Role Played by Signalling Pathways in Overcoming BRAF Inhibitor Resistance in Melanoma
Abstract
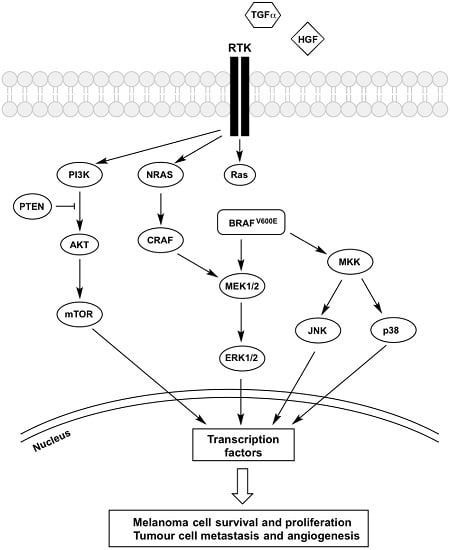
:1. Introduction
2. The BRAF-MEK-ERK Pathway
BRAF Inhibitor Resistance
3. Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTK)
4. PI3K-AKT-mTOR Pathway
5. JNK Pathway
6. p38 MAPK Pathway
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BIM | Bcl-2-like protein |
| BRAF | v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B |
| BRAFi | BRAF inhibitor |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| HGF | Hepatocyte growth factor |
| IGF1R | Insulin growth factor 1 receptor |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MEK | MAPK/ERK kinase |
| mTORC | mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) complex |
| PDGFRβ | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor β |
| PDK1 | 3-phoshoinositide dependent protein kinase-1 |
| PI3K-AKT-mTOR | Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-protein kinase B-mammalian target of rapamycin |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| PUMA | p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis |
| RAS | Rat sarcoma |
| RTK | Receptor tyrosine kinase |
| TGF-α | Transforming growth factor-α |
| UV | ultraviolet |
References
- Gordon, R. Skin cancer: An overview of epidemiology and risk factors. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2013, 29, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, M.H.; Macgregor, S.; Hayward, N.K. Melanoma genetics: Recent findings take us beyond well-traveled pathways. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1763–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australia, M.I. Melanoma Facts and Statistics. Available online: http://www.melanoma.org.au/about-melanoma/melanoma-skin-cancer-facts.html (accessed on 9 June 2017).
- Gray-Schopfer, V.; Wellbrock, C.; Marais, R. Melanoma biology and new targeted therapy. Nature 2007, 445, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.; Larkin, J. Vemurafenib: A new treatment for BRAF-V600 mutated advanced melanoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2012, 4, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maverakis, E.; Cornelius, L.A.; Bowen, G.M.; Phan, T.; Patel, F.B.; Fitzmaurice, S.; He, Y.; Burrall, B.; Duong, C.; Kloxin, A.M.; et al. Metastatic melanoma—A review of current and future treatment options. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2015, 95, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, R.J. The role of mitogen-activated protein targeting in melanoma beyond BRAFV600. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2016, 28, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Genomic Classification of Cutaneous Melanoma. Cell 2015, 161, 1681–1696. [Google Scholar]
- Heakal, Y.; Kester, M.; Savage, S. Vemurafenib (PLX4032): An orally available inhibitor of mutated BRAF for the treatment of metastatic melanoma. Ann. Pharmacother. 2011, 45, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, K.T.; Puzanov, I.; Kim, K.B.; Ribas, A.; McArthur, G.A.; Sosman, J.A.; O’Dwyer, P.J.; Lee, R.J.; Grippo, J.F.; Nolop, K.; et al. Inhibition of mutated, activated BRAF in metastatic melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stones, C.J.; Kim, J.E.; Joseph, W.R.; Leung, E.; Marshall, E.S.; Finlay, G.J.; Shelling, A.N.; Baguley, B.C. Comparison of responses of human melanoma cell lines to MEK and BRAF inhibitors. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagle, N.; Emery, C.; Berger, M.F.; Davis, M.J.; Sawyer, A.; Pochanard, P.; Kehoe, S.M.; Johannessen, C.M.; Macconaill, L.E.; Hahn, W.C.; et al. Dissecting therapeutic resistance to RAF inhibition in melanoma by tumor genomic profiling. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3085–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.Y.; Menzies, A.M.; Rizos, H. Mechanisms and strategies to overcome resistance to molecularly targeted therapy for melanoma. Cancer 2017, 123, 2118–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obaid, N.M.; Bedard, K.; Huang, W.Y. Strategies for Overcoming Resistance in Tumours Harboring BRAF Mutations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizos, H.; Menzies, A.M.; Pupo, G.M.; Carlino, M.S.; Fung, C.; Hyman, J.; Haydu, L.E.; Mijatov, B.; Becker, T.M.; Boyd, S.C.; et al. BRAF inhibitor resistance mechanisms in metastatic melanoma: Spectrum and clinical impact. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1965–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, A.S.; Hagan, S.; Rath, O.; Kolch, W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3279–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthusamy, V.; Piva, T.J. Melanoma Cell Signalling: Looking beyond RAS-RAF-MEK. In Skin Cancers-Risk Factors, Prevention and Therapy; La Porta, C.A.M., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 87–108. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, H.; Bignell, G.R.; Cox, C.; Stephens, P.; Edkins, S.; Clegg, S.; Teague, J.; Woffendin, H.; Garnett, M.J.; Bottomley, W.; et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 2002, 417, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascierto, P.A.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Grob, J.J.; Simeone, E.; Grimaldi, A.M.; Maio, M.; Palmieri, G.; Testori, A.; Marincola, F.M.; Mozzillo, N. The role of BRAF V600 mutation in melanoma. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, P.T.; Garnett, M.J.; Roe, S.M.; Lee, S.; Niculescu-Duvaz, D.; Good, V.M.; Jones, C.M.; Marshall, C.J.; Springer, C.J.; Barford, D.; et al. Mechanism of activation of the RAF-ERK signaling pathway by oncogenic mutations of B-RAF. Cell 2004, 116, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Digiovanna, J.J.; Stern, J.B.; Hornyak, T.J.; Raffeld, M.; Khan, S.G.; Oh, K.S.; Hollander, M.C.; Dennis, P.A.; Kraemer, K.H. Evidence of ultraviolet type mutations in xeroderma pigmentosum melanomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6279–6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikehata, H.; Ono, T. The mechanisms of UV mutagenesis. J. Radiat. Res. 2011, 52, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, R.H.; Ward, M.R.; Wu, H.; Medina, C.A.; Brose, M.S.; Volpe, P.; Nussen-Lee, S.; Haupt, H.M.; Martin, A.M.; Herlyn, M.; et al. Absence of BRAF mutations in UV-protected mucosal melanomas. J. Med. Genet. 2004, 41, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodis, E.; Watson, I.R.; Kryukov, G.V.; Arold, S.T.; Imielinski, M.; Theurillat, J.P.; Nickerson, E.; Auclair, D.; Li, L.; Place, C.; et al. A landscape of driver mutations in melanoma. Cell 2012, 150, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, J.A.; Fisher, D.E. The melanoma revolution: From UV carcinogenesis to a new era in therapeutics. Science 2014, 346, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Goel, V.; Haluska, F.G. PTEN signaling pathways in melanoma. Oncogene 2003, 22, 3113–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, R.; Becker, S.; Strebhardt, K. Stamping out RAF and MEK1/2 to inhibit the ERK1/2 pathway: An emerging threat to anticancer therapy. Oncogene 2016, 35, 2547–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pejkova, S.; Dzokic, G.; Tudzarova-Gjorgova, S.; Panov, S. Molecular Biology and Genetic Mechanisms in the Progression of the Malignant Skin Melanoma. Prilozi 2016, 37, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzivassiliou, G.; Song, K.; Yen, I.; Brandhuber, B.J.; Anderson, D.J.; Alvarado, R.; Ludlam, M.J.; Stokoe, D.; Gloor, S.L.; Vigers, G.; et al. RAF inhibitors prime wild-type RAF to activate the MAPK pathway and enhance growth. Nature 2010, 464, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulikakos, P.I.; Zhang, C.; Bollag, G.; Shokat, K.M.; Rosen, N. RAF inhibitors transactivate RAF dimers and ERK signalling in cells with wild-type BRAF. Nature 2010, 464, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trunzer, K.; Pavlick, A.C.; Schuchter, L.; Gonzalez, R.; McArthur, G.A.; Hutson, T.E.; Moschos, S.J.; Flaherty, K.T.; Kim, K.B.; Weber, J.S.; et al. Pharmacodynamic effects and mechanisms of resistance to vemurafenib in patients with metastatic melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, D.; Niessner, H.; Smalley, K.S.; Flaherty, K.; Paraiso, K.H.; Busch, C.; Sinnberg, T.; Vasseur, S.; Iovanna, J.L.; Driessen, S.; et al. Vemurafenib potently induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in BRAFV600E melanoma cells. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, ra7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrbeck, L.; Gong, J.N.; Lee, E.F.; Kueh, A.J.; Behren, A.; Tai, L.; Lessene, G.; Huang, D.C.; Fairlie, W.D.; Strasser, A.; et al. Hepatocyte growth factor renders BRAF mutant human melanoma cell lines resistant to PLX4032 by downregulating the pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins PUMA and BIM. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 2054–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, R.B.; Settleman, J.; Engelman, J.A. Potential therapeutic strategies to overcome acquired resistance to BRAF or MEK inhibitors in BRAF mutant cancers. Oncotarget 2011, 2, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.X.; Qi, X.Y. Targeting RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling in metastatic melanoma. IUBMB Life 2013, 65, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, V.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Estrem, S.; Li, S.; Gong, X.Q.; Buchanan, S.; Henry, J.R.; Starling, J.J.; Peng, S.B. Reactivation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway by FGF receptor 3 (FGFR3)/Ras mediates resistance to vemurafenib in human B-RAF V600E mutant melanoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 28087–28098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazarian, R.; Shi, H.; Wang, Q.; Kong, X.; Koya, R.C.; Lee, H.; Chen, Z.; Lee, M.K.; Attar, N.; Sazegar, H.; et al. Melanomas acquire resistance to B-RAF(V600E) inhibition by RTK or N-RAS upregulation. Nature 2010, 468, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.B.; Puzanov, I. Treatment of NRAS-mutant melanoma. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2015, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Laorden, B.; Viros, A.; Girotti, M.R.; Pedersen, M.; Saturno, G.; Zambon, A.; Niculescu-Duvaz, D.; Turajlic, S.; Hayes, A.; Gore, M.; et al. BRAF Inhibitors Induce Metastasis in RAS Mutant or Inhibitor-Resistant Melanoma Cells by Reactivating MEK and ERK Signaling. Sci. Signal 2014, 7, ra30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulikakos, P.I.; Persaud, Y.; Janakiraman, M.; Kong, X.; Ng, C.; Moriceau, G.; Shi, H.; Atefi, M.; Titz, B.; Gabay, M.T.; et al. RAF inhibitor resistance is mediated by dimerization of aberrantly spliced BRAF(V600E). Nature 2011, 480, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.B.; Sosman, J.A. Update on the targeted therapy of melanoma. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2013, 14, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tentori, L.; Lacal, P.M.; Graziani, G. Challenging resistance mechanisms to therapies for metastatic melanoma. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, J.; Vultur, A.; Lee, J.T.; Somasundaram, R.; Fukunaga-Kalabis, M.; Cipolla, A.K.; Wubbenhorst, B.; Xu, X.; Gimotty, P.A.; Kee, D.; et al. Acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors mediated by a RAF kinase switch in melanoma can be overcome by cotargeting MEK and IGF-1R/PI3K. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straussman, R.; Morikawa, T.; Shee, K.; Barzily-Rokni, M.; Qian, Z.R.; Du, J.; Davis, A.; Mongare, M.M.; Gould, J.; Frederick, D.T.; et al. Tumour micro-environment elicits innate resistance to RAF inhibitors through HGF secretion. Nature 2012, 487, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daud, A.; Bastian, B.C. Beyond BRAF in melanoma. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 355, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Girotti, M.R.; Pedersen, M.; Sanchez-Laorden, B.; Viros, A.; Turajlic, S.; Niculescu-Duvaz, D.; Zambon, A.; Sinclair, J.; Hayes, A.; Gore, M.; et al. Inhibiting EGF receptor or SRC family kinase signaling overcomes BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Huang, S.K.; Marzese, D.M.; Hsu, S.C.; Kawas, N.P.; Chong, K.K.; Long, G.V.; Menzies, A.M.; Scolyer, R.A.; Izraely, S.; et al. Epigenetic changes of EGFR have an important role in BRAF inhibitor-resistant cutaneous melanomas. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tynan, C.J.; Lo Schiavo, V.; Zanetti-Domingues, L.; Needham, S.R.; Roberts, S.K.; Hirsch, M.; Rolfe, D.J.; Korovesis, D.; Clarke, D.T.; Martin-Fernandez, M.L. A tale of the epidermal growth factor receptor: The quest for structural resolution on cells. Methods 2016, 95, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, G.M.; Quinn, D.G.; Camp, R.D.; Hawk, J.L.; Greaves, M.W. In Vivo studies of the action spectrum and time course for release of transforming growth factor-α by ultraviolet irradiation in man. Br. J. Dermatol. 1991, 125, 566–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piva, T.J.; Krause, D.R.; Ellem, K.O. UVC activation of the HeLa cell membrane “TGF alpha ase”, a metalloenzyme. J. Cell. Biochem. 1997, 64, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayerl, C.; Taake, S.; Moll, I.; Jung, E.G. Characterization of sunburn cells after exposure to ultraviolet light. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 1995, 11, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarhini, A.A.; Lin, Y.; Yeku, O.; LaFramboise, W.A.; Ashraf, M.; Sander, C.; Lee, S.; Kirkwood, J.M. A four-marker signature of TNF-RII TGF-α, TIMP-1 and CRP is prognostic of worse survival in high-risk surgically resected melanoma. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, C.H.; Lin, F.L.; Tong, K.B.; Hou, S.M.; Liu, J.F. Transforming growth factor α promotes osteosarcoma metastasis by ICAM-1 and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 89, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, C.; Ellerhorst, J.A.; Ekmekcioglu, S.; Greene, V.R.; Davies, M.A.; Grimm, E.A. Association of activated c-Met with NRAS-mutated human melanomas. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, E56–E65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, N.; Ahmed, S.; Janamanchi, V.; Tretiakova, M.; Zumba, O.; Krausz, T.; Jagadeeswaran, R.; Salgia, R. c-Met is a potentially new therapeutic target for treatment of human melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2246–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.H.; Cheng, C.Y.; Su, T.; Fu, X.Q.; Guo, H.; Li, T.; Tse, A.K.; Kwan, H.Y.; Yu, H.; Yu, Z.L. Quercetin inhibits HGF/c-Met signaling and HGF-stimulated melanoma cell migration and invasion. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; McTigue, M.A.; Rogers, A.; Lifshits, E.; Christensen, J.G.; Janne, P.A.; Engelman, J.A. Multiple mutations and bypass mechanisms can contribute to development of acquired resistance to MET inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etnyre, D.; Stone, A.L.; Fong, J.T.; Jacobs, R.J.; Uppada, S.B.; Botting, G.M.; Rajanna, S.; Moravec, D.N.; Shambannagari, M.R.; Crees, Z.; et al. Targeting c-Met in melanoma: Mechanism of resistance and efficacy of novel combinatorial inhibitor therapy. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergani, E.; Vallacchi, V.; Frigerio, S.; Deho, P.; Mondellini, P.; Perego, P.; Cassinelli, G.; Lanzi, C.; Testi, M.A.; Rivoltini, L.; et al. Identification of MET and SRC activation in melanoma cell lines showing primary resistance to PLX4032. Neoplasia 2011, 13, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Stones, C.; Joseph, W.R.; Leung, E.; Finlay, G.J.; Shelling, A.N.; Phillips, W.A.; Shepherd, P.R.; Baguley, B.C. Comparison of growth factor signalling pathway utilisation in cultured normal melanocytes and melanoma cell lines. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, P.; Singh, A.B.; Ellis, D.L.; Richmond, A. Constitutive activation of Akt/protein kinase B in melanoma leads to up-regulation of nuclear factor-kappaB and tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 7335–7342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Porta, C.; Paglino, C.; Mosca, A. Targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermúdez Brito, M.; Goulielmaki, E.; Papakonstanti, E.A. Focus on PTEN Regulation. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masaki, T.; Wang, Y.; DiGiovanna, J.J.; Khan, S.G.; Raffeld, M.; Beltaifa, S.; Hornyak, T.J.; Darling, T.N.; Lee, C.C.; Kraemer, K.H. High frequency of PTEN mutations in nevi and melanomas from xeroderma pigmentosum patients. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2014, 27, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Gan, W.; Chin, Y.R.; Ogura, K.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Blenis, J.; Cantley, L.C.; Toker, A.; et al. PtdIns(3,4,5)P(3)-dependent Activation of the mTORC2 Kinase Complex. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 1194–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, B.D.; Toker, A. AKT/PKB Signaling: Navigating the Network. Cell 2017, 169, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigelt, B.; Downward, J. Genomic Determinants of PI3K Pathway Inhibitor Response in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2012, 2, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, J.M.; Sharma, A.; Cheung, M.; Zimmerman, M.; Cheng, J.Q.; Bosenberg, M.W.; Kester, M.; Sandirasegarane, L.; Robertson, G.P. Deregulated Akt3 activity promotes development of malignant melanoma. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7002–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumaneng, K.; Schlegelmilch, K.; Russell, R.C.; Yimlamai, D.; Basnet, H.; Mahadevan, N.; Fitamant, J.; Bardeesy, N.; Camargo, F.D.; Guan, K.L. YAP mediates crosstalk between the Hippo and PI(3)K-TOR pathways by suppressing PTEN via miR-29. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 1322–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCubrey, J.A.; Steelman, L.S.; Abrams, S.L.; Lee, J.T.; Chang, F.; Bertrand, F.E.; Navolanic, P.M.; Terrian, D.M.; Franklin, R.A.; D’Assoro, A.B.; et al. Roles of the RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathways in malignant transformation and drug resistance. Adv. Enzyme Regul. 2006, 46, 249–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deuker, M.M.; Marsh Durban, V.; Phillips, W.A.; McMahon, M. PI3’-kinase inhibition forestalls the onset of MEK1/2 inhibitor resistance in BRAF-mutated melanoma. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meierjohann, S. Crosstalk signaling in targeted melanoma therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017, 36, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lito, P.; Pratilas, C.A.; Joseph, E.W.; Tadi, M.; Halilovic, E.; Zubrowski, M.; Huang, A.; Wong, W.L.; Callahan, M.K.; Merghoub, T.; et al. Relief of profound feedback inhibition of mitogenic signaling by RAF inhibitors attenuates their activity in BRAFV600E melanomas. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 668–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Will, M.; Qin, A.C.; Toy, W.; Yao, Z.; Rodrik-Outmezguine, V.; Schneider, C.; Huang, X.; Monian, P.; Jiang, X.; de Stanchina, E.; et al. Rapid induction of apoptosis by PI3K inhibitors is dependent upon their transient inhibition of RAS-ERK signaling. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, L.W.; Yu, S.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Ng, P.K.; Panupinthu, N.; Mitra, S.; Ju, Z.; Yu, Q.; Liang, H.; et al. Naturally occurring neomorphic PIK3R1 mutations activate the MAPK pathway, dictating therapeutic response to MAPK pathway inhibitors. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M.; Gallagher, E. From JNK to pay dirt: Jun kinases their biochemistry, physiology and clinical importance. IUBMB Life 2005, 57, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthusamy, V.; Piva, T.J. The UV response of the skin: A review of the MAPK, NFkB and TNFa signal transduction pathways. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2010, 302, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthusamy, V.; Hodges, L.D.; Macrides, T.A.; Boyle, G.M.; Piva, T.J. Effect of novel marine nutraceuticals on IL-1a-mediated TNF-a release from UVB-irradiated human melanocyte-derived cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2011, 2011, 728645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthusamy, V.; Piva, T.J. UVB-stimulated TNFa release from human melanocyte and melanoma cells is mediated by p38 MAPK. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 17029–17054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexaki, V.I.; Javelaud, D.; Mauviel, A. JNK supports survival in melanoma cells by controlling cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2008, 21, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koul, H.K.; Pal, M.; Koul, S. Role of p38 MAP Kinase Signal Transduction in Solid Tumors. Genes Cancer 2013, 4, 342–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keuling, A.M.; Andrew, S.E.; Tron, V.A. Inhibition of p38 MAPK enhances ABT-737-induced cell death in melanoma cell lines: Novel regulation of PUMA. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2010, 23, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, G.V.; Grob, J.J.; Nathan, P.; Ribas, A.; Robert, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Lane, S.R.; Mak, C.; Legenne, P.; Flaherty, K.T.; et al. Factors predictive of response, disease progression, and overall survival after dabrafenib and trametinib combination treatment: A pooled analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1743–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, R.J.; van der Westhuizen, A.; Bowden, N.A. Metastatic melanoma treatment: Combining old and new therapies. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 98, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, C.; Tian, J.; Liu, H.; Li, F.; Niu, H.; Zhu, B. Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-1 combined with anti-CTLA-4 immunotherapy to advanced melanoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine 2017, 96, e7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, H.R.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Schaider, H.; Wells, J.W. Overcoming resistance to targeted therapy with immunotherapy and combination therapy for metastatic melanoma. Oncotarget 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chan, X.Y.; Singh, A.; Osman, N.; Piva, T.J. Role Played by Signalling Pathways in Overcoming BRAF Inhibitor Resistance in Melanoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071527
Chan XY, Singh A, Osman N, Piva TJ. Role Played by Signalling Pathways in Overcoming BRAF Inhibitor Resistance in Melanoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(7):1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071527
Chicago/Turabian StyleChan, Xian Yang, Alamdeep Singh, Narin Osman, and Terrence J. Piva. 2017. "Role Played by Signalling Pathways in Overcoming BRAF Inhibitor Resistance in Melanoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 7: 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071527
APA StyleChan, X. Y., Singh, A., Osman, N., & Piva, T. J. (2017). Role Played by Signalling Pathways in Overcoming BRAF Inhibitor Resistance in Melanoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(7), 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071527