Ghrelin in Serum and Urine of Post-Partum Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
3.1. Significance of Urine and Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)
3.2. Associations between Ghrelin and BIA
3.3. Association of Ghrelin and the Nutritional Status
3.4. Associations between Ghrelin and Maternal Laboratory Results
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blumberg, J.; Ballares, V.; Durbin, J.L. Ethnic variations on gestational diabetes mellitus and evidence-based first-line interventions. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 31, 2641–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiefari, E.; Arcidiacono, B.; Foti, D.; Brunetti, A. Gestational diabetes mellitus: An updated overview. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2017, 40, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolic, D.; Al-Rasadi, K.; Al Busaidi, N.; Al-Waili, K.; Banerjee, Y.; Al-Hashmi, K.; Montalto, G.; Rizvi, A.A.; Rizzo, M.; Al-Dughaishi, T. Incretins, pregnancy, and gestational diabetes. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2016, 17, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skórzyńska-Dziduszko, K.E.; Kimber-Trojnar, Ż.; Patro-Małysza, J.; Olszewska, A.; Zaborowski, T.; Małecka-Massalska, T. An Interplay between obesity and inflammation in gestational diabetes mellitus. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2016, 17, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciniak, A.; Patro-Małysza, J.; Kimber-Trojnar, Ż.; Marciniak, B.; Oleszczuk, J.; Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, B. Fetal programming of the metabolic syndrome. Taiwan. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 56, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.J.; Hiscock, R.J.; Wein, P.; Walker, S.P.; Permezel, M. Gestational diabetes mellitus: Clinical predictors and long-term risk of developing type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study using survival analysis. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lappas, M.; Jinks, D.; Ugoni, A.; Louizos, C.C.; Permezel, M.; Georgiou, H.M. Post-partum plasma C-peptide and ghrelin concentrations are predictive of type 2 diabetes in women with previous gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes 2015, 7, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Díaz, R.A.; Gómez-Medina, M.P.; Ramírez-Soriano, E.; López-Robles, L.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; Saucedo, R.; Zarate, A.; Valladares-Salgado, A.; Wacher, N.H. Lower Plasma Ghrelin Levels are Found in Women with Diabetes-Complicated Pregnancies. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2016, 8, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifian, M.; Shiva, M.R.; Sepahi, M.A.; Shohadaee, S.; Esfandiar, N.; Fallah, F. Urinary Ghrelin Concentration in Children With Urinary Tract Infections Before and After Treatment. Arch. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. 2016, 4, 34096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, A.; López Soto, E.J.; Epelbaum, J.; Perelló, M. Is Ghrelin Synthesized in the Central Nervous System? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Lin, L.; Yue, J.; Wu, C.S.; Guo, C.A.; Wang, R.; Yu, K.J.; Devaraj, S.; Murano, P.; Chen, Z.; et al. Suppression of Ghrelin Exacerbates HFCS-Induced Adiposity and Insulin Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amitani, M.; Amitani, H.; Cheng, K.C.; Kairupan, T.S.; Sameshima, N.; Shimoshikiryo, I.; Mizuma, K.; Rokot, N.T.; Nerome, Y.; Owaki, T.; et al. The Role of Ghrelin and Ghrelin Signaling in Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poher, A.L.; Tschöp, M.H.; Müller, T.D. Ghrelin regulation of glucose metabolism. Peptides 2018, 100, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusu, C.C.; Racasan, S.; Moldovan, D.; Potra, A.; Tirinescu, D.; Budurea, C.; Orasan, R.; Patiu, I.M.; Bondor, C.; Vladutiu, D.; et al. Ghrelin and acyl ghrelin levels are associated with inflammatory and nutritional markers and with cardiac and vascular dysfunction parameters in hemodialysis patients. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahveci, H.; Laloglu, F.; Kilic, O.; Ciftel, M.; Kara, M.; Laloglu, E.; Yildirim, A.; Orbak, Z.; Ertekin, V.; Cesur, Y. Fasting and postprandial glucose, insulin, leptin, and ghrelin values in preterm babies and their mothers: Relationships among their levels, fetal growth, and neonatal anthropometry. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015, 28, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taskin, E.; Atli, B.; Kiliç, M.; Sari, Y.; Aydin, S. Serum, urine, and saliva levels of ghrelin and obestatin pre- and post-treatment in pediatric epilepsy. Pediatr. Neurol. 2014, 51, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyhanli, E.S.; Lok, U.; Gulacti, U.; Buyukaslan, H.; Atescelik, M.; Yildiz, M.; Onur, M.R.; Goktekin, M.C.; Aydın, S. Assessment of serum and urine ghrelin levels in patients with acute stroke. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ozkorucu, D.; Cetin, N.; Sav, N.M.; Yildiz, B. Urine and serum ghrelin, sCD80 and sCTLA-4 levels in doxorubicin-induced experimental nephrotic syndrome. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2016, 48, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellamy, L.; Casas, J.; Hingorani, A.; Williams, D. Type 2 diabetes mellitus after gestational diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2009, 373, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huopio, H.; Hakkarainen, H.; Pääkkönen, M.; Kuulasmaa, T.; Voutilainen, R.; Heinonen, S.; Cederberg, H. Long-Term changes in glucose metabolism after gestational diabetes: A double cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2014, 14, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghezzi, F.; Franchi, M.; Balestreri, D.; Lischetti, B.; Mele, M.C.; Alberico, S.; Bolis, P. Bioelectrical impedance analysis during pregnancy and neonatal birth weight. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2001, 98, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridner, S.H.; Dietrich, M.S.; Deng, J.; Bonner, C.M.; Kidd, N. Bioelectrical impedance for detecting upper limb lymphedema in nonlaboratory settings. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2009, 7, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, S.; Schulze, K.J.; Ali, H.; Labrique, A.B.; Shamim, A.A.; Rashid, M.; Mehra, S.; Christian, P.; West, K.P. Bioelectrical impedance among rural Bangladeshi Women during pregnancy and in the postpartum period. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2011, 29, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukaski, H.C.; Johnson, P.E.; Bolonchuk, W.W.; Lykken, G.I. Assessment of fat-free mass using bioelectrical impedance measurements of the human body. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1985, 41, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Mao, J.; Wang, W.; Qiou, J.; Yang, L.; Chen, S. Maternal fat free mass during pregnancy is associated with birth weight. Reprod. Health 2017, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlit, S.; Tuschy, B.; Stojakowits, M.; Weiss, C.; Leweling, H.; Sutterlin, M.; Kehl, S. Bioelectrical impedance analysis in pregnancy: Reference ranges. In Vivo 2013, 27, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berlit, S.; Stojakowits, M.; Tuschy, B.; Weiss, C.; Leweling, H.; Sütterlin, M.; Kehl, S. Bioelectrical impedance analysis in the assessment of pre-eclampsia. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2015, 291, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno Martinez, S.; Tufiño Olivares, E.; Chávez Loya, V.; Rodríguez Morán, M.; Guerrero Romero, F.; Levario Carrillo, M. Body composition in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Ginecol. Obstet. Mex. 2009, 77, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Purnell, J.Q.; Weigle, D.S.; Breen, P.; Cummings, D.E. Ghrelin levels correlate with insulin levels, insulin resistance, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, but not with gender, menopausal status, or cortisol levels in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 5747–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makovey, J.; Naganathan, V.; Seibel, M.; Sambrook, P. Gender differences in plasma ghrelin and its relations to body composition and bone—an opposite-sex twin study. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2007, 66, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, G.; An, W.; Zhang, W. Ghrelin fluctuation, what determines its production? Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2009, 41, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emerson, K., Jr.; Poindexter, E.L.; Kothari, M. Changes in total body composition during normal and diabetic pregnancy. Relation to oxygen consumption. Obstet. Gynecol. 1975, 45, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pöykkö, S.M.; Kellokoski, E.; Hörkkö, S.; Kauma, H.; Kesäniemi, Y.A.; Ukkola, O. Low plasma ghrelin is associated with insulin resistance, hypertension, and the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2546–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedl, M.; Maier, C.; Handisurya, A.; Luger, A.; Kautzky-Willer, A. Insulin resistance has no impact on ghrelin suppression in pregnancy. J. Intern. Med. 2007, 262, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hehir, M.P.; Laursen, H.; Higgins, M.F.; Brennan, D.J.; O’Connor, D.P.; McAuliffe, F.M. Ghrelin concentrations in maternal and cord blood of type 1 diabetic and non-diabetic pregnancies at term. Endocrine 2013, 43, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, S. The presence of the peptides apelin, ghrelin and nesfatin-1 in the human breast milk, and the lowering of their levels in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus. Peptides 2010, 31, 2236–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telejko, B.; Kuzmicki, M.; Zonenberg, A.; Modzelewska, A.; Niedziolko-Bagniuk, K.; Ponurkiewicz, A.; Wawrusiewicz-Kurylonek, N.; Nikolajuk, A.; Szamatowicz, J.; Laudanski, P.; et al. Ghrelin in gestational diabetes: Serum level and mRNA expression in fat and placental tissue. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2010, 118, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baykus, Y.; Gurates, B.; Aydin, S.; Celik, H.; Kavak, B.; Aksoy, A.; Sahin, I.; Deniz, R.; Gungor, S.; Guzel, S.P.; et al. Changes in serum obestatin, preptin and ghrelins in patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishi, Y.; Hiejima, H.; Mifune, H.; Sato, T.; Kangawa, K.; Kojima, M. Developmental changes in the pattern of ghrelin’s acyl modification and the levels of acyl-modified ghrelins in murine stomach. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 2709–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdstock, C.; Engström, B.E.; Ohrvall, M.; Lind, L.; Sundbom, M.; Karlsson, F.A. Ghrelin and adipose tissue regulatory peptides: Effect of gastric bypass surgery in obese humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 3177–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palik, E.; Baranyi, E.; Melczer, Z.; Audikovszky, M.; Szöcs, A.; Winkler, G.; Cseh, K. Elevated serum acylated (biologically active) ghrelin and resistin levels associate with pregnancy-induced weight gain and insulin resistance. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 76, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briggs, D.I.; Andrews, Z.B. A recent update on the role of ghrelin in glucose homeostasis. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2011, 7, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacko, S.K.; Haymond, M.W.; Sun, Y.; Marini, J.C.; Sauer, P.J.; Ma, X.; Sunehag, A.L. Effect of ghrelin on glucose regulation in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 302, E1055–E1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, L.; Wang, Z.; Ma, X.; Ren, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lu, J.; et al. Plasma ghrelin concentrations are negatively correlated with urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 348, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheirouri, S.; Alizadeh, M. Decreased Serum Levels of Ghrelin and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Premenopausal Women With Metabolic Syndrome. Lab. Med. 2018, 49, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viteri, O.A.; Sallman, M.A.; Berens, P.M.; Berens, P.D.; Amro, F.H.; Hutchinson, M.S.; Ramin, S.M.; Blackwell, S.C.; Refuerzo, J.S.; Smith, J.A. Potential of Metformin to Improve Cardiac Risk in Postpartum Women with Gestational Diabetes. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, S.; Geckil, H.; Karatas, F.; Donder, E.; Kumru, S.; Kavak, E.C.; Colak, R.; Ozkan, Y.; Sahin, I. Milk and blood ghrelin level in diabetics. Nutrition 2007, 23, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine (US) and National Research Council (US) Committee to Reexamine IOM Pregnancy Weight Guidelines; Rasmussen, K.M.; Yaktine, A.L. Weight Gain during Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups Consensus Panel. International association of diabetes and pregnancy study groups recommendations on the diagnosis and classification of hyperglycemia in pregnancy. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diabetes Poland (Polish Diabetes Association). 2018 Guidelines on the management of diabetic patients. A position of Diabetes Poland. Clin. Diabetol. 2018, 7, 1–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Variables | Control Group (n = 28) | GDM Group (n = 26) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Day of Delivery | |||
| fasting blood glucose (mg/dL) | 83.5 (73.0–91.0) | 85.0 (82.0–98.0) | 0.107 |
| gestational weight gain (kg) | 15.0 (8.0–15.6) | 13.3 (9.2–15.0) | 0.086 |
| ΔBMI 1 (kg/m2) | 5.4 (2.97–5.6) | 5.08 (3.11–5.72) | 0.085 |
| 2nd Day of Post-Partum Period | |||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.0 (21.0–23.9) | 28.8 (25.3–30.65) | 0.0011 * |
| ΔBMI 2 (kg/m2) | 2.49 (2.08–4.16) | 2.2 (2.11–2.7) | 0.306 |
| hemoglobin A1c (%) | 5.3 (4.6–5.4) | 5.5 (5.2–5.6) | 0.018 * |
| albumin (g/dL) | 3.68 (3.43–3.73) | 3.46 (3.37–3.64) | 0.007 * |
| total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 249.0 (188.0–287.0) | 209.0 (192.5–247.5) | 0.217 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 78.0 (75.0–82.0) | 67.5 (54.5–73.5) | 0.0013 * |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 129 (93–152) | 107 (85.5–129) | 0.146 |
| triglycerides (mg/dL) | 177 (150–254) | 240.5 (170–261) | 0.109 |
| serum ghrelin (ng/mL) | 0.933 (0.646–1.115) | 0.395 (0.19–1.226) | 0.116 |
| urine ghrelin (ng/mL) | 0.102 (0.096–0.288) | 0.212 (0.067–0.598) | 0.225 |
| total body water (L) | 30.1 (25.2–35.0) | 33.8 (31.1–35.6) | 0.0015 * |
| extracellular water (L) | 14.9 (13.0–15.7) | 16.3 (15.0–17.2) | 0.00014 ** |
| intracellular water (L) | 15.7 (13.5–17.8) | 17.3 (15.8–17.8) | 0.051 |
| lean tissue mass (kg) | 30.0 (27.0–37.2) | 31.7 (30.8–33.1) | 0.79 |
| lean tissue index (kg/m2) | 10.1 (9.4–13.1) | 11.8 (11.0–12.5) | 0.073 |
| fat tissue index (kg/m2) | 10.1 (9.1–13.8) | 15.1 (13.3–17.9) | 0.0012 * |
| body cell mass (kg) | 15.0 (12.8–20.1) | 17.1 (15.5–17.7) | 0.454 |
| BCMI (kg/m2) | 5.31 (4.8–7.17) | 6.19 (5.46–6.63) | 0.085 |
| Variables | All the Studied Women | Healthy Group | GDM Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum Ghrelin | Urine Ghrelin | Serum Ghrelin | Urine Ghrelin | Serum Ghrelin | Urine Ghrelin | |
| ΔBMI 1 | 0.313 * | −0.296 * | 0.6 * | −0.028 | 0.145 | 0.285 |
| BMI | −0.196 | −0.181 | −0.428 * | −0.771 *** | −0.394 | −0.018 |
| ΔBMI 2 | 0.368 * | −0.048 | 0.543 * | −0.028 | 0.331 | 0.284 |
| hemoglobin A1c | 0.022 | −0.199 | 0.319 | −0.377 | 0.115 | −0.303 |
| albumin | −0.012 | 0.079 | −0.086 | −0.086 | −0.036 | 0.1 |
| total cholesterol | −0.011 | 0.089 | −0.202 | 0.001 | 0.224 | 0.212 |
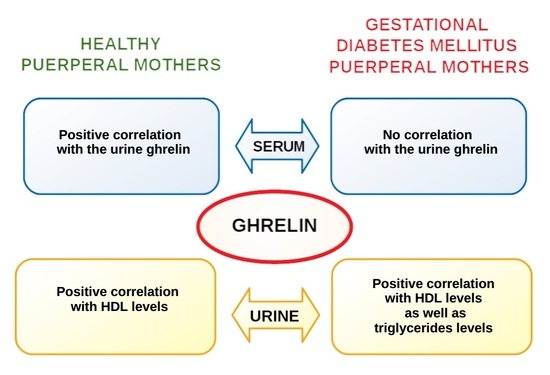
| HDL | −0.061 | 0.312 * | 0.145 | 0.696 ** | −0.115 | 0.491 * |
| LDL | 0.025 | −0.073 | −0.257 | −0.086 | 0.079 | −0.358 |
| triglycerides | 0.133 | 0.081 | 0.319 | −0.203 | 0.333 | 0.564 * |
| urine ghrelin | 0.116 | - | 0.543 * | - | 0.136 | - |
| total body water | −0.241* | −0.374 ** | −0.429 * | −0.943 *** | −0.427 * | −0.264 |
| extracellular water | −0.188 | −0.239 * | −0.486 * | −0.886 *** | −0.409 | −0.200 |
| intracellular water | −0.276 * | −0.377 * | −0.429 * | −0.714 ** | −0.630 * | −0.493 * |
| lean tissue mass | −0.288 * | −0.443 ** | −0.486 * | −0.829 *** | −0.600 * | −0.509 * |
| lean tissue index | −0.301 * | −0.452 *** | −0.486 * | −0.829 *** | −0.287 | −0.451 * |
| fat tissue index | −0.042 | 0.034 | 0.257 | −0.429 * | −0.355 | 0.045 |
| body cell mass | −0.294 * | −0.463 *** | −0.486 * | −0.829 *** | −0.442 * | −0.619 * |
| BCMI | −0.53 ** | −0.534 *** | −0.428 * | −0.943 *** | −0.29 | −0.509 * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kimber-Trojnar, Ż.; Patro-Małysza, J.; Skórzyńska-Dziduszko, K.E.; Oleszczuk, J.; Trojnar, M.; Mierzyński, R.; Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, B. Ghrelin in Serum and Urine of Post-Partum Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3001. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103001
Kimber-Trojnar Ż, Patro-Małysza J, Skórzyńska-Dziduszko KE, Oleszczuk J, Trojnar M, Mierzyński R, Leszczyńska-Gorzelak B. Ghrelin in Serum and Urine of Post-Partum Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(10):3001. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103001
Chicago/Turabian StyleKimber-Trojnar, Żaneta, Jolanta Patro-Małysza, Katarzyna E. Skórzyńska-Dziduszko, Jan Oleszczuk, Marcin Trojnar, Radzisław Mierzyński, and Bożena Leszczyńska-Gorzelak. 2018. "Ghrelin in Serum and Urine of Post-Partum Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 10: 3001. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103001
APA StyleKimber-Trojnar, Ż., Patro-Małysza, J., Skórzyńska-Dziduszko, K. E., Oleszczuk, J., Trojnar, M., Mierzyński, R., & Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, B. (2018). Ghrelin in Serum and Urine of Post-Partum Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(10), 3001. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103001