Glycine-Binding Site Stimulants of NMDA Receptors Alleviate Extrapyramidal Motor Disorders by Activating the Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Pathway
Abstract
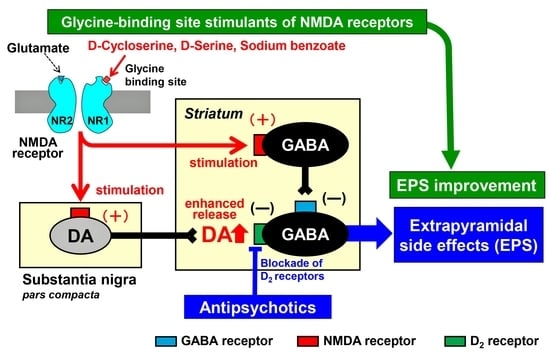
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Glycine-Site Stimulants of N-Methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) Receptors on Haloperidol-Induced Bradykinesia
2.2. Effects of d-Cycloserine on Haloperidol-Induced Fos Expression
2.3. Microinjection and In Vivo Microdialysis Studies with d-Cycloserine
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Evaluation of Bradykinesia
4.3. Analysis of Fos Protein Expression
4.4. Microinjection Study
4.5. In Vivo Microdialysis Study
4.6. Drugs
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AcS | Shell region of the nucleus accumbens |
| DCS | d-Cycloserine |
| dlST | Dorsolateral striatum |
| EPS | Extrapyramidal side effects |
| HAL | Haloperidol |
| IR | Immunoreactivity |
| L-NAME | L-NG-Nitro-l-arginine methyl ester |
| NMDA | N-Methyl-d-aspartate |
| NOS | Nitric oxide synthase |
| SNc | Substantia nigra pars compacta |
References
- Meltzer, H.Y. The mechanism of action of novel antipsychotic drugs. Schizophr. Bull. 1991, 17, 263–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapur, S.; Remington, G. Atypical antipsychotics: New directions and new challenges in the treatment of schizophrenia. Annu. Rev. Med. 2001, 52, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, Y. Therapeutic role of 5-HT1A receptors in the treatment of schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2011, 17, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, S.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Ohno, Y. Improving the treatment of schizophrenia: Role of 5-HT receptors in modulating cognitive and extrapyramidal motor functions. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2013, 12, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meltzer, H.Y.; Stahl, S.M. The dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia: A review. Schizophr. Bull. 1976, 2, 19–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeman, P. Dopamine receptors and the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Synapse 1987, 1, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, Y.; Ishida-Tokuda, K.; Ishibashi, T.; Sakamoto, H.; Tagashira, R.; Horisawa, T.; Yabuuti, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Kawabe, A.; Nakamura, M. Potential role of 5-HT2 and D2 receptor interaction in the atypical antipsychotic action of the novel succimide derivative, perospirone. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 49, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meltzer, H.Y.; Li, Z.; Kaneda, Y.; Ichikawa, J. Serotonin receptors: Their key role in drugs to treat schizophrenia. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 27, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, Y. New insight into the therapeutic role of 5-HT1A receptors in central nervous system disorders. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cull-Candy, S.; Brickley, S.; Farrant, M. NMDA receptor subunits: Diversity, development and disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2001, 11, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Lü, W.; Michel, J.C.; Goehring, A.; Du, J.; Song, X.; Gouaux, E. NMDA receptor structures reveal subunit arrangement and pore architecture. Nature 2014, 511, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingledine, R.; Borges, K.; Bowie, D.; Traynelis, S.F. The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999, 51, 7–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Javitt, D.C.; Zukin, S.R. Recent advances in the phencyclidine model of schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 1991, 148, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olney, J.W.; Farber, N.B. Glutamate receptor dysfunction and schizophrenia. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1995, 52, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyle, J.T. The glutamatergic dysfunction hypothesis for schizophrenia. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 1996, 3, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lees, K.R. Cerestat and other NMDA antagonists in ischemic stroke. Neurology 1997, 49, S66–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafini, G.; Howland, R.H.; Rovedi, F.; Girardi, P.; Amore, M. The role of ketamine in treatment-resistant depression: A systematic review. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2014, 12, 444–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deardorff, W.J.; Grossberg, G.T. Pharmacotherapeutic strategies in the treatment of severe Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2016, 17, 1789–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krystal, J.H.; Karper, L.P.; Seibyl, J.P.; Freeman, G.K.; Delaney, R.; Bremner, J.D.; Heninger, G.R.; Bowers, M.B.; Charney, D.S. Subanesthetic effects of the noncompetitive NMDA antagonist, ketamine, in humans. Psychotomimetic, perceptual, cognitive, and neuroendocrine responses. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1994, 51, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jentsch, J.D.; Roth, R.H. The neuropsychopharmacology of phencyclidine: From NMDA receptor hypofunction to the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 1999, 20, 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krystal, J.H.; D’Souza, D.C.; Petrakis, I.L.; Belger, A.; Berman, R.M.; Charney, D.S.; Abi-Saab, W.; Madonick, S. NMDA agonists and antagonists as probes of glutamatergic dysfunction and pharmacotherapies in neuropsychiatric disorders. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry. 1999, 7, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Kornhuber, H.H.; Holzmüller, B.; Schmid-Burgk, W.; Mergner, T.; Krzepinski, G. Reduction of cerebrospinal fluid glutamic acid in Huntigton’s chorea and in schizophrenic patients. Arch. Psychiatry Nervenkr. 1980, 228, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, J.T. NMDA receptor and schizophrenia: A brief history. Schizophr. Bull. 2012, 38, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraris, D.V.; Tsukamoto, T. Recent advances in the discovery of d-amino acid oxidase inhibitors and their therapeutic utility in schizophrenia. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goff, D.C. d-Cycloserine: An evolving role in learning and neuroplasticity in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2012, 38, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iha, H.A.; Kunisawa, N.; Tokudome, K.; Mukai, T.; Kinboshi, M.; Shimizu, S.; Ohno, Y. Immunohistochemical analysis of Fos protein expression for exploring brain regions related to central nervous system disorders and drug actions. In In Vivo Neuropharmacology and Neurophysiology; Philippou, A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 389–408. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, G.S.; Matsumura, H.; Fibiger, H.C. Induction patterns of Fos-like immunoreactivity in the forebrain as predictors of atypical antipsychotic activity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1994, 271, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, P.O.; Gervais, J.; Rouillard, C. Modification of haloperidol-induced pattern of c-fos expression by serotonin agonists. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1998, 10, 3546–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.K.; Shishido, Y.; Ichise-Shishido, S.; Kawazoe, T.; Ono, K.; Iwana, S.; Tomita, Y.; Yorita, K.; Sakai, T.; Fukui, K. Potential role for astroglial d-amino acid oxidase in extracellular d-serine metabolism and cytotoxicity. J. Biochem. 2006, 139, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Kong, H.; Tang, M.; Lu, M.; Ding, J.H.; Hu, G. d-Serine regulates proliferation and neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells from postnatal mouse forebrain. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2012, 18, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, A.; Fujita, Y.; Iyo, M.; Hashimoto, K. Effects of sodium benzoate on pre-pulse inhibition deficits and hyperlocomotion in mice after administration of phencyclidine. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2015, 27, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sershen, H.; Hashim, A.; Dunlop, D.S.; Suckow, R.F.; Cooper, T.B.; Javitt, D.C. Modulating NMDA receptor function with d-amino acid oxidase inhibitors: understanding functional activity in PCP-treated mouse model. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, A.; Noda, Y.; Kamei, H.; Ichihara, K.; Mamiya, T.; Nagai, T.; Sugiura, S.; Furukawa, H.; Nabeshima, T. Phencyclidine impairs latent learning in mice: Interaction between glutamatergic systems and sigma1 receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 2001, 24, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y.; Shimizu, S.; Imaki, J.; Ishihara, S.; Sofue, N.; Sasa, M.; Kawai, Y. Anticataleptic 8-OH-DPAT preferentially counteracts with haloperidol-induced Fos expression in the dorsolateral striatum and the core region of the nucleus accumbens. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, G.S.; Fibiger, H.C. Neuroleptics increase c-fos expression in the forebrain: Contrasting effects of haloperidol and clozapine. Neuroscience 1992, 46, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahm, D.S.; Brog, J.S. On the significance of subterritories in the “Accumbens” part of the rat ventral striatum. Neuroscience 1992, 50, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, T.; Tojima, R.; Nakamura, M.; Noguchi, H.; Ohno, Y. Effects of perospirone, a novel 5-HT2 and D2 receptor antagonist, on Fos protein expression in the rat forebrain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1999, 63, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Cunha, I.C.; Lopes, A.P.; Steffens, S.M.; Ferraz, A.; Vargas, J.C.; de Lima, T.C.; Neto, J.M.; Paschoalini, M.A.; Faria, M.S. The microinjection of AMPA receptor antagonist into the accumbens shell, but not into the accumbens core, induces anxiolysis in an animal model of anxiety. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 188, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishibashi, T.; Ikeda, K.; Ishida, K.; Yasui, J.; Tojima, R.; Nakamura, M.; Ohno, Y. Contrasting effects of SM-9018,a potential atypical antipsychotic, and haloperidol on c-fos mRNA expression in the rat striatum. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 303, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.Q.; Jin, X.L.; Chen, Y.T.; Jin, G.Z.; Shi, W.X. Effects of l-stepholidine on forebrain Fos expression: Comparison with clozapine and haloperidol. Neuropshychopharmacology 2005, 30, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, Y.; Shimizu, S.; Tokudome, K. Pathophysiological Roles of Serotonergic System in Regulating Extrapyramidal Motor Functions. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 1396–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laruelle, M. Schizophrenia: From dopaminergic to glutamatergic interventions. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2014, 14, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heresco-Levy, U.; Ermilov, M.; Shimoni, J.; Shapira, B.; Silipo, G.; Javitt, D.C. Placebo-controlled trial of d-cycloserine added to conventional neuroleptics, olanzapine, or risperidone in schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2002, 159, 480–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goff, D.C.; Cather, C.; Gottlieb, J.D.; Evins, A.E.; Walsh, J.; Raeke, L.; Otto, M.W.; Schoenfeld, D.; Green, M.F. Once-weekly d-cycloserine effects on negative symptoms and cognition in schizophrenia: An exploratory study. Schizophr. Res. 2008, 106, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, H.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Green, M.F.; Hellemann, G.; Huang, C.C.; Chen, P.W.; Tun, R.; Chang, Y.C.; Tsai, G.E. Add-on treatment of benzoate for schizophrenia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of d-amino acid oxidase inhibitor. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cain, C.K.; McCue, M.; Bello, I.; Creedon, T.; Tang, D.I.; Laska, E.; Goff, D.C. d-Cycloserine augmentation of cognitive remediation in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2014, 153, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, S.; Tatara, A.; Imaki, J.; Ohno, Y. Role of cortical and striatal 5-HT1A receptors in alleviating antipsychotic-induced extrapyramidal disorders. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 34, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, S.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Sobue, A.; Fujiwara, M.; Morimoto, T.; Ohno, Y. Interaction between anti-Alzheimer and antipsychotic drugs in modulating extrapyramidal motor disorders in mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 127, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatara, A.; Shimizu, S.; Masui, A.; Tamura, M.; Minamimoto, S.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Ochiai, M.; Mizobe, Y.; Ohno, Y. Atypical antipsychotic properties of AD-6048, a primary metabolite of blonanserin. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 138, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 6th ed.; Elsevier: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, S.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Tatara, A.; Kizu, T.; Andatsu, S.; Sobue, A.; Fujiwara, M.; Morimoto, T.; Ohno, Y. 5-HT1A agonist alleviates serotonergic potentiation of extrapyramidal disorders via postsynaptic mechanisms. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 46, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shimizu, S.; Sogabe, S.; Yanagisako, R.; Inada, A.; Yamanaka, M.; Iha, H.A.; Ohno, Y. Glycine-Binding Site Stimulants of NMDA Receptors Alleviate Extrapyramidal Motor Disorders by Activating the Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071416
Shimizu S, Sogabe S, Yanagisako R, Inada A, Yamanaka M, Iha HA, Ohno Y. Glycine-Binding Site Stimulants of NMDA Receptors Alleviate Extrapyramidal Motor Disorders by Activating the Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(7):1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071416
Chicago/Turabian StyleShimizu, Saki, Shunsaku Sogabe, Ryoto Yanagisako, Akiyoshi Inada, Megumi Yamanaka, Higor A. Iha, and Yukihiro Ohno. 2017. "Glycine-Binding Site Stimulants of NMDA Receptors Alleviate Extrapyramidal Motor Disorders by Activating the Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 7: 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071416
APA StyleShimizu, S., Sogabe, S., Yanagisako, R., Inada, A., Yamanaka, M., Iha, H. A., & Ohno, Y. (2017). Glycine-Binding Site Stimulants of NMDA Receptors Alleviate Extrapyramidal Motor Disorders by Activating the Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(7), 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071416