Estrogen, Estrogen Receptor and Lung Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Estrogen Receptor in Lung Cancer
3. Hormone Replacement Therapy and Lung Cancer Risk and Survival
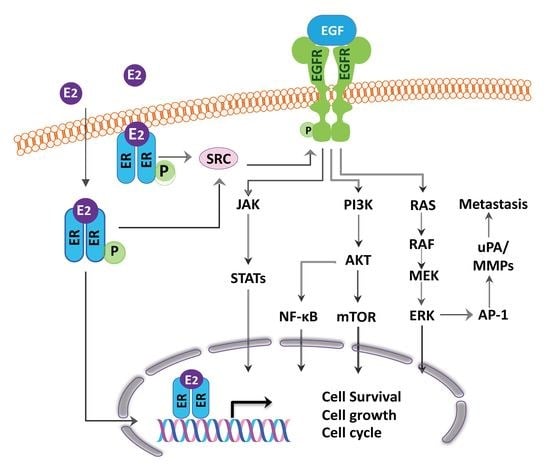
4. ER as Targets for Lung Cancer Therapy and Relationship with EGFR
5. Smoking Aggravates the Effect of Estrogen and Endocrine Disruptive Chemical Targeting ERβ from the Environment May Contribute to the Lung Carcinogenesis
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EDC | Endocrine disruptive chemical |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| ERα | Estrogen receptor α |
| ERβ | Estrogen receptor β |
| GPER | G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor |
| HRT | Hormone replacement therapy |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| OPN | Osteopontin |
| PM | Particulate matters |
| SCLC | Small cell lung cancer |
| SNPs | Single nucleotide polymorphisms |
References
- Nilsson, S.; Mäkelä, S.; Treuter, E.; Tujague, M.; Thomsen, J.; Andersson, G.; Enmark, E.; Pettersson, K.; Warner, M.; Gustafsson, J.A. Mechanisms of estrogen action. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 1535–1565. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paterni, I.; Granchi, C.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Minutolo, F. Estrogen receptors alpha (ERα) and beta (ERβ): Subtype-selective ligands and clinical potential. Steroids 2014, 90, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dostalova, P.; Zatecka, E.; Dvorakova-Hortova, K. Of oestrogens and sperm: A review of the roles of oestrogens and oestrogen receptors in male reproduction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slowikowski, B.K.; Lianeri, M.; Jagodzinski, P.P. Exploring estrogenic activity in lung cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2017, 44, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosselman, S.; Polman, J.; Dijkema, R. ER beta: Identification and characterization of a novel human estrogen receptor. FEBS Lett. 1996, 392, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, S.H.; Murray, T.; Bolden, S.; Wingo, P.A. Cancer statistics, 1999. CA Cancer J. Clin. 1999, 49, 8–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC); National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion; Office on Smoking and Health. Women and Smoking: A Report of the Surgeon General; U.S. Public Health Service, Office of the Surgeon General: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/tobacco (accessed on 20 May 2017).
- Health Promotion Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare, The Executive Yuan. Adult Smoking Behavior Survey. Available online: http://www.hpa.gov.tw (accessed on 20 May 2017).
- Hsu, L.H.; Chu, N.M.; Liu, C.C.; Tsai, S.Y.; You, D.L.; Ko, J.S.; Lu, M.C.; Feng, A.C. Sex-associated differences in non-small cell lung cancer in the new era: Is gender an independent prognostic factor? Lung Cancer 2009, 66, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taiwan Cancer Registry. Cancer incidence and mortality rates in Taiwan. Available online: http://tcr.cph.ntu.edu.tw (accessed on 20 May 2017).
- Hsu, L.H.; Liu, K.J.; Tsai, M.F.; Wu, C.R.; Feng, A.C.; Chu, N.M.; Kao, S.H. Estrogen adversely affects the prognosis of patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, E.A.; Wynder, E.L. Differences in lung cancer risk between men and women: Examination of the evidence. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1996, 88, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegfried, J.M. Women and lung cancer: Does oestrogen play a role? Lancet Oncol. 2001, 2, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, M.A.; Card, J.W.; Voltz, J.W.; Germolec, D.R.; Korach, K.S.; Zeldin, D.C. The impact of sex and sex hormones on lung physiology and disease: Lessons from animal studies. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2007, 293, L272–L278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandenberger, A.W.; Tee, M.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Chao, V.; Jaffe, R.B. Tissue distribution of estrogen receptors alpha (ER-alpha) and beta (ER-beta) mRNA in the midgestational human fetus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 3509–3512. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morani, A.; Barros, R.P.; Imamov, O.; Hultenby, K.; Arner, A.; Warner, M.; Gustafsson, J.A. Lung dysfunction causes systemic hypoxia in estrogen receptor beta knockout (ERbeta−/−) mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 7165–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrone, C.; Cassel, T.N.; Pettersson, K.; Piao, Y.S.; Cheng, G.; Ciana, P.; Maggi, A.; Warner, M.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Nord, M. Regulation of postnatal lung development and homeostasis by estrogen receptor beta. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 8542–8552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Farkas, A.M.; Parwani, A.V.; Lathrop, K.L.; Lenzner, D.; Land, S.R.; Srinivas, H. Estrogen receptor beta functions through nongenomic mechanisms in lung cancer cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabile, L.P.; Siegfried, J.M. Estrogen receptor pathways in lung cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2004, 6, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, H.; Ishii, A.; Washiya, K.; Konno, T.; Kon, H.; Yamaya, C.; Ono, I.; Minamiya, Y.; Ogawa, J. Estrogen receptor alpha and beta are prognostic factors in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5084–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, A.G.; Prysak, G.M.; Murphy, V.; Lonardo, F.; Pass, H.; Schwartz, J.; Brooks, S. Nuclear estrogen receptor beta in lung cancer: Expression and survival differences by sex. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 7280–7287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omoto, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nishida, K.; Tsuchiya, E.; Eguchi, H.; Nakagawa, K.; Ishikawa, Y.; Yamori, T.; Iwase, H.; Fujii, Y.; et al. Expression, function, and clinical implications of the estrogen receptor beta in human lung cancers. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 285, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabile, L.P.; Davis, A.L.; Gubish, C.T.; Hopkins, T.M.; Luketich, J.D.; Christie, N.; Finkelstein, S.; Siegfried, J.M. Human non-small cell lung tumors and cells derived from normal lung express both estrogen receptor alpha and beta and show biological responses to estrogen. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 2141–2150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ganti, A.K.; Sahmoun, A.E.; Panwalkar, A.W.; Tendulkar, K.K.; Potti, A. Hormone replacement therapy is associated with decreased survival in women with lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Inoue, M.; Sobue, T.; Tsugane, S. Reproductive factors, hormone use and the risk of lung cancer among middle-aged never-smoking Japanese women: A large-scale population-based cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 117, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niikawa, H.; Suzuki, T.; Miki, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Nagasaki, S.; Akahira, J.; Honma, S.; Evans, D.B.; Hayashi, S.; Kondo, T.; et al. Intratumoral estrogens and estrogen receptors in human non-small cell lung carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 4417–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Yanamala, N.; Lathrop, K.L.; Zhang, L.; Klein-Seetharaman, J.; Srinivas, H. Ligand-independent antiapoptotic function of estrogen receptor-beta in lung cancer cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 1737–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mah, V.; Marquez, D.; Alavi, M.; Maresh, E.L.; Zhang, L.; Yoon, N.; Horvath, S.; Bagryanova, L.; Fishbein, M.C.; Chia, D.; et al. Expression levels of estrogen receptor beta in conjunction with aromatase predict survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2011, 74, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chlebowski, R.T.; Schwartz, A.G.; Wakelee, H.; Anderson, G.L.; Stefanick, M.L.; Manson, J.E.; Rodabough, R.J.; Chien, J.W.; Wactawski-Wende, J.; Gass, M.; et al. Women’s Health Initiative, I. Oestrogen plus progestin and lung cancer in postmenopausal women (Women’s Health Initiative trial): A post-hoc analysis of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2009, 374, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatore, C.G.; Chien, J.W.; Au, D.H.; Satia, J.A.; White, E. Lung cancer and hormone replacement therapy: Association in the vitamins and lifestyle study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1540–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schabath, M.B.; Wu, X.; Vassilopoulou-Sellin, R.; Vaporciyan, A.A.; Spitz, M.R. Hormone replacement therapy and lung cancer risk: A case-control analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, A.G.; Wenzlaff, A.S.; Prysak, G.M.; Murphy, V.; Cote, M.L.; Brooks, S.C.; Skafar, D.F.; Lonardo, F. Reproductive factors, hormone use, estrogen receptor expression and risk of non small-cell lung cancer in women. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 5785–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.Y.; Hsiao, C.F.; Chang, G.C.; Tsai, Y.H.; Su, W.C.; Perng, R.P.; Huang, M.S.; Hsiung, C.A.; Chen, C.J.; Yang, P.C.; et al. Hormone replacement therapy and lung cancer risk in Chinese. Cancer 2007, 110, 1768–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Carloss, H.; Wyatt, S.W.; Riley, E. Hormone replacement therapy and survival in lung cancer in postmenopausal women in a rural population. Cancer 2009, 115, 4167–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayeni, O.; Robinson, A. Hormone replacement therapy and outcomes for women with non-small-cell lung cancer: Can an association be confirmed? Curr. Oncol. 2009, 16, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chlebowski, R.T.; Anderson, G.L.; Manson, J.E.; Schwartz, A.G.; Wakelee, H.; Gass, M.; Rodabough, R.J.; Johnson, K.C.; Wactawski-Wende, J.; Kotchen, J.M.; et al. Lung cancer among postmenopausal women treated with estrogen alone in the Women’s Health Initiative randomized trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellahcene, A.; Castronovo, V.; Ogbureke, K.U.; Fisher, L.W.; Fedarko, N.S. Small integrin-binding ligand N-linked glycoproteins (SIBLINGs): Multifunctional proteins in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zirngibl, R.A.; Chan, J.S.; Aubin, J.E. Divergent regulation of the Osteopontin promoter by the estrogen receptor-related receptors is isoform- and cell context dependent. J. Cell Biochem. 2013, 114, 2356–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Silva Rudland, S.; Martin, L.; Roshanlall, C.; Winstanley, J.; Leinster, S.; Platt-Higgins, A.; Carroll, J.; West, C.; Barraclough, R.; et al. Association of S100A4 and osteopontin with specific prognostic factors and survival of patients with minimally invasive breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.S.; Kim, H.J.; Chang, J.; Ahn, C.M.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, S.K. Elevated circulating level of osteopontin is associated with advanced disease state of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2007, 57, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, R.; Takahashi, F.; Ohashi, R.; Takahashi, F.; Ohashi, R.; Yoshioka, M.; Gu, T.; Tajima, K.; Unnoura, T.; Iwakami, S.; et al. Osteopontin is involved in the formation of malignant pleural effusion in lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2009, 63, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchardy, C.; Benhamou, S.; Schaffar, R.; Verkooijen, H.M.; Fioretta, G.; Schubert, H.; Vinh-Hung, V.; Soria, J.C.; Vlastos, G.; Rapiti, E. Lung cancer mortality risk among breast cancer patients treated with anti-estrogens. Cancer 2011, 117, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lother, S.A.; Harding, G.A.; Musto, G.; Navaratnam, S.; Pitz, M.W. Antiestrogen use and survival of women with non-small cell lung cancer in Manitoba, Canada. Horm. Cancer 2013, 4, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, L.H.; Feng, A.C.; Kao, S.H.; Liu, C.C.; Tsai, S.Y.; Shih, L.S.; Chu, N.M. Second primary lung cancers among breast cancer patients treated with anti-estrogens have a longer cancer-specific survival. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Del Prete, S.A.; Maurer, L.H.; Brinck-Johnsen, T.; Sorenson, G.D. 17-Beta-estradiol levels in patients with small cell carcinoma of the lung. J. Steroid Biochem. 1983, 18, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorenson, G.D.; Pettengill, O.S.; Brinck-Johnsen, T.; Cate, C.C.; Maurer, L.H. Hormone production by cultures of small-cell carcinoma of the lung. Cancer 1981, 47, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, C.S.; Eaton, K.D. Estrogen signaling in lung cancer: An opportunity for novel therapy. Cancers 2012, 4, 969–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, H. Estrogen receptors as the novel therapeutic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegfried, J.M.; Stabile, L.P. Estrongenic steroid hormones in lung cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2014, 41, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, Y.K.; Mak, P.; Hassan, S.; Ho, S.M. Estrogen receptor (ER)-beta isoforms: A key to understanding ER-beta signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2006, 103, 13162–13167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.T.; Chang, Y.L.; Shih, J.Y.; Lee, Y.C. The significance of estrogen receptor beta in 301 surgically treated non-small cell lung cancers. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2005, 130, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skov, B.G.; Fischer, B.M.; Pappot, H. Oestrogen receptor beta over expression in males with non-small cell lung cancer is associated with better survival. Lung Cancer 2008, 59, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nose, N.; Sugio, K.; Oyama, T.; Nozoe, T.; Uramoto, H.; Iwata, T.; Onitsuka, T.; Yasumoto, K. Association between estrogen receptor-beta expression and epidermal growth factor receptor mutation in the postoperative prognosis of adenocarcinoma of the lung. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raso, M.G.; Behrens, C.; Herynk, M.H.; Liu, S.; Prudkin, L.; Ozburn, N.C.; Woods, D.M.; Tang, X.; Mehran, R.J.; Moran, C.; et al. Immunohistochemical expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors identifies a subset of NSCLCs and correlates with EGFR mutation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5359–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabile, L.P.; Dacic, S.; Land, S.R.; Lenzner, D.E.; Dhir, R.; Acquafondata, M.; Landreneau, R.J.; Grandis, J.R.; Siegfried, J.M. Combined analysis of estrogen receptor beta-1 and progesterone receptor expression identifies lung cancer patients with poor outcome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouquette, I.; Lauwers-Cances, V.; Allera, C.; Brouchet, L.; Milia, J.; Nicaise, Y.; Laurent, J.; Delisle, M.B.; Favre, G.; Didier, A.; et al. Characteristics of lung cancer in women: Importance of hormonal and growth factors. Lung Cancer 2012, 76, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rades, D.; Setter, C.; Dahl, O.; Schild, S.E.; Noack, F. The prognostic impact of tumor cell expression of estrogen receptor-alpha, progesterone receptor, and androgen receptor in patients irradiated for nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer 2012, 118, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, C.; Helenius, G.; Fernandes, O.; Karlsson, M.G. Oestrogen receptor beta in NSCLC—Prevalence, proliferative influence, prognostic impact and smoking. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 2012, 120, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navaratnam, S.; Skliris, G.; Qing, G.; Banerji, S.; Badiani, K.; Tu, D.; Bradbury, P.A.; Leighl, N.B.; Shepherd, F.A.; Nowatzki, J.; et al. Differential role of estrogen receptor beta in early versus metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Horm. Cancer 2012, 3, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Liao, Y.; Tang, H.; Chen, G. The expression of estrogen receptors beta2, 5 identifies and is associated with prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Endocrine 2013, 44, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadota, K.; Eguchi, T.; Villena-Vargas, J.; Woo, K.M.; Sima, C.S.; Jones, D.R.; Travis, W.D.; Adusumilli, P.S. Nuclear estrogen receptor-alpha expression is an independent predictor of recurrence in male patients with pT1aN0 lung adenocarcinomas, and correlates with regulatory T-cell infiltration. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 27505–27518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.M.; Chiu, K.L.; Chen, T.S.; Chang, S.M.; Yang, S.Y.; Chen, L.H.; Ni, Y.L.; Sher, Y.P.; Yu, S.L.; Ma, W.L. Potential therapeutic benefit of combining gefitinib and tamoxifen for treating advanced lung adenocarcinoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 642041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skjefstad, K.; Grindstad, T.; Khanehkenari, M.R.; Richardsen, E.; Donnem, T.; Kilvaer, T.; Andersen, S.; Bremnes, R.M.; Busund, L.T.; Al-Saad, S. Prognostic relevance of estrogen receptor alpha, beta and aromatase expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Steroids 2016, 113, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Shimizu, K.; Kakegawa, S.; Ohtaki, Y.; Nagashima, T.; Kaira, K.; Horiguchi, J.; Oyama, T.; Takeyoshi, I. Prognostic significance of aromatase and estrogen receptor beta expression in EGFR wild-type lung adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Tse, L.A.; Wang, F. Prognostic value of estrogen receptors mRNA expression in non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Steroids 2015, 104, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Zhan, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Miu, Y.; Wang, X.; Jin, J.; Li, Q.; Lv, T.; et al. Prognostic value of the expression of estrogen receptor beta in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Ding, X.; Shen, Z.; Liu, Z.; An, T.; Duan, J.; Zhong, J.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J.; et al. ERbeta localization influenced outcomes of EGFR-TKI treatment in NSCLC patients with EGFR mutations. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, T.L.; Tzeng, C.R.; Yu, C.L.; Wang, Y.P.; Kao, S.H. Estrogen receptor-beta in mitochondria: Implications for mitochondrial bioenergetics and tumorigenesis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1350, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, L. Mitochondrial estrogen receptor beta inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell apoptosis via interaction with Bad. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2015, 35, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jacenik, D.; Cygankiewicz, A.I.; Krajewska, W.M. The G protein-coupled estrogen receptor as a modulator of neoplastic transformation. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 429, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konings, G.F.; Reynaert, N.L.; Delvoux, B.; Verhamme, F.M.; Bracke, K.R.; Brusselle, G.G.; Romano, A.; Vernooy, J.H. Increased levels of enzymes involved in local estradiol synthesis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 443, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revankar, C.M.; Cimino, D.F.; Sklar, L.A.; Arterburn, J.B.; Prossnitz, E.R. A transmembrane intracellular estrogen receptor mediates rapid cell signaling. Science 2005, 307, 1625–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, H.; Matsuda, K.; Hosokawa, K.; Nishi, M.; Morris, J.F.; Prossnitz, E.R.; Kawata, M. Expression of G protein-coupled receptor-30, a G protein-coupled membrane estrogen receptor, in oxytocin neurons of the rat paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 5842–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jala, V.R.; Radde, B.N.; Haribabu, B.; Klinge, C.M. Enhanced expression of G-protein coupled estrogen receptor (GPER/GPR30) in lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Liao, Y.; Fan, S.; Tang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Zhou, B.; Xiong, J.; Zhou, S.; Zou, M.; Wang, J. G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) mediates NSCLC progression induced by 17beta-estradiol (E2) and selective agonist G1. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, T.F.; Siu, E.R.; Esteves, C.A.; Monteiro, H.P.; Oliveira, C.A.; Porto, C.S.; Lazari, M.F. 17 beta-estradiol induces the translocation of the estrogen receptors ESR1 and ESR2 to the cell membrane, MAPK3/1 phosphorylation and proliferation of cultured immature rat Sertoli cells. Biol. Reprod. 2008, 78, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honma, N.; Hosoi, T.; Arai, T.; Takubo, K. Estrogen and cancers of the colorectum, breast, and lung in postmenopausal women. Pathol. Int. 2015, 65, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, K.; Shiraishi, K.; Yoshida, A.; Shinchi, Y.; Sanada, M.; Motooka, Y.; Fujino, K.; Mori, T.; Suzuki, M. Synchronous multiple lung adenocarcinomas: Estrogen concentration in peripheral lung. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, L.H.; Hsu, P.C.; Liao, T.L.; Feng, A.C.; Chu, N.M.; Kao, S.H. Pleural fluid osteopontin, vascular endothelial growth factor, and urokinase-type plasminogen activator levels as predictors of pleurodesis outcome and prognosticators in patients with malignant pleural effusion: A prospective cohort study. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatabe, Y.; Mitsudomi, T.; Takahashi, T. TTF-1 expression in pulmonary adenocarcinomas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2002, 26, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanzhi, W.; Yiping, H.; Ling, H.; Jianming, Z.; Qiang, L. The relationship between TTF-1 expression and EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinomas. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.P.; Huang, Y.T.; Chang, Y.L.; Yu, C.J.; Yang, C.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Shih, J.Y.; Yang, P.C. Clinical significance of thyroid transcription factor-1 in advanced lung adenocarcinoma under epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment. Chest 2012, 141, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, S.K.; Chu, P.G.; Weiss, L.M. Immunohistochemical expression of estrogen receptor in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2006, 14, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiser, C.M.; Greiser, E.M.; Doren, M. Menopausal hormone therapy and risk of lung cancer—Systematic review and meta-analysis. Maturitas 2010, 65, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chlebowski, R.T.; Wakelee, H.; Pettinger, M.; Rohan, T.; Liu, J.; Simon, M.; Tindle, H.; Messina, C.; Johnson, K.; Schwartz, A.; et al. Estrogen plus progestin and lung cancer: Follow-up of the Women’s Health Initiative randomized trial. Clin. Lung Cancer 2016, 17, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Shapiro, D.J. The immune system and inflammation in breast cancer. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 382, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Greten, F.R.; Karin, M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 2010, 140, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Abe, K.; Suzuki, S.; Niikawa, H.; Iida, S.; Hata, S.; Akahira, J.; Mori, K.; Evans, D.B.; et al. Intratumoral localization of aromatase and interaction between stromal and parenchymal cells in the non-small cell lung carcinoma microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6659–6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabile, L.P.; Rothstein, M.E.; Cunningham, D.E.; Land, S.R.; Dacic, S.; Keohavong, P.; Siegfried, J.M. Prevention of tobacco carcinogen-induced lung cancer in female mice using antiestrogens. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 2181–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mah, V.; Seligson, D.B.; Li, A.; Marquez, D.C.; Wistuba, I.I.; Elshimali, Y.; Fishbein, M.C.; Chia, D.; Pietras, R.J.; Goodglick, L. Aromatase expression predicts survival in women with early-stage non small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10484–10490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, O.K.; Marquez-Garban, D.C.; Fishbein, M.C.; Goodglick, L.; Garban, H.J.; Dubinett, S.M.; Pietras, R.J. Aromatase inhibitors in human lung cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 11287–11291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez-Garban, D.C.; Chen, H.W.; Goodglick, L.; Fishbein, M.C.; Pietras, R.J. Targeting aromatase and estrogen signaling in human non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1155, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, D.H.; Griner, L.M.; Keller, J.M.; Hu, X.; Southall, N.; Marugan, J.; David, J.M.; Ferrer, M.; Palena, C. Targeting estrogen receptor signaling with fulvestrant enhances immune and chemotherapy-mediated cytotoxicity of human lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 6204–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swedenborg, E.; Power, K.A.; Cai, W.; Pongratz, I.; Ruegg, J. Regulation of estrogen receptor beta activity and implications in health and disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 3873–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, E.R. Bidirectional signaling between the estrogen receptor and the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 17, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Endoh, H.; Masuhiro, Y.; Kitamoto, T.; Uchiyama, S.; Sasaki, H.; Masushige, S.; Gotoh, Y.; Nishida, E.; Kawashima, H.; et al. Activation of the estrogen receptor through phosphorylation by mitogen-activated protein kinase. Science 1995, 270, 1491–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez-Garban, D.C.; Chen, H.W.; Fishbein, M.C.; Goodglick, L.; Pietras, R.J. Estrogen receptor signaling pathways in human non-small cell lung cancer. Steroids 2007, 72, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Wu, Z.H.; Yang, X.Y. Role of estrogen in lung cancer based on the estrogen receptor-epithelial mesenchymal transduction signaling pathways. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 8, 2849–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Liao, Y.; Liu, C.; Huang, Q.; Liang, H.; Ai, B.; Fu, S.; Zhou, S. Estrogen promotes tumor metastasis via estrogen receptor beta-mediated regulation of matrix-metalloproteinase-2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegfried, J.M.; Farooqui, M.; Rothenberger, N.J.; Dacic, S.; Stabile, L.P. Interaction between the estrogen receptor and fibroblast growth factor receptor pathways in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 24063–24076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabile, L.P.; Lyker, J.S.; Gubish, C.T.; Zhang, W.; Grandis, J.R.; Siegfried, J.M. Combined targeting of the estrogen receptor and the epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer shows enhanced antiproliferative effects. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 1459–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietras, R.J.; Marquez, D.C.; Chen, H.W.; Tsai, E.; Weinberg, O.; Fishbein, M. Estrogen and growth factor receptor interactions in human breast and non-small cell lung cancer cells. Steroids 2005, 70, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, F.; Li, M.; Shan, W.L.; Qian, L.T.; Meng, S.P.; Zhang, X.L.; Wang, B.L. Correlation between epidermal growth factor receptor mutations and the expression of estrogen receptor-beta in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 2359–2365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Koh, Y.; Ando, M.; Ito, N.; Takeo, S.; Adachi, H.; Tagawa, T.; Kakegawa, S.; Yamashita, M.; Kataoka, K.; et al. Prospective analysis of oncogenic driver mutations and environmental factors: Japan Molecular Epidemiology For Lung Cancer Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2247–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, S.; Siegfried, J.M.; Traynor, A.M. Non-small-cell lung cancer and breast carcinoma: Chemotherapy and beyond. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, M.; Belli, C.; Villa, E.; Gregorc, V. Estrogen receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor as targets for dual lung cancer therapy: Not just a case? J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 684–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traynor, A.M.; Schiller, J.H.; Stabile, L.P.; Kolesar, J.M.; Eickhoff, J.C.; Dacic, S.; Hoang, T.; Dubey, S.; Marcotte, S.M.; Siegfried, J.M. Pilot study of gefitinib and fulvestrant in the treatment of post-menopausal women with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2009, 64, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov, U.S. National Institutes of Health. Available online: http://www.clinicaltrial.gov/ (accessed on 11 June 2017).
- Iida, S.; Kakinuma, H.; Miki, Y.; Abe, K.; Sakurai, M.; Suzuki, S.; Niikawa, H.; Akahira, J.; Suzuki, T.; Sasano, H. Steroid sulphatase and oestrogen sulphotransferase in human non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.J.; Li, J.; Hao, F.R.; Yuan, Y.; Li, J.Y.; Lu, W.; Zhou, T.Y. Dexamethasone suppresses the growth of human non-small cell lung cancer via inducing estrogen sulfotransferase and inactivating estrogen. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.Q.; Zheng, L.X.; Li, Z.Y.; Lin, T.Y. Clinicopathological significance of oestrogen receptor expression in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Int. Med. Res. 2017, 45, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamura, K.; Takeuchi, K.; Togashi, Y.; Hatano, S.; Ninomiya, H.; Motoi, N.; Mun, M.Y.; Sakao, Y.; Okumura, S.; Nakagawa, K.; et al. EML4-ALK lung cancers are characterized by rare other mutations, a TTF-1 cell lineage, an acinar histology, and young onset. Mod. Pathol. 2009, 22, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamura, K.; Ninomiya, H.; Ishikawa, Y.; Matsubara, O. Is the epidermal growth factor receptor status in lung cancers reflected in clinicopathologic features? Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2010, 134, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lehtio, J.; De Petris, L. Lung cancer proteomics, clinical and technological considerations. J. Proteom. 2010, 73, 1851–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indovina, P.; Marcelli, E.; Pentimalli, F.; Tanganelli, P.; Tarro, G.; Giordano, A. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics: The road to lung cancer biomarker discovery. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2013, 32, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagemann, I.S.; Devarakonda, S.; Lockwood, C.M.; Spencer, D.H.; Guebert, K.; Bredemeyer, A.J.; Al-Kateb, H.; Nguyen, T.T.; Duncavage, E.J.; Cottrell, C.E.; et al. Clinical next-generation sequencing in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer 2015, 121, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.Y.; Yang, T.Y.; Chen, K.C.; Li, Y.J.; Hsu, K.H.; Tsai, C.R.; Chen, C.Y.; Hsu, C.P.; Hsia, J.Y.; Chuang, C.Y.; et al. EGFR L858R mutation and polymorphisms of genes related to estrogen biosynthesis and metabolism in never-smoking female lung adenocarcinoma patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2149–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.Y.; Hsiao, C.F.; Chang, G.C.; Tsai, Y.H.; Su, W.C.; Chen, Y.M.; Huang, M.S.; Hsiung, C.A.; Chen, C.J.; Yang, P.C. EGFR polymorphisms, hormone replacement therapy and lung adenocarcinoma risk: Analysis from a genome-wide association study in never-smoking women. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.Y.; Hsiao, C.F.; Chang, G.C.; Tsai, Y.H.; Su, W.C.; Chen, Y.M.; Huang, M.S.; Tsai, F.Y.; Jiang, S.S.; Chang, I.S.; et al. Estrogen receptor gene polymorphisms and lung adenocarcinoma risk in never-smoking women. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belous, A.R.; Hachey, D.L.; Dawling, S.; Roodi, N.; Parl, F.F. Cytochrome P450 1B1-mediated estrogen metabolism results in estrogen-deoxyribonucleoside adduct formation. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meireles, S.I.; Esteves, G.H.; Hirata, R., Jr.; Peri, S.; Devarajan, K.; Slifker, M.; Mosier, S.L.; Peng, J.; Vadhanam, M.V.; Hurst, H.E.; et al. Early changes in gene expression induced by tobacco smoke: Evidence for the importance of estrogen within lung tissue. Cancer Prev. Res. 2010, 3, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Xu, X.; Mace, B.E.; Vanderveer, L.A.; Workman, L.R.; Slifker, M.J.; Sullivan, P.M.; Veenstra, T.D.; Clapper, M.L. Estrogen metabolism within the lung and its modulation by tobacco smoke. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olea, N.; Pazos, P.; Exposito, J. Inadvertent exposure to xenoestrogens. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 1998, 7, S17–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swedenborg, E.; Ruegg, J.; Makela, S.; Pongratz, I. Endocrine disruptive chemicals: Mechanisms of action and involvement in metabolic disorders. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swedenborg, E.; Pongratz, I.; Gustafsson, J.A. Endocrine disruptors targeting ERbeta function. Int. J. Androl. 2010, 33, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fucic, A.; Gamulin, M.; Ferencic, Z.; Rokotov, D.S.; Katic, J.; Bartonova, A.; Lovasic, I.B.; Merlo, D.F. Lung cancer and environmental chemical exposure: A review of our current state of knowledge with reference to the role of hormones and hormone receptors as an increased risk factor for developing lung cancer in man. Toxicol. Pathol. 2010, 38, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fucic, A.; Gamulin, M.; Ferencic, Z.; Katic, J.; von Krauss, M.K.; Bartonova, A.; Merlo, D.F. Environmental exposure to xenoestrogens and oestrogen related cancers: Reproductive system, breast, lung, kidney, pancreas, and brain. Environ. Health 2012, 11, S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, K.H.; Ho, C.C.; Hsai, T.C.; Tseng, J.S.; Su, K.Y.; Wu, M.F.; Chiu, K.L.; Yang, T.Y.; Chen, K.C.; Ooi, H.; et al. Identification of five driver gene mutations in patients with treatment-naive lung adenocarcinoma in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garon, E.B.; Pietras, R.J.; Finn, R.S.; Kamranpour, N.; Pitts, S.; Marquez-Garban, D.C.; Desai, A.J.; Dering, J.; Hosmer, W.; von Euw, E.M.; et al. Antiestrogen fulvestrant enhances the antiproliferative effects of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in human non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.D.; Gray, R.G.; Stewart, J.A.; Skinner, H.G.; Schiller, J.H. Tamoxifen does not reduce the risk of lung cancer in women. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, s7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| References | ER Subtype | Location | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kawai 2005 [20] | α | Cytoplasm | Worse |
| β | Nucleus | Better | |
| Schwartz 2005 [21] | β | Non-specified | Better (male) |
| Worse (female) * | |||
| Wu 2005 [51] | β | Nucleus | Better |
| Skov 2005 [52] | β | Nucleus | Better (male) |
| Worse (female) | |||
| Nose 2009 [53] | α | Cytoplasm | Worse |
| β | Nucleus | Better | |
| Raso 2009 [54] | β | Nucleus | Worse |
| Stabile 2011 [55] | β | Cytoplasm | Worse |
| Rouquette 2012 [56] | α | Nucleus | Better |
| Rades 2012 [57] | α | Non-specified | Worse |
| Karlsson 2012 [58] | β | Nucleus | Better |
| Navaratnam 2012 [59] | β1 | Nucleus | Better in earlier stage |
| Worse in later stage | |||
| Liu 2013 [60] | β2,5 | Cytoplasm | Better |
| Kadota 2015 [61] | α | Nucleus | Worse |
| Liu 2015 [62] | β | Cytoplasm | Better |
| Skjefstad 2016 [63] | β | Nucleus | Worse (female) |
| Tanaka 2016 [64] | β | Non-specified | Worse (male) |
| Patient Population | Allowed Prior Therapy | Treatment | Correlate Response with Receptors Expression | ClinicalTrials.Gov Identifier & Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage IIIB or IV NSCLC, both gender | ≥1 prior chemotherapy | Erlotinib + fulvestrant vs. Erlotinib | Yes | NCT00100854 Active, not recruiting (2004~) |
| Stage IIIB or IV NSCLC, both gender, ER or PR positive | Stable disease on erlotinib >2 months, prior chemotherapy not defined | Erlotinib + fulvestrant (single arm) | Before trial entry | NCT00592007 Terminated with results (2007~) |
| Stage IIIB or IV, postmenopausal women | Completed 4 cycles of induction platinum-based chemotherapy | Arm B-1. Best supportive care (BSC); Arm B-2. BSC + bevacizumab; Arm A-1. Fulvestrant + anastrozole; Arm A-2. Fulvestrant + anastrazole + bevacizumab | Yes | NCT00932152 Terminated with results (2010~) |
| Stage III or IV NSCLC, postmenopausal women | Chemotherapy, 0–1 line for EGFR mutations and 1–2 lines for EGFR wild type | Gefitinib + fulvestrant vs. Gefitinib for EGFR mutations; Erlotinib + fulvestrant vs. Erlotinib for EGFR wild type | No | NCT01556191 Recruiting (2012~) |
| Stage IV NSCLC, postmenopausal women | Phase I dose escalating study | Exemestane + premetrexed, carboplatin | No | NCT01664754 Active, not recruiting (2012~) |
| Stage III or IV NSCLC, postmenopausal women | Chemotherapy 1–3 line | Exemestane (single arm) | No | NCT02666105 Recruiting (2016~) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, L.-H.; Chu, N.-M.; Kao, S.-H. Estrogen, Estrogen Receptor and Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081713
Hsu L-H, Chu N-M, Kao S-H. Estrogen, Estrogen Receptor and Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(8):1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081713
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Li-Han, Nei-Min Chu, and Shu-Huei Kao. 2017. "Estrogen, Estrogen Receptor and Lung Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 8: 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081713
APA StyleHsu, L. -H., Chu, N. -M., & Kao, S. -H. (2017). Estrogen, Estrogen Receptor and Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(8), 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081713