Insulin Receptor Isoforms in Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Deregulation of IR in Cancer
2.1. IR Overexpression
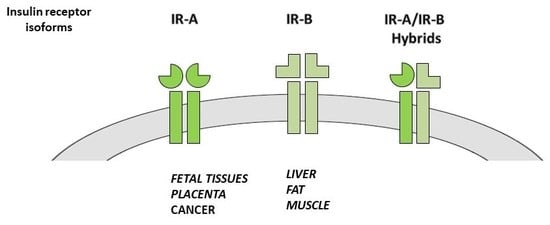
2.2. IR Isoform Expression
3. Mechanisms of Dysregulated IR Expression in Cancer
3.1. Alteration of Transcription
Transcription Factors
3.2. Post-Transcriptional Dysregulation
3.2.1. Alternative Splicing Regulatory Factors
- (a)
- (b)
- hnRNP family proteins are involved in pre-mRNA splicing, mRNA export, stability and translation [95,96]. hRNP H inhibits IR exon 11 splicing [79,97] and interacts with CUG-BP1 promoting a maximum inhibition of IR exon 11 inclusion. hnRNP A1 inhibits, while hnRNP F enhances, inclusion of exon 11 [80]. It has been shown that hnRNPA2/B1 is overexpressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues, but not in normal liver tissues. Moreover, when cancer dedifferentiates, nuclear hnRNPA2/B1 translocates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm [81].
- (c)
- SR (serin/arginine-rich) proteins are alternative splicing regulatory proteins that promote exon inclusion. They also regulate mRNA export and translation [98]. SRSF1 belongs to this family and compete with hnRNP A1 for the same splicing site. Together with SRp20 it promotes exon inclusion recognizing exon splicing enhancers in exon 11 [91]. Loss of SRp20/SRSF3 has been associated with increased IGF-2 and IR-A, which promotes proliferation, Wnt/b-catenin activation and induction of c-Myc along with the promotion of aberrant splicing and epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) genes’ expression. In a significant proportion of cancers SRp20/SRSF3 is absent or mutated, suggesting that this mechanism may contribute to the high IR-A:IR-B ratio in cancer cells (Table 2) [82]. Interestingly, insulin stimulation may induce proteasome-dependent degradation of SRp20/SRSF3, which in turn may favor IGF-2 and IR-A increase.
- (d)
- Muscleblind-like (MBNL) proteins are splicing enhancers involved in the alternative splicing of pre-mRNAs [99]. Antagonizing the action of CUG-BP1 [79,100], and interacting with other splicing regulators (such as hnRNP H), MBNL1 promotes exon 11 inclusion and favors IR-B isoform [101,102]. Indeed, downregulation of MBNL1 and upregulation of CUG-BP1 are associated with reduced IR-B levels [79,103], demonstrating a crucial role for these RNA-binding proteins in both IR-B expression and insulin sensitivity. Different splicing enhancers, such as MBNL1, MBNL2 and SRSF3, promote exon 11 inclusion favoring IR-B expression, while CUG-BP1 is a silencer that promotes exon 11 exclusion thus supporting IR-A predominance (Table 2) [91,102].
3.2.2. Non-Coding RNAs
3.3. Regulation of mRNA Turnover and Translation by RNA Binding Proteins (RBPs)
3.4. IR Degradation
4. Additional Roles of IR Alterations in Cancer Biology
4.1. Involvement in Cancer Cell Stemness
4.2. Correlation with Advanced Cancer Disease
4.3. The IR Implication in Resistance to Targeted Therapies
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tatulian, S.A. Structural dynamics of insulin receptor and transmembrane signaling. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 5523–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasca, F.; Pandini, G.; Sciacca, L.; Pezzino, V.; Squatrito, S.; Belfiore, A.; Vigneri, R. The role of insulin receptors and IGF-I receptors in cancer and other diseases. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 114, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, M.C.; McKern, N.M.; Ward, C.W. Insulin receptor structure and its implications for the IGF-I receptor. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2007, 17, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyts, P. The insulin receptor: A prototype for dimeric, allosteric membrane receptors? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008, 33, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, C.M.; Emanuelli, B.; Kahn, C.R. Critical nodes in signalling pathways: Insights into insulin action. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaid, H.; Antonescu, C.N.; Randhawa, V.K.; Klip, A. Insulin action on glucose transporters through molecular switches, tracks and tethers. Biochem. J. 2008, 413, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKern, N.M.; Lawrence, M.C.; Streltsov, V.A.; Lou, M.Z.; Adams, T.E.; Lovrecz, G.O.; Elleman, T.C.; Richards, K.M.; Bentley, J.D.; Pilling, P.A.; et al. Structure of the insulin receptor ectodomain reveals a folded-over conformation. Nature 2006, 443, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciacca, L.; Prisco, M.; Wu, A.; Belfiore, A.; Vigneri, R.; Baserga, R. Signaling differences from the A and B isoforms of the insulin receptor (IR) in 32D cells in the presence or absence of IR substrate-1. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 2650–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, S.A. The insulin receptor. J. Pediatr. 1984, 104, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Sanchez, C.; Mansilla, A.; de Pablo, F.; Zardoya, R. Evolution of the insulin receptor family and receptor isoform expression in vertebrates. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, J.; Groth, A.V.; Mynarcik, D.C.; Pluzek, L.; Gadsboll, V.L.; Whittaker, L.J. Alanine scanning mutagenesis of a type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor ligand binding site. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 43980–43986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullrich, A.; Gray, A.; Tam, A.W.; Yang-Feng, T.; Tsubokawa, M.; Collins, C.; Henzel, W.; Le Bon, T.; Kathuria, S.; Chen, E.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor primary structure: Comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986, 5, 2503–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belfiore, A.; Frasca, F.; Pandini, G.; Sciacca, L.; Vigneri, R. Insulin receptor isoforms and insulin receptor/insulin-like growth factor receptor hybrids in physiology and disease. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 586–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belfiore, A.; Malaguarnera, R.; Vella, V.; Lawrence, M.C.; Sciacca, L.; Frasca, F.; Morrione, A.; Vigneri, R. Insulin receptor isoforms in physiology and disease: An updated view. Endocr. Rev. 2017, 38, 379–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westermeier, F.; Saez, T.; Arroyo, P.; Toledo, F.; Gutierrez, J.; Sanhueza, C.; Pardo, F.; Leiva, A.; Sobrevia, L. Insulin receptor isoforms: An integrated view focused on gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 350–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denley, A.; Wallace, J.C.; Cosgrove, L.J.; Forbes, B.E. The insulin receptor isoform exon 11-(IR-A) in cancer and other diseases: A review. Horm. Metab. Res. 2003, 35, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frasca, F.; Pandini, G.; Scalia, P.; Sciacca, L.; Mineo, R.; Costantino, A.; Goldfine, I.D.; Belfiore, A.; Vigneri, R. Insulin receptor isoform A, a newly recognized, high-affinity insulin-like growth factor II receptor in fetal and cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 3278–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morcavallo, A.; Gaspari, M.; Pandini, G.; Palummo, A.; Cuda, G.; Larsen, M.R.; Vigneri, R.; Belfiore, A. Research resource: New and diverse substrates for the insulin receptor isoform a revealed by quantitative proteomics after stimulation with IGF-II or insulin. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 1456–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciacca, L.; Cassarino, M.F.; Genua, M.; Pandini, G.; Le Moli, R.; Squatrito, S.; Vigneri, R. Insulin analogues differently activate insulin receptor isoforms and post-receptor signalling. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 1743–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Flier, J.S.; Benecke, H.; Ransil, B.J.; Moller, D.E. Ligand-binding properties of the two isoforms of the human insulin receptor. Endocrinology 1993, 132, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benyoucef, S.; Surinya, K.H.; Hadaschik, D.; Siddle, K. Characterization of insulin/IGF hybrid receptors: Contributions of the insulin receptor L2 and Fn1 domains and the alternatively spliced exon 11 sequence to ligand binding and receptor activation. Biochem. J. 2007, 403, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanquart, C.; Achi, J.; Issad, T. Characterization of IRA/IRB hybrid insulin receptors using bioluminescence resonance energy transfer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaguarnera, R.; Belfiore, A. The emerging role of insulin and insulin-like growth factor signaling in cancer stem cells. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2014, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandini, G.; Medico, E.; Conte, E.; Sciacca, L.; Vigneri, R.; Belfiore, A. Differential gene expression induced by insulin and insulin-like growth factor-II through the insulin receptor isoform A. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 42178–42189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, J.A.; Varewijck, A.J. IGF-IR targeted therapy: Past, present and future. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2014, 5, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belfiore, A.; Malaguarnera, R. Insulin receptor and cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2011, 18, R125–R147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneri, R.; Goldfine, I.D.; Frittitta, L. Insulin, insulin receptors, and cancer. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2016, 39, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, V.; Pezzino, V.; Costantino, A.; Belfiore, A.; Giuffrida, D.; Frittitta, L.; Vannelli, G.B.; Brand, R.; Goldfine, I.D.; Vigneri, R. Elevated insulin receptor content in human breast cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 1503–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciacca, L.; Costantino, A.; Pandini, G.; Mineo, R.; Frasca, F.; Scalia, P.; Sbraccia, P.; Goldfine, I.D.; Vigneri, R.; Belfiore, A. Insulin receptor activation by IGF-II in breast cancers: Evidence for a new autocrine/paracrine mechanism. Oncogene 1999, 18, 2471–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljada, A.; Saleh, A.M.; Al-Aqeel, S.M.; Shamsa, H.B.; Al-Bawab, A.; Al Dubayee, M.; Ahmed, A.A. Quantification of insulin receptor mRNA splice variants as a diagnostic tumor marker in breast cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2015, 15, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Morehouse, C.; Streicher, K.; Higgs, B.W.; Gao, J.; Czapiga, M.; Boutrin, A.; Zhu, W.; Brohawn, P.; Chang, Y.; et al. Altered expression of insulin receptor isoforms in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breen, K.J.; O’Neill, A.; Murphy, L.; Fan, Y.; Boyce, S.; Fitzgerald, N.; Dorris, E.; Brady, L.; Finn, S.P.; Hayes, B.D.; et al. Investigating the role of the IGF axis as a predictor of biochemical recurrence in prostate cancer patients post-surgery. Prostate 2017, 77, 1288–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, M.E.; Gleave, M.E.; Zakikhani, M.; Bell, R.H.; Piura, E.; Vickers, E.; Cunningham, M.; Larsson, O.; Fazli, L.; Pollak, M. Insulin receptor expression by human prostate cancers. Prostate 2009, 69, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heni, M.; Hennenlotter, J.; Scharpf, M.; Lutz, S.Z.; Schwentner, C.; Todenhofer, T.; Schilling, D.; Kuhs, U.; Gerber, V.; Machicao, F.; et al. Insulin receptor isoforms A and B as well as insulin receptor substrates-1 and -2 are differentially expressed in prostate cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perks, C.M.; Zielinska, H.A.; Wang, J.; Jarrett, C.; Frankow, A.; Ladomery, M.R.; Bahl, A.; Rhodes, A.; Oxley, J.; Holly, J.M. Insulin receptor isoform variations in prostate cancer cells. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2016, 7, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.F.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, L.J.; Qi, W.J.; Li, X.P.; Wang, J.L.; Wei, L.H. Overexpression of the insulin receptor isoform A promotes endometrial carcinoma cell growth. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flannery, C.A.; Saleh, F.L.; Choe, G.H.; Selen, D.J.; Kodaman, P.H.; Kliman, H.J.; Wood, T.L.; Taylor, H.S. Differential expression of IR-A, IR-B and IGF-1R in endometrial physiology and distinct signature in adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 2883–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalli, K.R.; Falowo, O.I.; Bale, L.K.; Zschunke, M.A.; Roche, P.C.; Conover, C.A. Functional insulin receptors on human epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells: Implications for IGF-II mitogenic signaling. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 3259–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chettouh, H.; Fartoux, L.; Aoudjehane, L.; Wendum, D.; Claperon, A.; Chretien, Y.; Rey, C.; Scatton, O.; Soubrane, O.; Conti, F.; et al. Mitogenic insulin receptor-A is overexpressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma due to EGFR-mediated dysregulation of RNA splicing factors. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3974–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleem, E.; Nehrbass, D.; Klimek, F.; Mayer, D.; Bannasch, P. Upregulation of the insulin receptor and type I insulin-like growth factor receptor are early events in hepatocarcinogenesis. Toxicol. Pathol. 2011, 39, 524–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, Y.; Kubota, N.; Takamoto, I.; Obata, A.; Iwamoto, M.; Hayashi, T.; Aihara, M.; Kubota, T.; Nishihara, H.; Kadowaki, T. Role of insulin receptor substrates in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roudnicky, F.; Dieterich, L.C.; Poyet, C.; Buser, L.; Wild, P.; Tang, D.; Camenzind, P.; Ho, C.H.; Otto, V.I.; Detmar, M. High expression of insulin receptor on tumour-associated blood vessels in invasive bladder cancer predicts poor overall and progression-free survival. J. Pathol. 2017, 242, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Zhu, W.; Streicher, K.; Morehouse, C.; Brohawn, P.; Ge, X.; Dong, Z.; Yin, X.; Zhu, G.; Gu, Y.; et al. Increased IR-A/IR-B ratio in non-small cell lung cancers associates with lower epithelial-mesenchymal transition signature and longer survival in squamous cell lung carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andres, S.F.; Simmons, J.G.; Mah, A.T.; Santoro, M.A.; Van Landeghem, L.; Lund, P.K. Insulin receptor isoform switching in intestinal stem cells, progenitors, differentiated lineages and tumors: Evidence that IR-B limits proliferation. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 5645–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frittitta, L.; Sciacca, L.; Catalfamo, R.; Ippolito, A.; Gangemi, P.; Pezzino, V.; Filetti, S.; Vigneri, R. Functional insulin receptors are overexpressed in thyroid tumors: Is this an early event in thyroid tumorigenesis? Cancer 1999, 85, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, V.; Pandini, G.; Sciacca, L.; Mineo, R.; Vigneri, R.; Pezzino, V.; Belfiore, A. A novel autocrine loop involving IGF-II and the insulin receptor isoform-A stimulates growth of thyroid cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaguarnera, R.; Frasca, F.; Garozzo, A.; Giani, F.; Pandini, G.; Vella, V.; Vigneri, R.; Belfiore, A. Insulin receptor isoforms and insulin-like growth factor receptor in human follicular cell precursors from papillary thyroid cancer and normal thyroid. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avnet, S.; Sciacca, L.; Salerno, M.; Gancitano, G.; Cassarino, M.F.; Longhi, A.; Zakikhani, M.; Carboni, J.M.; Gottardis, M.; Giunti, A.; et al. Insulin receptor isoform A and insulin-like growth factor II as additional treatment targets in human osteosarcoma. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2443–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, M.C.; Clark, G.M.; Allred, D.C.; Goldfine, I.D.; Vigneri, R. Insulin receptor expression and clinical outcome in node-negative breast cancer. Proc. Assoc. Am. Physicians 1997, 109, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rostoker, R.; Abelson, S.; Bitton-Worms, K.; Genkin, I.; Ben-Shmuel, S.; Dakwar, M.; Orr, Z.S.; Caspi, A.; Tzukerman, M.; LeRoith, D. Highly specific role of the insulin receptor in breast cancer progression. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Gong, G.; Ben, Q.; Qiu, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, L. Increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Lee, M.S.; Tsai, P.Y.; Adler, A.S.; Curry, N.L.; Challa, S.; Freinkman, E.; Hitchcock, D.S.; Copps, K.D.; White, M.F.; et al. Ablation of insulin receptor substrates 1 and 2 suppresses Kras-driven lung tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4228–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, C.M.; Zimmermann, K.; Zillessen, P.; Pfeifer, A.; Racke, K.; Mayer, P. Non-small cell lung cancer cell survival crucially depends on functional insulin receptors. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vella, V.; Sciacca, L.; Pandini, G.; Mineo, R.; Squatrito, S.; Vigneri, R.; Belfiore, A. The IGF system in thyroid cancer: New concepts. Mol. Pathol. 2001, 54, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcaro, A.; Doepfner, K.T.; Boller, D.; Guerreiro, A.S.; Shalaby, T.; Jackson, S.P.; Schoenwaelder, S.M.; Delattre, O.; Grotzer, M.A.; Fischer, B. Novel role for insulin as an autocrine growth factor for malignant brain tumour cells. Biochem. J. 2007, 406, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harrington, S.C.; Weroha, S.J.; Reynolds, C.; Suman, V.J.; Lingle, W.L.; Haluska, P. Quantifying insulin receptor isoform expression in FFPE breast tumors. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2012, 22, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bjorner, S.; Rosendahl, A.H.; Simonsson, M.; Markkula, A.; Jirstrom, K.; Borgquist, S.; Rose, C.; Ingvar, C.; Jernstrom, H. Combined and individual tumor-specific expression of insulin-like growth factor-I receptor, insulin receptor and phospho-insulin-like growth factor-I receptor/insulin receptor in primary breast cancer: Implications for prognosis in different treatment groups. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 9093–9107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heidegger, I.; Kern, J.; Ofer, P.; Klocker, H.; Massoner, P. Oncogenic functions of IGF1R and INSR in prostate cancer include enhanced tumor growth, cell migration and angiogenesis. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2723–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keku, T.O.; Lund, P.K.; Galanko, J.; Simmons, J.G.; Woosley, J.T.; Sandler, R.S. Insulin resistance, apoptosis, and colorectal adenoma risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2005, 14, 2076–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, A.C.; Lund, P.K.; Hoyo, C.; Galanko, J.; Burcal, L.; Holston, R.; Massa, B.; Omofoye, O.; Sandler, R.S.; Keku, T.O. Elevated C-peptide and insulin predict increased risk of colorectal adenomas in normal mucosa. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, M.A.; Andres, S.F.; Galanko, J.A.; Sandler, R.S.; Keku, T.O.; Lund, P.K. Reduced insulin-like growth factor I receptor and altered insulin receptor isoform mRNAs in normal mucosa predict colorectal adenoma risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 2093–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forest, A.; Amatulli, M.; Ludwig, D.L.; Damoci, C.B.; Wang, Y.; Burns, C.A.; Donoho, G.P.; Zanella, N.; Fiebig, H.H.; Prewett, M.C.; et al. Intrinsic resistance to cixutumumab is conferred by distinct isoforms of the insulin receptor. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 1615–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vella, V.; Puppin, C.; Damante, G.; Vigneri, R.; Sanfilippo, M.; Vigneri, P.; Tell, G.; Frasca, F. DeltaNp73alpha inhibits PTEN expression in thyroid cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 2539–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avnet, S.; Perut, F.; Salerno, M.; Sciacca, L.; Baldini, N. Insulin receptor isoforms are differently expressed during human osteoblastogenesis. Differentiation 2012, 83, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, L.E.; Chuan, Y.C.; Lewitt, M.; Fernandez-Perez, L.; Carrasco-Rodriguez, S.; Sanchez-Gomez, M.; Flores-Morales, A. IGF-II regulates metastatic properties of choriocarcinoma cells through the activation of the insulin receptor. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2007, 13, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sciacca, L.; Mineo, R.; Pandini, G.; Murabito, A.; Vigneri, R.; Belfiore, A. In IGF-I receptor-deficient leiomyosarcoma cells autocrine IGF-II induces cell invasion and protection from apoptosis via the insulin receptor isoform A. Oncogene 2002, 21, 8240–8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Chang, Q.; Rubin, B.P.; Fletcher, C.D.; Morgan, T.W.; Mentzer, S.J.; Sugarbaker, D.J.; Fletcher, J.A.; Xiao, S. Insulin receptor activation in solitary fibrous tumours. J. Pathol. 2007, 211, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciacca, L.; Cassarino, M.F.; Genua, M.; Vigneri, P.; Giovanna Pennisi, M.; Malandrino, P.; Squatrito, S.; Pezzino, V.; Vigneri, R. Biological effects of insulin and its analogs on cancer cells with different insulin family receptor expression. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 1817–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusi, K.; Maezono, K.; Osman, A.; Pendergrass, M.; Patti, M.E.; Pratipanawatr, T.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Kahn, C.R.; Mandarino, L.J. Insulin resistance differentially affects the PI 3-kinase- and MAP kinase-mediated signaling in human muscle. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciacca, L.; Vigneri, R.; Tumminia, A.; Frasca, F.; Squatrito, S.; Frittitta, L.; Vigneri, P. Clinical and molecular mechanisms favoring cancer initiation and progression in diabetic patients. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 23, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, A.; Pandini, G.; Sarfstein, R.; Werner, H.; Manfioletti, G.; Vigneri, R.; Belfiore, A. HMGA1 protein is a positive regulator of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor gene. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 1919–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiefari, E.; Tanyolac, S.; Iiritano, S.; Sciacqua, A.; Capula, C.; Arcidiacono, B.; Nocera, A.; Possidente, K.; Baudi, F.; Ventura, V.; et al. A polymorphism of HMGA1 is associated with increased risk of metabolic syndrome and related components. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foti, D.; Iuliano, R.; Chiefari, E.; Brunetti, A. A nucleoprotein complex containing Sp1, C/EBP beta, and HMGI-Y controls human insulin receptor gene transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 2720–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlsson, C.; Kley, N.; Werner, H.; LeRoith, D. P53 regulates insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptor expression and IGF-I-induced tyrosine phosphorylation in an osteosarcoma cell line: Interaction between p53 and Sp1. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, N.J.; Resnik, J.L.; Reichart, D.B.; Strauss, B.; Haas, M.; Seely, B.L. Repression of the insulin receptor promoter by the tumor suppressor gene product p53: A possible mechanism for receptor overexpression in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 2781–2788. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baserga, R. Oncogenes and the strategy of growth factors. Cell 1994, 79, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, O.; Tjian, R. Transcriptional feedback control of insulin receptor by dFOXO/FOXO1. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 2435–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spriggs, K.A.; Cobbold, L.C.; Ridley, S.H.; Coldwell, M.; Bottley, A.; Bushell, M.; Willis, A.E.; Siddle, K. The human insulin receptor mRNA contains a functional internal ribosome entry segment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 5881–5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paul, S.; Dansithong, W.; Kim, D.; Rossi, J.; Webster, N.J.; Comai, L.; Reddy, S. Interaction of muscleblind, CUG-BP1 and hnRNP H proteins in DM1-associated aberrant IR splicing. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 4271–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talukdar, I.; Sen, S.; Urbano, R.; Thompson, J.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Webster, N.J. hnRNP A1 and hnRNP F modulate the alternative splicing of exon 11 of the insulin receptor gene. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Wu, F.; Sun, Y.; Fan, G.; Wang, Q. Up-regulation and subcellular localization of hnRNP A2/B1 in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, S.; Langiewicz, M.; Jumaa, H.; Webster, N.J. Deletion of serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 3 in hepatocytes predisposes to hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Hepatology 2015, 61, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Lou, C.; Xiao, H.; Yang, Y.; Cai, X.; Li, C.; Jia, S.; Huang, Y. Mir-128 regulation of glucose metabolism and cell proliferation in triple-negative breast cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2018, 105, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovat, F.; Fassan, M.; Gasparini, P.; Rizzotto, L.; Cascione, L.; Pizzi, M.; Vicentini, C.; Balatti, V.; Palmieri, D.; Costinean, S.; et al. miR-15b/16-2 deletion promotes B-cell malignancies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11636–11641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, H.; Enokida, H.; Chiyomaru, T.; Tatarano, S.; Hidaka, H.; Yamasaki, T.; Gotannda, T.; Tachiwada, T.; Nohata, N.; Yamane, T.; et al. Tumor suppressive microRNA-1 mediated novel apoptosis pathways through direct inhibition of splicing factor serine/arginine-rich 9 (SRSF9/SRp30c) in bladder cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahl, M.C.; Will, C.L.; Luhrmann, R. The spliceosome: Design principles of a dynamic RNP machine. Cell 2009, 136, 701–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Will, C.L.; Luhrmann, R. Spliceosome structure and function. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a003707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Shai, O.; Lee, L.J.; Frey, B.J.; Blencowe, B.J. Deep surveying of alternative splicing complexity in the human transcriptome by high-throughput sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1413–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.T.; Sandberg, R.; Luo, S.; Khrebtukova, I.; Zhang, L.; Mayr, C.; Kingsmore, S.F.; Schroth, G.P.; Burge, C.B. Alternative isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes. Nature 2008, 456, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Black, D.L. Protein diversity from alternative splicing: A challenge for bioinformatics and post-genome biology. Cell 2000, 103, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Talukdar, I.; Webster, N.J. SRp20 and CUG-BP1 modulate insulin receptor exon 11 alternative splicing. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminska, D.; Hamalainen, M.; Cederberg, H.; Kakela, P.; Venesmaa, S.; Miettinen, P.; Ilves, I.; Herzig, K.H.; Kolehmainen, M.; Karhunen, L.; et al. Adipose tissue INSR splicing in humans associates with fasting insulin level and is regulated by weight loss. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.T.; Donahue, J.M.; Xiao, L.; Cui, Y.; Rao, J.N.; Turner, D.J.; Twaddell, W.S.; Wang, J.Y.; Battafarano, R.J. The RNA-binding protein CUG-BP1 increases survivin expression in oesophageal cancer cells through enhanced mRNA stability. Biochem. J. 2012, 446, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Philips, A.V.; Timchenko, L.T.; Cooper, T.A. Disruption of splicing regulated by a CUG-binding protein in myotonic dystrophy. Science 1998, 280, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.K.; Kim, H.H.; Kuwano, Y.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Srikantan, S.; Subaran, S.S.; Gleichmann, M.; Mughal, M.R.; Martindale, J.L.; Yang, X.; et al. hnRNP C promotes APP translation by competing with FMRP for APP mRNA recruitment to P bodies. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shetty, S. Regulation of urokinase receptor mRNA stability by hnRNP C in lung epithelial cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2005, 272, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Dansithong, W.; Jog, S.P.; Holt, I.; Mittal, S.; Brook, J.D.; Morris, G.E.; Comai, L.; Reddy, S. Expanded CUG repeats dysregulate RNA splicing by altering the stoichiometry of the muscleblind 1 complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 38427–38438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepard, P.J.; Hertel, K.J. The SR protein family. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Konieczny, P.; Stepniak-Konieczna, E.; Sobczak, K. MBNL proteins and their target RNAs, interaction and splicing regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 10873–10887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, X.; Miller, J.W.; Mankodi, A.; Kanadia, R.N.; Yuan, Y.; Moxley, R.T.; Swanson, M.S.; Thornton, C.A. Failure of MBNL1-dependent post-natal splicing transitions in myotonic dystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 2087–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, T.H.; Charlet, B.N.; Poulos, M.G.; Singh, G.; Swanson, M.S.; Cooper, T.A. Muscleblind proteins regulate alternative splicing. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 3103–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sen, S.; Talukdar, I.; Liu, Y.; Tam, J.; Reddy, S.; Webster, N.J. Muscleblind-like 1 (MBNL1) promotes insulin receptor exon 11 inclusion via binding to a downstream evolutionarily conserved intronic enhancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 25426–25437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dansithong, W.; Paul, S.; Comai, L.; Reddy, S. MBNL1 is the primary determinant of focus formation and aberrant insulin receptor splicing in DM1. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 5773–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Her, S.; Kim, M.; Jang, I.S.; Park, J. The expression of damage-regulated autophagy modulator 2 (DRAM2) contributes to autophagy induction. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. Micrornas: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Slack, F.J. Oncomirs—MicroRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Maruyama, R.; Yamamoto, E.; Kai, M. DNA methylation and microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsugane, S.; Inoue, M. Insulin resistance and cancer: Epidemiological evidence. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Venables, J.P. Unbalanced alternative splicing and its significance in cancer. Bioessays 2006, 28, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M. Posttranscriptional gene regulation by long noncoding RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 3723–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisino, G.; Zhou, A.X.; Dahr, N.; Sabirsh, A.; Soundarapandian, M.M.; Perera, R.; Larsson-Lekholm, E.; Magnone, M.C.; Althage, M.; Tyrberg, B. Long noncoding RNAs are dynamically regulated during beta-cell mass expansion in mouse pregnancy and control beta-cell proliferation in vitro. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, B.C.; Graham, L.D.; Molloy, P.L. CRNDE, a long non-coding RNA responsive to insulin/IGF signaling, regulates genes involved in central metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marr, M.T., 2nd; D’Alessio, J.A.; Puig, O.; Tjian, R. IRES-mediated functional coupling of transcription and translation amplifies insulin receptor feedback. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olson, C.M.; Donovan, M.R.; Spellberg, M.J.; Marr, M.T., 2nd. The insulin receptor cellular IRES confers resistance to eIF4A inhibition. eLife 2013, 2, e00542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Velden, A.W.; Thomas, A.A. The role of the 5’ untranslated region of an mRNA in translation regulation during development. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1999, 31, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, J.R., 3rd; Roth, J.; Neville, D.M., Jr.; de Meyts, P.; Buell, D.N. Insulin-dependent regulation of insulin receptor concentrations: A direct demonstration in cell culture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarajan, A.; Petersen, M.C.; Nasiri, A.R.; Butrico, G.; Fung, A.; Ruan, H.B.; Kursawe, R.; Caprio, S.; Thibodeau, J.; Bourgeois-Daigneault, M.C.; et al. MARCH1 regulates insulin sensitivity by controlling cell surface insulin receptor levels. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, T.; Xu, Y. P53 and stem cells: New developments and new concerns. Trends Cell Biol. 2010, 20, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelenko, Z.; Gallagher, E.J.; Antoniou, I.M.; Sachdev, D.; Nayak, A.; Yee, D.; LeRoith, D. EMT reversal in human cancer cells after IR knockdown in hyperinsulinemic mice. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giani, F.; Vella, V.; Nicolosi, M.L.; Fierabracci, A.; Lotta, S.; Malaguarnera, R.; Belfiore, A.; Vigneri, R.; Frasca, F. Thyrospheres from normal or malignant thyroid tissue have different biological, functional, and genetic features. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E1168–E1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaguarnera, R.; Nicolosi, M.L.; Sacco, A.; Morcavallo, A.; Vella, V.; Voci, C.; Spatuzza, M.; Xu, S.Q.; Iozzo, R.V.; Vigneri, R.; et al. Novel cross talk between IGF-IR and DDR1 regulates IGF-IR trafficking, signaling and biological responses. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 16084–16105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mata, R.; Palladino, C.; Nicolosi, M.L.; Lo Presti, A.R.; Malaguarnera, R.; Ragusa, M.; Sciortino, D.; Morrione, A.; Maggiolini, M.; Vella, V.; et al. IGF-I induces upregulation of DDR1 collagen receptor in breast cancer cells by suppressing MIR-199a-5p through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 7683–7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belfiore, A.; Malaguarnera, R.; Nicolosi, M.L.; Lappano, R.; Ragusa, M.; Morrione, A.; Vella, V. A novel functional crosstalk between DDR1 and the IGF axis and its relevance for breast cancer. Cell Adh. Migr. 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vella, V.; Malaguarnera, R.; Nicolosi, M.L.; Palladino, C.; Spoleti, C.; Massimino, M.; Vigneri, P.; Purrello, M.; Ragusa, M.; Morrione, A.; et al. Discoidin domain receptor 1 modulates insulin receptor signaling and biological responses in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 43248–43270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vella, V.; Nicolosi, M.L.; Cantafio, P.; Massimino, M.; Lappano, R.; Vigneri, P.; Ciuni, R.; Gangemi, P.; Morrione, A.; Malaguarnera, R.; et al. DDR1 regulates thyroid cancer cell differentiation via IGF-2/IR-A autocrine signaling loop. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Dong, W.; Shen, H.; Xu, J.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Q.; Du, J. Combinational therapy enhances the effects of anti-IGF-1R mAb Figitumumab to target small cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, H.; Aleksic, T.; Haluska, P.; Macaulay, V.M. Can we unlock the potential of IGF-1R inhibition in cancer therapy? Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 1096–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Livingstone, C. IGF2 and cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2013, 20, R321–R339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malaguarnera, R.; Vella, V.; Nicolosi, M.L.; Belfiore, A. Insulin resistance: Any role in the changing epidemiology of thyroid cancer? Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2017, 8, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciacca, L.; Vella, V.; Frittitta, L.; Tumminia, A.; Manzella, L.; Squatrito, S.; Belfiore, A.; Vigneri, R. Long-acting insulin analogs and cancer. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 28, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, E.; Gokhale, P.C.; Koujak, S.; Brown, E.; Eyzaguirre, A.; Tao, N.; Rosenfeld-Franklin, M.; Lerner, L.; Chiu, M.I.; Wild, R.; et al. Compensatory insulin receptor (IR) activation on inhibition of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R): Rationale for cotargeting IGF-1R and IR in cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 2652–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulanet, D.B.; Ludwig, D.L.; Kahn, C.R.; Hanahan, D. Insulin receptor functionally enhances multistage tumor progression and conveys intrinsic resistance to IGF-1R targeted therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 10791–10798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dinchuk, J.E.; Cao, C.; Huang, F.; Reeves, K.A.; Wang, J.; Myers, F.; Cantor, G.H.; Zhou, X.; Attar, R.M.; Gottardis, M.; et al. Insulin receptor (IR) pathway hyperactivity in IGF-IR null cells and suppression of downstream growth signaling using the dual IGF-IR/IR inhibitor, BMS-754807. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 4123–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, C.; Manara, M.C.; Nicoletti, G.; Marino, M.T.; Lollini, P.L.; Astolfi, A.; Pandini, G.; Lopez-Guerrero, J.A.; Schaefer, K.L.; Belfiore, A.; et al. Efficacy of and resistance to anti-IGF-1R therapies in ewing’s sarcoma is dependent on insulin receptor signaling. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2730–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Pelzer, A.M.; Kiang, D.T.; Yee, D. Down-regulation of type I insulin-like growth factor receptor increases sensitivity of breast cancer cells to insulin. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulvihill, M.J.; Cooke, A.; Rosenfeld-Franklin, M.; Buck, E.; Foreman, K.; Landfair, D.; O’Connor, M.; Pirritt, C.; Sun, Y.; Yao, Y.; et al. Discovery of OSI-906: A selective and orally efficacious dual inhibitor of the IGF-1 receptor and insulin receptor. Future Med. Chem. 2009, 1, 1153–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheirandish, M.; Mahboobi, H.; Yazdanparast, M.; Kamal, W.; Kamal, M.A. Anti-cancer effects of metformin: Recent evidences for its role in prevention and treatment of cancer. Curr. Drug Metab. 2018, 19, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vella, V.; Nicolosi, M.L.; Giuliano, S.; Bellomo, M.; Belfiore, A.; Malaguarnera, R. PPAR-gamma agonists as antineoplastic agents in cancers with dysregulated IGF axis. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2017, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ru, Y.; Zhong, D.; Zhang, J.; Yao, L.; Li, X. Engineered ubiquitin ligase PTB-U-box targets insulin/insulin-like growth factor receptor for degradation and coordinately inhibits cancer malignancy. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 4945–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Cancer Type | Model | IR | IR-A | IR-B | IR-A:IR-B Ratio | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hormone-dependent | ||||||
| Breast | h-BC specimens |  | [28] | |||
| h-BC cell lines and specimens |  | [17,29] | ||||
| h-BC specimens |  |  |  | [30] | ||
| h-BC specimens |  |  |  | [31] | ||
| Prostate | h-PC specimens |  | [32,33] | |||
| h-PC specimens |  | [34] | ||||
| h-PC cell lines |  | [35] | ||||
| Endometrial | h-EC cell lines and specimens |  |  | [36] | ||
| h-EC specimens |  |  | [37] | |||
| Ovarian | h-OV cell lines |  |  | [38] | ||
| Hormone- independent | ||||||
| Liver | h-HCC specimens |  |  |  |  | [39] |
| r-HCC specimens |  | [40] | ||||
| m-HCC specimens |  |  | [41] | |||
| Bladder | h-BLC specimens |  | [42] | |||
| Lung | h-NSCLC specimens |  |  | [43] | ||
| h-LC specimens |  | [17] | ||||
| Colon | m-PCA, h-CC cell lines |  | [44] | |||
| h-CC specimens |  | [17] | ||||
| Thyroid | h-TC specimens |  | [45] | |||
| h-TC cell lines and specimens |  |  | [46] | |||
| h-TC cell lines |  | [47] | ||||
| Osteosarcoma | h-OS cell lines and specimens |  | [48] |
| Mechanism of Altered IR Expression | Dysregulation | References |
|---|---|---|
| IR transcription factors upregulation (Sp1, HMGA1, or FOXO1) | IR upregulation | [73] |
| p53 inactivation | IR upregulation | [75] |
| Enhanced IRES-mediated IR mRNA translocation to the ribosomes | IR upregulation | [78] |
| CUG-BP1 increase | Increased IRA:IRB ratio | [79] |
| hRNP H increase | Increased IRA:IRB ratio | [79] |
| hRNP A1 increase | Increased IRA:IRB ratio | [80] |
| hRNP A2/B1 increase | Increased IRA:IRB ratio | [81] |
| Loss of SRSF3 and SRp20 | Increased IGF2 and IRA:IRB ratio | [82] |
| MBNL downregulation | Increased IRA:IRB ratio | [79] |
| mir-128 downregulation | Increased IRA:IRB ratio | [83] |
| mir-15b/16-2 downregulation | Increased IRA:IRB ratio | [84] |
| mir-1 downregulation | Increased IRA:IRB ratio | [85] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vella, V.; Milluzzo, A.; Scalisi, N.M.; Vigneri, P.; Sciacca, L. Insulin Receptor Isoforms in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113615
Vella V, Milluzzo A, Scalisi NM, Vigneri P, Sciacca L. Insulin Receptor Isoforms in Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113615
Chicago/Turabian StyleVella, Veronica, Agostino Milluzzo, Nunzio Massimo Scalisi, Paolo Vigneri, and Laura Sciacca. 2018. "Insulin Receptor Isoforms in Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113615
APA StyleVella, V., Milluzzo, A., Scalisi, N. M., Vigneri, P., & Sciacca, L. (2018). Insulin Receptor Isoforms in Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113615