Insights into the Impact of Linker Flexibility and Fragment Ionization on the Design of CK2 Allosteric Inhibitors: Comparative Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies
Abstract
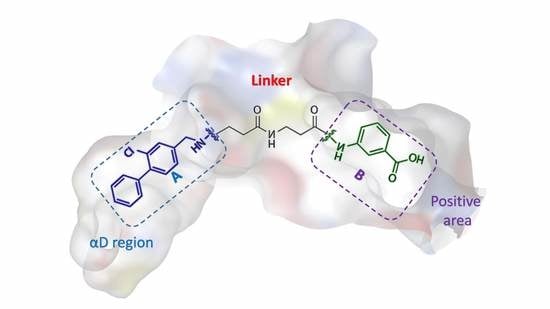
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies
2.1.1. Overall Features of Dynamic Behaviors
2.1.2. Comparative Analysis of Different Binding Modes of Three Compounds
2.2. Energy Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. System Setup and Parameters Preparation
4.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
4.3. MM/PBSA Calculations
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roskoski, R. Classification of small molecule protein kinase inhibitors based upon the structures of their drug-enzyme complexes. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 103, 26–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R. A historical overview of protein kinases and their targeted small molecule inhibitors. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 100, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaeger, S.; Gohlke, B.; Perrin, J.; Gupta, V.; Heinzlmeir, S.; Helm, D.; Qiao, H.; Bergamini, G.; Handa, H.; Savitski, M.M.; et al. Chemical Proteomics Reveals Ferrochelatase as a Common Off-target of Kinase Inhibitors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnieders, M.J.; Kaoud, T.S.; Yan, C.; Dalby, K.N.; Ren, P. Computational insights for the discovery of non-ATP competitive inhibitors of MAP kinases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Nielsen, T.E.; Clausen, M.H. FDA-approved small-molecule kinase inhibitors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 422–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ortega, C.E.; Seidner, Y.; Dominguez, I. Mining CK2 in cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filhol, O.; Giacosa, S.; Wallez, Y.; Cochet, C. Protein kinase CK2 in breast cancer: The CK2beta regulatory subunit takes center stage in epithelial plasticity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 3305–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, B.; Issinger, O.G. Protein kinase CK2 in human diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 1870–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozza, G.; Bortolato, A.; Moro, S. How druggable is protein kinase CK2? Med. Res. Rev. 2010, 30, 419–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozza, G.; Pinna, L.A.; Moro, S. Kinase CK2 Inhibition: An Update. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 671–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battistutta, R. Protein kinase CK2 in health and disease: Structural bases of protein kinase CK2 inhibition. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 1868–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarno, S.; Papinutto, E.; Franchin, C.; Bain, J.; Elliott, M.; Meggio, F.; Kazimierczuk, Z.; Orzeszko, A.; Zanotti, G.; Battistutta, R.; et al. ATP Site-Directed Inhibitors of Protein Kinase CK2: An Update. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Luan, Y.; Qi, X.M.; Li, M.; Gong, L.K.; Xue, X.A.; Wu, X.F.; Wu, Y.F.; Chen, M.; Xing, G.Z.; et al. Emodin Triggers DNA Double-Strand Breaks by Stabilizing Topoisomerase II-DNA Cleavage Complexes and by Inhibiting ATP Hydrolysis of Topoisomerase II. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 118, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, M.A.; Bain, J.; Kazimierczuk, Z.; Sarno, S.; Ruzzene, M.; Di Maira, G.; Elliott, M.; Orzeszko, A.; Cozza, G.; Meggio, F.; et al. The selectivity of inhibitors of protein kinase CK2: An update. Biochem. J. 2008, 415, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raaf, J.; Brunstein, E.; Issinger, O.G.; Niefind, K. The CK2 alpha/CK2 beta interface of human protein kinase CK2 harbors a binding pocket for small molecules. Chem. Biol. 2008, 15, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudet, B.; Moucadel, V.; Prudent, R.; Filhol, O.; Wong, Y.S.; Royer, D.; Cochet, C. Identification of chemical inhibitors of protein-kinase CK2 subunit interaction. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 316, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.M.; Dong, J.K.; Song, K.; Wang, T.D.; Huang, W.K.; Zhang, J.M.; Yang, X.Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, J. A novel allosteric site in casein kinase 2alpha discovered using combining bioinformatics and biochemistry methods. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brear, P.; De Fusco, C.; Hadje Georgiou, K.; Francis-Newton, N.J.; Stubbs, C.J.; Sore, H.F.; Venkitaraman, A.R.; Abell, C.; Spring, D.R.; Hyvonen, M. Specific inhibition of CK2alpha from an anchor outside the active site. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 6839–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papinutto, E.; Ranchio, A.; Lolli, G.; Pinna, L.A.; Battistutta, R. Structural and functional analysis of the flexible regions of the catalytic alpha-subunit of protein kinase CK2. J. Struct. Biol. 2012, 177, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Fusco, C.; Brear, P.; Iegre, J.; Georgiou, K.H.; Sore, H.F.; Hyvonen, M.; Spring, D.R. A fragment-based approach leading to the discovery of a novel binding site and the selective CK2 inhibitor CAM4066. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 3471–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, N.; Zhong, R. Structural basis for low-affinity binding of non-R2 carboxylate-substituted tricyclic quinoline analogs to CK2alpha: Comparative molecular dynamics simulation studies. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2015, 85, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhong, R.G. Exploring the crucial structural elements required for tricyclic quinoline analogs as protein kinase CK2 inhibitors by a combined computational analysis. Med. Chem. Res. 2013, 22, 4410–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhong, R.G. Structural basis for decreased affinity of Emodin binding to Val66-mutated human CK2 alpha as determined by molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Model. 2010, 16, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keseru, G.M.; Hann, M.M. What is the future for fragment-based drug discovery? Future Med. Chem. 2017, 9, 1457–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Moon, Y.; Hong, S. Identification of lead small molecule inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta using a fragment-linking strategy. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5669–5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, M.; Radeva, N.; Fanlo-Virgos, H.; Otto, S.; Klebe, G.; Hirsch, A.K. Fragment Linking and Optimization of Inhibitors of the Aspartic Protease Endothiapepsin: Fragment-Based Drug Design Facilitated by Dynamic Combinatorial Chemistry. Angew. Chem. 2016, 55, 9422–9426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zhao, H. Enriching screening libraries with bioactive fragment space. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 3594–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CERTARA. Available online: https://www.certara.com/ (accessed on 19 May 2017).
- Clark, M.; Cramer, R.D.; Vanopdenbosch, N. Validation of the General-Purpose Tripos 5.2 Force-Field. J. Comput. Chem. 1989, 10, 982–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, T.; Kollman, P.A. Application of the RESP methodology in the parametrization of organic solvents. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 8070–8079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besler, B.H.; Merz, K.M.; Kollman, P.A. Atomic Charges Derived from Semiempirical Methods. J. Comput. Chem. 1990, 11, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaussian.com. Available online: http://gaussian.com/ (accessed on 19 May 2017).
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of Simple Potential Functions for Simulating Liquid Water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Wang, H.; Ding, K.; Wang, J.; Pan, L.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, C. Interactions of benzotriazole UV stabilizers with human serum albumin: Atomic insights revealed by biosensors, spectroscopies and molecular dynamics simulations. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, D.A.; Cheatham, T.E., III; Darden, T.; Gohlke, H.; Luo, R.; Merz, K.M., Jr.; Onufriev, A.; Simmerling, C.; Wang, B.; Woods, R.J. The Amber biomolecular simulation programs. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1668–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Wu, C.; Chowdhury, S.; Lee, M.C.; Xiong, G.; Zhang, W.; Yang, R.; Cieplak, P.; Luo, R.; Lee, T.; et al. A point-charge force field for molecular mechanics simulations of proteins based on condensed-phase quantum mechanical calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 2003, 24, 1999–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, H.J.; Postma, J.V.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; DiNola, A.R.; Haak, J.R. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckaert, J.-P.; Ciccotti, G.; Berendsen, H.J.C. Numerical integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints:molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J. Comput. Phys. 1977, 23, 321–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N⋅log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollman, P.A.; Massova, I.; Reyes, C.; Kuhn, B.; Huo, S.; Chong, L.; Lee, M.; Lee, T.; Duan, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Calculating structures and free energies of complex molecules: Combining molecular mechanics and continuum models. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irina Massova, P.A.K. Combined molecular mechanical and continuum solvent approach (MM-PBSA/GBSA) to predict ligand binding. Perspect. Drug Discov. Des. 2000, 18, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitkoff, D.; Sharp, K.A.; Honig, B. Accurate Calculation of Hydration Free Energies Using Macroscopic Solvent Models. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 1978–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Kollman, P.A. Computational study of protein specificity: The molecular basis of HIV-1 protease drug resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 14937–14942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Morin, P.; Wang, W.; Kollman, P.A. Use of MM-PBSA in reproducing the binding free energies to HIV-1 RT of TIBO derivatives and predicting the binding mode to HIV-1 RT of efavirenz by docking and MM-PBSA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 5221–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Energy Term (kcal/mol) | CAM4066 | Compound 21 | Pre-CAM4066 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ΔEele | −110.41 ± 2.83 | −53.42 ± 3.87 | −11.17 ± 4.26 |
| ΔEvdw | −75.00 ± 3.16 | −65.18 ± 3.64 | −68.35 ± 4.09 |
| ΔEgas a | −185.41 ± 5.23 | −118.60 ± 3.64 | −79.52 ± 4.52 |
| ΔGnonpolar | −8.56 ± 0.13 | −8.29 ± 0.19 | −8.89 ± 0.18 |
| ΔGpolar | 139.29 ± 4.18 | 75.46 ± 4.42 | 40.24 ± 2.94 |
| ΔGsol b | 130.72 ± 3.15 | 67.16 ± 3.36 | 31.35 ± 2.96 |
| ΔGele c | 28.88 ± 5.32 | 22.04 ± 3.15 | 29.07 ± 3.98 |
| ΔGbinding d | −54.68 ± 4.87 | −51.43 ± 4.42 | −48.17 ± 3.33 |
| ΔΔGbinding | 0 | 3.25 | 6.51 |
| Compound | Fragment A | Linker | Fragment B | IC50 (μM) | Kd | PDB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAM4066 |  |  |  | 0.370 | 0.320 | 5CU4 |
| Pre-CAM4066 |  |  |  | n/a | n/a | n/d |
| 21 |  |  |  | n/a | 1.64 | 5MO8 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Zhang, N.; Qi, X.; Tang, S.; Sun, G.; Zhao, L.; Zhong, R.; Peng, Y. Insights into the Impact of Linker Flexibility and Fragment Ionization on the Design of CK2 Allosteric Inhibitors: Comparative Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010111
Zhou Y, Zhang N, Qi X, Tang S, Sun G, Zhao L, Zhong R, Peng Y. Insights into the Impact of Linker Flexibility and Fragment Ionization on the Design of CK2 Allosteric Inhibitors: Comparative Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(1):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010111
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yue, Na Zhang, Xiaoqian Qi, Shan Tang, Guohui Sun, Lijiao Zhao, Rugang Zhong, and Yongzhen Peng. 2018. "Insights into the Impact of Linker Flexibility and Fragment Ionization on the Design of CK2 Allosteric Inhibitors: Comparative Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 1: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010111
APA StyleZhou, Y., Zhang, N., Qi, X., Tang, S., Sun, G., Zhao, L., Zhong, R., & Peng, Y. (2018). Insights into the Impact of Linker Flexibility and Fragment Ionization on the Design of CK2 Allosteric Inhibitors: Comparative Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(1), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010111