Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Populus deltoides Leaf Extract via Modulating NF-κB and p38/JNK Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of P. deltoides Leaf Extract on LPS-Stimulated iNOS and NO in RAW 264.7 Cells
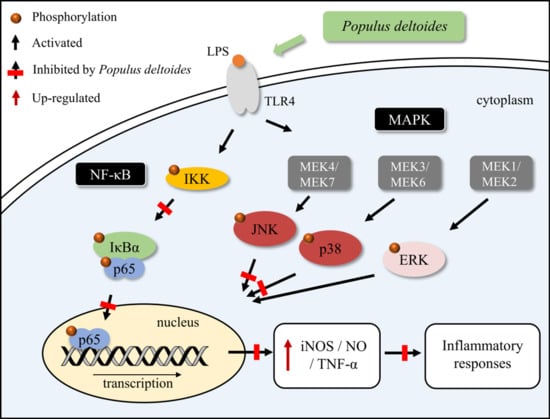
2.2. Effects of P. deltoides Leaf Extract on the NF-κB Signaling in LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells
2.3. Effects of P. deltoides Leaf Extract on MAPK Signaling in LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Methanol Extract of P. deltoides
4.2. RAW 264.7 Cell Culture and Cell Viability Assay
4.3. NO Production
4.4. ELISA
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Confocal Microscope Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Wang, C.-C. Inflammatory response of macrophages in infection. HBPD Int. 2014, 13, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, M.; Mackman, N. LPS induction of gene expression in human monocytes. Cell. Signal. 2001, 13, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.C.; Liang, Y.H.; Chiang, J.H.; Liu, F.C.; Lin, W.H.; Chang, S.J.; Lin, W.Y.; Wu, C.H.; Weng, J.R. Anti-inflammatory effects of Calophyllum inophyllum L. in RAW264.7 cells. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Cai, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Hou, B.; Zhu, X.; Qiu, L. Vaccaria hypaphorine alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation via inactivation of NFκB and ERK pathways in Raw 264.7 cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivashkiv, L.B. Inflammatory signaling in macrophages: Transitions from acute to tolerant and alternative activation states. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 2477–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biswas, S.K.; Allavena, P.; Mantovani, A. Tumor-associated macrophages: Functional diversity, clinical significance, and open questions. Semin. Immunopathol. 2013, 35, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, K.J.; Sheedy, F.J.; Fisher, E.A. Macrophages in atherosclerosis: A dynamic balance. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Gonzalez, J.F.; Mora-Fernandez, C. The role of inflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donate-Correa, J.; Martin-Nunez, E.; Muros-de-Fuentes, M.; Mora-Fernandez, C.; Navarro-Gonzalez, J.F. Inflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy. J. Diabetes. Res. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.A.; Das, A.; Ray, S.K.; Banik, N.L. Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines released from microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res. Bull. 2012, 87, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korhonen, R.; Lahti, A.; Kankaanranta, H.; Moilanen, E. Nitric oxide production and signaling in inflammation. Curr. Drug. Targets. Inflamm. Allergy. 2005, 4, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Jiang, W.; Dong, C.; Li, C.; Fu, X.; Min, L.; Tian, J.; Jin, H.; Shen, J. Anti-inflammatory effects of sophocarpine in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells via NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways. Toxicol. In Vitro 2012, 26, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.K.; Choi, E.J. Compromised MAPK signaling in human diseases: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 867–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neacsu, P.; Mazare, A.; Schmuki, P.; Cimpean, A. Attenuation of the macrophage inflammatory activity byTiO2 nanotubes via inhibition of MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 6455–6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Ryu, A.R.; Jin, S.; Jeon, Y.M.; Lee, M.Y. Chlorin e6-mediated photodynamic therapy suppresses P. acnes-induced inflammatory response via NFκB and MAPKs signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limtrakul, P.; Yodkeeree, S.; Pitchakarn, P.; Punfa, W. Anti-inflammatory effects of proanthocyanidin-rich red rice extract via suppression of MAPK, AP-1 and NF-κB pathways in Raw 264.7 macrophages. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2016, 10, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, P.; Aggarwal, A. NF-kB transcription factor: A key player in the generation of immune response. Curr. Sci. 2006, 90, 519–531. [Google Scholar]
- Doerks, T.; Copley, R.R.; Schultz, J.; Ponting, C.P.; Bork, P. Systematic identification of novel protein domain families associated with nuclear functions. Genome. Res. 2002, 12, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, N.D. Integrating cell-signalling pathways with NF-κB and IKK function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 8, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.Y.; Lee, M.J.; You, B.R.; Jin, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Yun, Y.R.; Kim, H.J. Allium hookeri root extract exerts anti-inflammatory effects by nuclear factor-κB down-regulation in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.C.; Jee, S.Y.; Lee, S.G.; Park, S.J.; Lee, J.R.; Kim, S.C. Anti-inflammatory activity of the methanol extract of moutan cortex in LPS-activated Raw264.7 cells. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2007, 4, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolac, U.K.; Ustuner, M.C.; Tekin, N.; Ustuner, D.; Colak, E.; Entok, E. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of Salvia officinalis on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in rats. J. Med. Food 2017, 20, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.P.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Kao, S.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of Perilla frutescens leaf extract on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akanda, M.R.; Park, B.Y. Involvement of MAPK/NF-κB signal transduction pathways: Camellia japonica mitigates inflammation and gastric ulcer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.T.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Jiang, C.H.; Chen, J.Q.; Ye, J.Q.; Jia, X.B.; Yang, Y.; Ni, Q.; Wang, S.X.; Song, J.; et al. Nauclea officinalis inhibits inflammation in LPS-mediated RAW 264.7 macrophages by suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 183, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, N.; Akram, M.; Daniyal, M.; Koltai, H.; Fridlender, M.; Gorelick, J. Antiinflammatory potential of medicinal plants: A source for therapeutic secondary metabolites. Adv. Agron. 2018, 150, 131–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeckler, G.A.; Gershenzon, J.; Unsicker, S.B. Phenolic glycosides of the Salicaceae and their role as anti-herbivore defenses. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 1497–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Thuong, P.T.; Min, B.-S.; Ngoc, T.M.; Hung, T.M.; Lee, I.S.; Na, M.; Seong, Y.-H.; Song, K.-S.; Bae, K. Phenolic glycosides with antioxidant activity from the stem bark of Populus davidiana. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1370–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.J.; Huang, H.T.; Huang, S.Y.; Lin, Z.H.; Shen, C.C.; Tsai, W.J.; Kuo, Y.H. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory phenolic glycosides from Clematis tashiroi. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1586–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Wang, H.; Gong, Z.; Huang, J.; Pei, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Tang, X. Antimicrobial and cytotoxic phenolics and phenolic glycosides from Sargentodoxa cuneata. Fitoterapia 2015, 101, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, P.E.; Garcia, B.J.; Gunter, L.E.; Jawdy, S.S.; Engle, N.; Yang, X.; Jacobson, D.A.; Hettich, R.L.; Tuskan, G.A.; Tschaplinski, T.J. Quantitative proteome profile of water deficit stress responses in eastern cottonwood (Populus deltoides) leaves. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, J.A. Amerindian medicinal plants; Typescript: Fulton, ML, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Pearl, I.A.; Darling, S.F. Studies of the hot water extractives of the bark and leaves of Populus deltoides bartr. Can. J. Chem. 1971, 49, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, S.; Chenault, J.; Augustin, S.; Venot, C. Isolation of a new phenolic compound from leaves of Populus deltoides. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 808–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, T.P.; Reichardt, P.B.; Bryant, J.P.; Werner, R.A.; Post, K.; Frisby, K. Chemical model for short-term induction in quaking aspen (Populus tremuloides) foliage against herbivores. J. Chem. Ecol. 1989, 15, 2335–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, D.T.; Schilling, M.C.; Hochwender, C.G.; Kaufman, A.D. Profiling phenolic glycosides in Populus deltoides and Populus grandidentata by leaf spray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwar, J.R.; Kanwar, R.K.; Burrow, H.; Baratchi, S. Recent advances on the roles of NO in cancer and chronic inflammatory disorders. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 2373–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, S.; Hoffmann, A. Crosstalk via the NF-κB signaling system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008, 19, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guerra, F.; Duplessis, S.; Kohler, A.; Martin, F.; Tapia, J.; Lebed, P.; Zamudio, F.; González, E. Gene expression analysis of Populus deltoides roots subjected to copper stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2009, 67, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uslu, C.; Karasen, R.M.; Sahin, F.; Taysi, S.; Akcay, F. Effects of aqueous extracts of Satureja hortensis L. On rhinosinusitis treatment in rabbit. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 88, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, C.; Röllinghoff, M.; Diefenbach, A. Reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen intermediates in innate and specific immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2000, 12, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baatar, D.; Siddiqi, M.Z.; Im, W.T.; Ul Khaliq, N.; Hwang, S.G. Anti-inflammatory effect of Ginsenoside Rh2-mix on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 murine macrophage cells. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.S.; Xiang, X.W.; Jin, H.X.; Guo, X.Y.; Liu, L.J.; Huang, Y.N.; OuYang, X.K.; Qu, Y.L. Composition and anti-inflammatory effect of polysaccharides from Sargassum horneri in RAW264.7 macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 88, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira-Leite, C.; Nunes, C.; Jamal, S.K.; Cuccovia, I.M.; Reis, S. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory therapy: A journey toward safety. Med. Res. Rev. 2017, 37, 802–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, Y.; Sobajima, J.; Higashi, M.; Ishiguro, T.; Fukuchi, M.; Ishibashi, K.; Mochiki, E.; Yakabi, K.; Kawano, T.; Tamaru, J.; et al. Coexpression of COX-2 and iNOS in angiogenesis of superficial esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. Surg. 2015, 100, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thieme, H. ber die phenolglykoside der gattung Populus. Planta Medica 1967, 15, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.-p.; Zheng, H.-q.; Liu, G.; Hu, F.-l. Development and validation of HPLC method for determination of salicin in poplar buds: Application for screening of counterfeit propolis. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.-C.; Chang, H.-H.; Wang, T.-M.; Chan, C.-P.; Lin, B.-R.; Yeung, S.-Y.; Yeh, C.-Y.; Cheng, R.-H.; Jeng, J.-H. Antiplatelet effect of catechol is related to inhibition of cyclooxygenase, reactive oxygen species, ERK/p38 signaling and thromboxane A2 production. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, V.A.; Lee, J.-W.; Kim, J.-Y.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.-S.; Kwon, Y.-S.; Chun, W. Phosphorylation of Akt mediates anti-inflammatory activity of 1-p-coumaroyl β-D-glucoside against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in RAW264. 7 cells. Korean. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.; Liu, D.; Yang, D.; He, K.; Bai, J.; Zhu, X. Antiinflammatory effects of tremulacin, a salicin-related substance isolated from Populus tomentosa carr. leaves. Phytomedicine 1994, 1, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Deng, Y.; Lv, H.; Qiu, J.; Chi, G.; Feng, H.D. (−)-salicin inhibits the LPS-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells and mouse models. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 26, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, C.S.; Kim, K.H.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, J.E.; Park, C.; Jeong, J.W. Salicin, an extract from white willow bark, inhibits angiogenesis by blocking the ROS-ERK pathways. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, J. Aspirin: A history, a love story. Consult. Pharm. 2012, 27, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinz, B.; Kraus, V.; Pahl, A.; Brune, K. Salicylate metabolites inhibit cyclooxygenase-2-dependent prostaglandin E2 synthesis in murine macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 274, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, C.H.; Hur, S.K.; Oh, O.-J.; Kim, S.S.; Nam, K.A.; Lee, S.K. Evaluation of natural products on inhibition of inducible cyclooxygenase (COX-2) and nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in cultured mouse macrophage cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 83, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muturi, E.J.; Ramirez, J.L.; Doll, K.M.; Bowman, M.J. Combined toxicity of three essential oils against Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) larvae. J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 1684–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-B.; Han, A.-R.; Park, E.-Y.; Kim, J.-Y.; Cho, W.; Lee, J.; Seo, E.-K.; Lee, K.-T. Inhibition of LPS-induced iNOS, COX-2 and cytokines expression by poncirin through the NF-κB inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 2345–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelova, H.; Hosek, J. TNF-α signalling and inflammation: Interactions between old acquaintances. Inflamm. Res. 2013, 62, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Sun, G.Q.; Gao, H.Y.; Li, R.S.; Soromou, L.W.; Chen, N.; Deng, Y.H.; Feng, H.H. Angelicin regulates LPS-induced inflammation via inhibiting MAPK/NF-κB pathways. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 185, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, M.Y.; Liao, M.F.; Chen, F.L.; Li, Y.C.; Yang, M.L.; Lin, R.H.; Kuan, Y.H. Luteolin attenuates the pulmonary inflammatory response involves abilities of antioxidation and inhibition of MAPK and NFκB pathways in mice with endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2660–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, R.J.; Chun, J.; Khan, S.; Kim, Y.S. Desoxyrhapontigenin, a potent anti-inflammatory phytochemical, inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory responses via suppressing NF-κB and MAPK pathways in RAW 264.7 cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 18, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, W.Y.; Fu, B.D.; Shen, H.Q.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, C.; Song, Z.; Qin, Q.Q.; Li, H.P.; Lv, S.; Wu, S.C.; et al. Sulfated derivative of 20(s)-ginsenoside Rh2 inhibits inflammatory cytokines through MAPKs and NF-kappa B pathways in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages. Inflammation 2012, 35, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerits, N.; Kostenko, S.; Moens, U. In vivo functions of mitogen-activated protein kinases: Conclusions from knock-in and knock-out mice. Transgenic Res. 2007, 16, 281–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, Y.E.; Lee, M.-Y. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Populus deltoides Leaf Extract via Modulating NF-κB and p38/JNK Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123746
Jeong YE, Lee M-Y. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Populus deltoides Leaf Extract via Modulating NF-κB and p38/JNK Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(12):3746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123746
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Ye Eun, and Mi-Young Lee. 2018. "Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Populus deltoides Leaf Extract via Modulating NF-κB and p38/JNK Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 12: 3746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123746
APA StyleJeong, Y. E., & Lee, M. -Y. (2018). Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Populus deltoides Leaf Extract via Modulating NF-κB and p38/JNK Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(12), 3746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123746