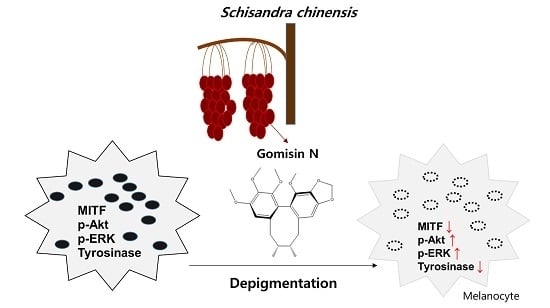
Gomisin N Inhibits Melanogenesis through Regulating the PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathways in Melanocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Gomisin N on Melanin Formation and Cell Viability
2.2. Effects of Gomisin N on Tyrosinase Activity
2.3. Effects of Gomisin N on the Inactivation of the MC1R Signaling Pathway
2.4. Effects of Gomisin N on the Phosphorylation of Akt and ERK1/2 in Melan-A Cells
2.5. Gomisin N Inhibited Melanogenesis in Zebrafish Embryos
2.6. Gomisin N reversed Rapamycin-induced Melanogenesis in Human MNT-1
Melanoma Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Measurement of Melanin Contents
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Tyrosinase Activity Assay
4.6. l-DOPA Staining in NHEM Cells
4.7. Zebrafish Experiments
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alaluf, S.; Atkins, D.; Barrett, K.; Blount, M.; Carter, N.; Heath, A. The impact of epidermal melanin on objective measurements of human skin colour. Pigment Cell Res. 2002, 15, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Mello, S.A.; Finlay, G.J.; Baguley, B.C.; Askarian-Amiri, M.E. Signaling Pathways in Melanogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Tobin, D.J.; Shibahara, S.; Wortsman, J. Melanin pigmentation in mammalian skin and its hormonal regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 1155–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrling, T.; Jung, K.; Fuchs, J. The role of melanin as protector against free radicals in skin and its role as free radical indicator in hair. Spectrochim Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2008, 69, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brozyna, A.A.; Jozwicki, W.; Roszkowski, K.; Filipiak, J.; Slominski, A.T. Melanin content in melanoma metastases affects the outcome of radiotherapy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 17844–17853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Wortsman, J.; Plonka, P.M.; Schallreuter, K.U.; Paus, R.; Tobin, D.J. Hair follicle pigmentation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Pawelek, J. l-tyrosine and l-dihydroxyphenylalanine as hormone-like regulators of melanocyte functions. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012, 25, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.Y. Recent progress in melasma pathogenesis. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2015, 28, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speeckaert, R.; van Gele, M.; Speeckaert, M.M.; Lambert, J.; van Geel, N. The biology of hyperpigmentation syndromes. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2014, 27, 512–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, R.M.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Slominski, A.T. The role of melanin pigment in melanoma. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 258–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Wortsman, J.; Tobin, D.J. The cutaneous serotoninergic/melatoninergic system: Securing a place under the sun. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, R.; Arora, P.; Garg, K.V. Cosmeceuticals for Hyperpigmentation: What is Available? J. Cutaneous Aesthet. Surg. 2013, 6, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamura, Y.; Coelho, S.G.; Wolber, R.; Miller, S.A.; Wakamatsu, K.; Zmudzka, B.Z.; Ito, S.; Smuda, C.; Passeron, T.; Choi, W.; et al. Regulation of human skin pigmentation and responses to ultraviolet radiation. Pigment Cell Res. 2007, 20, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, E.C.; Callender, V.D. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: A review of the epidemiology, clinical features, and treatment options in skin of color. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2010, 3, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sales-Campos, H.; Souza, P.R.; Peghini, B.C.; da Silva, J.S.; Cardoso, C.R. An overview of the modulatory effects of oleic acid in health and disease. Mini. Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvez, S.; Kang, M.; Chung, H.S.; Cho, C.; Hong, M.C.; Shin, M.K.; Bae, H. Survey and mechanism of skin depigmenting and lightening agents. Phytother. Res. 2006, 20, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Jiang, L.; Geng, C.; Cao, J.; Zhong, L. Hydroquinone-induced genotoxicity and oxidative DNA damage in HepG2 cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2008, 173, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enguita, F.J.; Leitao, A.L. Hydroquinone: Environmental pollution, toxicity, and microbial answers. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 542168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draelos, Z.D. Skin lightening preparations and the hydroquinone controversy. Dermatol. Ther. 2007, 20, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, J.H.; Lee, I.; Yun, S.K.; Kim, H.U.; Park, B.H.; Park, J.W. Saponified evening primrose oil reduces melanogenesis in B16 melanoma cells and reduces UV-induced skin pigmentation in humans. Lipids 2010, 45, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordell, G.A.; Colvard, M.D. Natural products and traditional medicine: Turning on a paradigm. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panossian, A.; Wikman, G. Pharmacology of Schisandra chinensis Bail: An overview of Russian research and uses in medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 118, 183–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Pang, S.; Yang, N.; Meng, H.; Liu, J.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Z.; Gao, W.; Chen, B.; et al. Beneficial effects of Schisandrin B on the cardiac function in mice model of myocardial infarction. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Jo, S.; Ryu, J.; Jeong, H.S.; Lee, G.; Ryu, M.H.; Jung, M.H.; Kim, H.; Kim, B.J. Effects of Schisandra chinensis Turcz. fruit on contact dermatitis induced by dinitrofluorobenzene in mice. Mol. Med. Report 2015, 12, 2135–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, J.N.; Cho, M.; So, I.; Jeon, J.H. The protective effects of Schisandra chinensis fruit extract and its lignans against cardiovascular disease: A review of the molecular mechanisms. Fitoterapia 2014, 97, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, O.H.; Chae, H.S.; Choi, J.H.; Choi, H.J.; Park, P.S.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, G.H.; So, H.Y.; Choo, Y.K.; Kweon, O.H.; et al. Effects of the Schisandra fructus water extract on cytokine release from a human mast cell line. J. Med. Food 2006, 9, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poma, A.; Bianchini, S.; Miranda, M. Inhibition of l-tyrosine-induced micronuclei production by phenylthiourea in human melanoma cells. Mutat. Res. 1999, 446, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, I.S.; Dong, Y.; Lee, I.S.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.S.; Woo, J.T.; Cha, B.Y. Melanogenesis-inducing effect of cirsimaritin through increases in microphthalmia-associated transcription factor and tyrosinase expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 8772–8788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busca, R.; Abbe, P.; Mantoux, F.; Aberdam, E.; Peyssonnaux, C.; Eychene, A.; Ortonne, J.P.; Ballotti, R. Ras mediates the cAMP-dependent activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) in melanocytes. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 2900–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busca, R.; Ballotti, R. Cyclic AMP a key messenger in the regulation of skin pigmentation. Pigment Cell Res. 2000, 13, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hah, Y.S.; Cho, H.Y.; Lim, T.Y.; Park, D.H.; Kim, H.M.; Yoon, J.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, C.Y.; Yoon, T.J. Induction of melanogenesis by rapamycin in human MNT-1 melanoma cells. Ann. Dermatol. 2012, 24, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, W.J.; Kim, E.Y.; Park, J.E.; Jo, S.Y.; Bang, S.H.; Chang, E.J.; Chang, S.E. Microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 is involved in melanogenesis via regulation of MITF expression in melanocytes. Sci. Report. 2016, 6, 19914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spritz, R.A.; Hearing, V.J., Jr. Genetic disorders of pigmentation. Adv. Hum. Genet. 1994, 22, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kadekaro, A.L.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, S.; Jameson, J.; Swope, V.B.; Cheng, T.; Kadakia, M.; Abdel-Malek, Z. α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone suppresses oxidative stress through a p53-mediated signaling pathway in human melanocytes. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasmeier, C.; Hume, A.N.; Bolasco, G.; Seabra, M.C. Melanosomes at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 3995–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brozyna, A.A.; Jozwicki, W.; Carlson, J.A.; Slominski, A.T. Melanogenesis affects overall and disease-free survival in patients with stage III and IV melanoma. Hum. Pathol. 2013, 44, 2071–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Kim, T.K.; Brozyna, A.A.; Janjetovic, Z.; Brooks, D.L.; Schwab, L.P.; Skobowiat, C.; Jozwicki, W.; Seagroves, T.N. The role of melanogenesis in regulation of melanoma behavior: Melanogenesis leads to stimulation of HIF-1α expression and HIF-dependent attendant pathways. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 563, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, M.K.; Hyun Leem, K.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, M.H. Inhibitory effect of Gastrodia elata extract on melanogenesis in HM3KO melanoma cells. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 64, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hemesath, T.J.; Price, E.R.; Takemoto, C.; Badalian, T.; Fisher, D.E. MAP kinase links the transcription factor Microphthalmia to c-Kit signalling in melanocytes. Nature 1998, 391, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Price, E.R.; Ding, H.F.; Badalian, T.; Bhattacharya, S.; Takemoto, C.; Yao, T.P.; Hemesath, T.J.; Fisher, D.E. Lineage-specific signaling in melanocytes. C-kit stimulation recruits p300/CBP to microphthalmia. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 17983–17986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolotto, C.; Abbe, P.; Hemesath, T.J.; Bille, K.; Fisher, D.E.; Ortonne, J.P.; Ballotti, R. Microphthalmia gene product as a signal transducer in cAMP-induced differentiation of melanocytes. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 142, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogenberg, V.; Ogmundsdottir, M.H.; Bergsteinsdottir, K.; Schepsky, A.; Phung, B.; Deineko, V.; Milewski, M.; Steingrimsson, E.; Wilmanns, M. Restricted leucine zipper dimerization and specificity of DNA recognition of the melanocyte master regulator MITF. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 2647–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, K.T.; Hodi, F.S.; Fisher, D.E. From genes to drugs: Targeted strategies for melanoma. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.H.; Seo, J.O.; Baek, S.H.; Kim, S.Y. Inhibitory effects of resveratrol on melanin synthesis in ultraviolet B-induced pigmentation in Guinea pig skin. Biomol. Ther. 2014, 22, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, T.R.; Lin, J.J.; Tsai, C.C.; Huang, T.K.; Yang, Z.Y.; Wu, M.O.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Su, C.C.; Wu, Y.J. Inhibition of melanogenesis by gallic acid: Possible involvement of the PI3K/Akt, MEK/ERK and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways in B16F10 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 20443–20458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yajima, I.; Kumasaka, M.Y.; Thang, N.D.; Goto, Y.; Takeda, K.; Yamanoshita, O.; Iida, M.; Ohgami, N.; Tamura, H.; Kawamoto, Y.; et al. RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/AKT Signaling in Malignant Melanoma Progression and Therapy. Dermatol. Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 354191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Moon, S.J.; Chung, J.H.; Kim, K.H.; Cho, K.H.; Park, K.C. Ceramide inhibits cell proliferation through AKT/PKB inactivation and decreases melanin synthesis in Mel-Ab cells. Pigment Cell Res. 2001, 14, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Baek, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, T.Y.; Yoon, T.J.; Hwang, J.S.; Kim, M.R.; Kwon, H.J.; Lee, C.H. Downregulation of melanin synthesis by haginin A and its application to in vivo lightening model. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartman, M.L.; Czyz, M. MITF in melanoma: Mechanisms behind its expression and activity. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Hwang, E.S.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, S.Y.; Kwon, S.B.; Park, K.C. Sphingosine-1-phosphate decreases melanin synthesis via sustained ERK activation and subsequent MITF degradation. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Gong, L.; Haddad, M.M.; Bischof, O.; Campisi, J.; Yeh, E.T.; Medrano, E.E. Regulation of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor MITF protein levels by association with the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme hUBC9. Exp. Cell Res. 2000, 255, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, D.C.; Cooper, P.J.; Hart, I.R. A line of non-tumorigenic mouse melanocytes, syngeneic with the B16 melanoma and requiring a tumour promoter for growth. Int. J. Cancer 1987, 39, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meira, W.V.; Heinrich, T.A.; Cadena, S.M.; Martinez, G.R. Melanogenesis inhibits respiration in B16-F10 melanoma cells whereas enhances mitochondrial cell content. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 350, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohguchi, K.; Tanaka, T.; Iliya, I.; Ito, T.; Iinuma, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Akao, Y.; Nozawa, Y. Gnetol as a potent tyrosinase inhibitor from genus Gnetum. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2003, 67, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, R.; Ishikawa, S.; Tomoda, H. Inhibition of tyrosinase activity and melanine pigmentation by 2-hydroxytyrosol. Acta Pharm. Sinica B 2014, 4, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chae, J.K.; Subedi, L.; Jeong, M.; Park, Y.U.; Kim, C.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.Y. Gomisin N Inhibits Melanogenesis through Regulating the PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathways in Melanocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020471
Chae JK, Subedi L, Jeong M, Park YU, Kim CY, Kim H, Kim SY. Gomisin N Inhibits Melanogenesis through Regulating the PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathways in Melanocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(2):471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020471
Chicago/Turabian StyleChae, Jae Kyoung, Lalita Subedi, Minsun Jeong, Yong Un Park, Chul Young Kim, Hakwon Kim, and Sun Yeou Kim. 2017. "Gomisin N Inhibits Melanogenesis through Regulating the PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathways in Melanocytes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 2: 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020471
APA StyleChae, J. K., Subedi, L., Jeong, M., Park, Y. U., Kim, C. Y., Kim, H., & Kim, S. Y. (2017). Gomisin N Inhibits Melanogenesis through Regulating the PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathways in Melanocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(2), 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020471