Bioinformatics Approaches for Fetal DNA Fraction Estimation in Noninvasive Prenatal Testing
Abstract
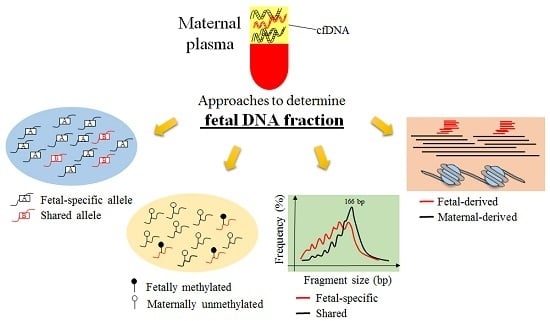
:1. Introduction
2. Current Approaches Developed to Estimate Fetal DNA Fraction
2.1. Y Chromosome-Based Approach
2.2. Maternal Plasma DNA Sequencing Data with Parental Genotype-Based Approach
2.3. High-Depth Sequencing Data of Maternal Plasma DNA-Based Approach
2.4. Shallow-Depth Maternal Plasma DNA Sequencing Data with Maternal Genotype-Based Approach
2.5. Shallow-Depth Maternal Plasma DNA Sequencing Data-Based Approach
2.6. Fetal Methylation Marker-Based Approach
2.7. Cell-Free DNA Size-Based Approach
2.8. Cell-Free DNA Nucleosome Track-Based Approach
3. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lo, Y.M.D.; Corbetta, N.; Chamberlain, P.F.; Rai, V.; Sargent, I.L.; Redman, C.W.; Wainscoat, J.S. Presence of fetal DNA in maternal plasma and serum. Lancet 1997, 350, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, R.W.K.; Chan, K.C.A.; Gao, Y.; Lau, V.Y.; Zheng, W.; Leung, T.Y.; Foo, C.H.; Xie, B.; Tsui, N.B.; Lun, F.M.; et al. Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal chromosomal aneuploidy by massively parallel genomic sequencing of DNA in maternal plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20458–20463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, R.W.K.; Akolekar, R.; Zheng, Y.W.; Leung, T.Y.; Sun, H.; Chan, K.C.A.; Lun, F.M.; Go, A.T.; Lau, E.T.; To, W.W.; et al. Non-invasive prenatal assessment of trisomy 21 by multiplexed maternal plasma DNA sequencing: Large scale validity study. BMJ 2011, 342, c7401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ehrich, M.; Deciu, C.; Zwiefelhofer, T.; Tynan, J.A.; Cagasan, L.; Tim, R.; Lu, V.; McCullough, R.; McCarthy, E.; Nygren, A.O.; et al. Noninvasive detection of fetal trisomy 21 by sequencing of DNA in maternal blood: A study in a clinical setting. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 204, 205.e201–205.e211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, D.W.; Platt, L.D.; Goldberg, J.D.; Abuhamad, A.Z.; Sehnert, A.J.; Rava, R.P. Genome-wide fetal aneuploidy detection by maternal plasma DNA sequencing. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 119, 890–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomaki, G.E.; Deciu, C.; Kloza, E.M.; Lambert-Messerlian, G.M.; Haddow, J.E.; Neveux, L.M.; Ehrich, M.; van den Boom, D.; Bombard, A.T.; Grody, W.W.; et al. DNA sequencing of maternal plasma reliably identifies trisomy 18 and trisomy 13 as well as down syndrome: An international collaborative study. Genet. Med. 2012, 14, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparks, A.B.; Struble, C.A.; Wang, E.T.; Song, K.; Oliphant, A. Noninvasive prenatal detection and selective analysis of cell-free DNA obtained from maternal blood: Evaluation for trisomy 21 and trisomy 18. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 206, 319.e1–319.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, M.E.; Wapner, R.J. Cell-free DNA analysis for noninvasive examination of trisomy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2582. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lo, Y.M.D.; Chan, K.C.A.; Sun, H.; Chen, E.Z.; Jiang, P.; Lun, F.M.; Zheng, Y.W.; Leung, T.Y.; Lau, T.K.; Cantor, C.R.; et al. Maternal plasma DNA sequencing reveals the genome-wide genetic and mutational profile of the fetus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 61ra91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, K.W.; Jiang, P.; Liao, G.J.; Chan, K.C.A.; Leung, T.Y.; Chiu, R.W.K.; Lo, Y.M.D. Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of monogenic diseases by targeted massively parallel sequencing of maternal plasma: Application to β-thalassemia. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Ge, H.; Li, X.; Jiang, T.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, P.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Ji, X.; et al. Haplotype-based approach for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia by maternal plasma DNA sequencing. Gene 2014, 544, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, M.; Li, X.; Ge, H.; Chen, F.; Han, M.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, D.; Xie, W.; Gao, Z.; Pan, X.; et al. Noninvasive prenatal testing for autosomal recessive conditions by maternal plasma sequencing in a case of congenital deafness. Genet. Med. 2014, 16, 972–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New, M.I.; Tong, Y.K.; Yuen, T.; Jiang, P.; Pina, C.; Chan, K.C.A.; Khattab, A.; Liao, G.J.; Yau, M.; Kim, S.M.; et al. Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia using cell-free fetal DNA in maternal plasma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E1022–E1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Ge, H.J.; Xiao, B.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Ying, X.M.; Pan, X.Y.; Wang, L.; Xie, W.W.; Ni, L.; et al. Haplotype-based approach for noninvasive prenatal tests of duchenne muscular dystrophy using cell-free fetal DNA in maternal plasma. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.K.; Lim, B.C.; Byeun, J.; Hwang, H.; Kim, K.J.; Hwang, Y.S.; Lee, J.; Park, J.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Namkung, J.; et al. Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of duchenne muscular dystrophy: Comprehensive genetic diagnosis in carrier, proband, and fetus. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, Y.Y.; Chik, K.W.; Chiu, R.W.K.; Ho, C.Y.; Lam, C.W.; Lo, Y.M.D. Predominant hematopoietic origin of cell-free DNA in plasma and serum after sex-mismatched bone marrow transplantation. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Jiang, P.; Chan, K.C.A.; Wong, J.; Cheng, Y.K.; Liang, R.H.; Chan, W.K.; Ma, E.S.; Chan, S.L.; Cheng, S.H.; et al. Plasma DNA tissue mapping by genome-wide methylation sequencing for noninvasive prenatal, cancer, and transplantation assessments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5503–E5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroun, M.; Lyautey, J.; Lederrey, C.; Olson-Sand, A.; Anker, P. About the possible origin and mechanism of circulating DNA apoptosis and active DNA release. Clin. Chim. Acta 2001, 313, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberry, M.; Maddocks, D.; Jones, M.; Abdel Hadi, M.; Abdel-Fattah, S.; Avent, N.; Soothill, P.W. Free fetal DNA in maternal plasma in anembryonic pregnancies: Confirmation that the origin is the trophoblast. Prenat. Diagn. 2007, 27, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canick, J.A.; Palomaki, G.E.; Kloza, E.M.; Lambert-Messerlian, G.M.; Haddow, J.E. The impact of maternal plasma DNA fetal fraction on next generation sequencing tests for common fetal aneuploidies. Prenat. Diagn. 2013, 33, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benn, P.; Cuckle, H. Theoretical performance of non-invasive prenatal testing for chromosome imbalances using counting of cell-free DNA fragments in maternal plasma. Prenat. Diagn. 2014, 34, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudecova, I.; Sahota, D.; Heung, M.M.; Jin, Y.; Lee, W.S.; Leung, T.Y.; Lo, Y.M.D.; Chiu, R.W.K. Maternal plasma fetal DNA fractions in pregnancies with low and high risks for fetal chromosomal aneuploidies. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lun, F.M.; Chiu, R.W.K.; Chan, K.C.A.; Leung, T.Y.; Lau, T.K.; Lo, Y.M.D. Microfluidics digital PCR reveals a higher than expected fraction of fetal DNA in maternal plasma. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, T.; Bunce, K.; Hogge, W.A.; Peters, D.G. Statistical model for whole genome sequencing and its application to minimally invasive diagnosis of fetal genetic disease. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1244–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, N.B.; Kadir, R.A.; Chan, K.C.A.; Chi, C.; Mellars, G.; Tuddenham, E.G.; Leung, T.Y.; Lau, T.K.; Chiu, R.W.K.; Lo, Y.M.D. Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of hemophilia by microfluidics digital PCR analysis of maternal plasma DNA. Blood 2011, 117, 3684–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygren, A.O.; Dean, J.; Jensen, T.J.; Kruse, S.; Kwong, W.; van den Boom, D.; Ehrich, M. Quantification of fetal DNA by use of methylation-based DNA discrimination. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomaki, G.E.; Kloza, E.M.; Lambert-Messerlian, G.M.; Haddow, J.E.; Neveux, L.M.; Ehrich, M.; van den Boom, D.; Bombard, A.T.; Deciu, C.; Grody, W.W.; et al. DNA sequencing of maternal plasma to detect down syndrome: An international clinical validation study. Genet. Med. 2011, 13, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaides, K.H.; Syngelaki, A.; Ashoor, G.; Birdir, C.; Touzet, G. Noninvasive prenatal testing for fetal trisomies in a routinely screened first-trimester population. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 207, 374.e371–374.e376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, W.W.; Jiang, P.; Tong, Y.K.; Lee, W.S.; Cheng, Y.K.; New, M.I.; Kadir, R.A.; Chan, K.C.A.; Leung, T.Y.; Lo, Y.M.D.; et al. Universal haplotype-based noninvasive prenatal testing for single gene diseases. Clin. Chem. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, G.J.; Lun, F.M.; Zheng, Y.W.; Chan, K.C.A.; Leung, T.Y.; Lau, T.K.; Chiu, R.W.K.; Lo, Y.M.D. Targeted massively parallel sequencing of maternal plasma DNA permits efficient and unbiased detection of fetal alleles. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Chan, K.C.A.; Liao, G.J.; Zheng, Y.W.; Leung, T.Y.; Chiu, R.W.K.; Lo, Y.M.D.; Sun, H. Fetalquant: Deducing fractional fetal DNA concentration from massively parallel sequencing of DNA in maternal plasma. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2883–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Peng, X.; Su, X.; Sun, K.; Yu, S.C.Y.; Chu, W.I.; Leung, T.Y.; Sun, H.; Chiu, R.W.K.; Lo, Y.M.D.; et al. FetalQuantSD: Accurate quantification of fetal DNA fraction by shallow-depth sequencing of maternal plasma DNA. NPJ Genom. Med. 2016, 1, 16013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Hannum, G.; Geis, J.; Tynan, J.; Hogg, G.; Zhao, C.; Jensen, T.J.; Mazloom, A.R.; Oeth, P.; Ehrich, M.; et al. Determination of fetal DNA fraction from the plasma of pregnant women using sequence read counts. Prenat. Diagn. 2015, 35, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.C.A.; Ding, C.; Gerovassili, A.; Yeung, S.W.; Chiu, R.W.K.; Leung, T.N.; Lau, T.K.; Chim, S.S.; Chung, G.T.; Nicolaides, K.H.; et al. Hypermethylated rassf1a in maternal plasma: A universal fetal DNA marker that improves the reliability of noninvasive prenatal diagnosis. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 2211–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lun, F.M.; Chiu, R.W.K.; Sun, K.; Leung, T.Y.; Jiang, P.; Chan, K.C.A.; Sun, H.; Lo, Y.M.D. Noninvasive prenatal methylomic analysis by genomewide bisulfite sequencing of maternal plasma DNA. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.C.; Chan, K.C.A.; Zheng, Y.W.; Jiang, P.; Liao, G.J.; Sun, H.; Akolekar, R.; Leung, T.Y.; Go, A.T.; van Vugt, J.M.; et al. Size-based molecular diagnostics using plasma DNA for noninvasive prenatal testing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8583–8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straver, R.; Oudejans, C.B.; Sistermans, E.A.; Reinders, M.J. Calculating the fetal fraction for noninvasive prenatal testing based on genome-wide nucleosome profiles. Prenat. Diagn. 2016, 36, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, Y.M.D.; Tein, M.S.; Lau, T.K.; Haines, C.J.; Leung, T.N.; Poon, P.M.; Wainscoat, J.S.; Johnson, P.J.; Chang, A.M.; Hjelm, N.M. Quantitative analysis of fetal DNA in maternal plasma and serum: Implications for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1998, 62, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, B.; El-Sheikhah, A.; Nicolaides, K.; Holzgreve, W.; Hahn, S. Optimized real-time quantitative PCR measurement of male fetal DNA in maternal plasma. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 1598–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, T.; Bunce, K.; Hogge, W.A.; Peters, D.G. A novel approach toward the challenge of accurately quantifying fetal DNA in maternal plasma. Prenat. Diagn. 2010, 30, 1226–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellis, M.A.; Hughes, K.; Hughes, S.; Ashton, J.R. Measuring paternal discrepancy and its public health consequences. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2005, 59, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Wang, Z.; Okano, M.; Nogami, M.; Li, Y.; He, W.W.; Okumura, K.; Li, E. Cloning, expression and chromosome locations of the human DNMT3 gene family. Gene 1999, 236, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestor, T.H. The DNA methyltransferases of mammals. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9, 2395–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, A. DNA methylation patterns and epigenetic memory. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, L.L.; Leung, T.N.; Lau, T.K.; Chow, K.C.; Lo, Y.M.D. Differential DNA methylation between fetus and mother as a strategy for detecting fetal DNA in maternal plasma. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.C.A.; Zhang, J.; Hui, A.B.; Wong, N.; Lau, T.K.; Leung, T.N.; Lo, K.W.; Huang, D.W.; Lo, Y.M.D. Size distributions of maternal and fetal DNA in maternal plasma. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, M.W.; Kircher, M.; Hill, A.J.; Daza, R.M.; Shendure, J. Cell-free DNA comprises an in vivo nucleosome footprint that informs its tissues-of-origin. Cell 2016, 164, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepard, T.H.; FitzSimmons, J.M.; Fantel, A.G.; Pascoe-Mason, J. Placental weights of normal and aneuploid early human fetuses. Pediatr. Pathol. 1989, 9, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.C.A.; Jiang, P.; Sun, K.; Cheng, Y.K.; Tong, Y.K.; Cheng, S.H.; Wong, A.I.; Hudecova, I.; Leung, T.Y.; Chiu, R.W.K.; et al. Second generation noninvasive fetal genome analysis reveals de novo mutations, single-base parental inheritance, and preferred DNA ends. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E8159–E8168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Approaches | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Y Chromosome [3,22] | Simple and accurate | NOT applicable for pregnancies with female fetuses |
| Maternal plasma DNA sequencing data with parental genotypes [9,30] | Direct and accurate | Paternal DNA may not be available |
| Targeted sequencing of maternal plasma DNA (FetalQuant) [31] | Sequencing maternal plasma DNA only; accurate | High sequencing depth is required |
| Shallow-depth sequencing of maternal plasma DNA coupled with maternal genotypes (FetalQuantSD) [32] | Shallow-depth sequencing of maternal plasma DNA; accurate | Maternal genotype requirement will add additional costs; the recalibration curve is required to be rebuilt for different sequencing and genotyping platforms |
| Shallow-depth maternal plasma DNA sequencing data (SeqFF) [33] | Only shallow-depth sequencing of maternal plasma DNA; single-end sequencing; easy to be integrated into the routine noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT) | Large-scale samples are needed to train the neutral network; need to improve the accuracy when the fetal DNA fraction is below 5% |
| Differantial methylation [17,26,34,35] | Accurate | Either bisulfite conversion or digestion with methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes may affect the accuracy; genome-wide bisulfite sequencing is too expensive and prohibitive for the routine NIPT |
| cfDNA fragment size [36] | Only shallow-depth sequencing of maternal plasma DNA; easy to be integrated into the routine NIPT | Moderate accuracy; paired-end sequencing would increase the costs |
| Nucleosome track [37] | Only shallow-depth sequencing of maternal plasma DNA | Lower accuracy; high-depth sequencing data is required during the training step |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, X.L.; Jiang, P. Bioinformatics Approaches for Fetal DNA Fraction Estimation in Noninvasive Prenatal Testing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020453
Peng XL, Jiang P. Bioinformatics Approaches for Fetal DNA Fraction Estimation in Noninvasive Prenatal Testing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(2):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020453
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Xianlu Laura, and Peiyong Jiang. 2017. "Bioinformatics Approaches for Fetal DNA Fraction Estimation in Noninvasive Prenatal Testing" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 2: 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020453
APA StylePeng, X. L., & Jiang, P. (2017). Bioinformatics Approaches for Fetal DNA Fraction Estimation in Noninvasive Prenatal Testing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(2), 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020453