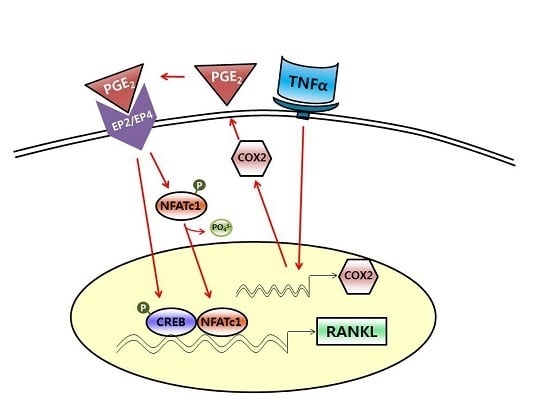
TNFα Increases RANKL Expression via PGE2-Induced Activation of NFATc1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Calcineurin/Nuclear Factor of Activated T-Cells (NFAT) Signaling Is Involved in Tumor Necrosis Factor α (TNFα)-Induced Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κB Ligand (RANKL) Expression
2.2. Inhibition of Calcineurin/NFAT Signaling Partially Reduces TNFα-Induced Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) Production
2.3. PGE2 Enhances RANKL Promoter Activity in an NFAT Binding Element-Dependent Manner
2.4. Cyclooxygenase (COX) Inhibitor Blocks TNFα-Induced Binding of NFATc1 and cAMP Response Element-Binding Protein (CREB) to the RANKL Promoter
2.5. The PGE2 Receptor Antagonists AH6809 and AH23848 Blocked TNFα-Induced Activation of NFAT and Binding of NFATc1 and CREB to the RANKL Promoter
2.6. TNFα Enhances RANKL Expression in a PGE2 Production- and NFAT Activation-Dependent Manner in Primary Cultured Mouse Calvarial Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Plasmid Construction
4.4. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay
4.7. Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.8. PGE2 Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Udagawa, N.; Takahashi, N.; Jimi, E.; Matsuzaki, K.; Tsurukai, T.; Itoh, K.; Nakagawa, N.; Yasuda, H.; Goto, M.; Tsuda, E.; et al. Osteoblasts/stromal cells stimulate osteoclast activation through expression of osteoclast differentiation factor/RANKL but not macrophage colony-stimulating factor: Receptor activator of NF-κB ligand. Bone 1999, 25, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Nakashima, T.; Hiroshi, N.; Penninger, J.M. RANKL-RANK signaling in osteoclastogenesis and bone disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2006, 12, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Manolagas, S.C.; O’Brien, C.A. Parathyroid hormone controls receptor activator of NF-κB ligand gene expression via a distant transcriptional enhancer. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 6453–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.L.; Bae, O.Y.; Baek, K.H.; Kwon, A.; Hwang, H.R.; Qadir, A.S.; Park, H.J.; Woo, K.M.; Ryoo, H.M.; Baek, J.H. High extracellular calcium-induced NFATc3 regulates the expression of receptor activator of NF-κB ligand in osteoblasts. Bone 2011, 49, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, K.K.; Bi, Y.M.; Wan, C.; Chuang, P.T.; Clemens, T.; Young, M.; Yang, Y.Z. Hedgehog signaling in mature osteoblasts regulates bone formation and resorption by controlling PTHrP and RANKL expression. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J.; Baek, K.; Baek, J.H.; Kim, H.R. The cooperation of CREB and NFAT is required for PTHrP-induced RANKL expression in mouse osteoblastic cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, G.J.; Utting, J.C.; Etheridge, S.L.; Arnett, T.R.; Genever, P.G. Wnt signalling in osteoblasts regulates expression of the receptor activator of NFκB ligand and inhibits osteoclastogenesis in vitro. J. Cell. Sci. 2006, 119, 1283–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Heulsmann, A.; Tondravi, M.M.; Mukherjee, A.; Abu-Amer, Y. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF) stimulates RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via coupling of TNF type 1 receptor and RANK signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cope, A.P.; Liblau, R.S.; Yang, X.D.; Congia, M.; Laudanna, C.; Schreiber, R.D.; Probert, L.; Kollias, G.; McDevitt, H.O. Chronic tumor necrosis factor alters T-cell responses by attenuating T-cell receptor signaling. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, Y.; Kaji, K.; Katogi, R.; Takeshita, S.; Kudo, A. Tumor necrosis factor-α induces differentiation of and bone resorption by osteoclasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 4858–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitazawa, R.; Kimble, R.B.; Vannice, J.L.; Kung, V.T.; Pacifici, R. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and tumor necrosis factor binding protein decrease osteoclast formation and bone resorption in ovariectomized mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 2397–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, U.H.; Ohlin, A. Tumor necrosis factors α and β can stimulate bone resorption in cultured mouse calvariae by a prostaglandin-independent mechanism. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1993, 8, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, B.M.; Mundy, G.R.; Chambers, T.J. Tumor necrosis factors α and β induce osteoblastic cells to stimulate osteoclastic bone resorption. J. Immunol. 1987, 138, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kitaura, H.; Kimura, K.; Ishida, M.; Kohara, H.; Yoshimatsu, M.; Takano-Yamamoto, T. Immunological reaction in TNF-α-mediated osteoclast formation and bone resorption in vitro and in vivo. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 181849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, W.; Amcheslavsky, A.; Takeshita, S.; Drissi, H.; Bar-Shavit, Z. TNF-α expression is transcriptionally regulated by RANK ligand. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 202, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, M.; Sudo, T.; Saito, T.; Osada, H.; Tsujimoto, M. Involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in osteoclastogenesis mediated by receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL). J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 31155–31161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossa, C.; Ehmann, K.; Liu, M.; Patil, C.; Kirkwood, K.L. MKK3/6-p38 MAPK signaling is required for IL-1β and TNF-α-induced RANKL expression in bone marrow stromal cells. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2006, 26, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narumiya, S.; Sugimoto, Y.; Ushikubi, F. Prostanoid receptors: Structures, properties, and functions. Physiol. Rev. 1999, 79, 1193–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Mizoguchi, T.; Take, I.; Kurihara, S.; Udagawa, N.; Takahashi, N. Prostaglandin E2 enhances osteoclastic differentiation of precursor cells through protein kinase A-dependent phosphorylation of TAK1. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 11395–11403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Okada, Y.; Pilbeam, C.C.; Lorenzo, J.A.; Kennedy, C.R.; Breyer, R.M.; Raisz, L.G. Knockout of the murine prostaglandin EP2 receptor impairs osteoclastogenesis in vitro. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 2054–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyaura, C.; Inada, M.; Matsumoto, C.; Ohshiba, T.; Uozumi, N.; Shimizu, T.; Ito, A. An essential role of cytosolic phospholipase a2α in prostaglandin E2-mediated bone resorption associated with inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trebino, C.E.; Stock, J.L.; Gibbons, C.P.; Naiman, B.M.; Wachtmann, T.S.; Umland, J.P.; Pandher, K.; Lapointe, J.M.; Saha, S.; Roach, M.L.; et al. Impaired inflammatory and pain responses in mice lacking an inducible prostaglandin E synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9044–9049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzawa, T.; Miyaura, C.; Inada, M.; Maruyama, T.; Sugimoto, Y.; Ushikubi, F.; Ichikawa, A.; Narumiya, S.; Suda, T. The role of prostaglandin e receptor subtypes (EP1, EP2, EP3, and EP4) in bone resorption: An analysis using specific agonists for the respective EPs. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 1554–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujino, H.; Xu, W.; Regan, J.W. Prostaglandin E2 induced functional expression of early growth response factor-1 by EP4, but not EP2, prostanoid receptors via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 12151–12156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.; Solle, M.; Audoly, L.P.; Tilley, S.L.; Stock, J.L.; McNeish, J.D.; Coffman, T.M.; Dombrowicz, D.; Koller, B.H. Receptors and signaling mechanisms required for prostaglandin E2-mediated regulation of mast cell degranulation and IL-6 production. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 4586–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hempel, S.L.; Monick, M.M.; Hunninghake, G.W. Lipopolysaccharide induces prostaglandin H synthase-2 protein and mRNA in human alveolar macrophages and blood monocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, J.A.; Belvisi, M.G.; Akarasereenont, P.; Robbins, R.A.; Kwon, O.J.; Croxtall, J.; Barnes, P.J.; Vane, J.R. Induction of cyclo-oxygenase-2 by cytokines in human pulmonary epithelial cells: Regulation by dexamethasone. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 113, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, S.; Ogtata, Y.; Shimizu, E.; Yamazaki, M.; Furuyama, S.; Sugiya, H. Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α)-induced prostaglandin E2 release is mediated by the activation of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) transcription via NFκB in human gingival fibroblasts. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2002, 238, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujihara, R.; Usui, M.; Yamamoto, G.; Nishii, K.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Okamatsu, Y.; Sato, T.; Asou, Y.; Nakashima, K.; Yamamoto, M. Tumor necrosis factor-α enhances RANKL expression in gingival epithelial cells via protein kinase a signaling. J. Periodontal Res. 2014, 49, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitara, D.; Aliprantis, A.O. Transcriptional regulation of bone and joint remodeling by NFAT. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 233, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winslow, M.M.; Pan, M.; Starbuck, M.; Gallo, E.M.; Deng, L.; Karsenty, G.; Crabtree, G.R. Calcineurin/NFAT signaling in osteoblasts regulates bone mass. Dev. Cell 2006, 10, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuvpilo, S.; Jankevics, E.; Tyrsin, D.; Akimzhanov, A.; Moroz, D.; Jha, M.K.; Schulze-Luehrmann, J.; Santner-Nanan, B.; Feoktistova, E.; Konig, T.; et al. Autoregulation of NFATc1/a expression facilitates effector t cells to escape from rapid apoptosis. Immunity 2002, 16, 881–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, J.; Fresno, M.; Iniguez, M.A. Expression and function of the nuclear factor of activated T-cells in colon carcinoma cells: Involvement in the regulation of cyclooxygenase-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 8686–8693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoni, I.; Ostuni, R.; Barresi, S.; di Gioia, M.; Broggi, A.; Costa, B.; Marzi, R.; Granucci, F. CD14 and NFAT mediate lipopolysaccharide-induced skin edema formation in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1747–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiriyama, M.; Ushikubi, F.; Kobayashi, T.; Hirata, M.; Sugimoto, Y.; Narumiya, S. Ligand binding specificities of the eight types and subtypes of the mouse prostanoid receptors expressed in chinese hamster ovary cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 122, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Kundu, N.; Rifat, S.; Walser, T.; Fulton, A.M. Prostaglandin E receptor EP4 antagonism inhibits breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 2923–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, T.; Moreno, J.J. Role of EP(1) and EP(4) PGE(2) subtype receptors in serum-induced 3T6 fibroblast cycle progression and proliferation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2002, 282, C280–C288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin-Osdoby, P.; Rothe, L.; Anderson, F.; Nelson, M.; Maloney, W.; Osdoby, P. Receptor activator of NF-κB and osteoprotegerin expression by human microvascular endothelial cells, regulation by inflammatory cytokines, and role in human osteoclastogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 20659–20672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, N.; Maeda, H.; Yoshimine, Y.; Akamine, A. Lipopolysaccharide stimulates expression of osteoprotegerin and receptor activator of NF-κB ligand in periodontal ligament fibroblasts through the induction of interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α. Bone 2004, 35, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Min, K.S.; Lee, H.D.; Oh, H.W.; Kim, E.C. Effect of cytosolic phospholipase A2 on proinflammatory cytokine-induced bone resorptive genes including receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand in human dental pulp cells. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, H.; Hozumi, A.; Osaki, M.; Fukushima, T.; Sakamoto, K.; Yonekura, A.; Tomita, M.; Furukawa, K.; Shindo, H.; Baba, H. Primary human bone marrow adipocytes support TNF-α-induced osteoclast differentiation and function through RANKL expression. Cytokine 2011, 56, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Kitaura, H.; Zhou, P.; Ross, F.P.; Teitelbaum, S.L. IL-1 mediates TNF-induced osteoclastogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainola, M.; Mandelin, J.; Liljestrom, M.; Konttinen, Y.T.; Salo, J. Imbalanced expression of RANKL and osteoprotegerin mRNA in pannus tissue of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2008, 26, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.C.; Sun, Y.T.; Chen, J.J.; Chiu, K.T. TNF-α-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human lung epithelial cells: Involvement of the phospholipase c-γ2, protein kinase c-α, tyrosine kinase, NF-κB-inducing kinase, and I-κB kinase 1/2 pathway. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 2719–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, J.; Long, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Li, J.; Fang, W.; Meng, Q.G. Role of NF-κB in TNF-α-induced COX-2 expression in synovial fibroblasts from human tmj. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, L.R.; Freitas, L.B.; Rosa, D.D.; Silva, F.R.; Silva, L.S.; Birtencourt, L.T.; Edelweiss, M.I.; Rosa, M.I. Accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging in ovarian tumor: A systematic quantitative review. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 204, 67.e1–67.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, J.M.; Wicks, J.R.; Audoly, L.P. The role of prostaglandin E2 receptors in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyaura, C.; Inada, M.; Suzawa, T.; Sugimoto, Y.; Ushikubi, F.; Ichikawa, A.; Narumiya, S.; Suda, T. Impaired bone resorption to prostaglandin E2 in prostaglandin e receptor EP4-knockout mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 19819–19823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, X.; Zuscik, M.J.; Drissi, M.H.; Schwarz, E.M.; O’Keefe, R.J. Fibroblasts express RANKL and support osteoclastogenesis in a COX-2-dependent manner after stimulation with titanium particles. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2005, 20, 1136–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalliolias, G.D.; Ivashkiv, L.B. Tnf biology, pathogenic mechanisms and emerging therapeutic strategies. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaaeddine, N.; DiBattista, J.A.; Pelletier, J.P.; Cloutier, J.M.; Kiansa, K.; Dupuis, M.; Martel-Pelletier, J. Osteoarthritic synovial fibroblasts possess an increased level of tumor necrosis factor-receptor 55 (TNF-r55) that mediates biological activation by TNF-α. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 24, 1985–1994. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alsalameh, S.; Amin, R.J.; Kunisch, E.; Jasin, H.E.; Kinne, R.W. Preferential induction of prodestructive matrix metalloproteinase-1 and proinflammatory interleukin 6 and prostaglandin E2 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts via tumor necrosis factor receptor-55. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 1680–1690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Yamazaki, M.; Zella, L.A.; Meyer, M.B.; Fretz, J.A.; Shevde, N.K.; Pike, J.W. Multiple enhancer regions located at significant distances upstream of the transcriptional start site mediate RANKL gene expression in response to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. J. Steroid Biochem. 2007, 103, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Ren, F.; Yue, W. Nfatc1 activation promotes the invasion of u251 human glioblastoma multiforme cells through COX-2. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 35, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkby, N.S.; Chan, M.V.; Zaiss, A.K.; Garcia-Vaz, E.; Jiao, J.; Berglund, L.M.; Verdu, E.F.; Ahmetaj-Shala, B.; Wallace, J.L.; Herschman, H.R.; et al. Systematic study of constitutive cyclooxygenase-2 expression: Role of NF-κB and NFAT transcriptional pathways. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Chikazu, D.; Voznesensky, O.S.; Herschman, H.R.; Kream, B.E.; Drissi, H.; Pilbeam, C.C. Parathyroid hormone induction of cyclooxygenase-2 in murine osteoblasts: Role of the calcium-calcineurin-NFAT pathway. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2010, 25, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Kim, H.J.; Li, Q.L.; Chi, X.Z.; Ueta, C.; Komori, T.; Wozney, J.M.; Kim, E.G.; Choi, J.Y.; Ryoo, H.M.; et al. Runx2 is a common target of transforming growth factor β1 and bone morphogenetic protein 2, and cooperation between Runx2 and Smad5 induces osteoblast-specific gene expression in the pluripotent mesenchymal precursor cell line C2C12. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 8783–8792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, S.N.; Kim, G.S.; Baek, J.H. P44/42 MAPK activation is necessary for receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand induction by high extracellular calcium. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 304, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayanagi, H.; Kim, S.; Koga, T.; Nishina, H.; Isshiki, M.; Yoshida, H.; Saiura, A.; Isobe, M.; Yokochi, T.; Inoue, J.; et al. Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elefteriou, F.; Ahn, J.D.; Takeda, S.; Starbuck, M.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Kondo, H.; Richards, W.G.; Bannon, T.W.; Noda, M.; et al. Leptin regulation of bone resorption by the sympathetic nervous system and cart. Nature 2005, 434, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Kitazawa, R.; Kondo, T.; Maeda, S.; Yamaguchi, A.; Kitazawa, S. Modulation of mouse RANKL gene expression by Runx2 and PKA pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 98, 1629–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.-J.; Baek, K.; Baek, J.-H.; Kim, H.-R. TNFα Increases RANKL Expression via PGE2-Induced Activation of NFATc1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030495
Park H-J, Baek K, Baek J-H, Kim H-R. TNFα Increases RANKL Expression via PGE2-Induced Activation of NFATc1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(3):495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030495
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Hyun-Jung, Kyunghwa Baek, Jeong-Hwa Baek, and Hyung-Ryong Kim. 2017. "TNFα Increases RANKL Expression via PGE2-Induced Activation of NFATc1" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 3: 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030495
APA StylePark, H. -J., Baek, K., Baek, J. -H., & Kim, H. -R. (2017). TNFα Increases RANKL Expression via PGE2-Induced Activation of NFATc1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(3), 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030495