Effects of Metal Ions, Temperature, and a Denaturant on the Oxidative Folding Pathways of Bovine α-Lactalbumin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
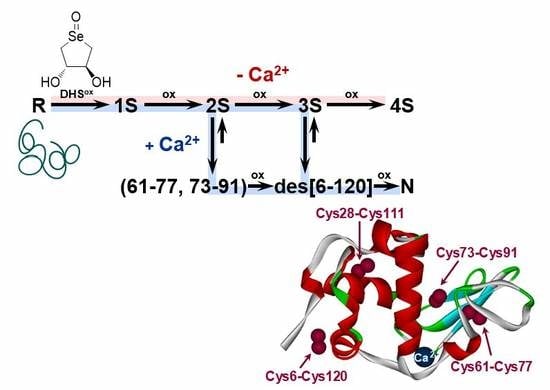
2.1. Stoichiometric Oxidation of R Using DHSox
2.2. SS Rearrangement of the Folding Intermediates
2.3. Effects of Metal Ions
2.4. Identification of I-1 and I-2
2.5. Structural Stability of N, I-1, and I-2
2.6. Effects of Temperature and a Denaturant
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Reduced αLA (R)
4.3. Oxidative Regeneration of Native αLA (N)
4.4. HPLC Analysis
4.5. ESI-MS Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AEMTS | 2-Aminoethyl methanethiosulfonate |
| αLA | Bovine α-lactalbumin |
| BPTI | Bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor |
| Cys | Cysteine |
| DHSox | trans-3,4-Dihydroxyselenolane oxide |
| DTTox | trans-4,5-Dihydroxy-1,2-dithiane |
| DTTred | Dithiothreitol |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| ESI-MS | Electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry |
| GdmCl | Guanidinium chloride |
| GSH | Reduced glutathione |
| GSSG | Oxidized glutathione |
| HEL | Hen egg white lysozyme |
| I-1 | A folding intermediate of αLA having three native SS bonds but lacking one native SS bond between Cys6-Cys120 |
| I-2 | A folding intermediate of αLA having two native SS bonds between Cys61-Cys77 and Cys73-Cys91 |
| N | Native form |
| R | Fully reduced form |
| RNase A | Bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A |
| RP-HPLC | Reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography |
| SH | Thiol |
| SS | Disulfide |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic acid |
| Tris | Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane hydrochloride |
References
- Creighton, T.E. Protein folding coupled to disulphide bond formation. Biol. Chem. 1997, 378, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Narayan, M.; Welker, E.; Wedemeyer, W.J.; Scheraga, H.A. Oxidative folding of proteins. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gething, M.-J.; Sambrook, J.F. Protein folding in the cell. Nature 1992, 355, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, H.F. Protein disulfide isomerase and assisted protein folding. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 29399–29402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, H.F. Protein, disulfide isomerase. Methods Enzymol. 1998, 290, 26–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Creighton, T.E.; Goldenberg, D.P. Kinetic role of a meta-stable native-like two-disulphide species in the folding transition of bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. J. Mol. Biol. 1984, 179, 497–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arolas, J.L.; Aviles, F.X.; Chang, J.; Ventura, S. Folding of small disulfide-rich proteins: clarifying the puzzle. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006, 31, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narayan, M. Disulfide bonds: Protein folding and subcellular protein trafficking. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 2272–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J. Diverse pathways of oxidative folding of disulfide proteins: Underlying causes and folding models. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 3414–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatrenet, B.; Chang, J. The bisulfide folding pathway of hirudin elucidated by stop/go folding experiments. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 20988–20996. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thannhauser, T.W.; Rothwarf, D.M.; Scheraga, H.A. Kinetic studies of the regeneration of recombinant hirudin variant 1 with oxidized and reduced dithiothreitol. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 2154–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissman, J.S.; Kim, P.S. Reexamination of the folding of BPTI: Predominance of native intermediates. Science 1991, 253, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwarf, D.M.; Scheraga, H.A. Regeneration of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A. 1. Steady-state distribution. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 2671–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwarf, D.M.; Scheraga, H.A. Regeneration of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A. 2. Kinetics of regeneration. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 2680–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Berg, B.V.D.; Chung, E.W.; Robinson, C.V.; Mateo, P.L.; Dobson, C.M. The oxidative refolding of hen lysozyme and its catalysis by protein disulfide isomerase. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 4794–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Berg, B.; Chung, E.W.; Robinson, C.V.; Dobson, C.M. Characterisation of the dominant oxidative folding intermediate of hen lysozyme. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 290, 781–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surguchev, A.; Surguchov, A. Conformational diseases: Looking into the eyes. Brain Res. Bull. 2010, 81, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanaman, T.C.; Brew, K.; Hill, R.L. The disulfide bonds of bovine α-lactalbumin. J. Biol. Chem. 1970, 245, 4583–4590. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuwajima, K. A folding model of α-lactalbumin deduced from the three-state denaturation mechanism. J. Mol. Biol. 1977, 114, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeguchi, M.; Sugai, S. Contribution of disulfide bonds to stability of the folding intermediate of α-lactalbumin. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 1989, 33, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewbank, J.J.; Creighton, T.E. Structural characterization of the disulfide folding intermediates of bovine α-lactalbumin. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 3694–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewbank, J.J.; Creighton, T.E. Pathway of disulfide-coupled unfolding and refolding of bovine α-lactalbumin. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 3677–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ptitsyn, O.B. Molten globule and protein folding. Adv. Protein Chem. 1995, 47, 83–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.C.; Peng, Z.; Kim, P.S. Bipartite structure of the α-lactalbumin molten globule. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 1995, 2, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwajima, K. The molten globule state of α-lactalbumin. FASEB J. 1996, 10, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.C.; Kim, P.S. A specific hydrophobic core in the α-lactalbumin molten globule. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 280, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redfield, C.; Schulman, B.A.; Milhollen, M.A.; Kim, P.S.; Dobson, C.M. α-lactalbumin forms a compact molten globule in the absence of disulfide bonds. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1999, 6, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassem, J.M. Future challenges of whey proteins. Int. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 10, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Makabe, K.; Tomoyori, K.; Maki, K.; Mukaiyama, A.; Kuwajima, K. Different folding pathways taken by highly homologous proteins, goat α-lactalbumin and canine milk lysozyme. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 396, 1361–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwajima, K. The molten globule state as a clue for understanding the folding and cooperativity of globular-protein structure. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 1989, 6, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, M.K.; Mossberg, A.-K.; Pettersson, J.; Linse, S.; Svanborg, C. Lipids as cofactors in protein folding: Stereo-specific lipid-protein interactions are required to form HAMLET (human α-lactalbumin made lethal to tumor cells). Protein Sci. 2003, 12, 2805–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwajima, K.; Nakamura, T. Antitumor Complexes Formed by Oleic Acid and Molten Globule Intermediates of Proteins. In Molecular Science of Fluctuations Toward Biological Functions; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; pp. 245–270. ISBN 978-443155840-8. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, K.R.; Brew, K. Calcium regulates folding and disulfide-bond formation in α-lactalbumin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989, 163, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J. The folding pathway of α-lactalbumin elucidated by the technique of disulfide scrambling. Isolation of on-pathway and off-pathway intermediates. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Li, L. Pathway of oxidative folding of α-lactalbumin: A model for illustrating the diversity of disulfide folding pathways. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 8405–8413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J. Evidence for the underlying cause of diversity of the disulfide folding pathway. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 4522–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomoyori, K.; Nakamura, T.; Makabe, K.; Maki, K.; Saeki, K.; Kuwajima, K. Sequential four-state folding/unfolding of goat α-lactalbumin and its N-terminal variants. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2012, 80, 2191–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, K.; Noguchi, M.; Singh, B.G.; Priyadarsini, K.I.; Fujio, K.; Kubo, Y.; Takayama, K.; Ando, S.; Iwaoka, M. A water-soluble selenoxide reagent as a useful probe for the reactivity and folding of polythiol peptides. FEBS Open Bio 2013, 3, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, K.; Dedachi, K.; Iwaoka, M. Rapid and quantitative disulfide bond formation for a polypeptide chain using a cyclic selenoxide reagent in an aqueous medium. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, K.; Kumakura, F.; Iwaoka, M. Characterization of kinetic and thermodynamic phases in the prefolding process of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A coupled with fast SS formation and SS reshuffling. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 10535–10542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, K.; Kumakura, F.; Iwaoka, M. Kinetic and thermodynamic analysis of the conformational folding process of SS-reduced bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A using a selenoxide reagent with high oxidizing ability. FEBS Open Bio 2012, 2, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, K.; Shibagaki, W.; Shinozaki, R.; Iwaoka, M. Reinvestigation of the oxidative folding pathways of hen egg white lysozyme: Switching of the major pathways by temperature control. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 13194–13212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brew, K.; Castellino, F.J.; Vanaman, T.C.; Hill, R.L. The complete amino acid sequence of bovine α-lactalbumin. J. Biol. Chem. 1970, 245, 4570–4582. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Permyakov, E.A.; Morozova, L.A.; Burstein, E.A. Cation binding effects on the pH, thermal and urea denaturation transitions in α-lactalbumin. Biophys. Chem. 1985, 21, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Stuart, D.I.; Acharya, K.R. α-lactalbumin possesses a distinct zinc binding site. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 19292–19298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Permyakov, E.A.; Berliner, L.J. α-Lactalbumin: Structure and function. FEBS Lett. 2000, 473, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwajima, K.; Ikeguchi, M.; Sugawara, T.; Hiraoka, Y.; Sugai, S. Kinetics of disulfide bond reduction in α-lactalbumin by dithiothreitol and molecular basis of superreactivity of the cys6-cys120 disulfide bond. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 8240–8249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohda, S.; Shimizu, A.; Ikeguchi, M.; Sugai, S. The superreactive disulfide bonds in α-lactalbumin and lysozyme. J. Protein Chem. 1995, 14, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J. Conformational isomers of denatured and unfolded proteins: Methods of production and applications. Protein J. 2009, 28, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewney, S.; Smith, L.J. Characterization of an alternative low energy fold for bovine α-lactalbumin formed by disulfide bond shuffling. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2012, 80, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.C.; Schulman, B.A.; Peng, Z.; Kim, P.S. Disulfide determinants of calcium-induced packing in α-lactalbumin. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrix, T.M.; Griko, Y.; Privalov, P. Energetics of structural domains in α-lactalbumin. Protein Sci. 1996, 5, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhlman, B.; Boice, J.A.; Wu, W.J.; Fairman, R.; Raleigh, D.P. Calcium binding peptides from α-lactalbumin: Implications for protein folding and stability. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 4607–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwaoka, M.; Takahashi, T.; Tomoda, S. Syntheses and structural characterization of water-soluble selenium reagents for the redox control of protein disulfide bonds. Heteroat. Chem. 2001, 12, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruice, T.W.; Kenyon, G.L. Novel alkyl alkanethiolsulfonate sulfhydryl reagents. Modification of derivatives of l-cysteine. J. Protein Chem. 1982, 1, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shinozaki, R.; Iwaoka, M. Effects of Metal Ions, Temperature, and a Denaturant on the Oxidative Folding Pathways of Bovine α-Lactalbumin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091996
Shinozaki R, Iwaoka M. Effects of Metal Ions, Temperature, and a Denaturant on the Oxidative Folding Pathways of Bovine α-Lactalbumin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(9):1996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091996
Chicago/Turabian StyleShinozaki, Reina, and Michio Iwaoka. 2017. "Effects of Metal Ions, Temperature, and a Denaturant on the Oxidative Folding Pathways of Bovine α-Lactalbumin" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 9: 1996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091996
APA StyleShinozaki, R., & Iwaoka, M. (2017). Effects of Metal Ions, Temperature, and a Denaturant on the Oxidative Folding Pathways of Bovine α-Lactalbumin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(9), 1996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091996