Uptake and Distribution of Fenoxanil-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Rice Plants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of MSNs and Fen@MSNs
2.2. In Vitro Release of Fenoxanil
2.3. Analytical Method Validation
2.4. Translocation of Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (FITC)-Labeled MSNs in Rice Plants
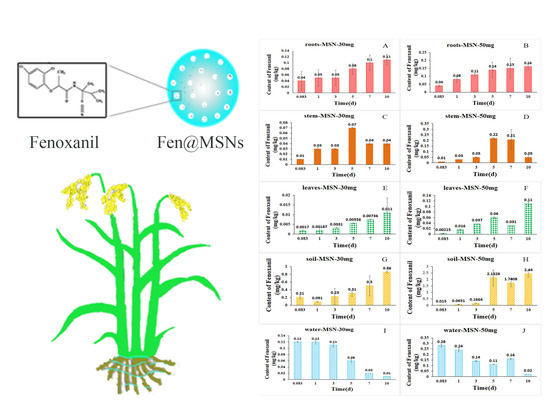
2.5. Uptake and Distribution of Fenoxanil-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Rice plants
2.6. Final Residues of Fenoxanil in Rice
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
3.3. Loading of Fenoxanil into Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
3.4. Synthesis of FITC-labeled MSNs
3.5. Fenoxanil Release
- Er: the accumulative release (%) of Fenoxanil from the nanoparticles;
- Ve: the volume of the release medium taken in a time interval (Ve = 0.8 mL);
- Ci: the Fenoxanil concentration in the release medium;
- i: the release time
- V0: the volume of the release medium (250 mL);
- n: the sample number;
- Mp: the total amount of pesticide entrapped in the nanoparticles.
3.6. Greenhouse Study
3.7. Sample Preparation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MSNs | mesoporous silica nanoparticles |
| Fen@MSNs | Fenoxanil-loaded MSNs |
| CTAB | cetyltrimethylammonium bromide |
| PSA | primary secondary amine |
| GCB | graphitized carbon black |
| FITC | fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| APTES | (3-Aminopropyl)triethoxysilane |
| SEM | scanning electron microscope |
| TEM | transmission electron microscope |
| BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller |
| BJH | Barrett–Joyner–Halenda |
| DLS | dynamic light scattering |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared |
| DAD | diode array detector |
| HPLC | high-performance liquid chromatography |
| HPLC–MS/MS | high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry |
| RSD | relative standard deviation |
| LOD | limit of detection |
| LOQ | limit of quantification |
| LSM | laser scanning microscope |
| MRL | maximum residue limit |
References
- Stamm, M.D.; Heng-Moss, T.M.; Baxendale, F.P.; Siegfried, B.D.; Blankenship, E.E.; Nauen, R. Uptake and translocation of imidacloprid, clothianidin and flupyradifurone in seed-treated soybeans. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.E.; Li, J.; Zheng, K.M.; Wang, D.P.; Wang, X.B.; Zhang, Y.P.; Xue, W.; Hu, D.Y. The systemic properties of chlorantraniliprole in rice plant by UPLC-HRMS. Agrochemicals 2017, 56, 176–179. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.S.; Liu, X.L.; Li, J.Q.; Si, N.G. Uptake and translocation behavior of new fungicide flumorph in cucumber plant. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2006, 27, 1887–1890. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.P.; Han, P.; Liu, J.L.; Si, N.G.; Wang, Y.H.; Liu, P.F.; Liu, X.L. Study on the systemic properties of SYP-Z048 in tomato seedling using high performance liquid chromatography. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2014, 16, 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Han, P.; Hu, B.; Ma, S.; Cao, Y.S. Evaluation of systemic properties of penflufen in wheat seedling using ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2017, 19, 729–734. [Google Scholar]
- Kresge, C.T.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Roth, W.J.; Vartuli, J.C.; Beck, J.S. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 1992, 359, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuthati, Y.; Kankala, R.K.; Lin, S.X.; Weng, C.F.; Lee, C.H. pH-Triggered Controllable Release of Silver-Indole-3 Acetic Acid Complexes from Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (IBN-4) for Effectively Killing Malignant Bacteria. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 2289–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuthati, Y.; Kankala, R.K.; Busa, P.; Lin, S.X.; Deng, J.P.; Mou, C.Y.; Lee, C.H. Phototherapeutic spectrum expansion through synergistic effect of mesoporous silica trio-nanohybrids against antibiotic-resistant gram-negative bacterium. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2017, 169, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankala, R.K.; Liu, C.G.; Chen, A.Z.; Wang, S.B.; Xu, P.Y.; Mende, L.K.; Liu, C.L.; Lee, C.H.; Hu, Y.F. Overcoming Multidrug Resistance through the Synergistic Effects of Hierarchical pH-Sensitive, ROS-Generating Nanoreactors. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 2431–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankala, R.K.; Kuthati, Y.; Liu, C.L.; Mou, C.Y.; Lee, C.H. Killing cancer cells by delivering a nanoreactor for inhibition of catalase and catalytically enhancing intracellular levels of ROS. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 86072–86081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, B.Y.; Kuthati, Y.; Kankala, R.K.; Kankala, S.; Deng, J.P.; Liu, C.L.; Lee, C.H. Utilization of Enzyme-Immobilized Mesoporous Silica Nanocontainers (IBN-4) in Prodrug-Activated Cancer Theranostics. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 2169–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, P.K.; Lin, S.X.; Tsai, M.J.; Leong, M.K.; Lin, S.R.; Kankala, R.K.; Lee, C.H.; Weng, C.F. Encapsulation of 16-Hydroxycleroda-3,13-Dine-16,15-Olide in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Natural Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Potentiated Hypoglycemia in Diabetic Mice. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X. Slow-release formulation of a new biological pesticide, pyoluteorin, with mesoporous silica. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.X.; Li, Z.Z.; Zou, H.K.; Liu, A.Q.; Chen, J.F. Controlled release of avermectin from porous hollow silica nanoparticles. Pest Manag. Sci. 2005, 61, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, H.X.; Sun, C.J.; Zhao, X.; Cui, B. Construction and evaluation of controlled-release delivery system of Abamectin using porous silica nanoparticles as carriers. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mas, N.; Galiana, I.; Hurtado, S.; Mondragon, L.; Bernardos, A.; Sancenon, F.; Marcos, M.D.; Amoros, P.; Abril-Utrillas, N.; Martinez-Manez, R.; et al. Enhanced antifungal efficacy of tebuconazole using gated pH-driven mesoporous nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 2597–2606. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardos, A.; Marina, T.; Zacek, P.; Perez-Esteve, E.; Martinez-Manez, R.; Lhotka, M.; Kourimska, L.; Pulkrabek, J.; Kloucek, P. Antifungal effect of essential oil components against Aspergillus niger when loaded into silica mesoporous supports. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2824–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanyika, H. Sustained release of fungicide metalaxyl by mesoporous silica nanospheres. J. Nanopart Res. 2013, 15, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torney, F.; Trewyn, B.G.; Lin, V.S.; Wang, K. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles deliver DNA and chemicals into plants. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, F.P.; Kuang, L.; Huang, C.A.; Jane, W.N.; Hung, Y.; Hsing, Y.i.C.; Mou, C.Y. A simple plant gene delivery system using mesoporous silica nanoparticles as carriers. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 5279–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Cao, L.; Ma, D.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Q.; Pan, C. Synthesis of Pyrimethanil-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles and Its Distribution and Dissipation in Cucumber Plants. Molecules 2017, 22, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Cao, L.; Ma, D.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Q.; Pan, C. Translocation, distribution and degradation of prochloraz-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles in cucumber plants. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brycht, M.; Skrzypek, S.; Robak, J.; Guzsvány, V.; Vajdle, O.; Zbiljić, J.; Nosal-Wiercińska, A.; Guziejewski, D.; Andrijewski, G. Ultra trace level determination of fenoxanil by highly sensitive square wave adsorptive stripping voltammetry in real samples with a renewable silver amalgam film electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 738, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Wei, P.; Wang, M.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y. Distribution of thifluzamide, fenoxanil and tebuconazole in rice paddy and dietary risk assessment. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2015, 98, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.W.; Ser, H.L.; Khan, T.M.; Chuah, L.H.; Pusparajah, P.; Chan, K.G.; Goh, B.H.; Lee, L.H. The Potential of Streptomyces as Biocontrol Agents against the Rice Blast Fungus, Magnaporthe oryzae (Pyricularia oryzae). Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, D.; Shamim, M.; Kumar, M.; Mishra, A.; Pandey, P.; Kumar, D.; Yadav, P.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Singh, K.N. Current Status of Conventional and Molecular Interventions for Blast Resistance in Rice. Rice Sci. 2017, 24, 299–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Wu, S.H.; Hung, Y.; Mou, C.Y. Size effect on cell uptake in well-suspended, uniform mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Small 2009, 5, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popat, A.; Liu, J.; Hu, Q.; Kennedy, M.; Peters, B.; Lu, G.Q.; Qiao, S.Z. Adsorption and release of biocides with mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, H.; Cao, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Huang, Q. Quaternized Chitosan-Capped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Nanocarriers for Controlled Pesticide Release. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.; Poulose, A.C.; Nagaoka, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Maekawa, T.; Kumar, D.S. Uptake of FITC labeled silica nanoparticles and quantum dots by rice seedlings: Effects on seed germination and their potential as biolabels for plants. J. Fluoresc. 2011, 21, 2057–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Hussain, H.I.; Yi, Z.; Rookes, J.E.; Kong, L.; Cahill, D.M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles enhance seedling growth and photosynthesis in wheat and lupin. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Q.; Dai, D.; Yuan, Y.; Qian, J.; Sha, S.; Shi, J.; Liu, C. Effect of size on the cellular endocytosis and controlled release of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular delivery. Biomed. Microdevices 2012, 14, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Sample | Models | Equation | Fitting Equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fenoxanil | Zero-order equation | y = a + bx | 4.266 + 1.42x | 0.95371 |
| First-order equation | y = a*(1 − exp(−b*x)) | 126.56*(1 − exp(−0.016*x)) | 0.99416 | |
| Higuchi | y = a*(x^(1/2)) + b | 10.725x1/2 + 0.28305 | 0.98287 | |
| Fen@MSNs | Zero-order equation | y = a + bx | 3.3376 + 0.77x | 0.98111 |
| First-order equation | y = a*(1 − exp(−b*x)) | 89.19*(1 − exp(−0.015*x)) | 0.99764 | |
| Higuchi | y = a*(x^(1/2)) + b | 7.654x1/2 − 6.6 | 0.99054 |
| Compound | Matrix | Standard Calibration Curve | LOD (mg/kg) | LOQ (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression Equation | R2 | ||||
| Fenoxanil | roots | y = 588191x + 14086 | 0.9968 | 0.0001 | 0.001 |
| stem | y = 536119x + 11018 | 0.9997 | 0.0001 | 0.001 | |
| rice | y = 513143x + 11661 | 0.9938 | 0.0001 | 0.001 | |
| leaves | y = 383365x + 15639 | 0.97 | 0.0001 | 0.001 | |
| soil | y = 565884x + 12994 | 0.9985 | 0.0001 | 0.001 | |
| water | y = 529117x + 33323 | 0.9276 | 0.0001 | 0.001 | |
| Sample | Spiked Level (mg/kg) | Average Recoveries (%) | RSD (%) | LOQ (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roots | 1.0 | 85 | 3 | 0.001 |
| 0.1 | 101 | 6 | ||
| 0.01 | 89 | 4 | ||
| Leaves | 1.0 | 79 | 2 | 0.001 |
| 0.1 | 95 | 6 | ||
| 0.01 | 88 | 7 | ||
| Stems | 1.0 | 87 | 9 | 0.001 |
| 0.1 | 90 | 3 | ||
| 0.01 | 105 | 6 | ||
| Rice | 1.0 | 88 | 8 | 0.001 |
| 0.1 | 79 | 4 | ||
| 0.01 | 99 | 7 | ||
| Water | 1.0 | 92 | 7 | 0.001 |
| 0.1 | 78 | 9 | ||
| 0.01 | 102 | 8 | ||
| Soil | 1.0 | 91 | 4 | 0.001 |
| 0.1 | 77 | 5 | ||
| 0.01 | 110 | 8 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Cao, L.; Cao, C.; Li, F.; Chen, C.; Xu, C.; Huang, Q.; Du, F. Uptake and Distribution of Fenoxanil-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Rice Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102854
Zhu F, Liu X, Cao L, Cao C, Li F, Chen C, Xu C, Huang Q, Du F. Uptake and Distribution of Fenoxanil-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Rice Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(10):2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102854
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Feng, Xingang Liu, Lidong Cao, Chong Cao, Fengmin Li, Caijun Chen, Chunli Xu, Qiliang Huang, and Fengpei Du. 2018. "Uptake and Distribution of Fenoxanil-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Rice Plants" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 10: 2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102854
APA StyleZhu, F., Liu, X., Cao, L., Cao, C., Li, F., Chen, C., Xu, C., Huang, Q., & Du, F. (2018). Uptake and Distribution of Fenoxanil-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Rice Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(10), 2854. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102854