H.; Tagawa, T.; et al. Ultra-Sensitive Detection of the Pretreatment EGFR T790M Mutation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with an EGFR-Activating Mutation Using Droplet Digital PCR. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3552–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequist, L.V.; Yang, J.C.; Yamamoto, N.; O’Byrne, K.; Hirsh, V.; Mok, T.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Tsai, C.M.; Boyer, M.; et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.L.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.P.; Feng, J.; Lu, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Hou, M.; Shi, J.H.; Lee, K.Y.; et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janne, P.A.; Yang, J.C.; Kim, D.W.; Planchard, D.; Ohe, Y.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Ahn, M.J.; Kim, S.W.; Su, W.C.; Horn, L.; et al. AZD9291 in EGFR inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Han, J.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Bazhenova, L.A.; Ou, S.H.; Pang, Y.K.; Hin, H.S.; Juan, O.; Son, J.; Janne, P. 190TiP: ELUXA 1: Phase II study of BI 1482694 (HM61713) in patients (pts) with T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) after treatment with an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR TKI). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, S139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Yang, J.C.; Lee, C.K.; Kurata, T.; Kim, D.W.; John, T.; Nogami, N.; Ohe, Y.; Mann, H.; Rukazenkov, Y.; et al. Osimertinib As First-Line Treatment of EGFR Mutation-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Mitsudomi, T. Not all epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer are created equal: Perspectives for individualized treatment strategy. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scagliotti, G.; von Pawel, J.; Novello, S.; Ramlau, R.; Favaretto, A.; Barlesi, F.; Akerley, W.; Orlov, S.; Santoro, A.; Spigel, D.; et al. Phase III Multinational, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of Tivantinib (ARQ 197) Plus Erlotinib versus Erlotinib Alone in Previously Treated Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2667–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, H.; Park, E.; Yun, C.H.; Sng, N.J.; Lucena-Araujo, A.R.; Yeo, W.L.; Huberman, M.S.; Cohen, D.W.; Nakayama, S.; Ishioka, K.; et al. Structural, biochemical, and clinical characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion mutations in lung cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 216ra177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederst, M.J.; Hu, H.; Mulvey, H.E.; Lockerman, E.L.; Garcia, A.R.; Piotrowska, Z.; Sequist, L.V.; Engelman, J.A. The Allelic Context of the C797S Mutation Acquired upon Treatment with Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitors Impacts Sensitivity to Subsequent Treatment Strategies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3924–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, J.A.; Zejnullahu, K.; Mitsudomi, T.; Song, Y.; Hyland, C.; Park, J.O.; Lindeman, N.; Gale, C.M.; Zhao, X.; Christensen, J.; et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 2007, 316, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappuzzo, F.; Janne, P.A.; Skokan, M.; Finocchiaro, G.; Rossi, E.; Ligorio, C.; Zucali, P.A.; Terracciano, L.; Toschi, L.; Roncalli, M.; et al. MET increased gene copy number and primary resistance to gefitinib therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, E.E.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Su, J.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhang, X.C.; Xu, C.R.; Yang, J.J.; Tu, H.Y.; Yan, H.H.; et al. A Higher Proportion of the EGFR T790M Mutation May Contribute to the Better Survival of Patients with Exon 19 Deletions Compared with Those with L858R. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1368–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequist, L.V.; Waltman, B.A.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Digumarthy, S.; Turke, A.B.; Fidias, P.; Bergethon, K.; Shaw, A.T.; Gettinger, S.; Cosper, A.K.; et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 75ra26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.; Holgado-Madruga, M.; Maroun, C.; Fixman, E.D.; Kamikura, D.; Fournier, T.; Charest, A.; Tremblay, M.L.; Wong, A.J.; Park, M. Association of the multisubstrate docking protein Gab1 with the hepatocyte growth factor receptor requires a functional Grb2 binding site involving tyrosine 1356. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 20811–20819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turke, A.B.; Zejnullahu, K.; Wu, Y.L.; Song, Y.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Lifshits, E.; Toschi, L.; Rogers, A.; Mok, T.; Sequist, L.; et al. Preexistence and clonal selection of MET amplification in EGFR mutant NSCLC. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, S.; Yamada, T.; Takeuchi, S.; Tachibana, K.; Minami, Y.; Yatabe, Y.; Mitsudomi, T.; Tanaka, H.; Kimura, T.; Kudoh, S.; et al. Hepatocyte growth factor expression in EGFR mutant lung cancer with intrinsic and acquired resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in a Japanese cohort. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequist, L.V.; von Pawel, J.; Garmey, E.G.; Akerley, W.L.; Brugger, W.; Ferrari, D.; Chen, Y.; Costa, D.B.; Gerber, D.E.; Orlov, S.; et al. Randomized phase II study of erlotinib plus tivantinib versus erlotinib plus placebo in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3307–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, T.; Ohmori, T.; Ohba, M.; Arata, S.; Kishino, Y.; Murata, Y.; Kusumoto, S.; Ishida, H.; Shirai, T.; Hirose, T.; et al. Acquired Resistance Mechanisms to Combination Met-TKI/EGFR-TKI Exposure in Met-Amplified EGFR-TKI-Resistant Lung Adenocarcinoma Harboring an Activating EGFR Mutation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 3040–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takezawa, K.; Pirazzoli, V.; Arcila, M.E.; Nebhan, C.A.; Song, X.; de Stanchina, E.; Ohashi, K.; Janjigian, Y.Y.; Spitzler, P.J.; Melnick, M.A.; et al. HER2 amplification: A potential mechanism of acquired resistance to EGFR inhibition in EGFR-mutant lung cancers that lack the second-site EGFRT790M mutation. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigematsu, H.; Takahashi, T.; Nomura, M.; Majmudar, K.; Suzuki, M.; Lee, H.; Wistuba, I.I.; Fong, K.M.; Toyooka, S.; Shimizu, N.; et al. Somatic mutations of the HER2 kinase domain in lung adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 1642–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.E.; Narasanna, A.; Perez-Torres, M.; Xiang, B.; Wu, F.Y.; Yang, S.; Carpenter, G.; Gazdar, A.F.; Muthuswamy, S.K.; Arteaga, C.L. HER2 kinase domain mutation results in constitutive phosphorylation and activation of HER2 and EGFR and resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, T.; Tanizaki, J.; Paranal, R.M.; Endoh, H.; Lydon, C.; Capelletti, M.; Repellin, C.E.; Choi, J.; Ogino, A.; Calles, A.; et al. Response Heterogeneity of EGFR and HER2 Exon 20 Insertions to Covalent EGFR and HER2 Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2712–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trowe, T.; Boukouvala, S.; Calkins, K.; Cutler, R.E., Jr.; Fong, R.; Funke, R.; Gendreau, S.B.; Kim, Y.D.; Miller, N.; Woolfrey, J.R.; et al. EXEL-7647 inhibits mutant forms of ErbB2 associated with lapatinib resistance and neoplastic transformation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2465–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimandi, M.; Romano, A.; Curia, M.C.; Muraro, R.; Fedi, P.; Aaronson, S.A.; Di Fiore, P.P.; Kraus, M.H. Cooperative signaling of ErbB3 and ErbB2 in neoplastic transformation and human mammary carcinomas. Oncogene 1995, 10, 1813–1821. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sergina, N.V.; Rausch, M.; Wang, D.; Blair, J.; Hann, B.; Shokat, K.M.; Moasser, M.M. Escape from HER-family tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy by the kinase-inactive HER3. Nature 2007, 445, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgillo, F.; Woo, J.K.; Kim, E.S.; Hong, W.K.; Lee, H.Y. Heterodimerization of insulin-like growth factor receptor/epidermal growth factor receptor and induction of survivin expression counteract the antitumor action of erlotinib. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 10100–10111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lee, J.C.; Lin, L.; Olivas, V.; Au, V.; LaFramboise, T.; Abdel-Rahman, M.; Wang, X.; Levine, A.D.; Rho, J.K.; et al. Activation of the AXL kinase causes resistance to EGFR-targeted therapy in lung cancer. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ware, K.E.; Marshall, M.E.; Heasley, L.R.; Marek, L.; Hinz, T.K.; Hercule, P.; Helfrich, B.A.; Doebele, R.C.; Heasley, L.E. Rapidly acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in NSCLC cell lines through de-repression of FGFR2 and FGFR3 expression. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, R.; Kawahara, A.; Watari, K.; Murakami, Y.; Sonoda, K.; Maeda, M.; Fujita, H.; Kage, M.; Uramoto, H.; Costa, C.; et al. Erlotinib resistance in lung cancer cells mediated by integrin beta1/Src/Akt-driven bypass signaling. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 6243–6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, C.; Basaki, Y.; Kawahara, A.; Nakashima, K.; Kage, M.; Izumi, H.; Kohno, K.; Uramoto, H.; Yasumoto, K.; Kuwano, M.; et al. Loss of PTEN expression by blocking nuclear translocation of EGR1 in gefitinib-resistant lung cancer cells harboring epidermal growth factor receptor-activating mutations. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8715–8725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uramoto, H.; Shimokawa, H.; Hanagiri, T.; Kuwano, M.; Ono, M. Expression of selected gene for acquired drug resistance to EGFR-TKI in lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2011, 73, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludovini, V.; Bianconi, F.; Pistola, L.; Chiari, R.; Minotti, V.; Colella, R.; Giuffrida, D.; Tofanetti, F.R.; Siggillino, A.; Flacco, A.; et al. Phosphoinositide-3-kinase catalytic alpha and KRAS mutations are important predictors of resistance to therapy with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Shigematsu, H.; Nomura, M.; Lockwood, W.W.; Sato, M.; Okumura, N.; Soh, J.; Suzuki, M.; Wistuba, I.I.; Fong, K.M.; et al. PIK3CA mutations and copy number gains in human lung cancers. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6913–6921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Bunn, P.A., Jr.; Franklin, W.A.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Thatcher, N.; Chang, A.; Parikh, P.; Pereira, J.R.; Ciuleanu, T.; et al. Molecular predictors of outcome with gefitinib in a phase III placebo-controlled study in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 5034–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, K.; Sequist, L.V.; Arcila, M.E.; Moran, T.; Chmielecki, J.; Lin, Y.L.; Pan, Y.; Wang, L.; de Stanchina, E.; Shien, K.; et al. Lung cancers with acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors occasionally harbor BRAF gene mutations but lack mutations in KRAS, NRAS, or MEK1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2127–E2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, T.; Ohmori, T.; Ohba, M.; Arata, S.; Murata, Y.; Kusumoto, S.; Ando, K.; Ishida, H.; Ohnishi, T.; Sasaki, Y. Distinct Afatinib Resistance Mechanisms Identified in Lung Adenocarcinoma Harboring an EGFR Mutation. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oser, M.G.; Niederst, M.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Engelman, J.A. Transformation from non-small-cell lung cancer to small-cell lung cancer: Molecular drivers and cells of origin. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e165–e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Youk, J.; Park, S.; An, Y.; Keam, B.; Kim, D.W.; Heo, D.S.; et al. Clonal History and Genetic Predictors of Transformation Into Small-Cell Carcinomas From Lung Adenocarcinomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3065–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.B.; Onder, T.T.; Jiang, G.; Tao, K.; Kuperwasser, C.; Weinberg, R.A.; Lander, E.S. Identification of selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput screening. Cell 2009, 138, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voon, D.C.; Huang, R.Y.; Jackson, R.A.; Thiery, J.P. The EMT spectrum and therapeutic opportunities. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yauch, R.L.; Januario, T.; Eberhard, D.A.; Cavet, G.; Zhu, W.; Fu, L.; Pham, T.Q.; Soriano, R.; Stinson, J.; Seshagiri, S.; et al. Epithelial versus mesenchymal phenotype determines in vitro sensitivity and predicts clinical activity of erlotinib in lung cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11 Pt 1, 8686–8698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuoriluoto, K.; Haugen, H.; Kiviluoto, S.; Mpindi, J.P.; Nevo, J.; Gjerdrum, C.; Tiron, C.; Lorens, J.B.; Ivaska, J. Vimentin regulates EMT induction by Slug and oncogenic H-Ras and migration by governing Axl expression in breast cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 1436–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.; Balmanno, K.; Hadfield, K.; Weston, C.; Cook, S.J. Activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway promotes phosphorylation and proteasome-dependent degradation of the BH3-only protein, Bim. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 18811–18816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luciano, F.; Jacquel, A.; Colosetti, P.; Herrant, M.; Cagnol, S.; Pages, G.; Auberger, P. Phosphorylation of Bim-EL by Erk1/2 on serine 69 promotes its degradation via the proteasome pathway and regulates its proapoptotic function. Oncogene 2003, 22, 6785–6793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, D.B.; Halmos, B.; Kumar, A.; Schumer, S.T.; Huberman, M.S.; Boggon, T.J.; Tenen, D.G.; Kobayashi, S. BIM mediates EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced apoptosis in lung cancers with oncogenic EGFR mutations. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, J.; Shimamura, T.; Perera, S.; Carlson, N.E.; Cai, D.; Shapiro, G.I.; Wong, K.K.; Letai, A. Proapoptotic BH3-only BCL-2 family protein BIM connects death signaling from epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition to the mitochondrion. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11867–11875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, A.C.; Corcoran, R.B.; Ebi, H.; Sequist, L.V.; Waltman, B.A.; Chung, E.; Incio, J.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Pollack, S.F.; Song, Y.; et al. BIM expression in treatment-naive cancers predicts responsiveness to kinase inhibitors. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, C.; Molina, M.A.; Drozdowskyj, A.; Gimenez-Capitan, A.; Bertran-Alamillo, J.; Karachaliou, N.; Gervais, R.; Massuti, B.; Wei, J.; Moran, T.; et al. The impact of EGFR T790M mutations and BIM mRNA expression on outcome in patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC treated with erlotinib or chemotherapy in the randomized phase III EURTAC trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.P.; Hillmer, A.M.; Chuah, C.T.; Juan, W.C.; Ko, T.K.; Teo, A.S.; Ariyaratne, P.N.; Takahashi, N.; Sawada, K.; Fei, Y.; et al. A common BIM deletion polymorphism mediates intrinsic resistance and inferior responses to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isobe, K.; Hata, Y.; Tochigi, N.; Kaburaki, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Makino, T.; Otsuka, H.; Sato, F.; Ishida, F.; Kikuchi, N.; et al. Clinical significance of BIM deletion polymorphism in non-small-cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, F.; Cheng, N.; Ren, R.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Ren, S.; et al. The Bim deletion polymorphism clinical profile and its relation with tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in Chinese patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer 2014, 120, 2299–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amado, R.G.; Wolf, M.; Peeters, M.; Van Cutsem, E.; Siena, S.; Freeman, D.J.; Juan, T.; Sikorski, R.; Suggs, S.; Radinsky, R.; et al. Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1626–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karapetis, C.S.; Khambata-Ford, S.; Jonker, D.J.; O’Callaghan, C.J.; Tu, D.; Tebbutt, N.C.; Simes, R.J.; Chalchal, H.; Shapiro, J.D.; Robitaille, S.; et al. K-ras mutations and benefit from cetuximab in advanced colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douillard, J.Y.; Oliner, K.S.; Siena, S.; Tabernero, J.; Burkes, R.; Barugel, M.; Humblet, Y.; Bodoky, G.; Cunningham, D.; Jassem, J.; et al. Panitumumab-FOLFOX4 treatment and RAS mutations in colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burtness, B.; Bauman, J.E.; Galloway, T. Novel targets in HPV-negative head and neck cancer: Overcoming resistance to EGFR inhibition. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, e302–e309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertotti, A.; Papp, E.; Jones, S.; Adleff, V.; Anagnostou, V.; Lupo, B.; Sausen, M.; Phallen, J.; Hruban, C.A.; Tokheim, C.; et al. The genomic landscape of response to EGFR blockade in colorectal cancer. Nature 2015, 526, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, T.M.; Iida, M.; Stein, A.P.; Corrigan, K.L.; Braverman, C.M.; Luthar, N.; Toulany, M.; Gill, P.S.; Salgia, R.; Kimple, R.J.; et al. AXL mediates resistance to cetuximab therapy. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5152–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardiello, F.; Bianco, R.; Caputo, R.; Caputo, R.; Damiano, V.; Troiani, T.; Melisi, D.; De Vita, F.; De Placido, S.; Bianco, A.R.; et al. Antitumor activity of ZD6474, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in human cancer cells with acquired resistance to antiepidermal growth factor receptor therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, M.; Siravegna, G.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Corti, G.; Crisafulli, G.; Ahronian, L.G.; Mussolin, B.; Kwak, E.L.; Buscarino, M.; Lazzari, L.; et al. Tumor Heterogeneity and Lesion-Specific Response to Targeted Therapy in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, D.L.; Iida, M.; Kruser, T.J.; Nechrebecki, M.M.; Dunn, E.F.; Armstrong, E.A.; Huang, S.; Harari, P.M. Epidermal growth factor receptor cooperates with Src family kinases in acquired resistance to cetuximab. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sok, J.C.; Coppelli, F.M.; Thomas, S.M.; Lango, M.N.; Xi, S.; Hunt, J.L.; Freilino, M.L.; Graner, M.W.; Wikstrand, C.J.; Bigner, D.D.; et al. Mutant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFRvIII) contributes to head and neck cancer growth and resistance to EGFR targeting. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5064–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagut, C.; Dalmases, A.; Bellosillo, B.; Crespo, M.; Pairet, S.; Iglesias, M.; Salido, M.; Gallen, M.; Marsters, S.; Tsai, S.P.; et al. Identification of a mutation in the extracellular domain of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor conferring cetuximab resistance in colorectal cancer. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobor, S.; Van Emburgh, B.O.; Crowley, E.; Misale, S.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Bardelli, A. TGFalpha and amphiregulin paracrine network promotes resistance to EGFR blockade in colorectal cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6429–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, B.C.; Fujii, T.; Dorfman, J.D.; Goodwin, J.M.; Zhu, A.X.; Lanuti, M.; Tanabe, K.K. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and integrin-linked kinase mediate sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in human hepatoma cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2391–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weickhardt, A.J.; Price, T.J.; Chong, G.; Gebski, V.; Pavlakis, N.; Johns, T.G.; Azad, A.; Skrinos, E.; Fluck, K.; Dobrovic, A.; et al. Dual targeting of the epidermal growth factor receptor using the combination of cetuximab and erlotinib: Preclinical evaluation and results of the phase II DUX study in chemotherapy-refractory, advanced colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iida, M.; Bahrar, H.; Brand, T.M.; Pearson, H.E.; Coan, J.P.; Orbuch, R.A.; Flanigan, B.G.; Swick, A.D.; Prabakaran, P.J.; Lantto, J.; et al. Targeting the HER Family with Pan-HER Effectively Overcomes Resistance to Cetuximab. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2175–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janjigian, Y.Y.; Smit, E.F.; Groen, H.J.; Horn, L.; Gettinger, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Riely, G.J.; Wang, B.; Fu, Y.; Chand, V.K.; et al. Dual inhibition of EGFR with afatinib and cetuximab in kinase inhibitor-resistant EGFR-mutant lung cancer with and without T790M mutations. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Eng, C.; Nowara, E.; Swieboda-Sadlej, A.; Tebbutt, N.C.; Mitchell, E.; Davidenko, I.; Stephenson, J.; Elez, E.; Prenen, H.; et al. Randomized phase Ib/II trial of rilotumumab or ganitumab with panitumumab versus panitumumab alone in patients with wild-type KRAS metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4240–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| EGFR TKIs | Approved Indication | Target |
|---|---|---|
| Gefitinib (Iressa) | Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with EGFR exon 19 deletions or exon 21 mutation (L858R) | EGFR |
| Erlotinib (Tarceva) | Metastatic or locally advanced NSCNC, with EGFR exon 19 deletions or exon 21 mutation (L858R) Metastatic or advanced pancreatic cancer in combination with gemcitabine | EGFR, PDGFR, c-Kit |
| Afatinib (Gilotrif) | Metastatic NSCLC with EGFR exon 19 deletions or exon 21 mutation (L858R) | EGFR, HER2, HER4 |
| Osimertinib (Tagrisso) | Metastatic EGFR T790M mutation-positive NSCLC, with progressive disease following first-line EGFR TKI therapy | EGFR T790M |
| Olmutinib (Olita) | Second-line treatment of NSCLC with the T790M mutation in EGFR (in Korea) | EGFR T790M |
| Lapatinib (Tykerb) | HER2-overexpressing breast cancer | EGFR, HER1, HER2 |
| Vandetanib (Caprelsa) | Medullary thyroid carcinoma | EGFR, VEGFR, Ret |
| EGFR-Targeted mAbs | Approved Indication | Target |
|---|---|---|
| Cetuximab (Erbitux) | Metastatic KRAS-negative CRC/SCCHN | EGFR |
| Panitumumab (Vectibix) | Metastatic KRAS-negative CRC | EGFR |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamaoka, T.; Ohba, M.; Ohmori, T. Molecular-Targeted Therapies for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Its Resistance Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112420
Yamaoka T, Ohba M, Ohmori T. Molecular-Targeted Therapies for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Its Resistance Mechanisms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(11):2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112420
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamaoka, Toshimitsu, Motoi Ohba, and Tohru Ohmori. 2017. "Molecular-Targeted Therapies for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Its Resistance Mechanisms" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 11: 2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112420
APA StyleYamaoka, T., Ohba, M., & Ohmori, T. (2017). Molecular-Targeted Therapies for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Its Resistance Mechanisms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112420