Apoprotein E and Reverse Cholesterol Transport
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cholesterol Efflux and Reverse Cholesterol Transport
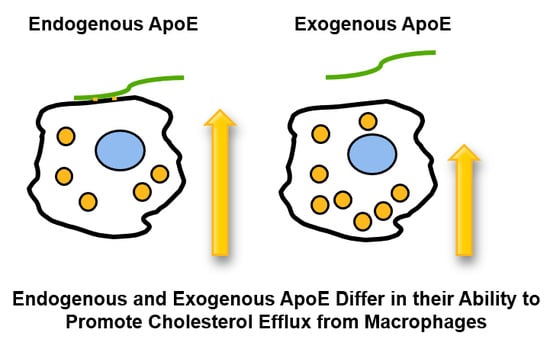
3. Cholesterol Efflux and ApoE
4. Reverse Cholesterol Transport and ApoE
5. Cholesterol Efflux, Hematopoiesis, and ApoE
6. ApoE Mimetic Peptides and Reverse Cholesterol Transport
7. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABCA1 | ATP binding cassette A1 |
| ABCG1 | ATP binding cassette G1 |
| AcLDL | acetylated LDL |
| Apo | apoprotein |
| CETP | cholesteryl ester transfer protein |
| HDL | high-density lipoprotein |
| HSPC | hemopoietic stem cell progenitor cells |
| LDL | low-density lipoprotein |
| SR-BI | scavenger receptor B1 |
| TICE | transintestinal cholesterol excretion |
| VLDL | very low density lipoprotein |
References
- Getz, G.S.; Reardon, C.A. Apoprotein E as a lipid transport and signaling protein in the blood, liver, and artery wall. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S156–S161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.H.; Reddick, R.L.; Piedrahita, J.A.; Maeda, N. Spontaneous hypercholesterolemia and arterial lesions in mice lacking apolipoprotein E. Science 1992, 258, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plump, A.S.; Smith, J.D.; Hayek, T.; Aalto-Setala, K.; Walsh, A.; Verstuyft, J.G.; Rubin, E.M.; Breslow, J.L. Severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice created by homologous recombination in ES cells. Cell 1992, 71, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getz, G.S.; Reardon, C.A. Do the Apoe-/- and Ldlr-/- Mice Yield the Same Insight on Atherogenesis? Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 1734–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linton, M.F.; Atkinson, J.B.; Fazio, S. Prevention of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice by bone marrow transplantation. Science 1995, 267, 1034–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisvert, W.A.; Spangenberg, J.; Curtiss, L.K. Treatment of severe hypercholesterolemia in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice by bone marrow transplantation. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasty, A.H.; Linton, M.F.; Brandt, S.J.; Babaev, V.R.; Gleaves, L.A.; Fazio, S. Retroviral gene therapy in ApoE-deficient mice: ApoE expression in the artery wall reduces early foam cell lesion formation. Circulation 1999, 99, 2571–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellosta, S.; Mahley, R.W.; Sanan, D.A.; Murata, J.; Newland, D.L.; Taylor, J.M.; Pitas, R.E. Macrophage-specific expression of human apolipoprotein E reduces atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic apolipoprotein E-null mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 2170–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Brewer, H.B., Jr.; Davidson, W.S.; Fayad, Z.A.; Fuster, V.; Goldstein, J.; Hellerstein, M.; Jiang, X.C.; Phillips, M.C.; Rader, D.J.; et al. Cholesterol efflux and atheroprotection: Advancing the concept of reverse cholesterol transport. Circulation 2012, 125, 1905–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.C. Molecular mechanisms of cellular cholesterol efflux. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 24020–24029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Collins, H.L.; Ranalletta, M.; Fuki, I.V.; Billheimer, J.T.; Rothblat, G.H.; Tall, A.R.; Rader, D.J. Macrophage ABCA1 and ABCG1, but not SR-BI, promote macrophage reverse cholesterol transport in vivo. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2216–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De la Llera-Moya, M.; Drazul-Schrader, D.; Asztalos, B.F.; Cuchel, M.; Rader, D.J.; Rothblat, G.H. The ability to promote efflux via ABCA1 determines the capacity of serum specimens with similar high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to remove cholesterol from macrophages. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temel, R.E.; Brown, J.M. A new model of reverse cholesterol transport: enTICEing strategies to stimulate intestinal cholesterol excretion. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jakulj, L.; van Dijk, T.H.; de Boer, J.F.; Kootte, R.S.; Schonewille, M.; Paalvast, Y.; Boer, T.; Bloks, V.W.; Boverhof, R.; Nieuwdorp, M.; et al. Transintestinal Cholesterol Transport Is Active in Mice and Humans and Controls Ezetimibe-Induced Fecal Neutral Sterol Excretion. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zanotti, I.; Reilly, M.P.; Glick, J.M.; Rothblat, G.H.; Rader, D.J. Overexpression of apolipoprotein A-I promotes reverse transport of cholesterol from macrophages to feces in vivo. Circulation 2003, 108, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annema, W.; Tietge, U.J. Regulation of reverse cholesterol transport—A comprehensive appraisal of available animal studies. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sontag, T.J.; Chellan, B.; Bhanvadia, C.V.; Getz, G.S.; Reardon, C.A. Alginic acid cell entrapment: A novel method for measuring in vivo macrophage cholesterol homeostasis. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedhachalam, C.; Narayanaswami, V.; Neto, N.; Forte, T.M.; Phillips, M.C.; Lund-Katz, S.; Bielicki, J.K. The C-terminal lipid-binding domain of apolipoprotein E is a highly efficient mediator of ABCA1-dependent cholesterol efflux that promotes the assembly of high-density lipoproteins. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 2583–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lek, M.T.; Cruz, S.; Ibe, N.U.; Beck, W.H.J.; Bielicki, J.K.; Weers, P.M.M.; Narayanaswami, V. Swapping the N- and C-terminal domains of human apolipoprotein E3 and AI reveals insights into their structure/activity relationship. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzone, T.; Pustelnikas, L.; Reardon, C.A. Post-translational regulation of macrophage apoprotein E production. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazzone, T.; Gump, H.; Diller, P.; Getz, G.S. Macrophage free cholesterol content regulates apolipoprotein E synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 11657–11662. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazzone, T.; Reardon, C. Expression of heterologous human apolipoprotein E by J774 macrophages enhances cholesterol efflux to HDL3. J. Lipid Res. 1994, 35, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Duan, H.; Mazzone, T. Apolipoprotein E-dependent cholesterol efflux from macrophages: Kinetic study and divergent mechanisms for endogenous versus exogenous apolipoprotein E. J. Lipid Res. 1999, 40, 1618–1627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Mazzone, T. LDL receptor binds newly synthesized apoE in macrophages. A precursor pool for apoe secretion. J. Lipid Res. 1999, 40, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Huang, Z.H.; Mazzone, T. Interaction with proteoglycans enhances the sterol efflux produced by endogenous expression of macrophage apoE. J. Lipid Res. 2001, 42, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Oram, J.F.; Mazzone, T. Sterol efflux mediated by endogenous macrophage ApoE expression is independent of ABCA1. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 2019–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.H.; Fitzgerald, M.L.; Mazzone, T. Distinct cellular loci for the ABCA1-dependent and ABCA1-independent lipid efflux mediated by endogenous apolipoprotein E expression. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanotti, I.; Pedrelli, M.; Poti, F.; Stomeo, G.; Gomaraschi, M.; Calabresi, L.; Bernini, F. Macrophage, but not systemic, apolipoprotein E is necessary for macrophage reverse cholesterol transport in vivo. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzone, T.; Basheeruddin, K. Dissociated regulation of macrophage LDL receptor and apolipoprotein E gene expression by sterol. J. Lipid Res. 1991, 32, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Gaynor, P.M.; Kruth, H.S. Apolipoprotein E produced by human monocyte-derived macrophages mediates cholesterol efflux that occurs in the absence of added cholesterol acceptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 28641–28646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.C. Apolipoprotein E isoforms and lipoprotein metabolism. IUBMB Life 2014, 66, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cullen, P.; Cignarella, A.; Brennhausen, B.; Mohr, S.; Assmann, G.; von Eckardstein, A. Phenotype-dependent differences in apolipoprotein E metabolism and in cholesterol homeostasis in human monocyte-derived macrophages. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 1670–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucic, D.; Huang, Z.H.; Gu de, S.; Altenburg, M.K.; Maeda, N.; Mazzone, T. Regulation of macrophage apoE secretion and sterol efflux by the LDL receptor. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altenburg, M.; Johnson, L.; Wilder, J.; Maeda, N. Apolipoprotein E4 in macrophages enhances atherogenesis in a low density lipoprotein receptor-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 7817–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahley, R.W.; Huang, Y.; Weisgraber, K.H. Putting cholesterol in its place: apoE and reverse cholesterol transport. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1226–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pamir, N.; Hutchins, P.M.; Ronsein, G.E.; Wei, H.; Tang, C.; Das, R.; Vaisar, T.; Plow, E.; Schuster, V.; Reardon, C.A.; et al. Plasminogen promotes cholesterol efflux by the ABCA1 pathway. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e92176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamir, N.; Hutchins, P.; Ronsein, G.; Vaisar, T.; Reardon, C.A.; Getz, G.S.; Lusis, A.J.; Heinecke, J.W. Proteomic analysis of HDL from inbred mouse strains implicates APOE associated with HDL in reduced cholesterol efflux capacity via the ABCA1 pathway. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, L.; Gharib, S.A.; Irwin, A.D.; Wijsman, E.; Vaisar, T.; Oram, J.F.; Heinecke, J.W. A macrophage sterol-responsive network linked to atherogenesis. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reardon, C.A.; Lingaraju, A.; Schoenfelt, K.Q.; Zhou, G.; Cui, C.; Jacobs-El, H.; Babenko, I.; Hoofnagle, A.; Czyz, D.; Shuman, H.; et al. Obesity and Insulin Resistance Promote Atherosclerosis through an IFNgamma-Regulated Macrophage Protein Network. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 3021–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, K.J.; Tabas, I. Macrophages in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Cell 2011, 145, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swirski, F.K.; Libby, P.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaide, P.; Luscinskas, F.W.; Weissleder, R.; Pittet, M.J. Ly-6Chi monocytes dominate hypercholesterolemia-associated monocytosis and give rise to macrophages in atheromata. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yvan-Charvet, L.; Pagler, T.; Gautier, E.L.; Avagyan, S.; Siry, R.L.; Han, S.; Welch, C.L.; Wang, N.; Randolph, G.J.; Snoeck, H.W.; et al. ATP-binding cassette transporters and HDL suppress hematopoietic stem cell proliferation. Science 2010, 328, 1689–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerterp, M.; Gourion-Arsiquaud, S.; Murphy, A.J.; Shih, A.; Cremers, S.; Levine, R.L.; Tall, A.R.; Yvan-Charvet, L. Regulation of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell mobilization by cholesterol efflux pathways. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 11, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, A.J.; Akhtari, M.; Tolani, S.; Pagler, T.; Bijl, N.; Kuo, C.L.; Wang, M.; Sanson, M.; Abramowicz, S.; Welch, C.; et al. ApoE regulates hematopoietic stem cell proliferation, monocytosis, and monocyte accumulation in atherosclerotic lesions in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4138–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouchareychas, L.; Raffai, R.L. Apolipoprotein E and Atherosclerosis: From Lipoprotein Metabolism to MicroRNA Control of Inflammation. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2018, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getz, G.S.; Wool, G.D.; Reardon, C.A. HDL apolipoprotein-related peptides in the treatment of atherosclerosis and other inflammatory disorders. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 3173–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielicki, J.K.; Zhang, H.; Cortez, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Narayanaswami, V.; Patel, A.; Johansson, J.; Azhar, S. A new HDL mimetic peptide that stimulates cellular cholesterol efflux with high efficiency greatly reduces atherosclerosis in mice. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hafiane, A.; Bielicki, J.K.; Johansson, J.O.; Genest, J. Apolipoprotein E derived HDL mimetic peptide ATI-5261 promotes nascent HDL formation and reverse cholesterol transport in vitro. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 1498–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafiane, A.; Bielicki, J.K.; Johansson, J.O.; Genest, J. Novel Apo E-Derived ABCA1 Agonist Peptide (CS-6253) Promotes Reverse Cholesterol Transport and Induces Formation of prebeta-1 HDL In Vitro. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, C.R.; Garber, D.W.; Anantharamaiah, G.M. Anti-inflammatory and cholesterol-reducing properties of apolipoprotein mimetics: A review. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 2007–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 ) from cholesterol-loaded macrophages to form nascent discoidal high-density lipoprotein (HDL) after interaction with ABC transporters (
) from cholesterol-loaded macrophages to form nascent discoidal high-density lipoprotein (HDL) after interaction with ABC transporters (  ). The nascent HDL with the effluxed cholesterol enters the plasma and via a number of steps (dashed line) is incorporated into mature spherical HDL particles. The HDL particles deliver the cholesterol to hepatocytes via interaction with scavenger receptor B1 (SR-BI) (
). The nascent HDL with the effluxed cholesterol enters the plasma and via a number of steps (dashed line) is incorporated into mature spherical HDL particles. The HDL particles deliver the cholesterol to hepatocytes via interaction with scavenger receptor B1 (SR-BI) (  ) or low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor family members (
) or low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor family members (  ). Alternatively, cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) can mediate the transfer of cholesterol from HDL to VLDL and the effluxed cholesterol taken up by hepatocytes via the LDL receptor’s recognition of apoE or apoB.
). Alternatively, cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) can mediate the transfer of cholesterol from HDL to VLDL and the effluxed cholesterol taken up by hepatocytes via the LDL receptor’s recognition of apoE or apoB.
 ) from cholesterol-loaded macrophages to form nascent discoidal high-density lipoprotein (HDL) after interaction with ABC transporters (
) from cholesterol-loaded macrophages to form nascent discoidal high-density lipoprotein (HDL) after interaction with ABC transporters (  ). The nascent HDL with the effluxed cholesterol enters the plasma and via a number of steps (dashed line) is incorporated into mature spherical HDL particles. The HDL particles deliver the cholesterol to hepatocytes via interaction with scavenger receptor B1 (SR-BI) (
). The nascent HDL with the effluxed cholesterol enters the plasma and via a number of steps (dashed line) is incorporated into mature spherical HDL particles. The HDL particles deliver the cholesterol to hepatocytes via interaction with scavenger receptor B1 (SR-BI) (  ) or low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor family members (
) or low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor family members (  ). Alternatively, cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) can mediate the transfer of cholesterol from HDL to VLDL and the effluxed cholesterol taken up by hepatocytes via the LDL receptor’s recognition of apoE or apoB.
). Alternatively, cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) can mediate the transfer of cholesterol from HDL to VLDL and the effluxed cholesterol taken up by hepatocytes via the LDL receptor’s recognition of apoE or apoB.

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Getz, G.S.; Reardon, C.A. Apoprotein E and Reverse Cholesterol Transport. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113479
Getz GS, Reardon CA. Apoprotein E and Reverse Cholesterol Transport. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113479
Chicago/Turabian StyleGetz, Godfrey S., and Catherine A. Reardon. 2018. "Apoprotein E and Reverse Cholesterol Transport" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113479
APA StyleGetz, G. S., & Reardon, C. A. (2018). Apoprotein E and Reverse Cholesterol Transport. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113479