Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 on Oxidative Stress and Nrf2 Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Oxidative Stress and Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 (Nrf2) Signaling
3. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1)
3.1. Synthesis and Metabolism
3.2. Pancreatic Effects
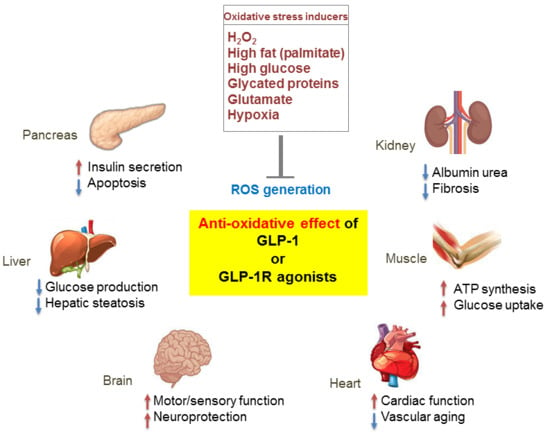
3.3. Extrapancreatic Effects
4. Antioxidant Effect of GLP-1 in Diabetes
4.1. In Vitro Studies
4.2. In Vivo Studies
4.3. Clinical Studies
5. Antioxidant Effect of GLP-1 in Diabetic Complications
6. Antioxidant Effect of GLP-1 in Neurological Diseases
7. Antioxidant Effect of GLP-1 in Senescence
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dandona, P.; Thusu, K.; Cook, S.; Snyder, B.; Makowski, J.; Armstrong, D.; Nicotera, T. Oxidative damageto DNA in diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1996, 347, 444–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soysal, P.; Isik, A.T.; Carvalho, A.F.; Fernandes, B.S.; Solmi, M.; Schofield, P.; Veronese, N.; Stubbs, B. Oxidative stressand frailty: A systematic review and synthesis of the best evidence. Maturitas 2017, 99, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are they linked? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, D.M.; Coombes, J.S.; Bennett, N.; Johnson, D.W.; Gobe, G.C. Oxidative stress, anti-oxidant therapies and chronic kidney disease. Nephrology 2012, 17, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tebay, L.E.; Robertson, H.; Durant, S.T.; Vitale, S.R.; Penning, T.M.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Hayes, J.D. Mechanisms of activation of the transcription factor Nrf2 by redox stressors, nutrient cues, and energy status and the pathways through which it attenuates degenerative disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 108–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niture, S.K.; Khatri, R.; Jaiswal, A.K. Regulation of Nrf2-an update. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 66, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Palacios, A.; Konigsberg, M.; Zazueta, C. Nrf2 signaling and redox homeostasis in the aging heart: A potential target to prevent cardiovascular diseases? Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 26, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kensler, T.W.; Wakabayashi, N.; Biswal, S. Cell survivalresponses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 47, 89–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howden, R. Nrf2 and cardiovascular defense. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 104308–104318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hybertson, B.M.; Gao, B. Role of the Nrf2 signaling system in health and disease. Clin. Genet. 2014, 86, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cominacini, L.; Mozzini, C.; Garbin, U.; Pasini, A.; Stranieri, C.; Solani, E.; Vallerio, P.; Tinelli, I.A.; Fratta Pasini, A. Endoplasmic reticulumstress and Nrf2 signaling in cardiovascular diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friling, R.S.; Bensimon, A.; Tichauer, Y.; Daniel, V. Xenobiotic-inducible expression of murine glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene is controlled by an electrophile-responsive element. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 6258–6262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jaiswal, A.K. Regulation of human NAD (P) H: Quinone oxidoreductase gene. Role of AP1 binding site contained within human antioxidant response element. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 15097–15104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orskov, C.; Rabenhoj, L.; Wettergren, A.; Kofod, H.; Holst, J.J. Tissue and plasma concentrations of amidated and glycine-extended glucagon-like peptide 1 in humans. Diabetes 1994, 43, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjems, L.L.; Holst, J.J.; Volund, A.; Madsbad, S. The influence of GLP-1 on glucose-stimulated insulin secretion: Effects on beta-cell sensitivity in type 2 and nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes 2003, 52, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Jun, H.S. Anti-diabetic actions of glucagon-like peptide-1 on pancreatic beta-cells. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2014, 63, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaca, M.; Magnan, C.; Kargar, C. Functional pancreaticbeta-cell mass: Involvement in type 2 diabetes and therapeutic intervention. Diabetes Metab. 2009, 35, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.J. The biology of incretin hormones. Cell. Metab. 2006, 3, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, A.J. Long-acting glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: A review of their efficacy and tolerability. Diabetes Care 2011, 34 (Suppl. 2), S279–S284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, A.J.; Lamarche, B.; Deacon, C.F.; Weisnagel, S.J.; Couture, P. Effects of sitagliptin therapy on markers of low-grade inflammation and cell adhesion molecules in patients with type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 2014, 63, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, M.; Mita, T.; Azuma, K.; Ebato, C.; Goto, H.; Nomiyama, T.; Fujitani, Y.; Hirose, T.; Kawamori, R.; Watada, H. Inhibition of monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells and attenuation of atherosclerotic lesion by a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, exendin-4. Diabetes 2010, 59, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, H.; Morii, T.; Fujishima, H.; Sato, T.; Shimizu, T.; Hosoba, M.; Tsukiyama, K.; Narita, T.; Takahashi, T.; Drucker, D.J.; et al. The protectiveroles of GLP-1R signaling in diabetic nephropathy: Possible mechanism and therapeutic potential. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romani-Perez, M.; Outeirino-Iglesias, V.; Gil-Lozano, M.; Gonzalez-Matias, L.C.; Mallo, F.; Vigo, E. Pulmonary GLP-1 receptor increases at birth and exogenous GLP-1 receptor agonists augmented surfactant-protein levels in litters from normal and nitrofen-treated pregnant rats. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, T.; Ito, S.; Tanimitsu, K.; Udagawa, S.; Oka, J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 inhibits LPS-induced IL-1beta production in cultured rat astrocytes. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 55, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H. Strategies of antioxidant defense. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 215, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmstrom, K.M.; Finkel, T. Cellular mechanisms and physiological consequences of redox-dependent signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 15, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valko, M.; Rhodes, C.J.; Moncol, J.; Izakovic, M.; Mazur, M. Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2006, 160, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marnett, L.J. Lipid peroxidation-DNA damage by malondialdehyde. Mutat. Res. 1999, 424, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siems, W.G.; Grune, T.; Esterbauer, H. 4-Hydroxynonenal formation during ischemia and reperfusion of rat small intestine. Life Sci. 1995, 57, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtman, E.R. Role of oxidant species in aging. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Del-Rio, M.; Velez-Pardo, C. The bad, the good, and the ugly about oxidative stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 163913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squier, T.C. Oxidative stress and protein aggregation during biological aging. Exp. Gerontol. 2001, 36, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, H. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and aging. J. Signal. Transduct. 2012, 2012, 646354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sa Junior, P.L.; Camara, D.A.D.; Porcacchia, A.S.; Fonseca, P.M.M.; Jorge, S.D.; Araldi, R.P.; Ferreira, A.K. The Roles of ROS in Cancer Heterogeneity and Therapy. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 2467940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, J.A.; Rifkin, W.J.; Rabbani, P.S.; Ceradini, D.J. The Nrf2/Keap1/ARE Pathway and Oxidative Stress as a Therapeutic Target in Type II Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 4826724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenner, P. Oxidative stressin Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 53 (Suppl. 3), S26–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayre, L.M.; Smith, M.A.; Perry, G. Chemistry and biochemistry of oxidative stress in neurodegenerative disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2001, 8, 721–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhalla, N.S.; Temsah, R.M.; Netticadan, T. Role of oxidative stress in cardiovascular diseases. J. Hypertens. 2000, 18, 655–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukreja, R.C.; Hess, M.L. The oxygenfree radical system: From equations through membrane-protein interactions to cardiovascular injury and protection. Cardiovasc. Res. 1992, 26, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dut, R.; Dizdar, E.A.; Birben, E.; Sackesen, C.; Soyer, O.U.; Besler, T.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative stress and its determinants in the airways of children with asthma. Allergy 2008, 63, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ercan, H.; Birben, E.; Dizdar, E.A.; Keskin, O.; Karaaslan, C.; Soyer, O.U.; Dut, R.; Sackesen, C.; Besler, T.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative stress and genetic and epidemiologic determinants of oxidant injury in childhood asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; He, T.; Farrar, S.; Ji, L.; Liu, T.; Ma, X. Antioxidants MaintainCellular Redox Homeostasis by Elimination of Reactive Oxygen Species. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 532–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.C.; Nguyen, T.; Pickett, C.B. Phosphorylation of Nrf2 at Ser-40 by protein kinase C regulates antioxidant response element-mediated transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 42769–42774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, S.P. The antioxidantresponse element and oxidative stress modifiers in airway diseases. Curr. Mol. Med. 2008, 8, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, J.D.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. The Nrf2 regulatory network provides an interface between redox and intermediary metabolism. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, S.C.; Hannink, M. PGAM5 tethers a ternary complex containing Keap1 and Nrf2 to mitochondria. Exp. Cell. Res. 2008, 314, 1789–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piantadosi, C.A.; Carraway, M.S.; Babiker, A.; Suliman, H.B. Heme oxygenase-1 regulates cardiac mitochondrial biogenesis via Nrf2-mediated transcriptional control of nuclear respiratory factor-1. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Abramov, A.Y. The emergingrole of Nrf2 in mitochondrial function. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Lamark, T.; Sjottem, E.; Larsen, K.B.; Awuh, J.A.; Overvatn, A.; McMahon, M.; Hayes, J.D.; Johansen, T. p62/SQSTM1 is a target gene for transcription factor NRF2 and creates a positive feedback loop by inducing antioxidant response element-driven gene transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 22576–22591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; He, X. Molecular basis of electrophilic and oxidative defense: Promises and perils of Nrf2. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 1055–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Surh, Y.J. Nrf2 as a novel molecular target for chemoprevention. Cancer Lett. 2005, 224, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigelius-Flohe, R.; Flohe, L. Basic principles and emerging concepts in the redox control of transcription factors. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2011, 15, 2335–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.M.; Fujita, Y.; Kieffer, T.J. Glucagon-like peptide-1: Glucose homeostasis and beyond. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2014, 76, 535–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.J.; Asa, S. Glucagon geneexpression in vertebrate brain. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 13475–13478. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scopsi, L.; Gullo, M.; Rilke, F.; Martin, S.; Steiner, D.F. Proprotein convertases (PC1/PC3 and PC2) in normal and neoplastic human tissues: Their use as markers of neuroendocrine differentiation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 80, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zheng, J.; Wang, S.; Lau, H.K.; Fathi, A.; Wang, Q. Cardiovascular Benefits of Native GLP-1 and its Metabolites: An Indicator for GLP-1-Therapy Strategies. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmi, V.; Sbraccia, P. GLP-1 receptor independent pathways: Emerging beneficial effects of GLP-1 breakdown products. Eat. Weight Disord. 2017, 22, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieffer, T.J.; Habener, J.F. The glucagon-like peptides. Endocr. Rev. 1999, 20, 876–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Rooij, J.; Rehmann, H.; van Triest, M.; Cool, R.H.; Wittinghofer, A.; Bos, J.L. Mechanism of regulation of the Epac family of cAMP-dependent RapGEFs. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 20829–20836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Egan, J.M.; Raygada, M.; Nadiv, O.; Roth, J.; Montrose-Rafizadeh, C. Glucagon-like peptide-1 affects gene transcription and messenger ribonucleic acid stability of components of the insulin secretory system in RIN 1046-38 cells. Endocrinology 1995, 136, 4910–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Iezzi, M.; Theander, S.; Antinozzi, P.A.; Gauthier, B.R.; Halban, P.A.; Wollheim, C.B. Suppression of Pdx-1 perturbs proinsulin processing, insulin secretion and GLP-1 signalling in INS-1 cells. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 720–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, M.C.; Bhatt, H.S.; Easom, R.A. NFAT regulatesinsulin gene promoter activity in response to synergistic pathways induced by glucose and glucagon-like peptide-1. Diabetes 2002, 51, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoglund, G.; Hussain, M.A.; Holz, G.G. Glucagon-like peptide 1 stimulates insulin gene promoter activity by protein kinase A-independent activation of the rat insulin I gene cAMP response element. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggio, L.L.; Drucker, D.J. Biology of incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2131–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Egan, J.M. The role of incretins in glucose homeostasis and diabetes treatment. Pharmacol. Rev. 2008, 60, 470–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derosa, G.; Maffioli, P. GLP-1 agonists exenatide and liraglutide: A review about their safety and efficacy. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 7, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leon, D.D.; Deng, S.; Madani, R.; Ahima, R.S.; Drucker, D.J.; Stoffers, D.A. Role of endogenous glucagon-like peptide-1 in islet regeneration after partial pancreatectomy. Diabetes 2003, 52, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buteau, J.; Foisy, S.; Rhodes, C.J.; Carpenter, L.; Biden, T.J.; Prentki, M. Protein kinaseCzeta activation mediates glucagon-like peptide-1-induced pancreatic beta-cell proliferation. Diabetes 2001, 50, 2237–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Xu, E.; Wong, V.; Rhodes, C.; Brubaker, P.L. Glucagon-like peptide-1 regulates proliferation and apoptosis via activation of protein kinase B in pancreatic INS-1 beta cells. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Habener, J.F. Glucagon-like peptide-1 activation of TCF7L2-dependent Wnt signaling enhances pancreatic beta cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 8723–8735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva Xavier, G.; Mondragon, A.; Sun, G.; Chen, L.; McGinty, J.A.; French, P.M.; Rutter, G.A. Abnormal glucosetolerance and insulin secretion in pancreas-specific Tcf7l2-null mice. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 2667–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farilla, L.; Bulotta, A.; Hirshberg, B.; Li Calzi, S.; Khoury, N.; Noushmehr, H.; Bertolotto, C.; Di Mario, U.; Harlan, D.M.; Perfetti, R. Glucagon-like peptide 1 inhibits cell apoptosis and improves glucose responsiveness of freshly isolated human islets. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 5149–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, S.; Toyonaga, T.; Kondo, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Tsuruzoe, K.; Kawashima, J.; Goto, H.; Kume, K.; Kume, S.; Sakakida, M.; et al. Enhanced expression of PDX-1 and Ngn3 by exendin-4 during beta cell regeneration in STZ-treated mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 327, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buteau, J.; Spatz, M.L.; Accili, D. Transcription factor FoxO1 mediates glucagon-like peptide-1 effects on pancreatic beta-cell mass. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, H.; Nourparvar, A.; Zhao, X.; Perfetti, R. Glucagon-like peptide-1 inhibits apoptosis of insulin-secreting cells via a cyclic 5′-adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase A- and a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent pathway. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 1444–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Pineyro, M.A.; Egan, J.M. Glucagon-like peptide 1 and exendin-4 convert pancreatic AR42J cells into glucagon- and insulin-producing cells. Diabetes 1999, 48, 2358–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Pineyro, M.A.; Wang, X.; Doyle, M.E.; Egan, J.M. Exendin-4 differentiation of a human pancreatic duct cell line into endocrine cells: Involvement of PDX-1 and HNF3beta transcription factors. J. Cell. Physiol. 2002, 192, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, H.; Holst, J.J.; Ahren, B. Glucagon-like peptide-1 reduces hepatic glucose production indirectly through insulin and glucagon in humans. Acta. Physiol. Scand. 1997, 160, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, C.J.; Henriksen, T.I.; Pedersen, B.K.; Solomon, T.P. Glucagon likepeptide-1-induced glucose metabolism in differentiated human muscle satellite cells is attenuated by hyperglycemia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, T.; Lahiri, D.K.; Chen, D.; Zhou, J.; Shaw, K.T.; Egan, J.M.; Greig, N.H. A novel neurotrophic property of glucagon-like peptide 1: A promoter of nerve growth factor-mediated differentiation in PC12 cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 300, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, T.; Lahiri, D.K.; Sambamurti, K.; Chen, D.; Mattson, M.P.; Egan, J.M.; Greig, N.H. Glucagon-like peptide-1 decreases endogenous amyloid-beta peptide (Abeta) levels and protects hippocampal neurons from death induced by Abeta and iron. J. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 72, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holscher, C. Potential role of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in neuroprotection. CNS Drugs 2012, 26, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsimihodimos, V.; Elisaf, M. Effects of incretin-based therapies on renal function. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 818, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wroge, J.; Williams, N.T. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists in Cardiac Disorders. Ann. Pharmacother 2016, 50, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.C.; Gusdon, A.M.; Liu, H.; Qu, S. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and inflammation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 14821–14830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blandino-Rosano, M.; Perez-Arana, G.; Mellado-Gil, J.M.; Segundo, C.; Aguilar-Diosdado, M. Anti-proliferative effect of pro-inflammatory cytokines in cultured beta cells is associated with extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway inhibition: Protective role of glucagon-like peptide-1. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 41, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Dear, A.E.; Knudsen, L.B.; Simpson, R.W. A long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue attenuates induction of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 and vascular adhesion molecules. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 201, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthsarathy, V.; Holscher, C. The type2 diabetes drug liraglutide reduces chronic inflammation induced by irradiation in the mouse brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 700, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, C.; Mega, C.; Goncalves, A.; Rodrigues-Santos, P.; Teixeira-Lemos, E.; Teixeira, F.; Fontes-Ribeiro, C.; Reis, F.; Fernandes, R. Sitagliptin prevent sinflammation and apoptotic cell death in the kidney of type 2 diabetic animals. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 538737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceriello, A. Oxidative stress and glycemic regulation. Metabolism 2000, 49 (Suppl. 1), 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, S.; Khan, A. Antioxidants and diabetes. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16 (Suppl. 2), S267–S271. [Google Scholar]
- Lenzen, S.; Drinkgern, J.; Tiedge, M. Low antioxidant enzyme gene expression in pancreatic islets compared with various other mouse tissues. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Fu, J.; Zheng, H.; Xue, P.; Yarborough, K.; Woods, C.G.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Andersen, M.E.; Pi, J. Deficiency in the nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 renders pancreatic beta-cells vulnerable to arsenic-induced cell damage. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 264, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Vaziri, N.D.; Masuda, Y.; Hajighasemi-Ossareh, M.; Robles, L.; Le, A.; Vo, K.; Chan, J.Y.; Foster, C.E.; Stamos, M.J.; et al. Pharmacological activation of Nrf2 pathway improves pancreatic islet isolation and transplantation. Cell. Transplant. 2015, 24, 2273–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uruno, A.; Furusawa, Y.; Yagishita, Y.; Fukutomi, T.; Muramatsu, H.; Negishi, T.; Sugawara, A.; Kensler, T.W.; Yamamoto, M. The Keap1-Nrf2 system prevents onset of diabetes mellitus. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 2996–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmstrom, K.M.; Baird, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hargreaves, I.; Chalasani, A.; Land, J.M.; Stanyer, L.; Yamamoto, M.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Abramov, A.Y. Nrf2 impacts cellular bioenergetics by controlling substrate availability for mitochondrial respiration. Biol. Open 2013, 2, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puddu, A.; Mach, F.; Nencioni, A.; Viviani, G.L.; Montecucco, F. An emergingrole of glucagon-like peptide-1 in preventing advanced-glycation-end-product-mediated damages in diabetes. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 591056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Millan, E.; Martin, M.A.; Goya, L.; Lizarraga-Mollinedo, E.; Escriva, F.; Ramos, S.; Alvarez, C. Glucagon-like peptide-1 improves beta-cell antioxidant capacity via extracellular regulated kinases pathway and Nrf2 translocation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 95, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tews, D.; Lehr, S.; Hartwig, S.; Osmers, A.; Paslack, W.; Eckel, J. Anti-apoptotic action of exendin-4 in INS-1 beta cells: Comparative protein pattern analysis of isolated mitochondria. Horm. Metab. Res. 2009, 41, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, E.; Fujimoto, S.; Sato, H.; Oneyama, C.; Kominato, R.; Sato, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Nishi, Y.; Okada, M.; Inagaki, N. Exendin-4 suppresses SRC activation and reactive oxygen species production in diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rat islets in an Epac-dependent manner. Diabetes 2011, 60, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Kim, E.H.; Jung, H.S.; Yang, D.; Park, E.Y.; Jun, H.S. EX4 stabilizes and activates Nrf2 via PKCδ, contributing to the prevention of oxidative stress-induced pancreatic beta cell damage. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 315, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomas, E.; Stanojevic, V.; Habener, J.F. GLP-1-derived nonapeptide GLP-1 (28–36) amide targets to mitochondria and suppresses glucose production and oxidative stress in isolated mouse hepatocytes. Regul. Pept. 2011, 167, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.L.; Huang, J.; Liu, J.; Jin, M.F.; Gu, M.; Hong, Y.; Wu, Z.R. Protective effect of recombinant human glucagon-like peptide-1 (rhGLP-1) pretreatment in STZ-induced diabetic mice. J. Pept. Sci. 2011, 17, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotfy, M.; Singh, J.; Rashed, H.; Tariq, S.; Zilahi, E.; Adeghate, E. Mechanism of the beneficial and protective effects of exenatide in diabetic rats. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 220, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoda, M.; Kanda, Y.; Hamamoto, S.; Tawaramoto, K.; Hashiramoto, M.; Matsuki, M.; Kaku, K. The human glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue liraglutide preserves pancreatic beta cells via regulation of cell kinetics and suppression of oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress in a mouse model of diabetes. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Saxena, N.K.; Lin, S.; Gupta, N.A.; Anania, F.A. Exendin-4, a glucagon-like protein-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, reverses hepatic steatosis in ob/ob mice. Hepatology 2006, 43, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.; Joharapurkar, A.; Dhanesha, N.; Kshirsagar, S.; Detroja, J.; Patel, K.; Gandhi, T.; Patel, K.; Bahekar, R.; Jain, M. Combination of omeprazole with GLP-1 agonist therapy improves insulin sensitivity and antioxidant activity in liver in type 1 diabetic mice. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceriello, A.; Esposito, K.; Testa, R.; Bonfigli, A.R.; Marra, M.; Giugliano, D. The possibleprotective role of glucagon-like peptide 1 on endothelium during the meal and evidence for an “endothelial resistance” to glucagon-like peptide 1 in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceriello, A.; Novials, A.; Ortega, E.; Canivell, S.; La Sala, L.; Pujadas, G.; Esposito, K.; Giugliano, D.; Genovese, S. Glucagon-like peptide 1 reduces endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and oxidative stress induced by both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2346–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, M.; Abate, N.; Chandalia, M.; Rizvi, A.A.; Giglio, R.V.; Nikolic, D.; Marino Gammazza, A.; Barbagallo, I.; Isenovic, E.R.; Banach, M.; et al. Liraglutide reduces oxidative stress and restores heme oxygenase-1 and ghrelin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes: A prospective pilot study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bunck, M.C.; Corner, A.; Eliasson, B.; Heine, R.J.; Shaginian, R.M.; Wu, Y.; Yan, P.; Smith, U.; Yki-Jarvinen, H.; Diamant, M.; et al. One-year treatment with exenatide vs. insulin glargine: Effects on postprandial glycemia, lipid profiles, and oxidative stress. Atherosclerosis 2010, 212, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, K.; Kotani, K.; Yagyu, H.; Ando, A.; Osuga, J.; Ishibashi, S. Effects of treatment with liraglutide on oxidative stress and cardiac natriuretic peptide levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrine 2014, 47, 962–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravassa, S.; Beaumont, J.; Huerta, A.; Barba, J.; Coma-Canella, I.; Gonzalez, A.; Lopez, B.; Diez, J. Association of low GLP-1 with oxidative stress is related to cardiac disease and outcome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A pilot study. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 81, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangmool, S.; Hemplueksa, P.; Parichatikanond, W.; Chattipakorn, N. Epac is required for GLP-1R-mediated inhibition of oxidative stress and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, G.; Zhang, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, P.; Ye, L.; Lu, K.; Duan, Q.; Zheng, A.; Qin, S. Exenatide protects against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis by improving mitochondrial function in H9c2 cells. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 239, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, G.; Zhang, D.; Yu, H.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, A.; Qin, S. Cardioprotective effects of exenatide against oxidative stress-induced injury. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Luo, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; Sun, D.; Zhang, R.; Su, T.; Ma, X.; Zeng, C.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 protects against cardiac microvascular injury in diabetes via a cAMP/PKA/Rho-dependent mechanism. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1697–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishibashi, Y.; Matsui, T.; Takeuchi, M.; Yamagishi, S. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) inhibits advanced glycation end product (AGE)-induced up-regulation of VCAM-1 mRNA levels in endothelial cells by suppressing AGE receptor (RAGE) expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 1405–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batchuluun, B.; Inoguchi, T.; Sonoda, N.; Sasaki, S.; Inoue, T.; Fujimura, Y.; Miura, D.; Takayanagi, R. Metformin and liraglutide ameliorate high glucose-induced oxidative stress via inhibition of PKC-NAD (P) H oxidase pathway in human aortic endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2014, 232, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Lin, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Guo, L. GLP-1 Inhibits High-Glucose-Induced Oxidative Injury of Vascular Endothelial Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendarto, H.; Inoguchi, T.; Maeda, Y.; Ikeda, N.; Zheng, J.; Takei, R.; Yokomizo, H.; Hirata, E.; Sonoda, N.; Takayanagi, R. GLP-1 analog liraglutide protects against oxidative stress and albuminuria in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats via protein kinase A-mediated inhibition of renal NAD (P) H oxidases. Metabolism 2012, 61, 1422–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civantos, E.; Bosch, E.; Ramirez, E.; Zhenyukh, O.; Egido, J.; Lorenzo, O.; Mas, S. Sitagliptin ameliorates oxidative stress in experimental diabetic nephropathy by diminishing the miR-200a/Keap-1/Nrf2 antioxidant pathway. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2017, 10, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, K.; Holscher, C. Drugs developedto treat diabetes, liraglutide and lixisenatide, cross the blood brain barrier and enhance neurogenesis. BMC Neurosci. 2012, 13, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teramoto, S.; Miyamoto, N.; Yatomi, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Oishi, H.; Arai, H.; Hattori, N.; Urabe, T. Exendin-4, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, provides neuroprotection in mice transient focal cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2011, 31, 1696–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, C.T.; Jou, M.J.; Cheng, T.Y.; Yang, C.H.; Yu, T.Y.; Li, P.C. Exendin-4-loaded PLGA microspheres relieve cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury and neurologic deficits through long-lasting bioactivity-mediated phosphorylated Akt/eNOS signaling in rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 1790–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscogiuri, G.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Gastaldelli, A.; Holst, J.J. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 and the Central/Peripheral Nervous System: Crosstalk in Diabetes. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Lu, D.; Li, T.; Ding, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Xu, A. The Neuroprotection of Liraglutide against Ischaemia-induced Apoptosis through the Activation of the PI3K/AKT and MAPK Pathways. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Bader, M.; Tamargo, I.; Rubovitch, V.; Tweedie, D.; Pick, C.G.; Greig, N.H. Liraglutide is neurotrophic and neuroprotective in neuronal cultures and mitigates mild traumatic brain injury in mice. J. Neurochem. 2015, 135, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeseburg, H.; de Boer, R.A.; Buikema, H.; van derHarst, P.; van Gilst, W.H.; Sillje, H.H. Glucagon-like peptide 1 prevents reactive oxygen species-induced endothelial cell senescence through the activation of protein kinase A. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Li, A.Q.; Zhou, T.F.; Zhang, M.Q.; Qin, X.M. Exendin-4 alleviates angiotensin II-induced senescence in vascular smooth muscle cells by inhibiting Rac1 activation via a cAMP/PKA-dependent pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2014, 307, C1130–C1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, Y.S.; Jun, H.-S. Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 on Oxidative Stress and Nrf2 Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010026
Oh YS, Jun H-S. Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 on Oxidative Stress and Nrf2 Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(1):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010026
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Yoon Sin, and Hee-Sook Jun. 2018. "Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 on Oxidative Stress and Nrf2 Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 1: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010026
APA StyleOh, Y. S., & Jun, H. -S. (2018). Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 on Oxidative Stress and Nrf2 Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(1), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010026