The Salt-Stress Response of the Transgenic Plum Line J8-1 and Its Interaction with the Salicylic Acid Biosynthetic Pathway from Mandelonitrile
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
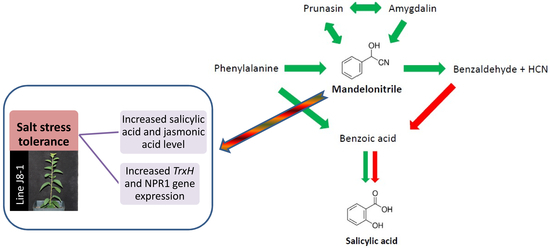
2.1. Metabolomic Analysis of SA Biosynthesis in Plum Plants
2.2. Effect on Stress-Related Hormones: SA, ABA and JA
2.3. Plant Growth, Chlorophyll Contents, and Chlorophyll Fluorescence
2.4. Redox State and the Gene Expression of Redox-Related Genes
2.5. Effect of MD and Phe on Soluble Leaf and Root Nutrient Content under Salt Stress Conditions
3. Discussion
3.1. Involvement of MD on SA Biosynthesis in Plum
3.2. Plant Performance of Plum under NaCl Stress
3.3. Stress-Related Hormones and NaCl Response
3.4. NaCl Effects on Redox State and Ion Homeostasis
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Metabolomic Analysis
4.3. Chlorophyll Determination and Chlorophyll Fluorescence
4.4. Ascorbate and Glutathione Analysis
4.5. Gene Expression
4.6. Determination of Soluble K+, Ca2+, Na+, and Cl− Content
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
References
- Hossain, M.S.; Dietz, K.J. Tuning of Redox Regulatory Mechanisms, Reactive Oxygen Species and Redox Homeostasis under Salinity Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta-Motos, J.; Ortuño, M.; Bernal-Vicente, A.; Diaz-Vivancos, P.; Sanchez-Blanco, M.; Hernandez, J. Plant Responses to Salt Stress: Adaptive Mechanisms. Agronomy 2017, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Tada, Y. Regulation of water, salinity, and cold stress responses by salicylic acid. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.I.; Fatma, M.; Per, T.S.; Anjum, N.A.; Khan, N.A. Salicylic acid-induced abiotic stress tolerance and underlying mechanisms in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Vivancos, P.; Bernal-Vicente, A.; Cantabella, D.; Petri, C.; Hernández, J.A. Metabolomic and Biochemical Approaches Link Salicylic Acid Biosynthesis to Cyanogenesis in Peach Plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 2057–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleadow, R.M.; Møller, B.L. Cyanogenic Glycosides: Synthesis, Physiology, and Phenotypic Plasticity. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 155–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catinot, J.; Buchala, A.; Abou-Mansour, E.; Metraux, J.P. Salicylic acid production in response to biotic and abiotic stress depends on isochorismate in Nicotiana benthamiana. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, D.; Nakajima, N.; Seo, S.; Mitsuhara, I.; Kamada, H.; Ohashi, Y. The phenylalanine pathway is the main route of salicylic acid biosynthesis in Tobacco mosaic virus infected tobacco leaves. Plant Biotechnol. 2006, 23, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Rockett, K.S.; Kørner, C.J.; Pajerowska-Mukhtar, K.M. Salicylic acid signalling: New insights and prospects at a quarter-century milestone. Essays Biochem. 2015, 58, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foyer, C.H.; Noctor, G. Oxidant and antioxidant signalling in plants: A re-evaluation of the concept of oxidative stress in a physiological context. Plant Cell Environ. 2005, 28, 1056–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foyer, C.H.; Noctor, G. Ascorbate and glutathione: The heart of the redox hub. Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira Dos Santos, C.; Rey, P. Plant thioredoxins are key actors in the oxidative stress response. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, Y.; Spoel, S.H.; Pajerowska-Mukhtar, K.; Mou, Z.; Song, J.; Wang, C.; Zuo, J.; Dong, X. Plant Immunity Requires Conformational Charges of NPR1 via S-Nitrosylation and Thioredoxins. Science 2008, 321, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brosché, M.; Kangasjärvi, J. Low antioxidant concentrations impact on multiple signalling pathways in Arabidopsis thaliana partly through NPR1. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 1849–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faize, M.; Faize, L.; Petri, C.; Barba-Espin, G.; Diaz-Vivancos, P.; Clemente-Moreno, M.J.; Koussa, T.; Rifai, L.A.; Burgos, L.; Hernandez, J.A. Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase enhance in vitro shoot multiplication in transgenic plum. J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 170, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Vivancos, P.; Faize, M.; Barba-Espin, G.; Faize, L.; Petri, C.; Hernández, J.A.; Burgos, L. Ectopic expression of cytosolic superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase leads to salt stress tolerance in transgenic plums. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2013, 11, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diaz-Vivancos, P.; Faize, L.; Nicolas, E.; Clemente-Moreno, M.J.; Bru-Martinez, R.; Burgos, L.; Hernandez, J.A. Transformation of plum plants with a cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase transgene leads to enhanced water stress tolerance. Ann. Bot. 2016, 117, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernal-Vicente, A.; Petri, C.; Hernández, J.A.; Diaz-Vivancos, P. The effect of abiotic and biotic stress on the salicylic acid biosynthetic pathway from mandelonitrile in peach. (under review).
- Acosta-Motos, J.-R.; Diaz-Vivancos, P.; Alvarez, S.; Fernandez-Garcia, N.; Jesus Sanchez-Blanco, M.; Antonio Hernandez, J. Physiological and biochemical mechanisms of the ornamental Eugenia myrtifolia L. plants for coping with NaCl stress and recovery. Planta 2015, 242, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta-Motos, J.R.; Diaz-Vivancos, P.; Alvarez, S.; Fernandez-Garcia, N.; Jesus Sanchez-Blanco, M.; Hernandez, J.A. NaCl-induced physiological and biochemical adaptative mechanisms in the ornamental Myrtus communis L. plants. J. Plant Physiol. 2015, 183, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantabella, D.; Piqueras, A.; Acosta-Motos, J.R.; Bernal-Vicente, A.; Hernandez, J.A.; Diaz-Vivancos, P. Salt-tolerance mechanisms induced in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni: Effects on mineral nutrition, antioxidative metabolism and steviol glycoside content. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boatwright, J.L.; Pajerowska-Mukhtar, K. Salicylic acid: An old hormone up to new tricks. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Guo, J.; Zhu, A.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, M. Exogenous jasmonic acid can enhance tolerance of wheat seedlings to salt stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 104 (Suppl. C), 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Zhu, Z.J. Exogenous salicylic acid alleviates NaCl toxicity and increases antioxidative enzyme activity in Lycopersicon esculentum. Biol. Plant. 2008, 52, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Motos, J.R.; Ortuño, M.F.; Álvarez, S.; López-Climent, M.F.; Gómez-Cadenas, A.; Sánchez-Blanco, M.J. Changes in growth, physiological parameters and the hormonal status of Myrtus communis L. plants irrigated with water with different chemical compositions. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 191 (Suppl. C), 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhai, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; He, S. Transcript profile analysis reveals important roles of jasmonic acid signalling pathway in the response of sweet potato to salt stress. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khokon, A.R.; Okuma, E.; Hossain, M.A.; Munemasa, S.; Uraji, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Mori, I.C.; Murata, Y. Involvement of extracellular oxidative burst in salicylic acid-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente-Moreno, M.J.; Diaz-Vivancos, P.; Piqueras, A.; Antonio Hernandez, J. Plant growth stimulation in Prunus species plantlets by BTH or OTC treatments under in vitro conditions. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 169, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Qi, M.; Mei, C. Endogenous salicylic acid protects rice plants from oxidative damage caused by aging as well as biotic and abiotic stress. Plant J. 2004, 40, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herrera-Vasquez, A.; Salinas, P.; Holuigue, L. Salicylic acid and reactive oxygen species interplay in the transcriptional control of defense genes expression. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlot, A.C.; Dempsey, D.A.; Klessig, D.F. Salicylic acid, a multifaceted hormone to combat disease. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2009, 47, 177–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelhaye, E.; Rouhier, N.; Jacquot, J.P. The thioredoxin h system of higher plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2004, 42, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Morita, S.; Hirano, E.; Yokoi, H.; Masumura, T.; Tanaka, K. A Novel cis-Element That Is Responsive to Oxidative Stress Regulates Three Antioxidant Defense Genes in Rice. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Issakidis-Bourguet, E.; Mouaheb, N.; Meyer, Y.; Miginiac-Maslow, M. Heterologous complementation of yeast reveals a new putative function for chloroplast m-type thioredoxin. Plant J. 2001, 25, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.-J.; Zhao, B.-C.; Ge, W.-N.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Song, Y.; Sun, D.-Y.; Guo, Y. An Apoplastic H-Type Thioredoxin Is Involved in the Stress Response through Regulation of the Apoplastic Reactive Oxygen Species in Rice. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 1884–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jayakannan, M.; Bose, J.; Babourina, O.; Rengel, Z.; Shabala, S. Salicylic acid in plant salinity stress signalling and tolerance. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 76, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba-Espin, G.; Clemente-Moreno, M.J.; Alvarez, S.; Garcia-Legaz, M.F.; Hernandez, J.A.; Diaz-Vivancos, P. Salicylic acid negatively affects the response to salt stress in pea plants. Plant Biol. 2011, 13, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernal-Vicente, A.; Cantabella, D.; Hernández, J.A.; Diaz-Vivancos, P. The effect of mandelonitrile, a recently described salicylic acid precursor, on peach plant response against abiotic and biotic stresses. Plant Biol. 2018, 20, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Lou, C. Involvement of nitric oxide in the signal transduction of salicylic acid regulating stomatal movement. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon, D.I. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1949, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vivancos, P.D.; Dong, Y.P.; Ziegler, K.; Markovic, J.; Pallardo, F.V.; Pellny, T.K.; Verrier, P.J.; Foyer, C.H. Recruitment of glutathione into the nucleus during cell proliferation adjusts whole-cell redox homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana and lowers the oxidative defence shield. Plant J. 2010, 64, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellny, T.K.; Locato, V.; Vivancos, P.D.; Markovic, J.; De Gara, L.; Pallardo, F.V.; Foyer, C.H. Pyridine Nucleotide Cycling and Control of Intracellular Redox State in Relation to Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Activity and Nuclear Localization of Glutathione during Exponential Growth of Arabidopsis Cells in Culture. Mol. Plant 2009, 2, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarnocka, W.; Karpiński, S. Friend or foe? Reactive oxygen species production, scavenging and signaling in plant response to environmental stresses. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 122, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Treatment | TASC (µmol g−1 FW) | ASC (µmol g−1 FW) | Ascorbate Redox State | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −NaCl | Control | 1.2 ± 0.16 c | 0.9 ± 0.08 ab | 0.74 ± 0.03 a |
| MD Phe | 1.3 ± 0.03 bc 1.7 ± 0.03 c | 0.9 ± 0.04 ab 1.2 ± 0.05 a | 0.73 ± 0.01 a 0.69 ± 0.02 a | |
| +NaCl | Control | 1.7 ± 0.09 ab | 1.2 ± 0.03 a | 0.69 ± 0.05 a |
| MD Phe | 1.2 ± 0.06 ab 2.1 ± 0.26 a | 0.8 ± 0.04 b 1.2 ± 0.16 a | 0.72 ± 0.00 a 0.57 ± 0.02 b |
| Treatment | TGSH (nmol g−1 FW) | GSH (nmol g−1 FW) | Glutathione Redox State | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −NaCl | Control | 91.1 ± 4.82 c | 86.7 ± 4.25 c | 0.95 ± 0.01 ab |
| MD Phe | 90.1 ± 1.94 c 104.9 ± 7.60 c | 86.1 ± 1.47 c 98.3 ± 6.99 bc | 0.96 ± 0.00 a 0.93 ± 0.00 ab | |
| +NaCl | Control | 104.9 ± 6.66 bc | 96.9 ± 6.62 bc | 0.92 ± 0.00 b |
| MD Phe | 140.5 ± 6.40 a 120.5 ± 6.55 ab | 131.7 ± 6.38 a 112.0 ± 5.63 ab | 0.94 ± 0.00 ab 0.93 ± 0.01 ab |
| Treatment | ASC (µmol g−1 FW) | GSH (nmol g−1 FW) | GSSG (nmol g−1 FW) | Glutathione Redox State | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −NaCl | Control | 4.6 ± 0.7 b | 109.5 ± 1.9 a | 11.4 ± 1.1 b | 0.91 ± 0.01 a |
| MD Phe | 3.7 ± 0.2 bc 4.5 ± 0.6 b | 99.6 ± 5.2 a 114.5 ± 5.4 a | 37.5 ± 1.4 a 30.1 ± 2.8 a | 0.72 ± 0.02 c 0.79 ± 0.02 b | |
| +NaCl | Control | 3.4 ± 0.4 bc | 103.5 ± 7.5 a | 13.5 ± 1.0 b | 0.88 ± 0.01 a |
| MD Phe | 7.1 ± 1.5 a 1.8 ± 0.2 c | 79.3 ± 8.0 b 114.2 ± 6.9 a | 36.3 ± 3.3 a 30.2 ± 2.1 a | 0.68 ± 0.02 c 0.79 ± 0.01 b |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernal-Vicente, A.; Cantabella, D.; Petri, C.; Hernández, J.A.; Diaz-Vivancos, P. The Salt-Stress Response of the Transgenic Plum Line J8-1 and Its Interaction with the Salicylic Acid Biosynthetic Pathway from Mandelonitrile. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113519
Bernal-Vicente A, Cantabella D, Petri C, Hernández JA, Diaz-Vivancos P. The Salt-Stress Response of the Transgenic Plum Line J8-1 and Its Interaction with the Salicylic Acid Biosynthetic Pathway from Mandelonitrile. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113519
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernal-Vicente, Agustina, Daniel Cantabella, Cesar Petri, José Antonio Hernández, and Pedro Diaz-Vivancos. 2018. "The Salt-Stress Response of the Transgenic Plum Line J8-1 and Its Interaction with the Salicylic Acid Biosynthetic Pathway from Mandelonitrile" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113519
APA StyleBernal-Vicente, A., Cantabella, D., Petri, C., Hernández, J. A., & Diaz-Vivancos, P. (2018). The Salt-Stress Response of the Transgenic Plum Line J8-1 and Its Interaction with the Salicylic Acid Biosynthetic Pathway from Mandelonitrile. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113519