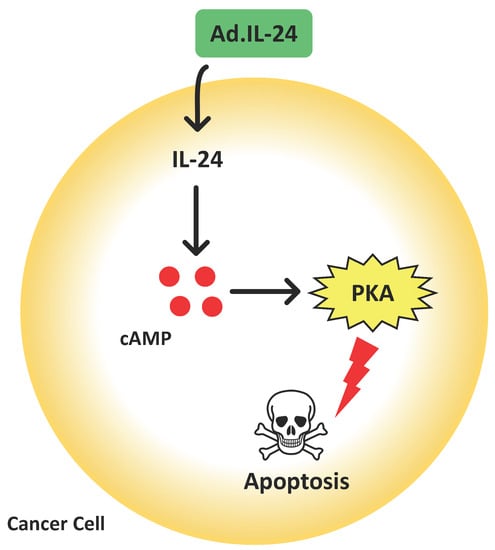
IL-24 Promotes Apoptosis through cAMP-Dependent PKA Pathways in Human Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. IL-24 Regulates the Expression and Phosphorylation of ATF4
2.2. IL-24-Mediated Activation of PKA
2.3. Inhibiting PKA Activity Abrogates the IL-24 Killing Effect
2.4. IL-24 Activates TP53, a Downstream Target of PKA Activity
2.5. PKA Activation Mediates the IL-24 Extrinsic Apoptotic Effect
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells Culture and Reagents
4.2. Virus Infection
4.3. MTT Assays
4.4. Annexin V Binding Assays
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. cAMP Assay
4.7. Immunofluorescence
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chada, S.; Mhashilkar, A.M.; Liu, Y.; Nishikawa, T.; Bocangel, D.; Zheng, M.; Vorburger, S.A.; Pataer, A.; Swisher, S.G.; Ramesh, R.; et al. Mda-7 Gene Transfer Sensitizes Breast Carcinoma Cells to Chemotherapy, Biologic Therapies and Radiotherapy: Correlation with Expression of Bcl-2 Family Members. Cancer Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, Z.X.; Wang, Z.H. Combination of IL-24 and cisplatin inhibits cervical cancer growth in a Xenograft nude mice model. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2011, 12, 3293–3298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sauane, M.; Lebedeva, I.V.; Su, Z.Z.; Choo, H.T.; Randolph, A.; Valerie, K.; Dent, P.; Gopalkrishnan, R.V.; Fisher, P.B. Melanoma Differentiation Associated Gene-7/Interleukin-24 Promotes Tumor Cell-Specific Apoptosis through Both Secretory and Nonsecretory Pathways. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2988–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, R.; Mhashilkar, A.M.; Tanaka, F.; Saito, Y.; Branch, C.D.; Sieger, K.; Mumm, J.B.; Stewart, A.L.; Boquoi, A.; Dumoutier, L.; et al. Melanoma Differentiation-associated Gene 7/Interleukin (IL)-24 Is a Novel Ligand That Regulates Angiogenesis via the IL-22 Receptor Melanoma Differentiation-associated Gene 7/Interleukin (IL)-24 Is a Novel Ligand That Regulates Angiogenesis via. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5105–5113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, R.; Ito, I.; Gopalan, B.; Saito, Y.; Mhashilkar, A.M.; Chada, S. Ectopic production of MDA-7/IL-24 inhibits invasion and migration of human lung cancer cells. Mol Ther. 2004, 9, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeki, T.; Mhashilkar, A.; Swanson, X.; Zou-Yang, X.H.; Sieger, K.; Kawabe, S.; Branch, C.D.; Zumstein, L.; Meyn, R.E.; Roth, J.A.; et al. Inhibition of human lung cancer growth following adenovirus-mediated mda-7 gene expression in vivo. Oncogene 2002, 21, 4558–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, W.; Zhang, K.; Liu, X.Y. Synergistic antitumor effect of TRAIL and IL-24 with complete eradication of hepatoma in the CTGVT-DG strategy. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai) 2012, 44, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Owen, S.; Ruge, F.; Jiang, W.E.N.G. Interleukin-24 (IL-24) Expression and Biological Impact on HECV Endothelial Cells. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 2015, 12, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Persaud, L.; De Jesus, D.; Brannigan, O.; Richiez-Paredes, M.; Huaman, J.; Alvarado, G.; Riker, L.; Mendez, G.; Dejoie, J.; Sauane, M. Mechanism of action and applications of interleukin 24 in immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, W.; Herrera, C.; Mighty, J.; Shumskaya, M.; Redenti, S.M.; Sauane, M. Sigma 1 receptor plays a prominent role in IL-24-induced cancer-specific apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 439, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Wu, M.; Zhang, L.; Thompson, R.; Nath, A.; Chan, C. Signaling dynamics of palmitate-induced ER stress responses mediated by ATF4 in HepG2 cells. BMC Syst. Biol. 2013, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapio, L.; Di Maiolo, F.; Illiano, M.; Esposito, A.; Chiosi, E.; Spina, A.; Naviglio, S. Targeting protein kinase a in cancer therapy: An update. EXCLI J. 2014, 13, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yusta, B.; Baggio, L.L.; Estall, J.L.; Koehler, J.A.; Holland, D.P.; Li, H.; Pipeleers, D.; Ling, Z.; Drucker, D.J. GLP-1 receptor activation improves β cell function and survival following induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell MeTable 2006, 4, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Persaud, L.; Zhong, X.; Alvarado, G.; Do, W.; Dejoie, J.; Zybsteva, A.; Aktas, B.H.; Sauane, M. eIF2α Phosphorylation Mediates IL24-induced Apoptosis through Inhibition of Translation. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Wang, H.-G. CHOP is involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis by enhancing DR5 expression in human carcinoma cells. Am. Soc. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 279, 45495–45502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mccullough, K.D.; Martindale, J.L.; Aw, T.; Holbrook, N.J.; Cullough, K.D.M.C.; Klotz, L. Gadd153 Sensitizes Cells to Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress by Down-Regulating Bcl2 and Perturbing the Cellular Redox State Gadd153 Sensitizes Cells to Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress by Down-Regulating Bcl2 and Perturbing the Cellular Redox State. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puthalakath, H.; O’Reilly, L.A.; Gunn, P.; Lee, L.; Kelly, P.N.; Huntington, N.D.; Hughes, P.D.; Michalak, E.M.; McKimm-Breschkin, J.; Motoyama, N.; et al. ER stress triggers apoptosis by activating BH3-only protein Bim. Cell 2007, 129, 1337–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Samuels, Y.; Li, Q.; Krokowski, D.; Guan, B.-J.; Wang, C.; Jin, Z.; Dong, B.; Cao, B.; Feng, X.; et al. Oncogenic PIK3CA mutations reprogram glutamine metabolism in colorectal cancer. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takayanagi, S.; Fukuda, R.; Takeuchi, Y.; Tsukada, S.; Yoshida, K. Gene regulatory network of unfolded protein response genes in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Stress Chaperones 2013, 18, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pataer, A.; Vorburger, S.A.; Chada, S.; Balachandran, S.; Barber, G.N.; Roth, J.A.; Hunt, K.K.; Swisher, S.G. Melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7 protein physically associates with the double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase PKR. Mol. Ther. 2005, 11, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, D.; Su, Z.-Z.; Lebedeva, I.V.; Sauane, M.; Gopalkrishnan, R.V.; Valerie, K.; Dent, P.; Fisher, P.B. mda-7 (IL-24) Mediates selective apoptosis in human melanoma cells by inducing the coordinated overexpression of the GADD family of genes by means of p38 MAPK. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10054–10059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Bocangel, D.; Ramesh, R.; Ekmekcioglu, S.; Grimm, E.A.; Chada, S. IL-24 overcomes TMZ-resistance and enhances cell death by downregulation of MGMT in human melanoma cells. Gene 2009, 7, 3842–3851. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, X.B.; Zheng, J.W.; Wang, C.J.; Chen, K.; Hu, H.Y.; Hu, H.Y.; Hu, H.; Yu, Y.; Wu, Z.D. Adenovirus vector expressing MDA-7/IL-24 selectively induces growth arrests and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines independent of the state of p53 gene. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2006, 14, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sainz-Perez, A.; Gary-Gouy, H.; Gaudin, F.; Maarof, G.; Marfaing-Koka, A.; de Revel, T.; Dalloul, A. IL-24 induces apoptosis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells engaged into the cell cycle through dephosphorylation of STAT3 and stabilization of p53 expression. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 6051–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiscella, M.; Ullrich, S.J.; Zambrano, N.; Shields, M.T.; Lin, D.; Lees-Miller, S.P.; Anderson, C.W.; Mercer, W.E.; Appella, E. Mutation of the serine 15 phosphorylation site of human p53 reduces the ability of p53 to inhibit cell cycle progression. Oncogene 1993, 8, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Unger, T.; Sionov, R.V.; Moallem, E.; Yee, C.L.; Howley, P.M.; Oren, M.; Haupt, Y. Mutations in serines 15 and 20 of human p53 impair its apoptotic activity. Oncogene 1999, 18, 3205–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Webley, K.; Bond, J.A.; Jones, C.J.; Blaydes, J.P.; Craig, A.; Hupp, T.; Wynford-Thomas, D. Posttranslational modifications of p53 in replicative senescence overlapping but distinct from those induced by DNA damage. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 2803–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shieh, S.Y.; Ikeda, M.; Taya, Y.; Prives, C. DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of p53 alleviates inhibition by MDM2. Cell 1997, 91, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siliciano, J.D.; Canman, C.E.; Taya, Y.; Sakaguchi, K.; Appella, E.; Kastan, M.B. DNA damage induces phosphorylation of the amino-terminus of p53. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 3471–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bean, L.J.; Stark, G.R. Phosphorylation of serines 15 and 37 is necessary for efficient accumulation of p53 following irradiation with UV. Oncogene 2001, 20, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amano, T.; Nakamizo, A.; Mishra, S.K.; Gumin, J.; Shinojima, N.; Sawaya, R.; Lang, F.F. Simultaneous phosphorylation of p53 at serine 15 and 20 induces apoptosis in human glioma cells by increasing expression of pro-apoptotic genes. J. Neurooncol. 2009, 92, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiong, Y. A p53 amino-terminal nuclear export signal inhibited by DNA damage-induced phosphorylation. Science 2001, 292, 1910–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalan, B.; Litvak, A.; Sharma, S.; Mhashilkar, A.M.; Chada, S. Activation of the Fas-FasL Signaling Pathway by MDA-7/IL-24 Kills Human Ovarian Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 3017–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Dong, A.; Gu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; He, L.; Qian, C.; Qian, Q.; et al. The antitumor activity of TRAIL and IL-24 with replicating oncolytic adenovirus in colorectal cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tong, A.W.; Nemunaitis, J.; Su, D.; Zhang, Y.; Cunningham, C.; Senzer, N.; Netto, G.; Rich, D.; Mhashilkar, A.; Parker, K.; et al. Intratumoral injection of INGN 241, a nonreplicating adenovector expressing the melanoma-differentiation associated gene-7 (mda-7/IL24): Biologic outcome in advanced cancer patients. Mol. Ther. 2005, 11, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Su, Z.Z.; Lin, J.J.; Goldstein, N.I.; Young, C.S.; Fisher, P.B. The melanoma differentiation associated gene mda-7 suppresses cancer cell growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9160–9165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebedeva, I.V.; Su, Z.; Chang, Y.; Kitada, S.; Reed, J.C.; Fisher, P.B. The cancer growth suppressing gene mda-7 induces apoptosis selectively in human melanoma cells. Oncogene 2002, 21, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sauane, M.; Gupta, P.; Lebedeva, I.V.; Su, Z.Z.; Sarkar, D.; Randolph, A.; Valerie, K.; Gopalkrishnan, R.V.; Fisher, P.B. N-glycosylation of MDA-7/IL-24 is dispensable for tumor cell-specific apoptosis and “bystander” antitumor activity. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11869–11877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauane, M.; Su, Z.Z.; Dash, R.; Liu, X.; Norris, J.S.; Sarkar, D.; Lee, S.G.; Allegood, J.C.; Dent, P.; Spiegel, S.; et al. Ceramide plays a prominent role in MDA-7/IL-24-induced cancer-specific apoptosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 222, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanker, M.; Gopalan, B.; Patel, S.; Bocangel, D.; Chada, S.; Ramesh, R. Vitamin E succinate in combination with mda-7 results in enhanced human ovarian tumor cell killing through modulation of extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways. Cancer Lett. 2007, 254, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Narayanan, S.; Vazquez, A.; Carpizo, D.R. Small molecule compounds targeting the p53 pathway: Are we finally making progress? Apoptosis 2014, 19, 1055–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebedeva, I.; Rando, R.; Ojwang, J.; Cossum, P.; Stein, C.A. Bcl-xL in prostate cancer cells: Effects of overexpression and down-regulation on chemosensitivity. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 6052–6060. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]







© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Persaud, L.; Mighty, J.; Zhong, X.; Francis, A.; Mendez, M.; Muharam, H.; Redenti, S.M.; Das, D.; Aktas, B.H.; Sauane, M. IL-24 Promotes Apoptosis through cAMP-Dependent PKA Pathways in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113561
Persaud L, Mighty J, Zhong X, Francis A, Mendez M, Muharam H, Redenti SM, Das D, Aktas BH, Sauane M. IL-24 Promotes Apoptosis through cAMP-Dependent PKA Pathways in Human Breast Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113561
Chicago/Turabian StylePersaud, Leah, Jason Mighty, Xuelin Zhong, Ashleigh Francis, Marifer Mendez, Hilal Muharam, Stephen M. Redenti, Dibash Das, Bertal Huseyin Aktas, and Moira Sauane. 2018. "IL-24 Promotes Apoptosis through cAMP-Dependent PKA Pathways in Human Breast Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113561
APA StylePersaud, L., Mighty, J., Zhong, X., Francis, A., Mendez, M., Muharam, H., Redenti, S. M., Das, D., Aktas, B. H., & Sauane, M. (2018). IL-24 Promotes Apoptosis through cAMP-Dependent PKA Pathways in Human Breast Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113561