Quercetin Attenuates Manganese-Induced Neuroinflammation by Alleviating Oxidative Stress through Regulation of Apoptosis, iNOS/NF-κB and HO-1/Nrf2 Pathways
Abstract
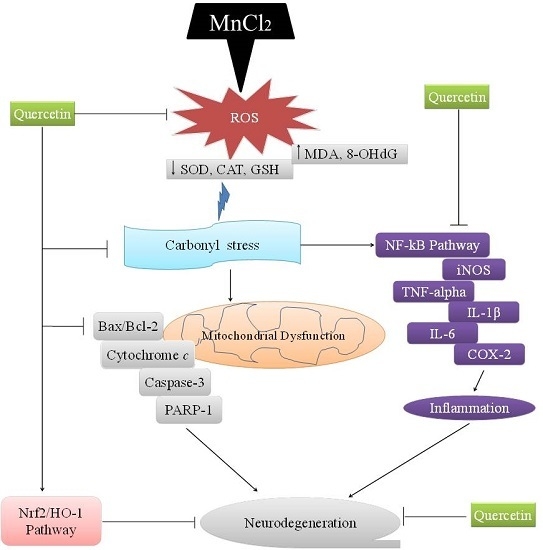
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Protective Effect of QCT on Mn-Induced Cytotoxicity in SK-N-MC Cells
2.2. QCT Attenuated Mn-Induced Oxidative Stress in SK-N-MC Cells
2.3. QCT Attenuates Mn-Induced the Loss of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (ΔΨm) and Apoptosis in SK-N-MC Cells
2.4. QCT Down-Regulates the P-IκBα/NF-kB and Up-Regulates the HO-1/ Nrf2 Activity in SK-N-MC Cells
2.5. The Beneficial Effect of QCT on Hematological Parameters against Mn-Induce Toxicity in Rat Brain
2.6. QCT Decreased ROS and Protein Carbonyl Levels and Restores Cu/Zn-SOD Activity on Mn-Induced Oxidative Damage in the Rat Brain
2.7. QCT Decreases the Expression of Inflammatory Markers against Mn-Induced Neuroinflammation in the Rat Brain
2.8. QCT Down-Regulates the NF-κB, iNOS mRNA Levels and Up-Regulates the Nrf2, HO-1 mRNA Levels in the Rat Brain
2.9. QCT Decreased Neuroapoptosis Induced by Mn in the Rat Brain
2.10. Effect of Treatment on Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Changes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Viability
4.2. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Activity
4.3. Measurement of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Level
4.4. Antioxidant Status
4.5. Measurement of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (ΔΨm)
4.6. Apoptosis Assay
4.7. Experimental Animal and Treatments
4.8. Neurological Scoring
4.9. Preparation of Peripheral Blood Smears and Differential Counts of WBC
4.10. Tissue Homogenates
4.11. Collection of Brain Slices
4.12. Assay of ROS
4.13. Protein Carbonyls Assay
4.14. Assay of Cu/Zn-SOD Activity
4.15. Quantitative Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.16. Western Blot Analysis
4.17. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
4.18. Statistical Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Mn | Manganese |
| QCT | Quercetin |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| WBC | White blood cell |
| h | Hour |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase 1 |
| WBC | White blood cell |
| 8-OHdG | 8-Hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| iNOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| SD | Sprague-dawley |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer solution |
| DCFH-DA | 2′,7′-dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction |
| OCT | Optimal cutting temperature |
References
- Underwood, E.J. Trace metals in human and animal health. J. Hum. Nutr. 1981, 35, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, A.P.; Schneider, J.A.; Nelson, B.C.; Atha, D.H.; Jain, A.; Soliman, K.F.; Aschner, M.; Mazzio, E.; Renee Reams, R. Manganese-induced oxidative DNA damage in neuronal SH-SY5Y cells: Attenuation of thymine base lesions by glutathione and N-acetylcysteine. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 218, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkelstein, Y.; Milatovic, D.; Aschner, M. Modulation of cholinergic systems by manganese. Neurotoxicology 2007, 28, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aschner, M.; Aschner, J.L. Manganese neurotoxicity: Cellular effects and blood–brain barrier transport. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1991, 15, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, Y.; Zhang, N.; Fitsanakis, V.A.; Avison, M.J.; Gore, J.C.; Aschner, M. Differential deposition of manganese in the rat brain following subchronic exposure to manganese: A T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging study. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2008, 10, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Selikhova, M.; Fedoryshyn, L.; Matviyenko, Y.; Komnatska, I.; Kyrylchuk, M.; Krolicki, L.; Friedman, A.; Taylor, A.; Jager, H.R.; Lees, A.; et al. Parkinsonism and dystonia caused by the illicit use of ephedrone—A longitudinal study. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 2224–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mena, I.; Marin, O.; Fuenzalida, S.; Cotzias, G.C. Chronic manganese poisoning. Clinical picture and manganese turnover. Neurology 1967, 17, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calne, D.B.; Chu, N.S.; Huang, C.C.; Lu, C.S.; Olanow, W. Manganism and idiopathic parkinsonism: Similarities and differences. Neurology 1994, 44, 1583–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, G.B.; Leonard, A.; Hantson, P. Carcinogenicity, mutagenicity and teratogenicity of manganese compounds. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2002, 42, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, H.B.; Bertolucci, P.H.; Pereira, J.S.; Lima, J.G.; Andrade, L.A. Chronic exposure to the fungicide maneb may produce symptoms and signs of CNS manganese intoxication. Neurology 1988, 38, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Cai, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, S.; Wang, Y.; Ye, L. α-Synuclein overexpression during manganese-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Brain Res. Bull. 2010, 81, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spahr, L.; Butterworth, R.F.; Fontaine, S.; Bui, L.; Therrien, G.; Milette, P.C.; Lebrun, L.H.; Zayed, J.; Leblanc, A.; Pomier-Layrargues, G. Increased blood manganese in cirrhotic patients: Relationship to pallidal magnetic resonance signal hyperintensity and neurological symptoms. Hepatology 1996, 24, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimund, J.M.; Dietemann, J.L.; Warter, J.M.; Baumann, R.; Duclos, B. Factors associated to hypermanganesemia in patients receiving home parenteral nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 19, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardle, C.A.; Forbes, A.; Roberts, N.B.; Jawhari, A.V.; Shenkin, A. Hypermanganesemia in long-term intravenous nutrition and chronic liver disease. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 1999, 23, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynard, L.S.; Cotzias, G.C. The partition of manganese among organs and intracellular organelles of the rat. J. Biol. Chem. 1955, 214, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, H.; Nishida, M.; Yoshimura, T.; Takada, J.; Koyama, M. Partition of divalent and total manganese in organs and subcellular organelles of MnCl2-treated rats studied by ESR and neutron activation analysis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 841, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, H.R.; Chae, H.J. Apoptosis induced by manganese on neuronal SK-N-MC cell line: Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and mitochondria dysfunction. Environ. Health Toxicol. 2011, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, H.R.; Chae, H.J. The effects of 3, 4 or 5 amino salicylic acids on manganese-induced neuronal death: ER stress and mitochondrial complexes. Toxicology 2011, 25, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahar, E.; Lee, G.H.; Bhattarai, K.R.; Lee, H.Y.; Choi, M.K.; Rashid, H.O.; Kim, J.Y.; Chae, H.J.; Yoon, H. Polyphenolic extract of euphorbia supina attenuates manganese-induced neurotoxicity by enhancing antioxidant activity through regulation of ER stress and ER stress-mediated apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Duynhoven, J.; Vaughan, E.E.; Jacobs, D.M.; Kemperman, R.A.; van Velzen, E.J.; Gross, G.; Roger, L.C.; Possemiers, S.; Smilde, A.K.; Dore, J.; et al. Metabolic fate of polyphenols in the human superorganism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4531–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.A.; Zhang, S.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, J. Quercetin induces human colon cancer cells apoptosis by inhibiting the nuclear factor-κB Pathway. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2015, 11, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erlund, I. Review of the flavonoids quercetin, hesperetin, and naringenin. Dietary sources, bioactivities, bioavailability, and epidemiology. Nutr. Res. 2004, 24, 851–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comalada, M.; Camuesco, D.; Sierra, S.; Ballester, I.; Xaus, J.; Galvez, J.; Zarzuelo, A. In vivo quercitrin anti-inflammatory effect involves release of quercetin, which inhibits inflammation through down-regulation of the NF-κB pathway. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Zheng, Y.L.; Luo, L.; Wu, D.M.; Sun, D.X.; Feng, Y.J. Quercetin reverses d-galactose induced neurotoxicity in mouse brain. Behav. Brain Res. 2006, 171, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempuraj, D.; Castellani, M.L.; Petrarca, C.; Frydas, S.; Conti, P.; Theoharides, T.C.; Vecchiet, J. Inhibitory effect of quercetin on tryptase and interleukin-6 release, and histidine decarboxylase mRNA transcription by human mast cell-1 cell line. Clin. Exp. Med. 2006, 6, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Papp, L.V.; Fang, J.; Rodriguez-Nieto, S.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Holmgren, A. Inhibition of mammalian thioredoxin reductase by some flavonoids: Implications for myricetin and quercetin anticancer activity. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 4410–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.S.; Wang, J.L.; Feng, D.Y.; Qin, H.Z.; Wen, H.; Yin, Z.M.; Gao, G.D.; Li, C. Protective effect of quercetin against oxidative stress and brain edema in an experimental rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, H.H.; Woo, J.; Anderson, J.H.; Cannon, D.C.; Handel, S.F.; Hevezi, J.M. Radioiodinated fibrinogen for clot detection in a canine model of cervical carotid thrombosis. J. Nucl. Med. 1978, 19, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.A.; Abdul, H.M.; Joshi, G.; Opii, W.O.; Butterfield, D.A. Protective effect of quercetin in primary neurons against Aβ(1–42): Relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2009, 20, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Chander, V.; Chopra, K. The effect of quercetin, a bioflavonoid on ischemia/reperfusion induced renal injury in rats. Arch. Med. Res. 2004, 35, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinaci, M.K.; Erkasap, N.; Kucuk, A.; Koken, T.; Tosun, M. Effects of quercetin on apoptosis, NF-κB and NOS gene expression in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Exp. Ther. Med. 2012, 3, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.Y.; Chen, Z.; Jasmer, K.J.; Chuang, D.Y.; Gu, Z.; Hannink, M.; Simonyi, A. Quercetin attenuates inflammatory responses in BV-2 microglial cells: Role of MAPKs on the NRF2 pathway and induction of heme oxygenase-1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Moon, S.K.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, G.Y. Quercetin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in BV2 microglial cells by suppressing the NF-κB pathway and activating the NRF2-dependent HO-1 pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 17, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saw, C.L.; Guo, Y.; Yang, A.Y.; Paredes-Gonzalez, X.; Ramirez, C.; Pung, D.; Kong, A.N. The berry constituents quercetin, kaempferol, and pterostilbene synergistically attenuate reactive oxygen species: Involvement of the NRF2-ARE signaling pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 72, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco-Pozo, C.; Mizgier, M.L.; Speisky, H.; Gotteland, M. Differential protective effects of quercetin, resveratrol, rutin and epigallocatechin gallate against mitochondrial dysfunction induced by indomethacin in Caco-2 cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2012, 195, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Li, B.; Zhou, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Xiao, X.; Tang, S. Curcumin attenuates quinocetone induced apoptosis and inflammation via the opposite modulation of NRF2/HO-1 and NF-κB pathway in human hepatocyte L02 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 95, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Tang, S.; Deng, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Velkov, T.; Li, J.; Xiao, X. Lycopene attenuates colistin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice via activation of the NRF2/HO-1 pathway. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Z.M.; Zhang, K.B.; Wang, T.P.; Sribastav, S.S.; Liu, W.S.; Liu, T. Role of death receptor, mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum pathways in different stages of degenerative human lumbar disc. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 990–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahar, E.; Kim, H.; Yoon, H. ER stress-mediated signaling: Action potential and Ca2+ as key players. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterfield, T.A.; Best, T.M.; Merrick, M.A. The dual roles of neutrophils and macrophages in inflammation: A critical balance between tissue damage and repair. J. Athl. Train. 2006, 41, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Li, X.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, P.; Fu, J.; Yao, B.; Zhou, Z. ER stress and ER stress-mediated apoptosis are involved in manganese-induced neurotoxicity in the rat striatum in vivo. Neurotoxicology 2015, 48, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertug, P.U.; Aydinoglu, F.; Goruroglu Ozturk, O.; Singirik, E.; Ogulener, N. Comparative study of the quercetin, ascorbic acid, glutathione and superoxide dismutase for nitric oxide protecting effects in mouse gastric fundus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 698, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanti Bhooshan Pandey, S.I.R. Protection of protein carbonyl formation by quercetin in erythrocytes subjected to oxidative stress. Med. Chem. Res. 2010, 10, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, S.M.; Rothwell, N.J.; Gibson, R.M. The role of inflammation in CNS injury and disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, P.F.; Pillinger, M.H.; Attur, M.; Marjanovic, N.; Dave, M.; Park, J.; Bingham, C.O.; Al-Mussawir, H.; Abramson, S.B. Resolution of inflammation: Prostaglandin E2 dissociates nuclear trafficking of individual NF-κB subunits (p65, p50) in stimulated rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 6924–6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strayhorn, W.D.; Wadzinski, B.E. A novel in vitro assay for deubiquitination of IκBα. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2002, 400, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barcelos, R.P.; Bresciani, G.; Rodriguez-Miguelez, P.; Cuevas, M.J.; Soares, F.A.; Barbosa, N.V.; Gonzalez-Gallego, J. Diclofenac pretreatment effects on the toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor κB-mediated inflammatory response to eccentric exercise in rat liver. Life Sci. 2016, 148, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoja, C.; Benigni, A.; Remuzzi, G. The Nrf2 pathway in the progression of renal disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rourke, B.; Cortassa, S.; Aon, M.A. Mitochondrial ion channels: Gatekeepers of life and death. Physiology 2005, 20, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debatin, K.M.; Poncet, D.; Kroemer, G. Chemotherapy: Targeting the mitochondrial cell death pathway. Oncogene 2002, 21, 8786–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazebnik, Y.A.; Kaufmann, S.H.; Desnoyers, S.; Poirier, G.G.; Earnshaw, W.C. Cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase by a proteinase with properties like ICE. Nature 1994, 371, 346–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, T.; Popescu, B.O.; Cedazo-Minguez, A. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease: Why did antioxidant therapy fail? Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 427318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amos-Kroohs, R.M.; Bloor, C.P.; Qureshi, M.A.; Vorhees, C.V.; Williams, M.T. Effects of developmental exposure to manganese and/or low iron diet: Changes to metal transporters, sucrose preference, elevated zero-maze, open-field, and locomotion in response to fenfluramine, amphetamine, and MK-801. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, L.L.; Li, G.J.; Guo, W.; Liang, W.; Zheng, W. Alteration of serum concentrations of manganese, iron, ferritin, and transferrin receptor following exposure to welding fumes among career welders. Neurotoxicology 2005, 26, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokozawa, T.; Kim, Y.A.; Kim, H.Y.; Okamoto, T.; Sei, Y. Protective effect of the Chinese prescription Kangen-karyu against high glucose-induced oxidative stress in LLC-PK1 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 109, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]













© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bahar, E.; Kim, J.-Y.; Yoon, H. Quercetin Attenuates Manganese-Induced Neuroinflammation by Alleviating Oxidative Stress through Regulation of Apoptosis, iNOS/NF-κB and HO-1/Nrf2 Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091989
Bahar E, Kim J-Y, Yoon H. Quercetin Attenuates Manganese-Induced Neuroinflammation by Alleviating Oxidative Stress through Regulation of Apoptosis, iNOS/NF-κB and HO-1/Nrf2 Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(9):1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091989
Chicago/Turabian StyleBahar, Entaz, Ji-Ye Kim, and Hyonok Yoon. 2017. "Quercetin Attenuates Manganese-Induced Neuroinflammation by Alleviating Oxidative Stress through Regulation of Apoptosis, iNOS/NF-κB and HO-1/Nrf2 Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 9: 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091989
APA StyleBahar, E., Kim, J. -Y., & Yoon, H. (2017). Quercetin Attenuates Manganese-Induced Neuroinflammation by Alleviating Oxidative Stress through Regulation of Apoptosis, iNOS/NF-κB and HO-1/Nrf2 Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(9), 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091989